Introduction
For businesses to succeed in the modern business climate and acquire a competitive advantage, they need an efficient brand management plan. In order for enterprises to have a strong brand presence and match their product offerings with the cultural norms and viewpoints of their target audience, strategic brand management techniques are also essential (Li, Larimo, and Leonidou, 2020). With an emphasis on its brand repositioning initiatives and social media involvement, this research examines the brand management approach of Colombian tea company Hind. In response to millennials’ rising inclination for natural and healthy products and greater affinity for digital platforms, Hind began a mission to cater to millennial consumers. In this research, Hind’s brand repositioning strategy is thoroughly examined in the context of social media integration. This analysis offers insightful information about how well the approach achieves organizational objectives. Additionally, this paper makes use of the social identity theory to describe how social media may help brands evolve based on possible effects on customer perception and commercial success.
Hindu’s Brand Expansion Strategy
Through product diversification and market realignment, Hind has launched a brand extension plan to spur growth and solidify its market position (Instante Shop, n.d.). As an instance, Hinduism introduced distinctive black tea and herbal tea offers in an effort to position itself as the preferred option of healthy beverages. In order to meet changing consumer demands and take advantage of market trends toward healthier food options, the firm has created new product categories such as flavored teas, ready-to-drink iced tea, and speciality teas. Additionally, Hind’s dedication to providing healthier options was demonstrated by the launch of ground-breaking goods like Red Fruits tea, a calorie-free mix created with natural sweeteners (Instante Shop, n.d.). The zero-calorie product’s commercial success highlighted the Hindu brand’s capacity to capitalize on shifting consumer preferences, and its foray into non-alcoholic beverages, like Summer Tea, showed its adaptability in satisfying customer requirements across a range of consumption situations. With the help of these product growth techniques, Hindu was able to reach a wider audience and establish itself as a supplier of a variety of nutritious beverage alternatives (Tsimonis and Dimitriadis, 2014). As a result, a strategic point of distinction was built to increase market share and foster consumer loyalty.
Target Audience Expansion
Following a market assessment, Hindú recognized the need to target younger generations composed of the millennial and centennial consumers, who exhibit a strong inclination towards natural, healthy foods and beverages, making them ideal targets for the brand expansion efforts. Among the strategies employed by Hindú to achieve this was partnering with the marketing firm Básica to gain a deeper understanding of these target audiences and their preferences. The target customers were engaged through social media platforms and celebrity endorsements to generate a positive brand sentiment based on conversations centered around themes of entrepreneurship, fitness, trends, and travel. Moreover, Hindu leveraged the power of user-generated content and peer recommendations to successfully connect with younger consumers in building a digital community around the brand (Verhoeven and Johnson, 2017). The repositioning of the brand with the tagline ‘Vive el momento’ reflected the efforts to resonate with the target audience’s desire for holistic well-being and self-care. This enabled the company to establish emotional connections with millennials and centennials, positioning itself as a brand that caters to their needs and preferences.
Market Penetration
Hindú realized the importance of an effective distribution strategy to penetrate the market and expand its reach by evaluating different distribution channels, including small local stores (SLSs), convenience, and hard discount stores, to ensure optimal product availability and visibility. By understanding the dynamics of SLSs, Hindú implemented packaging and display enhancements to make its products more appealing to consumers. The strategic decision to invest in better-presented products increased costs but enabled the brand to capture a significant portion of the SLS market, which represents 20% of total tea sales. Similarly, Hindú leveraged convenience stores and hard discount stores, capitalizing on the private brand model and the growing popularity of these channels among Colombian consumers. In addition, the brand pursued an ambitious export strategy to diversify its market presence beyond Colombia. Hindú successfully expanded its exports to various countries in the Americas by identifying neighboring markets with favorable purchasing power, such as Venezuela, and leveraging the depreciating Colombian peso. The brand’s commitment to international growth was underpinned by strategic partnerships with local distributors possessing export marketing expertise.
