Introduction
Aside from the Internet, the cell phone sector is among the fastest-growing industries. The mobile phones industry have undergone significant changes, and their market has increased internationally. From 1995, the mobile phone industry has expanded from 20 million to over 200 million wireless cellphones and other devices in use globally. Aside from the Internet, the cell phone sector is among the fastest-growing industries. The mobile phones industry have undergone significant changes, and their market has increased internationally. Huawei Company has gained a significant share of the technology industry especially the smartphones market in Europe and other parts of the world.
Situational Analysis
Economic factors
Huawei’s performance is influenced by both the Chinese economy and the economies of its core market, which is mostly the Europe. The correlation between these economic indicators and the company’s success is simple. If the company’s target markets does well fiscally, Huawei will most probably sell more cellphones in the markets (Kang and Xuehua 187). Currently, the Europe has a strong economy, providing Huawei with a constant flow of trade irrespective of economic conditions in other areas of the globe. In particular, labor prices in the nation are fast growing, driving Huawei’s operational costs (particularly manufacturing costs) to rise accordingly. The ever-rising Chinese may have a good as well as an adverse impact on Huawei’s profitability.
Social Factors
Many people consider Chinese products cheap and associate them with poor quality. This perception continues to affect Huawei’s sales in Western countries, especially the United States. It is a widely held belief that Chinese products are substandard and Huawei, being a Chinese firm with many of its clients in the United States must combat this label with improved marketing techniques (Li 21). Some consumers in Western countries deliberately stay away from technology brands such as Huawei due to their origin. Huawei should invest more in research and development to eliminate the mentality that its products are substandard.
The ever-growing China’s economy continues to offer Huawei an opportunity for growth. China’s economy is expanding daily due to the country’s dense population of over 1.4 billion people (Li 25). Huawei merchandise has a large market because of the country’s large population. Moreover, a huge population produces a high demand for items as the number of purchasers grows (Li 26). Smartphones are now popular and the trend is projected to continue, ensuring the long-term viability of Huawei, which has made significant investments in smartphone production.
Technological Factors
Research and Development (R&D) in the smartphone sector has pushed the boundaries of innovation and inventiveness. Of all environmental considerations, Huawei’s technological edge is the most essential, allowing it to gain a dominating position in China. Huawei’s significant concentration on Research and Development (R&D), along with its 5G plan, has helped the corporation to stay ahead of the competition. With the introduction of the world’s first commercial LTE system in 2009, the firm launched 5G development. The fifth-generation mobile communications technology, 5G, is the successor to 3G and 4G, boasting increased speed, cheaper cost, and energy savings. Nevertheless, 5G technology demands new hardware, which must be supplied by constituent makers elsewhere in the world.
Political Environment
The Chinese market, which forms the largest percentage of Huawei’s revenues, is characterized by a significant influence from the ruling party. Therefore, any incidence that affects Chinese politics has a strong effect on Huawei’s profit margin. The Chinese government heavily encourages smart production in its most recent government strategy, “Made in China 2025” (Kang and Xuehua 187) Using its technological advantages in IoT technology, cloud services, and big data, Huawei will continue to be a key vendor to the state (Kang and Xuehua 190). The government’s control of the Chinese market could boost Huawei’s profitability as well as affects its operations.
Protectionism policies by Western countries such as the United States have had a significant impact on Huawei’s profitability. For instance, the sanctions imposed by the U.S on Huawei due to questions of information security have forced the company to shift to other market segments (Jia 56). Presently, none of the US networks deal with Huawei products, and consumers in the West have been urged to avoid purchasing devices manufactured by the company (Jia 57). The protectionist policies have caused Huawei to scale down its operations in the United States.
Ecological Environment
The environmental regulations imposed by the European Union and other countries have significantly affected Huawei’s production and operations in the region. Smartphones make for a large amount of the e-waste generated in Europe each year. Given the volume of e-waste generated by both hardware and service providers, the industry is focusing on waste management and decreasing its environmental impact (Kang and Xuehua 193). Due to industrial waste, Huawei has violated environmental rules. If the enterprise continues to breach environmental regulations, the European Union and the United States may impose sanctions on Beijing and the company. Owing to the increased e-waste in the EU region, Huawei is bound to a slew of environmental regulations, which mostly influence its manufacturing processes.
