Introduction
To complete this assessment, three nations selected are India, the United States, and Japan. India is located in the southern region of Asia, with a total population of more than 1.35 billion. The USA is known as the United States of America, consists of 50 states and is expected to cover nearly 3.8 million square miles. The country’s total population is around 331 million as per the reports from 2018(Roberts et al. 2018). The third country for this assessment is Japan, located in the East Asia region with a total population of 125 million. Lastly, New Zealand is located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, which consists of over 700 islands. The total population of New Zealanders as of 2021 is slightly more than 5 million.
Indian government policies towards the ageing population are specific towards delivering financial support to assisted older populations. The USA government has established a wide range of facilities to assist older people. On the other hand, the Japanese government is very specific about offering healthcare benefits to the older community. Lastly, the New Zealand government follows ten principal policies for older people, which consist of both financial and non-financial facilities.
A brief analysis of the government policies in all four countries will be presented in the following section. Once the analysis of the government policy is done, the policies of India, the USA and Japan will be compared with the policies of New Zealand. In the next part of the assessment, the life expectancy of all four counties will be compared with a proper graph, and differences will be evaluated. Lastly, changes that need to be implemented in New Zealand’s ageing policy will be provided in the recommendation section.
It has been found that Japan has a higher expectancy rate compared to New Zealand. While analysing the government policies, it has been found that Japan’s government policies are very specific to offering healthcare benefits to citizens. Based on the healthcare policies of Japan, further strategies have been developed from the context of New Zealand, and suggestions have been provided.
Analysis of government policies for aged population
Government policies in each country
India
A national policy statement has been developed in order to support people who belong to the age group called the elderly. Some of the major factors in which the Indian government has invested to make older people’s life easier are financial security, physical security, shelter, and healthcare. The discrimination between the male elderly and female elderly has been monitored through government policies (Paul & Asirvatham, 2016). People over 60 are being offered to lead their lives in a creative, active, and productive way. Instruments such as insurance have been introduced to make sure people of rural and urban areas are able to save an attractive amount of money. The Government of India also started an old-age pension scheme to increase financial security for older people.
United States
The USA has designated policies for the ageing of the people of the nation. AoA (Administration of Aging) is the regulatory body for designing the policies for the aged population in the country. An act called Older Americans Act has been developed in order to provide sufficient benefit to the older people of the country. Offering homes to the older community to empower them is the key motive behind the provisions designed under Older Americans Act 1965. The Act is very specific to people who are over the age of 60 years old. The USA government also has taken the initiative to promote health and nutrition. ONHPP (Office of Nutrition and Health Promotion Programs) are being taken into consideration by AoA to promote health to the older population of the country (ACL, 2021). ADEPP is a program started by the US government to support aged people with disabilities. Brain health, chronic disorder, elder abuse prevention, fall prevention, the government and specific initiatives are prioritising all issues have been taken into consideration to support.
Japan
The Government of Japan is very concerned about the country’s older citizens. Health is the major aspect on which the government has been focused. To regulate the health of older people, the government established a universal health insurance scheme in 1961 (Matsuda, 2019). The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan is associated with the government initiative toward offering facilities for older people. Some of the most prominent diseases that can be found among older people are malignancy, cerebrovascular disease, heart diseases and pneumonia. The death rate of older people is significantly higher in Japan due to such diseases. As the quality of life among older people deteriorates due to health-related issues, the country’s government policies are specific towards benefiting health services.
New Zealand
The New Zealand government has started with a positive ageing strategy. The primary reason behind this initiative is to offer improved opportunities to the older people to participate in the community. Developing networking is really essential for older people to get aware of the facilities offered by the government. To enhance the experience, the government has developed an international year for older persons. A ten-goal principle has been adopted by the government of New Zealand, which includes improving income, health, housing, transport, and place. The 10-principle policy is also focused on increasing cultural diversity; the government also focused on delivering a high-quality life experience to the people who are living in rural areas. Improving attitude, offering employment to older people, and offering opportunities in the community are integral parts of the government policies of New Zealand.
