Introduction
In a global environment, strategic marketing is a rapidly evolving and complicated discipline that centers on developing and putting into practice marketing plans to break into foreign markets (Clarkson, 2023). Businesses are increasingly going outside of their own country to take advantage of new growth prospects and achieve a competitive advantage in today’s globally connected world. This calls for a thorough awareness of the various cultures, consumer behaviors, legal systems, and market dynamics that occur across international borders. Strategic marketing in a global setting entails customizing goods, services, and advertising campaigns to address the unique requirements and preferences of clients from around the world. To determine the most promising regions for expansion and to create powerful marketing strategies that appeal to regional consumers, thorough market analysis and research are necessary. To manage the difficulties of entering international markets, businesses must also take into account a variety of entrance techniques, such as exporting, licensing, partnership arrangements, or direct investing.
Managing cultural sensitivity, language limitations, worldwide legislation, and a variety of competitive landscapes are just a few of the many difficulties that come with global strategic marketing. Nevertheless, a broad and expanding global consumer base presents a wealth of opportunities for savvy global marketers to seize. This calls for a trifecta of original thought, flexibility, and a readiness to accept cultural variances (Gielens, 2021). We will examine the method of strategic marketing from a worldwide perspective in this research and offer suggestions for Sainsbury’s PLC, a major UK supermarket, as it attempts to increase its global footprint. We strive to provide Sainsbury’s with well-informed plans to support successful international expansion through a detailed examination of possible markets and a critical review of the retail grocery sector in the target country.
Main evaluation
1) Market Selection: Canada
A detailed investigation and analysis of many different variables have been done to support this conclusion, recommending Canada as the next overseas destination for Sainsbury’s supermarkets such as:
1.1 Size and Prospects of the Market: Canada is a desirable location for Sainsbury’s expansion due to its size and prospective market. With an estimated population of more than 38 million people and a strong and expanding economy, the nation presents numerous prospects for growth. There is a large opportunity for Sainsbury’s to capitalize on a lucrative market given the expected value of the grocery retail sector in Canada at CAD 150 billion (Breunig & Sainsbury, 2023).
In addition, the steadily rising disposable income of Canadian consumers provides Sainsbury’s with a favorable business environment. In line with Sainsbury’s offerings, people are increasingly likely to spend money on convenience and high-quality goods when their purchasing power grows. Furthermore, Sainsbury’s has a chance to adapt to these changes and represent itself as a brand that satisfies the changing needs of the Canadian market thanks to the changing tastes of consumers towards healthy and sustainable food options. Encouraging conditions exist for Sainsbury’s to make an appearance and flourish in the Canadian supermarket retail sector thanks to the sizeable and expanding economy of Canada as well as the buying habits of its people (PA., 2023). Sainsbury’s can successfully enter the Canadian market while developing a solid presence there by leveraging these market characteristics.
Environment in terms of politics and regulations: A safe and favorable foundation for Sainsbury’s international ventures is provided by the political and regulatory climate in Canada. Since the political climate in the nation is stable, new enterprises can operate with a sense of security and predictability. Sainsbury’s is able to concentrate on its approach to entering markets thanks to this consistency, which lowers the risk involved with global expansion. Meanwhile, Canada’s welcoming climate for international businesses generates a business-friendly environment(Żuk, 2022). Sainsbury’s trademark and products are protected in the market because of the robust legal system of the nation, which safeguards intellectual property rights. In addition, as long as fair competition is upheld, Sainsbury’s can engage in rivalry with both domestic and foreign rivals on an equal footing.
Sainsbury’s expansion plans benefit from Canada’s involvement in international trade accords. Being a G7 member and having ratified trade pacts like the CUSMA (Canada, the United States, and Mexico Agreement) gives access to a larger market (DUFOUR & DUCASSE, 2020). The movement of products and services is also facilitated by the lower trade barriers imposed by such accords, which make it simpler for Sainsbury’s to bring in and sell goods in the Canadian market. A favorable and encouraging atmosphere is created for Sainsbury’s to enter and succeed in the Canadian market through Canada’s stable political environment, business-friendly environment, and involvement in trade agreements. Due to the reduction of risks and obstacles, Sainsbury’s is better able to take advantage of the numerous opportunities presented by the nation’s retail grocery industry.
