Introduction
This report provides an in-depth analysis of the readiness for change and needs as pertains to the U.S. branch of a Singapore software solutions company. This is a document developed by an HR consultant who was commissioned to assess the ability of employees and leadership to implement the needed changes. The end goal is, therefore, to coordinate the performance of the U.S branch so that it fits into the CEO’s plans for growth and penetration at the United States market level.
Visual analysis of Employee Engagement Survey
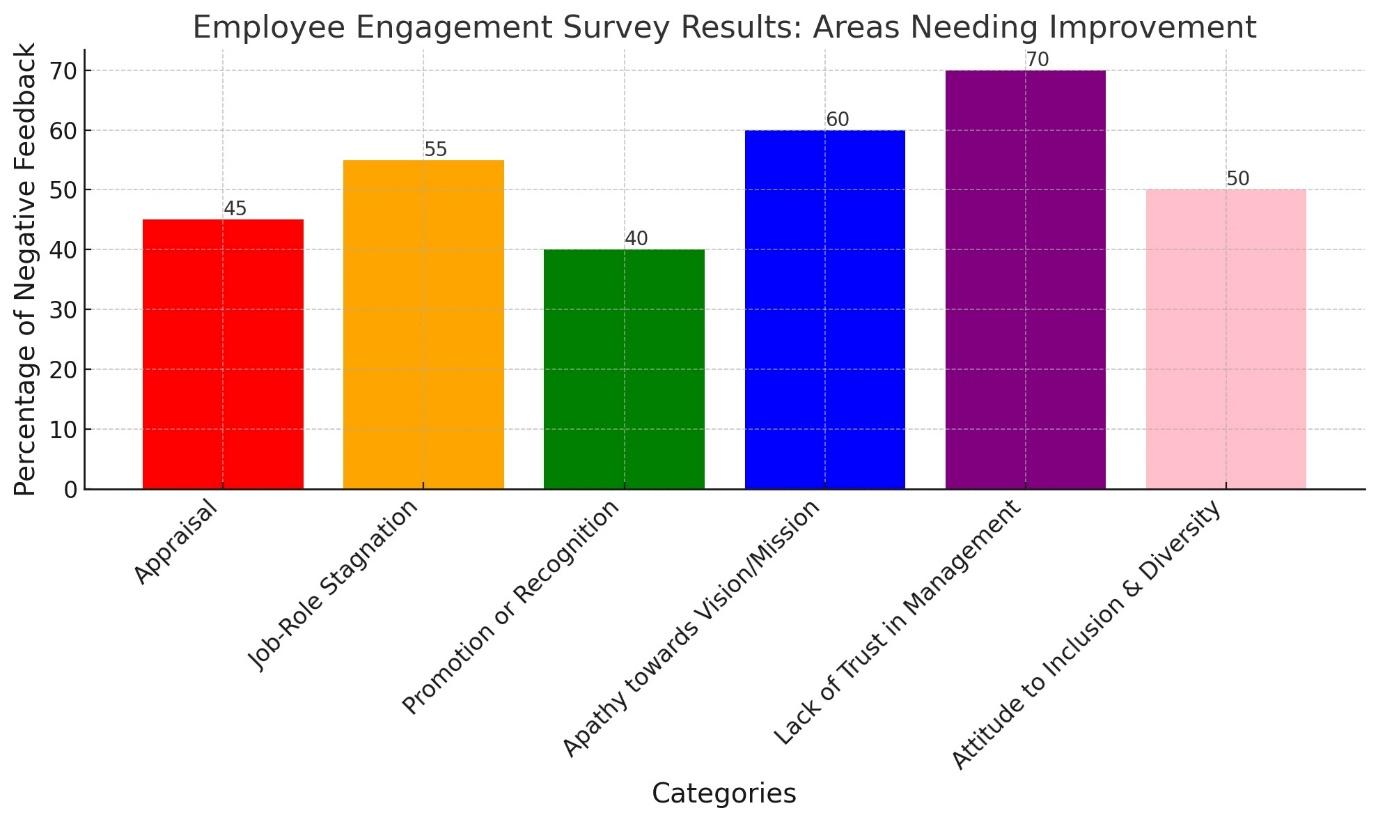
Appraisal, Job-Role Stagnation and Promotion or Recognition
An examination of the results obtained from Employee Engagement Surveys shows serious discontent with employees concerning evaluation processes, settled roles at work and absence of promotion or recognition. Graphical representations of data are able to depict the difference between what employees expect and how well their expectations have been met in a positive or negative way labor market This section brings out the importance of a reformed appraisal system and well-defined career progression paths to stop stagnation in job roles as also better recognition systems.