Comparison of New Zealand with other countries
While comparing New Zealand’s government policy for older people with Indians, it can be determined that the Indian government is very specific towards offering financial benefits to the older people rather than non-financial benefits such as free transportation, housing, and others. Through further research, it has been observed that the poor economic condition of the nation has prevented the government from taking such high initial investment for offering better opportunities through housing and transport (Lodha & De Sousa, 2018). However, in New Zealand, the government is very specific towards offering non-financial benefits such as offering opportunities to participate in the community, increasing cultural diversity, health benefits and others.
Awareness of health and nutrition is one of the major factors being regulated by the USA government among the people that belong to the age group of 60+. Apart from promoting awareness of nutrition value, the USA government has also developed policies to benefit older people with brain disease, chronic disorder, and others. Fall prevention is another major program performed by the US government for older people. However, the New Zealand government has not really specified the policies for each of the health conditions. For example, there is no specific facility to offer benefits to older people from preventing falls.
While comparing Japan’s government policies, it has been observed that the policies are designed in such a way so that people get benefits during their poor health conditions. From statistics, it has been found that malignancy, cerebrovascular disease, heart diseases and pneumonia are the major health issues in Japan that are solely responsible for the death of a wide range of the older population in the country (Katagiri, Konishi & Ueda, 2020). The government has developed policies to prevent people from these diseases and reduce the mortality rate. However, in New Zealand, the government has policies specific to health benefits, but it is not limited to other aspects. In other words, the New Zealand government has developed policies while focusing on other aspects such as transport, housing, community building, cultural diversity, and others.
Discussion of Statistical Data of Life expectancy
Comparison of life expectancies
To compare the life expectancy of India, the USA and Japan, three different graphs have been produced. In each of the graphics, the life expectancy of each one of the countries from three selected countries and New Zealand has been presented. To offer better visibility in the result, the life expectancy rate has been categorised as “Male” and “Female”. Through each diagram, the comparison will be provided with New Zealand’s prospects. All data was collected from the “World Bank” to prepare the diagrams.
Comparison with New Zealand and India
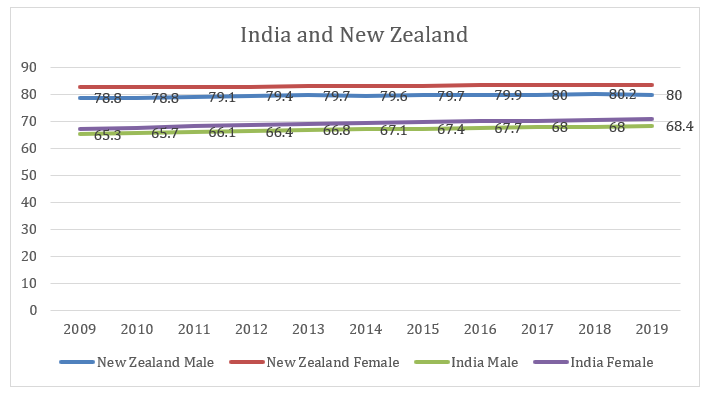
Figure 1: Life expectancy rate of India and New Zealand
(Source: World Bank, 2021)
By comparing the life expectancy of India and New Zealand, it can be determined that life expectancy for both males and females is higher in New Zealand compared to India. However, while looking into the improvement rate of life expectancy, it can be observed that India is maintaining a better position. In other words, In the base year (2009), India had a life expectancy for males of 65.3 years. After ten years in 2019, the life expectancy of a male in India will be 68.4 years. An improvement of 3.1 years has been observed, while in New Zealand, the life expectancy improved only 1.2 years. More precisely, from 2009 to 2019, India’s life expectancy improved from 78.8 years to 80 years.