Cultural Competence: Sainsbury’s has an edge when it enters the Canadian market because the UK and Canada share similar cultures. For Sainsbury’s business in Canada, the fact that English is the primary language in both nations makes communication easier and lowers language barriers. Due to Canadian consumers’ familiarity with foreign brands and products, this shared language also makes it easier for businesses to be recognized and for customers to interact with them.In addition, Canadian shoppers are known for being open to experimenting with new and diverse products, which is consistent with Sainsbury’s image as a merchant carrying a broad range of goods. The chances of Sainsbury’s being well-received in the Canadian market are improved by this commonality in culture (Damnjanovic, 2019).
To meet the unique demands and tastes of Canadian customers, Sainsbury’s must also understand how crucial it is to localize its offers. Although there are certain cultural similarities, Canadian consumer behavior, taste preferences, and purchasing habits also have unique nuances that should be carefully considered. For Sainsbury’s to be successful in this new market, it will be essential to modify its product lineups, packaging, and marketing tactics to appeal to Canadian consumers. For Sainsbury’s introduction into the Canadian market, the cultural similarity between the UK and Canada offers a strong base (Jones , 2023). An advantage for Sainsbury’s could come from capitalizing on linguistic similarities and consumer receptivity to foreign brands. The business’s capacity to comprehend and adjust to the unique cultural subtleties of the Canadian customer base will be crucial to its ability to enter the market successfully.
Competitive Environment: Retail grocery sales in Canada are highly competitive, with Loblaws, Walmart, and Metro leading the sector. While entering the market in such a cutthroat climate may present difficulties, Sainsbury’s may use its track record of providing high-quality goods and first-rate customer care to set itself apart. Sainsbury’s needs to carefully analyze the market positioning and strategies of its main rivals in order to successfully navigate the competitive landscape.Sainsbury’s can find gaps and unexplored potential in the Canadian market by looking at the tactics and advantages of competitors(Steinman, 2019). Sainsbury’s will be able to take a strategic stance to meet customer wants that are not entirely supplied by existing businesses by being aware of the differentiating characteristics of each competitor. For Sainsbury’s to establish a distinctive market position in Canada, uniqueness through a variety of products, pricing, promotions, and personalized services is crucial.
Also, Sainsbury’s can use its knowledge of best practices from around the world and its worldwide expertise to introduce fresh ideas and winning marketing tactics to Canada. Sainsbury’s may get an advantage in the marketplace by putting into practice methods that have been successful in other regions while customizing them for the Canadian market.Despite the fierce competition in Canada’s grocery retail sector, Sainsbury’s may differentiate itself by highlighting its strengths in goods quality as well as client service. Sainsbury’s will be able to develop a compelling approach to market entry that appeals to Canadian consumers and establishes the foundation for achievement in this new foreign market by conducting a thorough investigation of competitors and finding market gaps.
Entry-level Marketing Plan: According to the study’s findings and analyses, Sainsbury’s should enter the Canadian market gradually. Prioritizing the creation of an online presence in the first stage will allow you to gauge how well the brand and its products are received by the market. To accomplish this and reach a larger customer base, e-commerce platforms and relationships with regional distributors might be used. Sainsbury’s will be able to assess client preferences, gather useful information, and adjust its product lineup and marketing tactics with the help of an online presence (Olabode , 2023). Sainsbury’s can move on to the next stage of its market penetration strategy, which entails constructing physical stores selectively in prime areas across Canada, once the brand achieves traction and develops a devoted client base. Sainsbury’s will be able to offer an improved shopping experience, draw in a wider clientele, and improve its market position as a result of its entry into physical retail.
Sainsbury’s can reduce risks and financial outlays while exploring the Canadian market by entering it gradually. Sainsbury’s is able to modify and tweak its offerings in response to current market feedback and customer preferences thanks to this method of gradual expansion. Additionally, it gives you the freedom to expand your business when the brand has solidified its acceptance and position in the Canadian market (Arora & Patro, 2021).A wise method for Sainsbury’s to enter and successfully traverse the highly competitive grocery retail industry in Canada is a phased market entrance approach that starts with a website and progressively transitions into physical shops.
Customer Trends: In Canada, consumer trends point to a rise in the need for more affordable, sustainable, and healthy food options. Sainsbury’s needs to match its product selection with these popular consumer preferences in order to succeed in the Canadian market. One important tactic is to draw attention to the company’s private label goods, which can satisfy customers’ needs for cheaper, healthier, and more environmentally friendly options. Furthermore, Sainsbury’s should highlight its selection of fresh produce because Canadian shoppers place a high value on fresh and high-quality food selections(Brouwer, 2021). Sainsbury’s can effectively woo people who care about their health and set itself apart from rivals by sourcing locally and emphasizing the quality and freshness of its products.