The Brand Repositioning Strategy
Hindú embarked on a brand repositioning strategy to target millennial consumers by recognizing the need to remain relevant and engage with younger generations. The target demographic cohort is characterized by a higher affinity for natural and healthy products and hence represents a valuable market segment for Hindú to tap. The rationale behind the repositioning was to align the brand with the evolving preferences and lifestyles of millennials, thereby driving brand resonance and market growth. The company understood that its traditional brand image, primarily associated with black tea and herbal teas, m not resonate strongly with millennial consumers who sought more diverse and innovative beverage options (Verhoeven and Johnson, 2017). Therefore, the brand repositioning strategy aimed to bridge this gap and market Hindú as a brand that offers a range of natural and healthy beverages suited to the preferences of the millennial audience.
Implementing the repositioning strategy
The brand repositioning strategy was centered around the tagline ‘Vive el Momento,’ which reflected Hindu’s commitment to connecting with millennials on a deeper emotional level (Instante Shop, n.d.). The execution of the repositioning strategy revolved around leveraging digital platforms and influential bloggers to engage with the target audience and build a strong brand community. The brand gained valuable insights into millennial consumers’ preferences, behaviors, and digital interactions by partnering with the marketing firm Básica. The research informed the development of thematic axes aligned with millennial interests, such as entrepreneurship, fitness, trends, and travel. Hindú employed influential bloggers to develop user-generated content and create authentic connections with the millennial audience. That digital engagement strategy enabled it to shift its brand perception from a traditional tea company to a lifestyle brand that resonated with millennial values and aspirations. Hindú effectively communicated its brand message and product offerings to millennials through the strategic use of social media platforms. The brand’s Instagram accounts, managed by bloggers representing the thematic axes, allowed it to showcase products, share recipes, and foster a sense of community among its target audience. They facilitated seamless purchasing opportunities for millennial consumers, capitalizing on their preference for convenient and accessible online shopping experiences by integrating the Instante Shop virtual store.
The strategy implementation could be further explained using the Ansoff Matrix to analyze growth opportunities for the company from the product and market perspectives. The Ansoff matrix is composed of four major elements, including market development, market penetration, product development, and diversification, as illustrated in Figure 1.0.
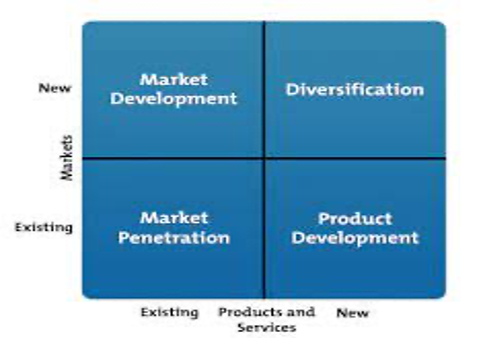
Figure 1.0: The Ansoff Matrix
Market penetration
Hindú’s initial market penetration strategy involved focusing on its existing market, which was primarily composed of traditional tea consumers in Colombia. The company recognized the need to extend its market reach beyond the tea category and tap into new consumer segments. To achieve this, Hindú pursued a brand repositioning strategy targeting millennial consumers by leveraging their preferences for natural and healthy products to penetrate deeper into the existing (Meyers, 1996).
Product development
Hindú’s product development strategy involved introducing new product lines and diversifying its offerings to cater to the changing preferences of consumers. The company expanded its portfolio beyond black tea and herbal teas to include a variety of innovative and healthier options. This included green tea, flavored teas, fruit teas, and non-alcoholic beverages to help the company extend its market share and meet the evolving customer demands.
Market development
In terms of market development, Hindú explored opportunities to expand into new markets both domestically and internationally based on a deep recognition of the growth potential in emerging economies through exports. Hindú successfully entered various countries in the Americas, expanding its market presence and increasing its exports. This market development strategy allowed Hindú to reach new consumers and diversify its revenue streams beyond its traditional market in Colombia.
Diversification
Hindu pursued a robust brand positioning strategy centered on portfolio diversification as the company expanded its product offerings beyond the traditional tea category. This entailed introducing new lines such as RTD teas and non-alcoholic beverages to appeal to a broader range of consumers and reduce the reliance on a single product category.