Marketing Objectives and Marketing Strategies
Current Marketing Strategy
Huawei uses the segmentation, targeting, and positioning strategy (STP) and aggressive promotional activities in the European market. This strategy will enable the company to swiftly dominate the foreign market, grow market share, and allow overseas customers to embrace their products in the shortest time possible (Lin 45). STP strategy is concerned with economic efficiency, identifying the most important segments for a company, and then designing a marketing approach and product positioning strategy for every segment.
Current Marketing Objectives
Segmentation of Overseas Markets
Offshore segmentation is the activity of partitioning the total foreign market into several sub-markets with varied products and market pairings based on distinct segmentation methodologies. For investment, the regions with the greatest income expectations are picked. The worldwide industrial product market is partitioned based on factors such as user size, end consumers, purchasing, and organizational features (Lin 45). Because of the distinct features of the global mobile communications sector, Huawei has divided the international telecommunications market into European markets, American markets, the Pacific Region, the Gulf Region, and Africa.
Targeting
The European market is the primary target segment for Huawei’s global marketing strategy, with specific market competitiveness methods adopted for each nation. Due to the technological competitiveness in the European market, Huawei can steadily improve 5G capabilities to fulfill the demands of customers in various areas (Jia 56). Huawei may target other market segments outside the European countries such as UAE and Africa to sustain the pace of innovation and to stay up with the development of cutting-edge technology. This strategy can improve the company’s technological strength and provide it a competitive advantage in development. Furthermore, it may accelerate the return of capital by providing sufficient confidence and support for future technical research and development. Huawei should enhance its marketing strategies to suit the demands of the European segment as well as explore other markets segments across the globe.
Positioning
Huawei’s product positioning must differentiate it from rivals’ goods and represent brand distinctions. As its products, the company has successfully positioned 5G broadband network solutions (mobile switching systems, base station systems, and 5G mobile phones). Overseas corporations have an unparalleled merit in the European segment; yet, Huawei has prevailed over many demanding European market evaluations, indicating that its 5G gadgets are not technologically inferior to those of abroad firms (Li 25). In comparison to multinational enterprises with unique advantages, Huawei has a competitive edge, notably in terms of product cost performance and corporate tech support abilities, with multiple benefits such as higher costs, efficient networks, and rapid service. Figure 1 depicts the company’s European market position. Huawei’s unique product strategy is key to its survival in the European and other market segments across the globe.
Marketing Programs
Price
Huawei uses cost and demand pricing strategies. The cost demand approach is primarily based on product cost plus product anticipation income (Dmitrijevs 1138). This strategy primarily completes two aspects of work, namely, accurate accounting cost, and determining the portion of the revenue based on market demand and product variety (Dmitrijevs 1138). On the other hand, the demand pricing technique is based on social consumer demands, taking into account purchasing habits, economic status, and the price elasticity of product and service demand.
Product
Huawei’s business is diverse and separated into various divisions that serve the requirements of government institutions. Business and individual consumers. The company’s whole business is separated into a carrier, consumer, and enterprise business segments (Yueyuan 76). The enterprise division creates a digital infrastructure system by utilizing emerging ICT cloud-based services and IOT to deliver products and services that benefit industries. On the other hand, the carrier business division offers a variety of products, applications, and business solutions to global telecom carriers, including wireless networks (Jia 56). The consumer business is the main business sector, making up the majority of its sales. This category manufactures and sells cellphones as well as smartphone apps to consumers and enterprises. The diverse business divisions embraced by Huawei have been critical to the company’s increased profitability and stability.
Place
Despite being located in China, Huawei has created a global presence. The company’s operations are extended throughout over 180 countries. In addition, the brand has built long-term agreements with over 12000 merchants (Yueyuan 77). While Huawei is a Chinese company and one of the country’s top tech businesses, it has effectively controlled its large network by establishing a wide global supply chain (Jia 58). Collaboration with other enterprises and significant players in the technology industry has enabled Huawei to broaden its global reach.
Promotion
Huawei employs both digital and conventional methods of promotion. The firm distributes its cellphones all around the world via e-commerce sites, which also act as an important promotional tool. Furthermore, social media and other forms of digital marketing are critical components of the company’s marketing plan. As part of its marketing strategy, the firm has partnered with a number of small and big organizations throughout the world. Strategic promotional strategies have increased Huawei’s brand recognition in several regional marketplaces.
Recommendations
Huawei should adopt different price strategies for different market segments. Adoption of low-cost approaches in price competition in foreign markets may commonly open the market quickly, but it may also quickly lead to a price war (Jia 57). Considering factors such as comprehensive price placement, adaptive pricing techniques may effectively increase corporate price competitiveness and avoid the price competition vicious circle (Jia 57). A flexible pricing strategy will ensure that the firm masters the market price competitiveness.