Comparison with New Zealand and the USA
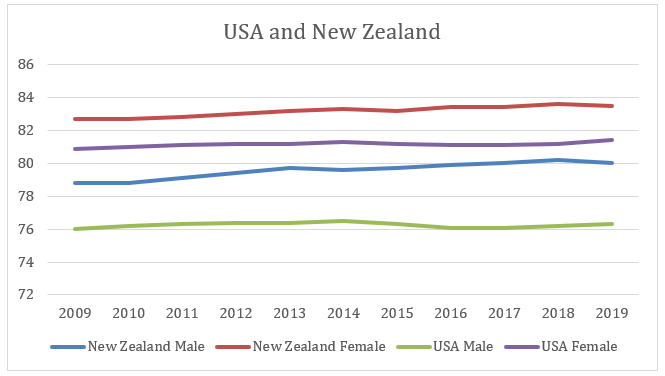
Figure 2: Life expectancy rate of the USA and New Zealand
(Source: World Bank, 2021)
While looking into the year wise life expectancy of the USA, it can be observed that there is a huge fall in the life expectancy trend between the years 2014-2015. As a result, there is no major improvement in the life expectancy rate between the tenure of 2009 to 2019. As a result, in 2009, life expectancy for a male was 76 years which increased to 76.3 years in 2019. Similar observations were also found in the case of females; in 2009 life expectancy of females was 80.9 years which increased by only .5 years at the end of 2019. However, the improvement in the life expectancy rate was positive in males and females. New Zealand achieved a growth of 1.2 years life expectancy from 2009 to 2019 for males; .8 year is the improvement rate for females.
Comparison with New Zealand and Japan
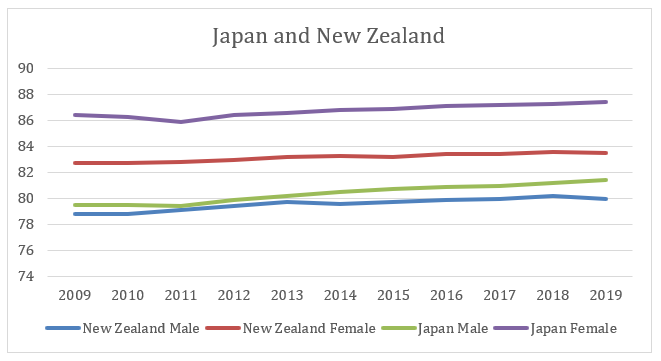
Figure 3: Life expectancy rate of Japan and New Zealand
(Source: World Bank, 2021)
Japan is the only selected country that has a higher life expectancy than New Zealand’s life expectancy rate. Both males and women in Japan have a higher life expectancy. Apart from higher life expectancy. Japan is in a position that offers improvement in the life expectancy rate. For example, within the selected ten years tenure, Japan has improved 1.9 years life expectancy for males while the rate becomes 1 year for females. However, in the case of New Zealand, the improvement rate of life expectancy is quite lesser as the country has only improved 1.2 years and .8 years for males and females, respectively.
Reasons for differences in life expectancy
Before identifying the reasons for the difference, the areas in which the differences have occurred need to be identified. From the selected three countries, only one country is offering better life expectancy than Japan. Though the life expectancy of India is lesser than New Zealand, the rate of improvement in life expectancy is significantly visible. Lastly, the USA is not showing a positive life expectancy figure hence, considering the USA is not going to offer any better value in the context.
By investigation, it has been observed that technology is the key factor that has offered better life expectancy in Japan. In other words, Japan has effectively implemented the technologies in the healthcare sector to make sure the population’s health condition could be improved (Kitao, 2018). While looking into the government policies adopted by the country, it can be observed that the country’s government is highly focused on healthcare rather than any other aspects. To develop the policies, the government initially conducted research on the causes of death. Through investigation, the Japanese government found that malignancy, cerebrovascular disease, heart diseases, and pneumonia are some of the major diseases that lead to significant deaths (Hsu & Yamada, 2019). As a result, they developed some healthcare policies that will help people prevent these diseases.