Implications and Future Outlook
Hindú successfully connected with millennial consumers who prioritize natural, healthy, and socially engaging experiences through embracing a more contemporary and dynamic brand image. The repositioning effort has positioned Hindú as a brand that caters to the needs and aspirations of millennials, thereby increasing its relevance and desirability within this key consumer segment (Popoli, 2017). Moreover, their digital engagement strategy has allowed the brand to build a loyal and interactive community of millennial consumers. The brand has further cultivated strong brand advocacy and enhanced its brand equity among millennials by fostering meaningful conversations, sharing user-generated content, and leveraging peer recommendations Hindú’s long-term brand repositioning strategy opens doors for continued growth and expansion. The brand can explore new product offerings that align with millennial preferences by capitalizing on the popularity of health-conscious lifestyles and the rising demand for diverse and innovative beverage options. Expanding its portfolio to include ready-to-drink (RTD) options, exploring new flavor profiles, or introducing innovative packaging formats can further enhance Hindú’s market potential among millennials.
However, Hindú should remain cognizant of potential challenges and risks associated with its brand repositioning strategy. Although targeting millennials can be lucrative, it is equally a highly competitive market segment. Thus, Hindú must continuously innovate and differentiate its offerings to maintain a competitive edge and its appeal to millennials. Additionally, the brand should carefully manage the balance between retaining its traditional consumer base and attracting new millennial customers, ensuring that its brand identity remains consistent and embraced across diverse consumer groups. Furthermore, Hindú should closely monitor the evolving preferences and trends within the millennial demographic to adapt its brand strategy accordingly. As consumer behaviors and digital platforms continue to evolve, the brand must stay agile and proactive in engaging with millennials through social media and other emerging digital channels (Hayward, 2016). Hindú can effectively respond to changing consumer demands and sustain its growth trajectory by regularly analyzing consumer insights, tracking market trends, and investing in research and development
The Potential Growth Scenarios
Scenario 1 – Pursue Growth within the Tea Category
In this scenario, Hindú would focus on expanding its market share within the existing tea category by maintaining core products, such as black tea, herbal teas, and flavored teas, while leveraging a strong brand recognition and reputation to capture a larger portion of the market. This scenario would offer Hindu to leverage its rich market experience and knowledge for the continuous improvement and alignment of the brand positioning strategies with the evolving consumer needs. For instance, continued refinement of the existing tea products would position Hindus to respond to the changing consumer preferences more effectively compared to if they tried new products (Cavusgil et al., 2017). However, this scenario would also create some limitations on the extent of market share that Hindus can occupy.
Pros of this scenario
- Pursuing growth in its traditional product segments would enable Hindu to secure market dominance by reinforcing its position as the preferred brand within the tea category. This would contribute significantly to maintaining a sustainable competitive advantage over other tea brands.
- This scenario offers Hindu an opportunity to build market recognition through brand consistency and capitalize on the established brand identity to attract and build customer loyalty. A consistent brand identity would foster a strategic resonance with tea consumers from the past, current, and future generations.
- Concentrating efforts on the existing tea portfolio would enable Hindú to leverage its production and distribution capabilities in optimizing operational efficiency and cost management strategies.
Cons of this scenario
- Continued growth in the tea category would limit the growth potential of Hindu as the tea market in Colombia has a relatively low per capita consumption compared to other countries, indicating that the efforts can yield to a certain extent only (Jobber and Ellis-Chadwick, 2020a).
- The market for tea products is already saturated, considering the significant presence of several other players competing to extend their share. Therefore, further extension may yield significantly lower returns on investment due to the potential saturation of the market.
- A sole focus on the tea category may limit Hindú’s ability to capitalize on emerging trends and consumer preferences for new and innovative beverages. This implies a potential of losing its competitive edge over the emerging players who present highly diversified products to the market.
Impact on Brand Identity
The decision to pursue growth within the tea category effectively aligns with Hindú’s heritage and reinforces its brand identity as a traditional company with a deep understanding of the sociocultural values that shape tea consumption habits in Columbia. This scenario offers a robust framework for the company to maintain its strategic association with natural, healthy beverages, upholding its image as a trusted provider of high-quality teas (Jobber, and Ellis-Chadwick, 2020b). However, this scenario may restrict the brand’s ability to evolve and appeal to the changing tastes and preferences of younger generations.
