Abstract
This essay provides a framework for connecting stakeholder theory and user-centred design by analyzing the case of Samsung. The emergence of Industry 4.0 has demarcated the smartphone as the number one in the technology revolution, with Samsung assuming an important role in this area. From this perspective, the study analyzes the stakeholder engagement strategies and organizational capabilities of Samsung and points out the key areas of identification and suggestions for further development. Through the lens of the Balanced Scorecard framework, the analysis manifests Samsung as an innovative business by fitting the stakeholder requirements to various innovation drivers from the financial, consumer, performance, and learning points of view. Apart from that, this report considers market research and consumer insights. Therefore, it stresses the need to strengthen communication with key players (stakeholders). Applying practical examples, the study suggests a holistic model which combines an adaptation of stakeholder theory, a user-centric approach and UX essentials to assist organizations in addressing the needs of different stakeholders and continue meeting high-quality user experience and commercial success. The research above adds to the academia and the practice as it brings the stakeholder theory into the user-centred design practices for the sustainability of development. Also, it gives the digital era an edge.
Introduction
In the fast-paced digital landscape of Industry 4.0, smartphones have become an icon of technological development that has changed societal norms and individual behaviour. Among the leaders of this innovative era is Samsung Electronics, with a commanding position derived from its product innovations and a massive stakeholder network (Nogalski., 2020). The report starts with the investigation of the area where stakeholder theory and user-centred design intersect; Samsung Electronics is used as a case study. By examining Samsung’s stakeholder engagement strategies and the organisation’s competency as a whole, this research will determine what aspects are in alignment and where improvement is required. In applying the Balanced Scorecard Framework, the analysis draws out Samsung’s efforts to meet stakeholder needs and forge growth in innovation across the financial, consumer, performance, and learning realms.
