Abstract
Performance management is a basic process that includes setting clear objectives, giving progressing criticism and assessing worker advance to drive person and organizational victory. This paper characterizes performance management as a ceaseless communication handle between supervisors and workers that adjusts person objectives with an organization’s destinations. It examines components of performance management, counting objective setting, progressing criticism and assessment processes. Moreover, this paper analyzes different strategies to assess worker execution, such as self-assessment, realistic rating scales, constrained positioning, and basic incidents.
Furthermore, the noteworthiness of inspiration in driving worker execution is investigated with Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs hypothesis being checked on for its one of a kind capacity to persuade workers at all organizational levels. The hypothesis proposes that people have five essential needs- physiological, security, social, regard, and self-actualization- which must be met to feel propelled towards accomplishing their full potential.
In conclusion, effective performance management improves individual productivity. It fosters organizational success by aligning efforts towards common objectives while promoting open communication between managers and employees about expectations for growth opportunities. Additionally, consideration of different motivational theories, such as Maslow’s hierarchy, can assist managers in creating an environment where individuals feel valued at all levels, ultimately contributing to improved organizational success.
Introduction
Performance management is a systematic and continuing process that sets goals, provides feedback, and evaluates employee performance to increase effectiveness and meet organizational goals. It is crucial to HRM since it affects employee motivation, engagement, and productivity. This article will define performance management, including goal formulation, feedback, and evaluation. Additionally, this article will examine how popular employee performance evaluation approaches improve organizational success. Motivation and its impact on employee performance will also be discussed. Finally, Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs will be examined for its unique potential to encourage employees.
Defining Performance Management
Performance management entails setting clear standards and giving frequent feedback to align company and employee career goals. This collaborative method, led by managers or supervisors, aligns everyday duties with company goals and identifies growth opportunities (Aguinis, 2019). Employees understand their daily involvement in accomplishing senior management goals by constantly conveying work duties and targets. This allows quick remedial action if issues develop, ensuring the organization’s goals are accomplished on schedule. Performance management ensures that everyone works toward the same goal and allows for personal growth and development by communicating effectively between employers and employees.
Components of Performance Management
Performance management has various components that work together to ensure employee success. These components include goal setting, ongoing feedback and evaluation processes.
Goal Setting
Effective performance management is built upon setting clear and meaningful employee goals (see Figure 1.2). These goals serve as a crucial map, guiding employees towards their desired destination and outlining what is expected of them along the way (Locke et al., 2019). Not only do they provide a roadmap for success, but they also promote alignment between individual efforts and the overall objectives of the organization. By defining specific job responsibilities and performance expectations, goals clarify employees’ tasks and aid in prioritization (Aguinis, 2019). Moreover, setting achievable yet challenging goals can motivate employees by giving them a sense of direction and purpose. The feeling of accomplishment after reaching these targets further boosts their motivation levels. In summary, goal setting drives employee engagement and fosters organizational success through focused efforts towards common objectives.
Ongoing Feedback
Successful performance management depends on normal input to assist people get it how their activities impact their victory and the generally advance of the organization (Poon, 2023). Criticism may be a crucial instrument that permits workers to see the relationship between their practices and their affect on individual effectiveness and key objectives. Prompt, detailed, and commonsense input is vital because it empowers workers to form fundamental alterations expeditiously. It moreover offers directors a chance to recognize model execution or address any potential ranges for change. By giving reliable input, directors can keep track of employees’ advance and give bolster when needed.
Moreover, normal criticism makes an environment of open communication where representatives feel esteemed and spurred to perform at their best. It advances straightforwardness between directors and workers by cultivating legitimate discussions that adjust person objectives with organizational targets. This makes a difference construct a positive work environment culture where everybody works successfully towards common objectives. Frequent criticism cultivates a development attitude by encouraging steady learning, improvement, and advancement among people inside an organization. It guarantees that endeavors center on nonstop advancement instead of fair keeping up the status quo.
Evaluation Processes
As part of performance management, it is pivotal for organizations to routinely assess worker advance towards assembly set up objectives. This includes conducting execution evaluations at annually planned interims (Furubo, 2020). These assessments come in different shapes, counting 360-degree and administrator assessments, and serve as a formal implies of checking representative development and pinpointing ranges for improvement (Furubo, 2020). Through performance evaluations, managers can pick up important experiences into an individual’s advancement inside their part. By giving organized criticism on their execution against foreordained targets, workers can reflect on their qualities and ranges requiring change to shape future objective setting. In addition, these appraisals permit directors to recognize tall entertainers who merit acknowledgment or require extra back for career movement (Furubo, 2020).
Overall, steady assessment through formal performance evaluations is basic for viable workforce administration. It encourages a data-driven approach to following worker advance with set targets whereas giving openings for normal communication between directors and representatives with respect to desires and improvement objectives (Furubo, 2020). Eventually, this leads to a propelled workforce superior prepared to realize organizational objectives effectively.