In the Canadian grocery store sector, convenience is also a key component. To give customers a seamless and effective experience, Sainsbury’s should concentrate on optimizing its online purchasing and delivery services. Loyalty and satisfaction with customers will be enhanced by providing numerous delivery choices and quick order fulfillment. Sainsbury’s can establish itself as a formidable competitor in the Canadian supermarket market by focusing on private label goods, quality produce, and convenience while also matching its product offerings with customer trends. The viability of Sainsbury’s worldwide development will depend on its ability to comprehend and respond to the changing tastes of Canadian consumers (Babin & Li, 2022).
Chain of distribution and logistics: Sainsbury’s should place a high priority on investing in a strong supply chain and transportation network for a successful debut in the Canadian market. In order to meet consumer expectations and maintain a high standard of customer satisfaction, a strong network of suppliers is vital for maintaining effective operations and timely product delivery.The key to simplifying the supply chain and lowering lead times will be to form strategic alliances with regional distributors and suppliers(Ye, Lau, 2021). Sainsbury’s can guarantee a consistent and effective flow of items from the point of origin to the stores or doorsteps of consumers by collaborating closely with dependable local partners.
The procedures involved in managing stocks, warehousing, and shipping will all be improved by adopting advanced logistics technology and systems. Real-time monitoring and analytics solutions will improve visibility and control across the whole supply chain, enabling speedy responses to shifting market demands and reducing disruptions. Consumers in Canada who are concerned about the environment will be attracted by a supply chain that places an emphasis on durability and environmental responsibility. Sainsbury’s may portray itself as an environmentally conscious brand and get a competitive edge in the market by putting an emphasis on eco-friendly practices and packaging. Sainsbury’s global growth strategy in Canada depends heavily on an effective and flexible logistical and supply-chain network. The strengthening of the brand’s image and position in the fiercely competitive Canadian grocery industry will result from investing in these areas, which will also guarantee smooth operations(Yenugula , 2023).
2) Target Country Based Research and Analysis:
Sainsbury’s introduction into a new overseas market depends on conducting research and analysis specific to the target country. Studying demographic information, cultural factors, and economic indicators is necessary to comprehend consumer behavior, preferences, and buying habits. In order to better target its marketing initiatives, Sainsbury’s can use the research to pinpoint trends that influence consumer behavior. An effective market entry strategy must take into account consumer demand for certain goods, preferred purchasing styles, and price sensitivity. By strategically positioning itself and meeting the unique requirements of the new worldwide market, Sainsbury’s can increase its prospects of success and long-term growth in the international economy(Kim & Kim, 2022). This is made possible by having in-depth knowledge of the grocery retailing sector.
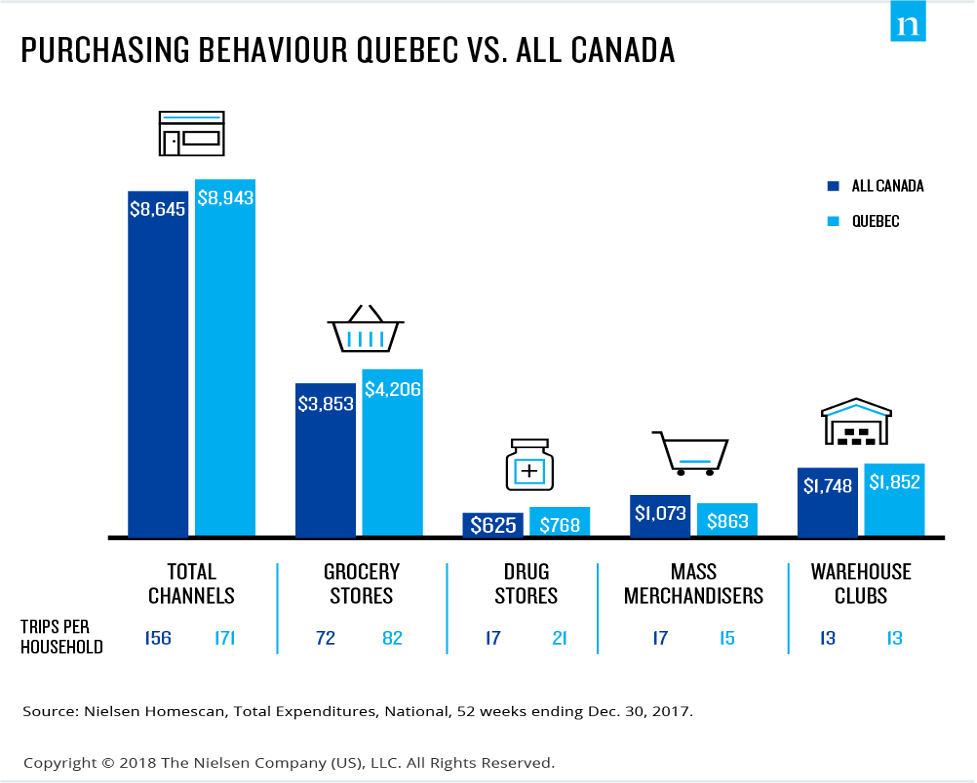
Graph showing the general trends in Canadian purchasing behavior