Last but not least, as a part of the process, we are also using market research and consumer insights to improve the market understanding and keep the communication channels open. Relying on the existing research literature, we suggest a comprehensive framework uniting stakeholder theory, user-centred design, and UX principles. It aspires to give enterprises a way out to traverse a complex web of stakeholder expectations with better customer experience and business growth. However, this research will assist academics and professionals by providing indispensable knowledge on combining stakeholder theory with user-centred design, which, in turn, would help achieve sustainable development and competitive advantage in the computing era.
Case Study Observation – The Shareholders of Samsung
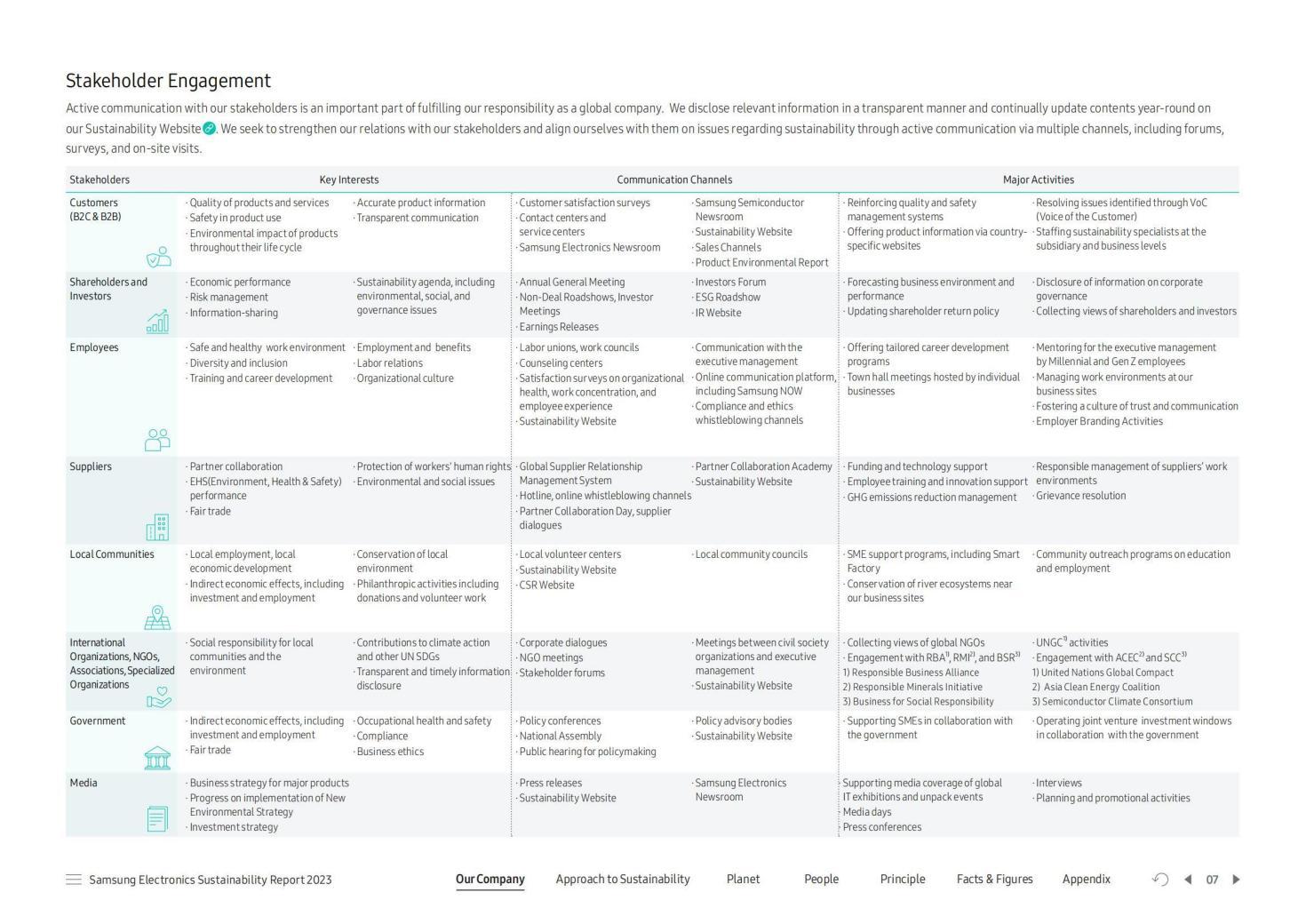
According to the Samsung Electronics Sustainability Report 2023, the connection between the company and its stakeholders is as follows:
In the B2C markets, consumers evaluate brands based on technical features, reliability, and after-sales performance, respectively. Moreover, in the B2B market, there are these three factors that are paid more attention to: attributes such as prices, services and product quality in higher grades. Innovation in products and services is mostly driven by consumers (B2C), who directly impact sales and market share.
In exchange for their money, Samsung’s shareholders and investors anticipate competitive returns, open communication, and well-defined strategic goals. They are the key decision-makers in Samsung’s strategy and finances because of their voting rights and financial stake in the firm.
Workers at Samsung anticipate a positive company culture, competitive pay, possibilities for advancement, and a safe workplace. They are fundamental to how Samsung does business internally, affectingaffect both product quality and the brand’s image.
Its suppliers ask Samsung to maintain open communication, pay on time, and work with them for the long haul. Their reliability and effectiveness in operation affect the supply chain and pricing structure of Samsung’s products.
The locals have been lobbying for Samsung to invest in the area, create employment, and launch social responsibility initiatives. Regarding operating circumstances and reputation in the region, their support is vital to Samsung’s social license.
Samsung is under pressure from non-governmental organizations (NGOs), associations, and specialist groups to ensure that its business practices align with international norms, are environmentally conscious, and are socially responsible. In doing so, they impact public opinion and policymakers, affecting Samsung’s worldwide operations.
The government is asking Samsung to follow the rules and be more involved in collecting taxes. A key factor in the company’s ability to legally operate and access markets is the government’s regulatory policymaking and execution.