As per the research by Asaka et al. (2020), Japan has fewer deaths due to health diseases and cancer. While looking into the strategies adopted by the country to deal with the major issue, it has been found that the food habit of Japan itself is responsible for the high life expectancy. Reducing salt and salty food is the primary reason for reducing heart disease. As a result, the country’s mortality rate has been reduced significantly. Studies have also stated that the government has imposed some regulations in the preparation process of food to ensure a better life expectancy rate (Hasan et al., 2019). However, the New Zealand government is not really focused on the health factor, but health is an integral part of their ten principles for older age people.
Increasing life expectancy rate over the years is a visible factor in India. While looking into causes of increasing life expectancy rate in India, it has been found that improvement of housing conditions, sanitation and education are highly responsible for the increasing figure. In addition to this, government policies are highly specific towards offering financial security and health facilities through insurance (Srivastava & Gill, 2020). As Indians get a cash amount to spend on their lives, they invest the money on the factors that lead them to get a better life. At the same time, being a developing country, education helps Indians to identify the factors associated with a better lifestyle. On the other hand, the New Zealand government is not primarily focused on health; rather, they are focused on offering non-monetary benefits such as transportation, income opportunity, and cultural diversity. During the older age, healthcare is the primary necessity that needs to be provided, as New Zealand has not put the primary focus on it; therefore, growth in the life expectancy rate in New Zealand is lesser than in India.
Recommendations
As per the comparison of the life expectancy of New Zealand with Japan, it has been found that Japan is capable of maintaining a better life expectancy. The country is also growing life expectancy with each passing year. As technology adoption in healthcare is the key aspect, it is highly recommended to the government of New Zealand that they must procure technologies that can be integrated into the healthcare sector. To integrate technologies into healthcare, partnership with IT service providing companies needs to be performed. Adoption of technologies such as telemedicine, portal technology, mHealth needs to be introduced exclusively for the older age population (Kudinov et al. 2021).
The technologies that need to be adopted by the healthcare facilities of New Zealand should reduce the service delivery time and offer better health test results with better accuracy. In other words, advanced devices for testing echocardiography must be adopted by the healthcare sector of New Zealand. As a result, people with heart disease will be able to identify the heart condition and take the treatment process as soon as possible (Gökalp et al., 2018).
In addition to this, it has been observed that transportation, cultural diversity, opportunity to be a part of a community, and income opportunities are some of the major prospects offered by the New Zealand government (Feng & Glinskaya, 2020). For such offerings, a lot of investment is made by the government as well. Based on the government policies of Japan, it is highly recommended to the government of New Zealand to reduce the spending on such areas; rather, they must allocate more budget on healthcare. Developed countries such as the USA, Australia, and Russia allocate the maximum budget for the healthcare facilities of their country’s people. A similar approach must be adopted by the New Zealand government to ensure better life expectancy.
By looking into India’s life expectancy rate, it can be observed that growth in the life expectancy rate has increased over the years. Further investigation has revealed that a structured insurance opportunity helped the country to experience a growth in the life expectancy rate (Rajpal, Kumar & Joe, 2018). The Government of New Zealand is also recommended to opt for similar insurance opportunities for the New Zealanders. As a result, people after 60+ will be getting medical assistance from the government’s end. The insurance must be capable enough to cover all the expenses of elderly disease such as cardiovascular disease, heart disease, cancer, brain disease and others. The covered expense must include doctor fees, cost of medicine, cost of equipment and surgery.
Conclusion
As per the discussion part of the report, it can be determined that three different countries have been selected randomly to compare their life expectancy rate with New Zealand. All these countries are India, the USA, and Japan. Through the analysis, it has been found that Japan is maintaining the best life expectancy rate compared to the other two countries. Even Japan holds a higher life expectancy than New Zealand. Government policies of all four countries, India, USA, Japan, and New Zealand, have been disclosed in the assessment from the perspective of older ageing. Through the comparison of government policies, the cause of higher life expectancy in Japan has been identified. Adoption of technologies is an external factor that has ensured a better life expectancy rate in Japan.