It is crucial for Sainsbury’s global market launch to identify and evaluate important rivals in Canada. In order to do this, it is necessary to research both domestic and foreign competitors in the supermarket retail market. Sainsbury’s receives useful insights into possible competitive advantages or gaps in the market it may take advantage of by analyzing its competitors’ market share, product offers, pricing tactics, and general posture. Sainsbury’s can strategically position itself and effectively differentiate its offerings in the new market by knowing the advantages and disadvantages of its rivals(Heydari , 2020). This study gives the business the information it needs to create an appealing offering of value that appeals to customers and distinguishes it from its rivals, increasing its chances of succeeding in the new worldwide market.
In addition to competitive and consumer research, evaluation of the current distribution channels is essential. Sainsbury’s may efficiently improve the delivery of its goods to customers by having a thorough understanding of the supply chain, transportation, and infrastructure for grocery delivery in theCanada. The business may guarantee prompt and dependable service, boosting client satisfaction, by determining the most efficient means of distribution. Furthermore, Sainsbury’s can use this data to evaluate the difficulties and expenses involved in developing distribution networks or collaborating with regional businesses. By making well-informed choices in this area, the business will be able to operate more efficiently and succeed in expanding to new foreign markets(Gajewska, 2019).
In order to successfully enter a market, pricing methods must be carefully considered, as must the political climate as well as the purchasing power of the populace in the target nation. Insights on price points that are in line with the tastes of the local population can be gained by examining the pricing approaches of the market’s current competitors in the retail food sector. Sainsbury’s must choose whether to contend on pricing or set itself apart based on the quality of its goods, client satisfaction, or other aspects. Sainsbury’s will be able to establish a competitive position and successfully entice the target market by comprehending the price sensitivity of the local market and the value assigned to various products (MIW Haeruddin, 2019). With the help of this pricing study, Sainsbury’s can be sure that it achieves the proper balance between perceived value and affordability, which will eventually help the company succeed in entering the market and experience continued success in the emerging global market.
To successfully enter the market, Sainsbury’s must fully comprehend the regulatory environment of the target nation. In order to do this, you must have knowledge of the trade policies, import/export rules, tax regulations, and other regulations that can have an impact on how the company conducts its business. The smooth introduction into the market and avoidance of potential legal stumbling blocks that can limit the company’s expansion depend on compliance with local laws. Sainsbury’s can create a solid base for the company’s operations in the new foreign market, cultivate a good rapport with community leaders, and win consumers’ trust by taking on regulatory matters.Infractions of the pertinent rules and regulations may have expensive repercussions, harm one’s reputation, and even cause company disruptions. For Sainsbury’s to effectively negotiate its market entrance journey and establish a sustainable future in the new global marketplace, a thorough understanding of the regulatory environment of the target country is essential(Zhang, 2023).
One cannot undervalue the importance of conducting an investigation into the culture of the target nation. Consumer preferences, purchasing patterns, and communication preferences are influenced by cultural influences. Sainsbury’s achievement in the new market may be greatly impacted by changing its advertising and branding to reflect the customs and principles of the target country. This includes taking into account linguistic issues, visual components, and knowledge of regional traditions and customs (Chen & Antonelli, 2020).