Samsung must provide news and be transparent to the media. They greatly affect Samsung’s reputation because they mould public perception, which in turn affects customer behaviour and investment confidence.
Bundy et al. (2018, p.476) present the theory of organization-stakeholder fit (O-S fit), which, by emphasizing the compatibility that arises when an organization’s traits align with those of a stakeholder, explains why an organization and its stakeholders behave cooperatively. In addition, the theory distinguishes between two aspects of O-S fit: value congruence and strategic complementarity. The former refers to the degree to which organizational and stakeholder values are congruent, and the latter to the extent to which strategic requirements and resources are complementary. Cooperation becomes more useful when there is a good fit between a company and its stakeholders regarding important features.
To sum up, the organizational structure of Samsung Electronics and its stakeholders are intricately related and mutually influential. In addition to better managing and meeting the demands of its stakeholders, Samsung Electronics may increase its competitiveness and innovation in the worldwide market by streamlining its organizational structure.
Analysis – Balanced Scorecard
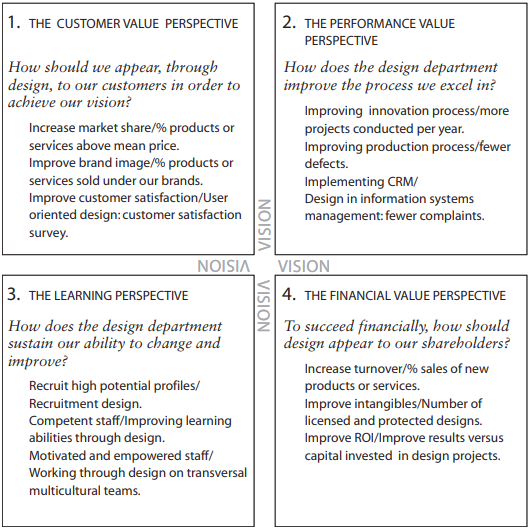
The Balanced Scorecard provides an organization with a comprehensive way to measure performance and guide strategy implementation through four dimensions: financial value, consumer value, performance value, and learning (Borja, 2006, pp.44-55). The Balanced Scorecard is used to analyze the process of Samsung Electronic’s transformation of stakeholder needs into innovation drivers and identify the existing problems, which can provide insight into its support for cross-department collaboration and rapid innovation.
The Financial Value Perspective
Samsung invested 25 trillion won in high-tech in 2018 to maintain its leading position in the industry and planned to invest 180 trillion won over the next three years (Samsung, 2018). Samsung Electronics’ huge R&D spending shows its commitment to innovation but also requires high capital efficiency and a clear return on investment (ROI) from a financial perspective. Excessive R&D spending may compress profits without corresponding market returns, even leading to corporate crisis. For example, Nokia, Motorola and Blackberry have all experienced corporate crises due to market judgment and investment mistakes (Nair et al., 2014).
Samsung needs to implement more refined R&D budget management to ensure that every investment contributes to Samsung’s long-term financial performance. At the same time, the market potential assessment of new projects should be strengthened to ensure the effective use of R&D funds.
The Customer Value Perspective
According to the official website of Samsung Electronics, Samsung has made various efforts to meet the different needs of the public. For example, establishing design centres in other regions can timely sense the needs of local consumers (Samsung, 2024) to seize the new demand market for the first time. While Samsung has successfully met consumer demand for high-tech products, in the face of increasingly diverse consumer demands, the company needs to ensure that its innovations can keep pace with market trends and customer expectations.
Samsung Electronics needs to strengthen consumerits interaction and feedback mechanism and use data analysis to understand customer needs better. These insights are then integrated into the product development process to facilitate product innovation closer to market needs.
The Performance Value Perspective
Samsung has taken steps to optimize its internal organizational structure to facilitate cross-division collaboration. For example, one of the 7 Supply Chain Transformations in Samsung is setting up a cross-functional team called ‘Voice of Business’ to promote cooperation between departments (SupplyChainOpz, 2013). This model encourages employees from different backgrounds to share knowledge and ideas, thereby accelerating the process of a product from concept to market. However, in some cases, large firms’ hierarchical structure and sectoral barriers may impede rapid innovation and decision making.