Methods of Evaluating Employee Performance
Various methods are used to evaluate employees’ performance, such as self-assessment, graphic rating scales, forced ranking and critical incidents (Furubo, 2020). Each method has its strengths and limitations in terms of effectiveness.
Self-Assessment
Self-assessment helps employees evaluate their performance against objectives or skills. It lets people evaluate their accomplishments and discover opportunities for improvement (see Figure 1. 4..). Employees may own their development through this technique. One benefit of self-assessment is that it helps people identify their strengths and flaws. Employees can identify their strengths and weaknesses by self-evaluation. This can help them create achievable improvement targets. Due to their reliance on self-perception, self-assessments have limits. This may not be true since people prefer to regard themselves more positively than others. Inclusive self-assessment in performance appraisals benefits people and businesses. It supports personal growth and open communication between managers and employees regarding development possibilities. Self-assessment can aid evaluation if objectivity is checked.
Graphic Rating Scales
Graphic rating scales, which provide numerical values to predetermined criteria, are extensively used to evaluate employee performance (Dessler et al., 2020). This evaluation ensures that assessors’ scores are consistent and makes it easy to compare employee performance. However, it uses subjective views rather than statistics (Figure 1.1). Thus, visual rating scales can be consistent and efficient in evaluating performance, but they may only sometimes fully reflect an employee’s genuine talents or contributions to the firm. Organizations must utilize this strategy cautiously and consider adding other metrics and feedback methods to analyze employee performance.
Forced Ranking Method
The Forced Ranking Method is a performance evaluation approach that entails categorizing employees based on their rank in terms of performance. This method involves ranking employees from the most outstanding to the least performing and placing them in predefined categories like top, average, and low performers. While this strategy can be advantageous in identifying high-potential employees, it may also breed unhealthy competition among colleagues due to its competitive nature (Taherdoost, 2019). Employers can clearly distinguish their top-performing workers from those who may require additional support and development opportunities using this method. However, organizations must consider the potentially tense environment this approach could create among their workforce. In order to maintain a positive work culture and avoid discord among staff members, thoughtful communication and transparent performance evaluation systems must be implemented alongside the Forced Ranking Method.
Critical Incidents Method
The Critical Incidents Method evaluates employee performance by closely monitoring particular acts or behaviours that show excellent or mediocre performance. This method records cases of outstanding or unsatisfactory employee behaviour ((Taherdoost, 2019)). This strategy gives supervisors and staff concrete evaluation examples and encourages open discussion. Managers must work hard to document occurrences. The Critical instances Method delivers a comprehensive review by recording notable instances that reveal an employee’s work performance strengths and weaknesses. It emphasizes real-life circumstances rather than generalizations, improving appraisal objectivity (Armstrong & Baron, 2018). The feedback loop between supervisors and subordinates encourages open communication and prompts the resolution of performance issues.
The negative is that supervisors must meticulously record and document Critical Incidents. To find major occurrences for evaluation, they must regularly examine employee behaviour. Managers need good analytical abilities to evaluate each incident’s influence on employee performance. While managers may find it difficult, the Critical Incidents Method provides a robust framework for fair and objective performance reviews.
The Role of Motivation in Employee Performance
Motivation is the internal drive that compels individuals to behave in ways directed towards achieving certain goals (Niati et al., 2021). As discussed earlier, goal setting is an essential component of performance management. Goals provide direction for employees’ efforts, which can increase motivation levels by giving them something to work towards. Employee motivation is crucial to job satisfaction and engagement, increasing organizational productivity (Niati et al., 2021).
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory
Maslow’s HierarchyNeedneedsory is one of the oldest motivational theories used by Abraham Maslow in 1943 (Trivedi et al., 2019). This theory suggests that individuals have five basic needs that must be fulfilled in order for them to be motivated and satisfied. The hierarchy includes physiological, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization needs (Trivedi et al., 2019). (see Figure 1.3).
Physiological Needs
These are the most basic human necessities, such as food, water and shelter. Individuals must satisfy these fundamental requirements before focusing on higher-level goals.
Safety Needs
Once physiological needs are met, individuals seek security and stability within their environment. This may include job security or a safe workplace.
Social Needs
Humans need belongingness and interpersonal relationships, including friendship and love. People value being part of a supportive team, which motivates them to achieve common goals.
Esteem Needs
This level refers to the need for recognition from others and self-achievement. It includes external validation through receiving praise from supervisors or colleagues and internal recognition of one’s accomplishments.
Self-Actualization
Maslow’s hierarchy’s top level symbolizes an individual’s desire to realize their full potential via difficult employment that permits personal progress (Niati et al., 2021). Highly motivated, focused, and fulfilled careerists are frequently at this level.