Scenario 2 – Diversifying into Adjacent Categories
This scenario reflects an opportunity for Hindu to extend the product portfolio beyond the traditional tea category by introducing complementary products such as cookies or cereals. Further diversification of the product portfolio would enable Hindu to create and boost new revenue streams by taking advantage of the already established brand equity and health credentials in the tea. Consequently, the company would be better positioned to take advantage of the technological advancements to create innovative products that resonate with the needs of emerging market niches.
Pros of this Scenario
- Diversifying into adjacent categories would allow Hindú to further diversify the product range, catering to the varying needs of its growing consumer base and leveraging the new market opportunities to position strategically for competitiveness.
- Diversification beyond the tea category presents an opportunity for Hindú to leverage its existing customer base and distribution channels to cross-sell the new products, enhancing customer loyalty and driving sales revenue.
- The brand equity and positive associations Hindú has established within the tea category can transfer to the new product categories, giving the brand a head-start in terms of consumer trust and recognition.
Cons of this scenario
- Diversifying into new categories may dilute Hindu’s brand identity as a tea specialist. This is because the consumers may perceive the company as less focused on perfecting the current offerings, posing significant risks of losing the unique value proposition associated with the tea categories.
- The company will become vulnerable to competitive challenges of security market share from the already established players with greater resources and presence in the new product segments. Therefore, Hindú would need to invest in marketing, distribution, and product development to compete effectively.
- Expanding into new categories requires Hindú to develop new capabilities in product development, manufacturing, and supply chain management, which may entail additional costs and operational challenges.
Impact on Brand Identity
Diversification into adjacent categories presents an opportunity for Hindú to broaden its brand identity beyond tea. While it may introduce risks of brand dilution and challenges in maintaining a unique brand image, strategic diversification can help Hindú appeal to a wider range of consumers and adapt to changing market dynamics. This scenario also implies an opportunity to expand revenue streams, strengthening the competitive positioning of Hindu further.
Scenario 3: International Expansion and Export Markets
This scenario implies a strategic alignment with the current focus on globalization and the emerging overseas markets. Hindus could consider expanding its presence in international markets through export opportunities. The company already has a strong brand reputation, which implies lesser bottlenecks in venturing the foreign markets in Europe, Asia, and the West, which have a massive growth potential. However, Hindus may need strategic investments in market research to understand the sociocultural dynamics that influence consumer behavior, especially from the perspective of Hofstede’s dimensions. This would not only reduce the risks of market failure but also drive customer loyalty.
Pros of this scenario
- International markets offer significant growth potential, allowing Hindú to access larger consumer bases and tap into regions with higher per capita tea consumption.
- Expanding into export markets will enable Hindú to diversify its revenue streams, reducing dependence on the domestic market and mitigating the risks associated with local economic fluctuations.
- Successful international expansion enhances brand recognition and elevates Hindú’s reputation as a global tea brand, strengthening its market positioning and potential for future growth.
Cons of this scenario
- The company is likely to face market entry barriers created by the liabilities of foreignness in adapting to local tastes and preferences, navigating regulatory requirements, establishing distribution networks, and building brand awareness.
- International markets are often crowded with established brands and local competitors, creating a need for new entrants like Hindú to differentiate and make strategic investments in marketing and distribution through collaboration with local stakeholders (Cajiao and Leal, (2021).
- Expanding into international markets necessitates the creation of efficient supply chains and ensuring product quality throughout the distribution process, which may involve logistical complexities and additional costs.
Impact on Brand Identity
International expansion presents an opportunity for Hindú to position itself as a globally recognized brand, reinforcing its heritage and reputation for quality tea products. The company can leverage the already established value proposition to venture into new markets and create a stronger brand identity that emphasizes the ability to serve diverse cultural preferences beyond the home market. Unlike the other scenarios presented in this report, the focus on international market expansion holds unlimited potential for strengthening Hindu’s brand identity.