Samsung could further simplify its organizational structure and promote flat management. More cross-functional teams can also be established to enhance collaboration and knowledge-sharing between different departments to accelerate innovation.
The Learning Perspective
Samsung has invested significantly in developing technology and management talent, such as Samsung Advanced Institute for Technology Development. The institute offers a variety of training courses covering the latest technological fields, like artificial intelligence and 5G networks, aiming to enhance employees’ professional skills and innovation capabilities (SAIT, 2024). In a fast-changing technology landscape, continuous learning and adaptation are required. Company culture is equally important for encouraging innovation and accepting failure as a learning experience.
Samsung must strengthen its continuous learning and career development programmes, especially in emerging technologies. At the same time, Samsung also needs to create a corporate culture that encourages exploration and tolerates failure to support innovative thinking and behaviour.
From the perspective of BSC dimensions, Samsung has taken several measures to support cross-department collaboration and rapid innovation, including significant R&D investment and organizational structure optimization. However, critical analysis shows that the company still has space for improvement in keeping up with consumer demand and further breaking down internal barriers. To stay competitive in the global market, Samsung needs to constantly adjust its strategy and ensure that its R&D investment and organizational capabilities align with market needs and stakeholder expectations.
Discussion – Market research and consumer insights
The accompanying Balanced Scorecard study identifies Samsung Electronics’ performance highlights and possible issue areas across four dimensions. Samsung has taken initiatives to improve market and customer insights, retain a flexible organizational structure, and engage stakeholders. However, there are obstacles and limits in execution that necessitate rigorous study for future improvement.
Enhancing Market and Consumer Insights
First, Samsung should do extensive consumer behaviour research, which entails employing tools to study customers’ purchase decisions, including their wants, motives, attitudes, and actions (Solan, 2020). customer behaviour research offers Samsung detailed insights into customer preferences and behaviour patterns, allowing it to optimize product development and marketing tactics. This improves the accuracy of Samsung’s product market placement.
Next, Samsung can conduct ethnographic and log research to better understand user experience (Rosenthal and Capper 2006). This research approach uses long-term observation and interviews to acquire information on the consumer culture of the area. Furthermore, user experience design theory stresses considering user behaviour, emotion, and cognition throughout the design process (Rico-Olarte et al., 2018). Samsung may utilize these data to create products that better match customers’ habits and requirements, increasing consumer loyalty and engagement with Samsung.
Furthermore, Samsung may employ the consumer segmentation to conduct more precise market segmentation and targeting (Kara and Kaynak, 1997). Using this segmentation strategy, Samsung may fulfil the Design for Diversity, Equality, and Inclusion (DEI) goal by providing more tailored and differentiated products and services to diverse customer groups.
Strengthening Communication and Cooperation with Stakeholders
Samsung, among others, can appropriately adopt the two-way symmetric communication model in creating and nurturing interactive relationships with primary stakeholders (ERTÜRK and BERKMAN, 2016). In this manner, Samsung gets an opportunity to learn more about the needs of stakeholders and foster understanding on both sides. In particular, Samsung designs integrated communication solutions that provide for direct interactions with stakeholders. Using these platforms, Samsung can publish the latest news, product updates and corporate responsibility activities and engage stakeholders by submitting questions, comments, and suggestions. For effective communication, Samsung should set up a quick response system. Further, Samsung should organize recurrent face-to-face exchange activities as a practical step to show its support for open communication and collaboration.
Combination of Organizational Capabilities and Market Needs
Firstly, using the STP marketing approach enables Samsung to improve demandaandnunderstanding preferencesdelwal,2020). Through refining market segmenting, Samsung can find customer clusters that require special offerings and then select target markets that align with the company’s competencies to form unique product and service positioning strategies. This not only improves market response efficiency but also strengthens customers’ brand identities.