In summary, Maslow’s theory motivates employees by emphasizing the necessity for comprehensive management that addresses all human needs (Niati et al., 2021). Managers may motivate and improve performance by knowing people’s needs to be pleased.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Organizations must manage performance by defining goals, offering feedback, and assessing employee progress. Clarity on expectations, growth opportunities, and appreciation of successes motivates personnel. Different approaches evaluate employee performance, each having pros and cons. Lastly, Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs theory emphasizes recognizing individual needs while motivating employees, which improves organizational effectiveness. Managers must grasp performance management and motivation theories to encourage personnel to meet company goals.
References
Aguinis, H. (2019). Performance management for dummies. John Wiley & Sons.
Furubo, J. E. (2020). Learning from evaluations: the Swedish experience. In Can Governments Learn? (pp. 45-65). Routledge.
Locke, E. A., & Latham, G. P. (2019). The development of goal setting theory: A half-century retrospective. Motivation Science, 5(2), 93.
Niati, D. R., Siregar, Z. M. E., & Prayoga, Y. (2021). The effect of training on work performance and career development: the role of motivation as intervening variable. Budapest International Research and Critics Institute (BIRCI-Journal): Humanities and Social Sciences, 4(2), 2385-2393.
Poon, R. (2023). Exploring What Essential Elements Are Needed for Ongoing Performance Feedback (Doctoral dissertation, The Chicago School of Professional Psychology).
Taherdoost, H. (2019). What is the best response scale for survey and questionnaire design; review of different lengths of rating scale/attitude scale/Likert scale. Hamed Taherdoost, 1-10.
Trivedi, A. J., & Mehta, A. (2019). Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs-Theory of Human Motivation. International Journal of Research in all Subjects in Multi Languages, 7(6), 38-41.
Appendix
Figure 1.1 Graphic scale.
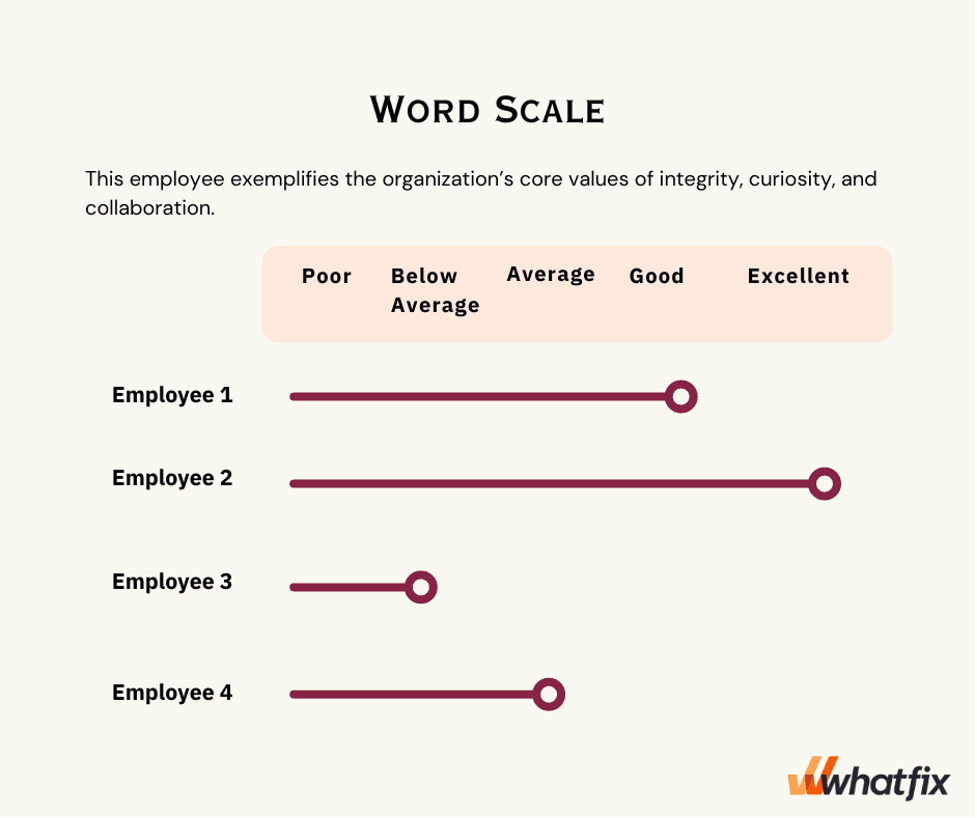
Figure 1.2 Goal setting
Figure 1.3
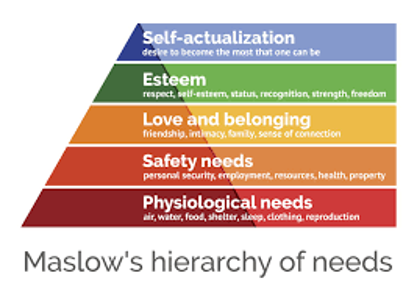
Figure 1. 4.. self-assessment

 write
write