Hindu’s Brand Strategy in the Context of Social Media
Marketing strategies in the contemporary business environment are primarily defined by the dimensions of digital marketing, especially through social media. The growing rate of social media usage due to the advancements in the Internet of Things (IoT) and other communication technologies has caused a paradigm shift from traditional marketing through the mainstream media to digital advertisements (Nadanyiova, Majerova, and Gajanova, 2021). As a result, social media has become a powerful platform to communicate brand value proposition through online engagements with the target customers. Hindu’s brand strategy can be understood from multiple perspectives of the social identity theory and Uses and Gratifications Theory in the context of social media. These theoretical frameworks underscore the factors that influence consumer’s purchase decisions in the digital realm, which has caused unprecedented disruption in business marketing in the current age.
Social Identity Theory
According to Wang (2017), the social identity theory provides a conceptual link between the shared sociocultural values of a community and their consumption patterns, asserting that individuals derive a sense of self and identity through their association with specific social groups. For instance, a potential customer is likely to purchase from a brand that is popular within their social circles due to the influence of the past communication of brand value through social media reviews by friends or peers. Brands like Hindu can leverage the fundamental principles of this theory to build strong connections with their target audience and foster brand loyalty. For instance, Hindú recognizes the need to build a community and a sense of belonging among the current and target customers through continuous engagements on the digital forums. The brand has demonstrated commitment to fostering a strong brand identity through strategic investments in building social media presence in existing and emerging markets. Hindú’s brand strategy aligns with Social Identity Theory by providing a platform for consumers to form social connections, share experiences, and express their association based on their past experiences with the products (Ahmad and Guerrero, 2020). Therefore, facilitating the construction of a social identity around the brand deepens the emotional connection with the social media users, fostering a stronger brand loyalty and advocacy in the international markets. Hindú employs the following digital brand management strategies to foster a sustainable social identity among the customers:
- Hindú has created themed Instagram accounts representing popular individuals who embody different aspects of its target audience’s lifestyle, such as entrepreneurship, fitness, trends, and travel in the target markets (McGowan, Shiu, and Hassan, 2016). This implies an opportunity for Hindu’s potential customers who follow these celebrities to connect with like-minded individuals who share similar interests and values.
- Hindú actively encourages its social media followers to create and share their content featuring the products. Resharing user-generated content and engaging with social media users in real time reinforces a sense of community and strengthens the bond between the brand and its customers (McGowan, Shiu, and Hassan, 2016).
- The company has effectively aligned its brand value with the expectations and needs of the target audience through a greater emphasis on natural and healthy living. Therefore, promoting these values consistently through social media content enables the brand to strengthen its market appeal while creating an opportunity for the customers to incorporate the brand into their self-identity.
Uses and Gratifications Theory
As Hindu implements more targeted investments in brand positioning, the role of social media as a mediator of the customer relations can be further explained based on the fundamental principles of Uses and Gratifications Theory, which suggests that individuals actively consume media to fulfill specific needs and gratifications (Ehikwe, Egede and Chuks-Nwosu, 2013). These principles reflected the need for Hindu to understand the underlying factors that influence consumer preferences to ensure that the social media engagement strategies effectively satisfy their needs, particularly in the context of product information. Insights into the gratifications that social media users seek to derive form the basis for their brand sentiment, creating a need for Hindu to ensure that its social media content is relevant to the changing preferences and expectations of the target customers. The company could enhance the value of its social media presence and strengthens the bond between the brand and the target customers by providing informative, entertaining, and socially interactive content (Ehikwe, Egede, and Chuks-Nwosu, 2013). With the current understanding of the gratifications sought by its target audience on social media, Hindu could implement the following social media strategies to fulfill the needs:
- Provide informative and educational content to keep the target audience informed about the value derived from the consumption of the unique tea products by Hindus. A particular emphasis on the health benefits of the product offerings would fill the knowledge gap and appeal to other social media users as an authoritative market leader in the tea industry.
- The social media content and scope within which the customers are engaged could go beyond product promotion by introducing additional elements, such as entertainment, to inspire the target customers to engage with the brand (Falgoust et al., 2022). For instance, the brand could include visually appealing images, engaging videos, and inspiring quotes related to tea, lifestyle, and healthy living. The extension beyond the scope of product offerings to address other topics that are important to the target customers would be a strategic point of differentiation.