Second, improving the application of dynamic capability theory (Gremme and Wohlgemuth, 2017) is critical for Samsung to react to the continuously changing market environment. By expanding its understanding of market developments, Samsung adapts its approach to match consumers’ changing wants. Quick deployment of resources and skills will enable Samsung to react swiftly to market developments. Simultaneously, supporting a culture of continual innovation and learning inside the business will strengthen the company’s adaptability and innovation capabilities.
Finally, improving internal processes through value chain analysis (Ensign, 2001) will offer Samsung with a more efficient and cost-effective operating model. By identifying and improving the company’s major value activities, Samsung may improve productivity, lower costs, and ultimately increase customer value in critical areas like as R&D, production, marketing, and service. Furthermore, by integrating supply chain management and strengthening collaboration with partners, Samsung can increase the overall reaction speed and efficiency of the value chain, allowing it to better satisfy customer expectations and strengthen its market competitiveness.
Literature Review
Based on the study and debate of the stakeholders of Samsung Electronics, it is clear that users are the most important. Samsung Electronics’ services, goods, and funding are all geared toward customers. The upkeep of the stakeholder network is also concerned with retaining existing users and identifying future users. As a result, user-centered theory is critical for applying stakeholder theory.
Theoretical Framework
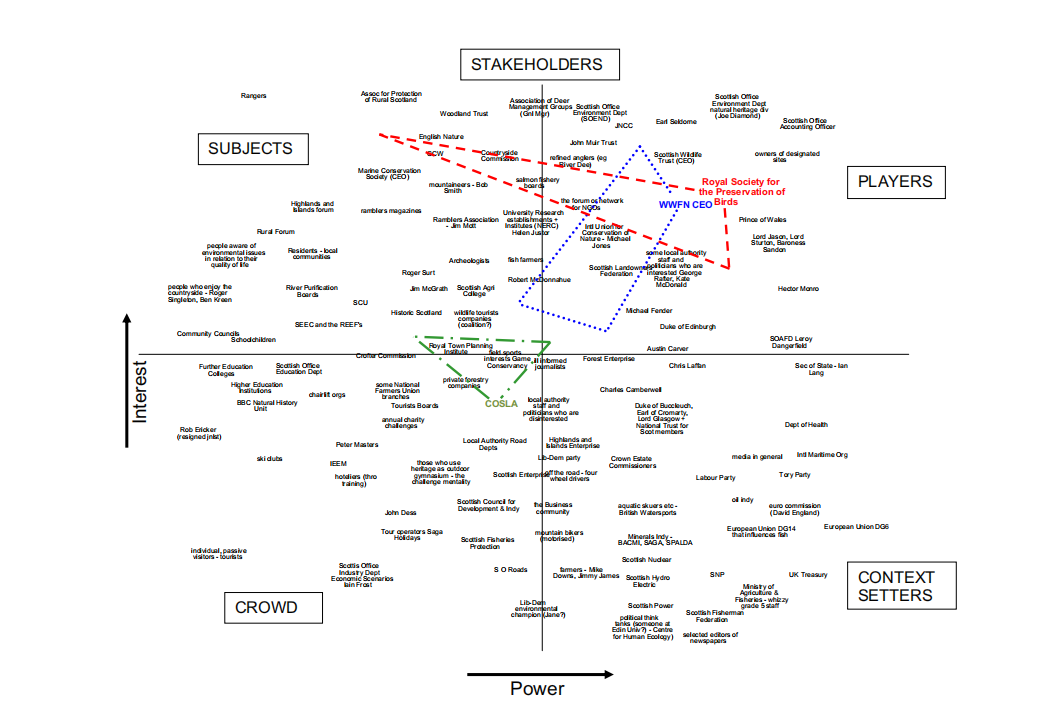
Edward Freeman initially systematized stakeholder theory in 1984 with Strategic Management: A Stakeholder Approach, which highlighted the need of identifying and managing all key parties, or stakeholders, in a company’s operations. In Fran and Colin’s (2011) Power-interest Grid, customers are among the SUBJECTS and PLAYERS, based on their interest and power in the organization. PLAYERS, or high-interest customers, are essential stakeholders in the organization’s strategic management and require ongoing management attention.