Overall, For Sainsbury’s foreign growth to be successful, extensive research and evaluation of the retail supermarket marketplace in the country of interest must be conducted. The business’s market entry strategy will be influenced by its knowledge of consumer behavior, preferences, and shopping patterns, as well as by its knowledge of its main rivals and distribution networks. Equally important elements to take into account are pricing tactics and knowledge of the cultural and legal environment. With this in-depth knowledge at hand, Sainsbury’s can modify its marketing strategy and product lines to satisfy the unique requirements of the new foreign market, enhancing its chances of success and long-term expansion on a global scale.
3) Recommendations:
I suggest the following entry approach for Sainsbury’s based on research and analysis done on the Canadian grocery market:
- Digital presence: Sainsbury’s should concentrate on building an effective digital presence if it wants to penetrate the Canadian market. Developing a specific e-commerce platform for this purpose or working with already established online marketplaces can accomplish this. Sainsbury’s can reduce the expenses and risks associated with the initial phase of the project while also learning a lot about the Canadian market. With an online presence, the business will be able to gauge demand, identify customer preferences, and test the market without having to make significant investments in traditional stores(PANTELIMON , 2020). With this method, it is possible to implement an adaptable and agile entrance strategy and to modify and improve offerings in response to current market trends and client feedback.
- Strategic Collaborations: As a crucial method of getting into the Canadian market, Sainsbury’s should seek strategic alliances with regional distributors and suppliers. The organization can tap into an existing network of suppliers by developing agreements with established distributors, which reduces logistical obstacles and time-to-market. These collaborations will also help Sainsbury’s better grasp local market conditions and consumer preferences. By collaborating with Canadian suppliers, the grocery chain will be able to provide a diverse choice of products that resonate with Canadian consumers, increasing its competitiveness. Furthermore, strategic alliances will bring significant insights into local rules, customs, and commercial practices, allowing Sainsbury’s to more efficiently manage the complexity of the Canadian market(Balcom, 2023).
- Flagship Locations in Major Cities: Sainsbury’s should think about constructing flagship stores in prominent locations within important cities as it gathers steam and builds a strong online presence in Canada. To take advantage of high foot traffic regions and reach a broad client base, these flagship shops should be strategically placed. By establishing physical interactions, Sainsbury’s can improve the recognition and authority of its brand and forge closer ties with Canadian customers. In-person interaction with the company and its goods will be possible for customers at the flagship locations, which will also offer an immersive shopping experience. By combining its online and offline distribution channels, Sainsbury will strengthen its position in the Canadian commercial grocery sector and demonstrate its dedication to providing top-notch customer service and high-quality goods(Gupta & Ramachandran, 2021).
- Localization: Sainsbury’s should adopt a localization plan that specifically adjusts its offerings to the demands and tastes of Canadian customers if it wants to be successful in that market. Creating a wide product mix that complements regional culture and customer preferences is required for this strategy. Produce purchased locally supports local farmers in Canada and appeals to consumers who place a premium on sustainability and freshness(Babin , 2023). Additionally, supporting Canadian companies and goods will encourage a sense of belonging and trust, creating a solid customer base. By adopting localization, Sainsbury’s can present itself as a company that respects and comprehends the Canadian market, boosting its competitiveness and giving it a solid presence in the nation’s retail grocery market.
- Focusing on sustainability and health: Sainsbury’s should heavily emphasize sustainability and nutritious food choices if it wants to attract the interest of Canadians who are concerned about their health and the environment. The brand can attract customers who value ethical and sustainable consumption by demonstrating its dedication to these practices. It will be more in line with the interests of this market segment to increase the variety of private label goods, notably organic and environmentally responsible ones. Sainsbury’s might highlight its initiatives to advertise healthier products and demonstrate its commitment to building a more environmentally friendly food ecosystem in its advertising efforts and shop displays. Sainsbury’s may effectively portray itself as an environmentally conscious and health-focused brand in the Canadian commercial grocery sector by incorporating these ideas into its business model(Abdelmoety, 2022).
- Affordable Prices: Sainsbury’s needs to execute a strategic pricing strategy that offers value for money while preserving product quality in the intensely competitive Canadian grocery industry. The brand can attract customers who are sensitive to pricing by offering reasonable prices and positioning itself as a sensible purchase. Sainsbury’s will be able to adapt its pricing strategy and react quickly to market changes thanks to routine price monitoring and comparisons with significant competitors. The business should also convey the advantages of its products with regard to their prices and be open and honest about its pricing practices(Khairazi, 2021). Sainsbury’s can forge a solid presence in the Canadian commercial grocery market and successfully compete with existing rivals by continually delivering on its commitment to affordable prices and value.