When picking on a marketing channel, the company should take into account both the existing state of the market dynamics and the trajectory of future developments. This strategy ensures that the chosen channel can respond to changes in the global market environment. Following Huawei’s success in the European market, the company should refine its approach and use the commissioning agent channel model to expand its own sales force (Lin 45). Establishing robust marketing and distribution channel will be critical to Huawei’s dominance in the European market.
Conclusion
Huawei Company has gained a significant share of the technology industry especially the smartphones market in Europe and other parts of the world. One of the reasons for Huawei’s achievement is the fact that the firm creates goods and fixes its pricing in accordance with the economic conditions of the market segment. The company uses the segmentation, targeting, and positioning strategy (STP) and aggressive promotional activities in the European market, a strategy that has enabled the company to swiftly dominate the foreign market, grow market share and allow overseas customers to embrace their products in the shortest time possible. To gain dominance in the European and other market segments, Huawei should adopt a flexible pricing strategy and establish a marketing channel that takes into account the existing state of the market structure as well as the direction of future changes.
Works Cited
Dmitrijevs, Romans. “Research on Marketing Strategy of Huawei Mobile Phone in European Market.” Open Journal of Business and Management 8.03, 2020, pp.1138.
Jia, Liande. Huawei Mobile International Market Development Strategy Research. Diss. Dublin, National College of Ireland, 2020.
Kang, Maohua, and Xuehua Wen. “A Brief Global Market Research on Huawei 5G.” Frontiers in Economics and Management 2.2, 2021, pp.187-194.
Li, Yuanyuan. “Research on Huawei Mobile Phone Marketing Strategy Based on Market Segmentation Theory.” 5th Annual International Conference on Social Science and Contemporary Humanity Development (SSCHD 2019). Atlantis Press, 2019.
Lin, Chen. “The Analysis of Huawei International Marketing Strategy.” Siam University (2017).
Yueyuan, Yang. “Analysis on the Customer Segmentation of Huawei Company.” 6th International Conference on Financial Innovation and Economic Development (ICFIED 2021). Atlantis Press, 2021.
Appendices
Figure 1. Huawei’s European Market Position
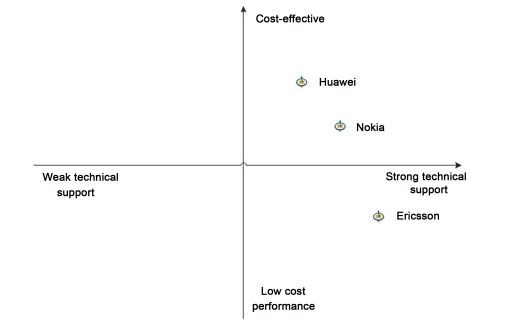
Source: Feng, B. (2019). Research on European Marketing Strategy of Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd. Master Thesis, Changchun: Jilin University of Finance and Economics.
Table 1. Features of Huawei’s overseas segments.
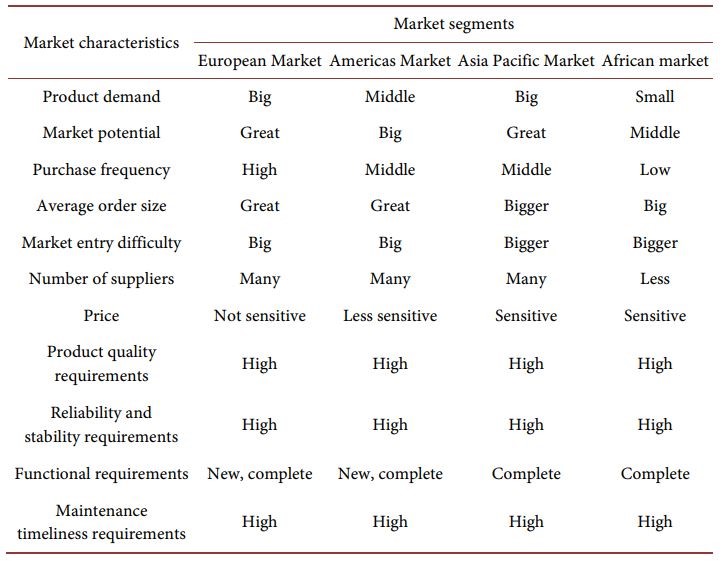
Source: Source: Yao Tian. Research on Huawei’s Overseas Market Strategy [D]. Beijing: University of International Business and Economics, 2012.
 write
write