User-centered design (UCD) is a design process that focuses on the needs, expectations, and limitations of users (Norman and Draper, 1986). User experience (UX) design focuses not only on how a product functions and looks beautiful, but also on how the product meets the needs and expectations of users (Allam and Dahlan, 2013). UX design is a key practice to implement user-centered design theory.
Therefore, stakeholder theory provides a framework to comprehensively consider the impact of corporate activities, while user-centered design theory and UX design practice are specific methods and enhancements to realize this theory and improve user satisfaction and engagement.
Existing Literature
Stakeholder Theory: The State of the Art represents the authoritative works in the field of stakeholder theory. The definition, scope and key concepts of stakeholder theory are thoroughly discussed in the book, aiming to clarify the basic principles and applications of the theory. By analyzing a series of practical cases, it shows the application of stakeholder theory in different industries and organizations, and how to solve the conflicts of interest in practice. It provides suggestions for future stakeholder theory research, including further development of the theory, exploration of emerging topics, and potential application of the theory in new areas. (Freeman, 2010)
Towards a UX Manifesto is a report on the “UX Manifesto” workshop, which introduces a variety of frameworks for assessing UX research, such as Grid analysis, citation analysis, and content analysis. The paper delves into the present status of research and future developments in the UX area. The study also describes a user experience project that blends non-instrumental quality and emotional user reactions with typical instrumental-focused methodologies, as well as user experience research ideas, policies, and programs. (Laws et al, 2007.)
Collaboration in Creative Design: Methods and Tools refers to the junction of user experience (UX) design, stakeholder theory, and user-centered theory, all of which focus on user and stakeholder demands. User experience design focuses on the sensations and experiences that people have when utilizing products or services. To ensure product success and consumer happiness, designers must take into account these demands and expectations throughout the design process.
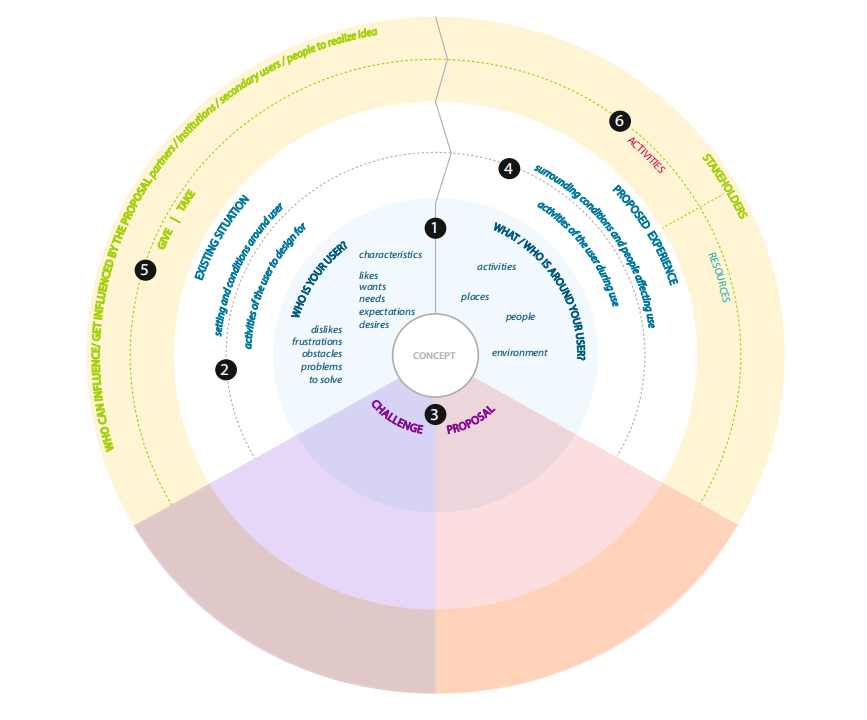
The book provides a novel design process for user and stakeholder demands called the value design method, which attempts to integrate user knowledge, business understanding, and stakeholder expectations and roles to handle the complexity and size of design challenges. The process was carried out using the Value Design Canvas, a visualization tool that can be utilized in multi-stakeholder design workshops. It is divided into six sections, each representing one of the analysis and synthesis phases’ debate subjects. Area 1 is used to determine user attributes, user context and surroundings, marketable solutions, and potential stakeholders. Area 2 identifies typical user actions. Area 3 is utilized to discover problems, unmet demands, and competing stakeholder interests. Area 4 is used to create the fundamental usage scenario, whereas Area 5 is utilized to establish the give-and-take connections amongst stakeholders. Area 6 identifies the role of stakeholders in implementation. (2016)
Research Gap
While stakeholder theory, user-centered theory, and UX design are all essential components of modern corporate management and product development, there is a significant vacuum in empirical research and theoretical frameworks that investigate their effective integration. Currently, the literature lacks thorough guidance on how to integrate these three factors in order to completely comprehend the connection between stakeholder demands and user experience design.