- Publicity and Marketing: Sainsbury’s needs to use effective marketing and promotion tactics to build brand recognition and draw customers if it wants to succeed in the Canadian market. The corporation needs to adjust its marketing initiatives to reflect the interests and values of Canadian consumers. Sainsbury’s will be able to successfully interact with its target demographic by using social media channels, influencer outreach, and regional marketing channels. Customers can be encouraged to make repeat purchases and develop a sense of loyalty through personalized promotions, loyalty programs, and special incentives. The brand will also be able to connect with Canadian customers on an individual basis by sponsoring regional events and community projects. Sainsbury’s may develop and succeed in the new market by investing in strategically targeted marketing initiatives that help it become a dependable and relevant option in the eyes of Canadian consumers (Dimitrieska & Efremova, 2021).
- Adherence to Regulations and Compliance:Sainsbury’s must place a high priority on compliance with Canadian laws and standards if it hopes to succeed in entering the market there. To prevent potential legal and moral problems, it is crucial to follow the rules for food safety, labelling, and packaging. To make sure that all laws and rules pertaining to the commercial grocery sector in Canada are being complied with, the company should review them in great detail. To manage the complex nature of the Canadian legal environment, it can be helpful to form a specialized team or collaborate with regional regulatory affairs specialists. Sainsbury’s may increase its standing in the market and provide the groundwork for long-term success by establishing a commitment to observing all applicable laws and regulations in Canada and earning the confidence of government officials.(Charlebois, 2021)
Conclusion
A strong argument is made for Sainsbury’s foreign expansion in the studies and evaluations done on the Canadian grocery store sector. Strong market potential is provided by Canada’s expanding population, strong economy, and favorable consumer trends. Foreign investments have a secure base thanks to the country’s attractive economic climate and stable political climate. Sainsbury’s can successfully establish its reputation in Canada by taking a phased approach and concentrating on its website, collaborations, and flagship shops. Sainsbury’s will be prepared for achievement in this new global marketplace by putting an emphasis on localization, sustainability, and affordable prices, along with targeted advertising initiatives. Sainsbury’s will be able to address the particular requirements of Canadian consumers through the suggested strategies, which will also guarantee a successful international endeavor.
References
‘Creating an entry strategy into a selected market’ (2019) Global Marketing Management System, pp. 99–136. doi:10.1142/9789813201088_0004.
Abdelmoety, Z.H., Aboul-Dahab, S. and Agag, G. (2022) ‘A cross cultural investigation of retailers commitment to CSR and customer citizenship behaviour: The role of Ethical Standard and value relevance’, Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 64, p. 102796. doi:10.1016/j.jretconser.2021.102796.
Arora, S. and Patro, A. (2021) ‘Inclusivity and empowerment—grow and let grow’, Global Business and Organizational Excellence, 41(1), pp. 21–30. doi:10.1002/joe.22136.
Babin, B.J. et al. (2023) CB: Consumer behaviour. Toronto: Cengage.
Babin, R. and Li, Y. (2022) ‘Digital transformation of grocery retail: Loblaw (teaching case)’, SSRN Electronic Journal [Preprint]. doi:10.2139/ssrn.4138488.
Balcom, R. et al. (2023) ‘Sustainable production and distribution practices in Atlantic Canadian short Food Supply Chains: Explorative study’, Frontiers in Sustainable Food Systems, 7. doi:10.3389/fsufs.2023.1121006.
Breunig, R. and Sainsbury, T. (2023) ‘Too much of a good thing? Australian cash transfer replacement rates during the pandemic’, Australian Economic Review, 56(1), pp. 70–90. doi:10.1111/1467-8462.12501.
Brouwer, I.D.(2021) ‘Reverse thinking: Taking a healthy diet perspective towards food systems transformations’, Food Security, 13(6), pp. 1497–1523. doi:10.1007/s12571-021-01204-5.
Charlebois, S. et al. (2021) ‘A review of Canadian and International Food Safety Systems: Issues and recommendations for the future’, Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety, 20(5), pp. 5043–5066. doi:10.1111/1541-4337.12816.
Chen, P.-J. and Antonelli, M. (2020) ‘Conceptual models of food choice: Influential factors related to foods, individual differences, and Society’, Foods, 9(12), p. 1898. doi:10.3390/foods9121898.
Clarkson, F. (2023) Strategic Marketing in a Global Context, pp. 1–27.