- Hindú should develop effective models for active social media engagement by responding to comments, addressing queries, and initiating conversations to gather insights about the brand sentiment (Falgoust et al., 2022). This interaction fosters a sense of social connection and fulfills the need for social interaction and community engagement.
References
Ahmad, N. and Guerrero, E. (2020). Influence of Social Media on Brand Awareness: A Study on Small Businesses. [online] Available at: http://hig.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1392939/FULLTEXT01.pdf.
Cajiao, A. and Leal, D. (2021). Hindú: Revitalizing a Colombian Tea Brand. [online] hbsp.harvard.edu. Available at: https://hbsp.harvard.edu/product/W21014-PDF-ENG.
Cavusgil, S.T., Knight, G.A. and Riesenberger, J.R. (2017) International business [electronic resource]: the new realities. Fourth edition. Boston: Pearson. Available at: http://www.vlebooks.com/vleweb/product/openreader?id=BedsUni&isbn=9781292152844
Ehikwe, A., Egede and Chuks-Nwosu, E. (2013). Uses And Gratification Theory And The Optimization Of The Media In The Privatization Of State Owned Enterprises In Nigeria. [online] 4(16). Available at: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/234646116.pdf.
Falgoust, G., Winterlind, E., Moon, P., Parker, A., Zinzow, H. and Madathil, K.C. (2022). Applying the uses and gratifications theory to identify motivational factors behind young adult’s participation in viral social media challenges on TikTok. Human Factors in Healthcare, 2, p.100014. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hfh.2022.100014.
Hayward, M. (2016) How to build long-term brand loyalty. WARC. Available at: https://0-www-warc-com.brum.beds.ac.uk/content/article/bestprac/how-to-build-long-term-brand-loyalty/107303.
Instante Shop (n.d.). Herbal Healthy Tea. [online] Instante Shop. Available at: https://instante.shop/.
Jobber, D. and Ellis-Chadwick, F. (2020a) ‘Marketing planning: An overview of strategic analysis and decision-making,’ in Principles and practice of marketing. Ninth edition. Maidenhead: McGraw-Hill Higher Education, pp. 595–626. Available at: https://contentstore.cla.co.uk/secure/link?id=b1315c71-45de-ea11-80cd-005056af4099.
Jobber, D. and Ellis-Chadwick, F. (2020b) ‘Value through brands,’ in Principles and practice of marketing. Ninth edition. Maidenhead: McGraw-Hill Higher Education, pp. 241–278. Available at: https://contentstore.cla.co.uk/secure/link?id=59a1343b-45de-ea11-80cd-005056af4099
Li, F., Larimo, J. and Leonidou, L.C. (2020). Social Media Marketing Strategy: definition, conceptualization, taxonomy, validation, and Future Agenda. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 49(1), pp.51–70. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-020-00733-3.
McGowan, M., Shiu, E. and Hassan, L.M. (2016). The influence of social identity on value perceptions and intention. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 16(3), pp.242–253. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/cb.1627.
Myers, J.H. (1996) Segmentation and Positioning for Strategic Marketing Decisions. New York: McGraw-Hill Education – Europe.
Nadanyiova, M., Majerova, J. and Gajanova, L. (2021). Digital marketing, competitive advantage, marketing communication, social media, consumers. Marketing and Management of Innovations, 5(4), pp.92–103. doi:https://doi.org/10.21272/mmi.2021.4-08.
Popoli, P. (2017) Advancing insights on brand management. InTech. Available at: http://www.intechopen.com/books/advancing-insights-on-brand-management
Tsimonis, G. and Dimitriadis, S. (2014). Brand Strategies in Social Media. [online] ResearchGate. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262575006_Brand_Strategies_in_Social_Media
Verhoeven, B. and Johnson, L. (2017). Business Model Innovation Portfolio Strategy for Growth Under Product-Market Configurations. Journal of Business Models, [online] 5(1), pp.35–50. Available at: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/229011889.pdf.
Wang, T. (2017). Social identity dimensions and consumer behavior in social media. Asia Pacific Management Review, [online] 22(1), pp.45–51. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmrv.2016.10.003.
 write
write