There is a lack of explicit criteria or frameworks for incorporating stakeholder opinions into UX design processes. A thorough framework is required not only to understand the requirements and expectations of numerous stakeholders, including end users, but also to guide designers and decision-makers on how to incorporate these demands into design methods. Such assistance is necessary for developing products and services that are not only appealing but also meet the needs of all stakeholders. Although stakeholder theory is widely used in strategic management, its relevance to the process of UX design remains largely uncharted. Knowing what key stakeholders want, expect and what can be the implications is critical for increasing acceptability and apportion of the design solution success rates. Consequently, the question arises if the stakeholder analysis can add to UX approach and how.
Due to these limitations, this study aims at offering an integrated model based on stakeholder theory, user-centered theory, and UX design principles. Such system would make organizations more responsive to needs of all major stakeholders as a result of which, products and services produced will emphasize user satisfaction and will also consider wider stakeholder issues.
Current Study
The main goal of this literature review is to present an elaborate framework that can combine all the main principles of stakeholder theory, user-centered theory, and UX design principals. Using this model, organizations can be assisted in achieving a fit between the needs and requirements of all major stakeholders and that products and services are all about users.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this report has presented a holistic synthesis of the analysis that links stakeholder theory with the principles of user-centered design, using Samsung Electronics as a case study. Having analyzed Samsung stakeholder engagement strategies and organizational capabilities, this research has found key areas of alignment and improvement prospects. The Balanced Scorecard framework has provided guidance regarding Samsung’s initiatives to transform stakeholder needs into innovation drivers across the financial, customer, internal process, and learning and growth perspectives. In addition, the report has emphasized the role of market research and customer insights in strengthening communication with stakeholders and improving product development approaches. Relying on the current literature, an effective theoretical model has been developed to help organizations in negotiating the intricate combination of stakeholder needs and user experience design. This research brings an understanding of the practical implementation of stakeholder theory in user-centred design practices that could contribute both to the academic community and the industry by promoting sustenance and competitive advantage in the digital era, which is dynamic. Going forward, the recommendations, framework and guiding principles provided in this report can be utilized by practitioners to integrate stakeholder insights in UX design strategies which will improve the product development process and help in achieving long-term organizational success and resilience.
Reference
Ackermann, F. and Eden, C., 2011. ‘Strategic Management of Stakeholders: Theory and Practice’, Long Range Planning, 44(3), pp. 179–196. doi: 10.1016/j.lrp.2010.08.001.
Allam, A.H. and Dahlan, H.M., 2013. User experience: challenges and opportunities. Journal of Information Systems Research and Innovation, 3(1), pp.28-36.