Damnjanovic, V. (2019) ‘Entry market strategy for Weaver chatbot using the Digital B2B model’, 2019 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence: Applications and Innovations (IC-AIAI) [Preprint]. doi:10.1109/ic-aiai48757.2019.00014.
Dimitrieska, S. and Efremova, T. (2021) ‘Loyalty programs: Do companies really make consumers loyal?’, Entrepreneurship, 9(2), pp. 23–32. doi:10.37708/ep.swu.v9i2.2.
DUFOUR, G. and DUCASSE, D. (2020) ‘“America first” and the return of economic isolationism and nationalism to the United States: A historic turning point for international trade law’, Canadian Yearbook of international Law/Annuaire canadien de droit international, 57, pp. 223–255. doi:10.1017/cyl.2020.15.
Gajewska, T. et al. (2019) ‘The impact of the level of customer satisfaction on the quality of e-commerce services’, International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, 69(4), pp. 666–684. doi:10.1108/ijppm-01-2019-0018.
Gielens, K. et al. (2021) ‘The future of private labels: Towards a smart private label strategy’, Journal of Retailing, 97(1), pp. 99–115. doi:10.1016/j.jretai.2020.10.007.
Gupta, S. and Ramachandran, D. (2021) ‘Emerging market retail: Transitioning from a product-centric to a customer-centric approach’, Journal of Retailing, 97(4), pp. 597–620. doi:10.1016/j.jretai.2021.01.008.
Heydari, M., Lai, K.K. and Zhou, X. (2020) ‘Creating sustainable order fulfillment processes through managing the risk: Evidence from the Disposable Products Industry’, Sustainability, 12(7), p. 2871. doi:10.3390/su12072871.
Jones, L., Minto-Coy, I.D. and Elo, M. (2023) ‘The socio-economic impact of Transnational Diaspora Entrepreneurship: An investigation of UK-based African Caribbean Entrepreneurial Diaspora on the Caribbean’, Research Handbook on Transnational Diaspora Entrepreneurship, pp. 177–207. doi:10.4337/9781788118699.00019.
Khairazi, R. (2021) ‘The objectivity of the Business Competition Supervisory Commission in deciding business competition cases in Indonesia’, Indonesia Private Law Review, 2(1), pp. 1–10. doi:10.25041/iplr.v2i1.2146.
Kim, D.Y. and Kim, S. (2022) ‘The impact of scarcity during the COVID-19 pandemic on consumer psychological well-being and hoarding behavior’, Breaking Boundaries [Preprint]. doi:10.31274/itaa.13390.
Olabode, O.E (2023) ‘Disruptive market shift: Conceptualization, antecedents, and response mechanisms’, Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 192, p. 122577. doi:10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122577.
PA., R.C.O.A.R.L. (2023) Red Queen retail race;an innovation pandemic in the era of digitization. OXFORD: OXFORD UNIV PRESS UK.
PANTELIMON, F.-V., GEORGESCU, T.M. and POSEDARU, B.-S. (2020) ‘The impact of mobile e-commerce on GDP: A comparative analysis between Romania and Germany and how covid-19 influences the e-commerce activity worldwide’, Informatica Economica, 24(2/2020), pp. 27–41. doi:10.24818/issn14531305/24.2.2020.03.
Steinman, J. (2019) Grocery story: The promise of food co-ops in the age of Grocery Giants. Gabriola Island: New Society Publishers.
Ye, Y., Hung Lau, K. and Teo, L. (2021) ‘Transforming Supply Chains for a new competitive market alignment – a case study of Chinese fashion apparel companies’, International Journal of Logistics Research and Applications, 26(3), pp. 365–397. doi:10.1080/13675567.2021.1951690.
Yenugula, M., Sahoo, S.K. and Goswami, S.S. (2023) ‘Cloud computing in Supply Chain Management: Exploring the relationship’, Management Science Letters, 13(3), pp. 193–210. doi:10.5267/j.msl.2023.4.003.
Zhang, H. (2023) ‘Risk and control of cross border e-commerce enterprises from the perspective of Internal Audit’, Highlights in Business, Economics and Management, 11, pp. 321–326. doi:10.54097/hbem.v11i.8151.
Żuk, P. (2022) ‘The sense of socio-economic threat and the perception of climate challenges and attitudes towards energy transition among residents of coal basins: The case of turoszów basin in Poland’, SSRN Electronic Journal [Preprint]. doi:10.2139/ssrn.4252206.
 write
write