By considering the government policies, it has been observed that being focused on healthcare benefits is one of the key aspects of Japan’s government. In other words, Japan’s government policies are designed in such a way so that older people of Japan get better healthcare facilities during their older age. More precisely, they will get better treatment for elderly diseases such as cardiovascular disease, heart disease and others. It has been observed that though India’s life expectancy rate is lower than New Zealand still India has had higher growth in life expectancy rate over the years. The condition of life expectancy rate is quite stable in the USA. In other words, no major growth or fall in the life expectancy rate in the USA has been observed.
References
ACL (2021). Administration on Aging. Retrieved from: https://acl.gov/about-acl/administration-aging
Asaka, M., Kobayashi, M., Kudo, T., Akino, K., Asaka, Y., Fujimori, K., … & Kato, M. (2020). Gastric cancer deaths by age group in Japan: outlook on preventive measures for elderly adults. Cancer Science, 111(10), 3845-3853.
Feng, Z., & Glinskaya, E. (2020). Aiming Higher: Advancing Public Social Insurance for Long-term Care to Meet the Global Aging Challenge: Comment on” Financing Long-term Care: Lessons From Japan”. International Journal of Health Policy and Management, 9(8), 356.
Gökalp, E., Gökalp, M. O., Çoban, S., & Eren, P. E. (2018, September). Analysing opportunities and challenges of integrated blockchain technologies in healthcare. In Eurosymposium on systems analysis and design (pp. 174-183). Springer, Cham.
Hasan, M. A., Frame, D. J., Chapman, R., & Archie, K. M. (2019). Emissions from the road transport sector of New Zealand: Key drivers and challenges. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(23), 23937-23957.
Hsu, M., & Yamada, T. (2019). Population aging, health care, and fiscal policy reform: the challenges for Japan. The Scandinavian Journal of Economics, 121(2), 547-577.
Katagiri, M., Konishi, H., & Ueda, K. (2020). Aging and deflation from a fiscal perspective. Journal of Monetary Economics, 111, 1-15.
Kitao, S. (2018). Policy uncertainty and cost of delaying reform: The case of aging Japan. Review of Economic Dynamics, 27, 81-100.
Kudinov, D. A., Borisov, I. V., Elykomov, V. A., & Nomokonova, E. A. (2021). Overview of Promising Information Technologies in the Healthcare System from the Position of a System Approach. In Complex Systems: Innovation and Sustainability in the Digital Age (pp. 225-235). Springer, Cham.
Lodha, P., & De Sousa, A. (2018). Geriatric mental health: The challenges for India. Journal of Geriatric Mental Health, 5(1), 16.
Matsuda, S. (2019). Health policy in Japan–current situation and future challenges. JMA Journal, 2(1), 1-10.
Paul, N. S. S., & Asirvatham, M. (2016). Geriatric health policy in India: The need for scaling-up implementation. Journal of family medicine and primary care, 5(2), 242.
Rajpal, S., Kumar, A., & Joe, W. (2018). Economic burden of cancer in India: Evidence from cross-sectional nationally representative household survey, 2014. PloS one, 13(2), e0193320.
Roberts, A. W., Ogunwole, S. U., Blakeslee, L., & Rabe, M. A. (2018). The population 65 years and older in the United States: 2016. Suitland, MD, USA: US Department of Commerce, Economics and Statistics Administration, US Census Bureau.
Srivastava, S., & Gill, A. (2020). Untreated morbidity and treatment-seeking behaviour among the elderly in India: Analysis based on National Sample Survey 2004 and 2014. SSM-population health, 10, 100557.
World Bank (2021). Life expectancy at birth. Retrieved from: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SP.DYN.LE00.MA.IN?end=2019&start=2008&view=chart
 write
write