Borja de Mozota, B., 2006. ‘The four powers of design: A value model in design management’,Design Management Review, spring, 17(2): 44-53. Available at: http://www.dmi.org/dmi/html/publications/journal/fullabstract_d.jsp?itemID=06172BOR44 (Accessed: 14 March 2024)
Bundy, J., Vogel, R. M. and Zachary, M. A., 2018. ‘Organization-Stakeholder Fit: A Dynamic Theory of Cooperation, Compromise, and Conflict between an Organization and Its Stakeholders’, Strategic Management Journal, 39(2), pp. 476–501.
Collaboration in creative design: methods and tools. 1st ed. 2016 edn., 2016. Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Ensign, P.C. (2001) ‘Value chain analysis and competitive advantage’. Journal of general Management, 27(1), pp.18-42.
ERTÜRK, K. O. and BERKMAN, A. N., 2016. ‘Corporate Governance As a Communication Policy in Two-Way Symmetrical Public Relations Model’, Omer Halisdemir Universitesi Iktisadi ve Idari Bilimler Fakültesi Dergisi, 9(2).
Freeman, R. E., 2010. Stakeholder theory : the state of the art. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Freeman, R. E., 2010. Strategic management : a stakeholder approach. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Gremme, K.-M. and Wohlgemuth, V., 2017. Dynamic capabilities: a systematic literature review of theory and practice. Mannheim.
Kara, A. and Kaynak, E., 1997. ‘Markets of a single customer: exploiting conceptual developments in market segmentation’. European journal of marketing, 31(11/12), pp.873-895.
Khandelwal, K., Jakhar, T. and Khandelwal, T., 2020. ‘Segmentation, Targeting and Positioning’. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN, pp.2395-0056.
Law, E. L.-C., Hassenzahl, A. P. O. S. V. M. and Blythe, M., 2007. ‘Towards a Ux Manifesto’, PEOPLE AND COMPUTERS, 2(Edit 21), pp. 205–206.
Michael Herh., 2023. Samsung Electronics Joins Top 5 Global Brand Club; Only Korean Brand. Business Korea. 206206. Retrieved from https://www.businesskorea.co.kr/news/articleView.html?idxno=206206 . Accessed 10 March 2024
Nair, H.A., Sri Ramalu, S. and Kumar M, D., 2014. Impact of innovation capacity and anticipatory competence on organizational health: A resource based study of Nokia, Motorola and Blackberry. International Journal of Economic Research, 11(2), pp.395-415.
Nogalski, B., 2020. The Future of Management. Industry 4.0 and Digitalization. Wydawnictwo UJ.
Norman, D. A. and Draper, S. W. (eds)., 1986. User centered system design : new perspectives on human-computer interaction. Hillsdale, N.J.: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Rico-Olarte, C., López, D. M. and Kepplinger, S.,2018. ‘Design, User Experience, and Usability: Theory and Practice : 7th International Conference, Duxu 2018, Held As Part of Hci International 2018, Las Vegas, Nv, Usa, July 15-20, 2018, Proceedings, Part I’, in Towards a Conceptual Framework for the Objective Evaluation of User Experience. Cham : Springer International Publishing : Springer, pp. 546–559.
Rosenthal, S. R. and Capper, M., 2006. ‘Ethnographies in the Front End: Designing for Enhanced Customer Experiences*’, Journal of Product Innovation Management, 23(3), pp. 215–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-5885.2006.00195.x.
Samsung., 2018. Samsung Newsroom. Available at: https://news.samsung.com/global/samsung-steps-up-investment-for-future-growth-takes-initiative-to-build-innovation-ecosystem (Accessed: 16 March 2024)
Samsung., 2024. Samsung Design. Available at: https://design.samsung.com/global/ (Accessed: 16 March 2024)
Solan, H.P., 2020. ‘Review paper on factors influencing consumer behaviour’. Test Engineering & Management, 83(3), pp.7059-7066.
 write
write