Lack of Passion about the Vision, Mission and Values
Survey information reveals an increasing trend of disconnect between the organization’s vision, mission and value as well as its employees. Through the use of pie charts and trend lines, employee engagement declines as well as their willingness to participate in programs that seek to promote these foundational elements. The above visual data demonstrates the need for strategies that will effectively re-engage employees with core values of organization.
Absence of Trust in Managers, Particularly Senior Level Executives
The use of data visualization techniques like sentiment analysis displays an extremely low level of trust for management and especially the top leadership. The analysis implies that communication and the display of transparency should be vitally important to rebuilding trust.
The Impression of the Organization Attitude towards Inclusion and Diversity
The results from the surveys indicate doubt about organization commitment to inclusion and diversity. Stacked bar graphs demonstrate the way employees perceive themselves to be underrepresented and undervalued by various employee groups thus emphasizing that modern workplace needs a more inclusive culture.
Confidence in Change Management Practices of Employees
From the Employee Engagement Surveys and Leaders’ Self-Evaluations, it seems that there is a widespread lack of faith in company leaderships as well its change management practices. This chapter delves into the fundamental reasons for this loss of confidence and recommends steps that increase leadership credibility and efficiency in change management (OREG & BERSON, 2011).
Demand for Change among Employees and Leaders.
There is a clear need for change between the leadership and employees. This part analyzes the crucial areas that need to be addressed immediately in order to avoid additional disengagement and fit the branch’s performance into strategic aims of an organization (Busari et al., 2019; Chalofsky et al., 2014).
Middle Managers and the Adoption Mindset
Middle managers are integral in achieving the role of linking senior leaders and frontline employees (Busari et al., 2019; Chalofsky et al., 2014). This section assesses their current level of preparedness in developing an adoption-oriented mindset, which then specifies the support and resources required to enable them successfully lead their teams through this process.
Leadership Styles and Power Distribution as Change Readiness Modifiers
This section of the report evaluates how leadership styles and power distribution within an organization influences change readiness. It supports a more participative leadership style, as well as the decentralization of power for the purpose of improving worker engagement and openness to change.
Change Readiness/Trust Enhancement Opportunities
Finding and eliminating the causes of resistance is very important for growing readiness to change and trust (Busari et al., 2019; Chalofsky et al., 2014). This chapter analyzes various types of resistance using Forms of Resistance Grid and suggests approaches to initiating an effective dialogue with employees regarding change.
Cultural Dimension and Hofstede’s Model
Between the American employees and Singaporean headquarters, there are major differences in culture that prevent effective change management. Through the application of Hofstede’s cultural dimensions model, this section discusses how individualism and perhaps one other dimension—say uncertainty avoidance or power distance affects cross-cultural communication as well as business practices. It elaborates on how these cultural differences have transpired in the workplace by giving several specific examples taken from Exit Interviews, Employee Engagement Surveys and Leaders’ Self-Evaluations.
Conclusion
The results from this evaluation evidence the significant demand for specific change management interventions that reflect distinct challenges of operations in U.S.’s branch selection. With a focus on improving communication skills, leadership credibility and developing cultural understanding the enterprise can strengthen its ability to change and is thus better prepared for achieving strategic objectives in American market.
References
Busari, A. H., Khan, S. N., Abdullah, S. M., & Mughal, Y. H. (2019). Transformational leadership style, followership, and factors of employees’ reactions towards organizational change. Journal of Asia Business Studies, 14(2), 181–209. https://doi.org/10.1108/jabs-03-2018-0083
Chalofsky, N., Rocco, T. S., & Michael Lane Morris. (2014). Handbook of human resource development. Pfeiffer.
OREG, S., & BERSON, Y. (2011). LEADERSHIP AND EMPLOYEES’ REACTIONS TO CHANGE: THE ROLE OF LEADERS’ PERSONAL ATTRIBUTES AND TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP STYLE. Personnel Psychology, 64(3), 627–659. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-6570.2011.01221.x
 write
write