Background
Logistics and supply chain management are crucial components of modern business operations. In a fiercely competitive, globally integrated economy, good supply chain management can differentiate between success and failure for many businesses (Fosso Wamba et al., 2018). Supply chain management is the coordination of all operations involved in producing and delivering goods and services, from the procurement of raw materials to the delivery to the final customer. Successful supply chain management can lead to cost savings, better speed and agility, and increased customer satisfaction (Raman et al., 2018). However, firms confront significant challenges due to the increasing complexity of supply networks.
The escalating complexity and globalization of supply chains are two of the most significant challenges for the supply chain management. As organizations expand abroad and rely on increasing suppliers and partners, the supply chain becomes increasingly complex and challenging to manage (Schniederjans & Ozcan, 2016). This may lead to delays, inferior quality, and increased costs. The fact that organizations must navigate diverse regulatory and compliance duties across multiple nations and regions adds complexity.
Increasing demand for real-time information and visibility provides another challenge for the supply chain management. Customers and business partners require real-time data on the status of orders, inventory levels, and shipping tracking. Nevertheless, the typical way of supply chain management, which relies on disconnected systems and human processes, frequently fails to provide the necessary visibility and real-time data (Wang & Wang, 2016).
With the advent of big data and analytics, businesses have a tremendous opportunity to solve these problems and improve their supply chain management methods. Big data characterizes the massive and complex datasets generated by modern business operations. Analytics refers to the methods and tools used to evaluate these datasets in order to gain knowledge and drive decision-making (Oncioiu et al., 2019). Businesses may enhance decision-making, expand supply chain visibility, and streamline operations by employing big data and analytics.
One of the primary ways that big data and analytics may help firms overcome supply chain management challenges is by enhancing visibility. By collecting and analyzing data from all points throughout the supply chain, businesses may gain a more thorough picture of their operations, including inventory levels, demand trends, and supplier performance (Raut et al., 2021). This can aid firms in identifying possible bottlenecks and inefficiencies, allowing them to fix them before they become significant issues.
Predictive analytics is another way big data and analytics may help firms improve their supply chain management. By examining historical data, finding patterns and trends, and constructing predictive models, businesses may foresee future demand and supply chain issues (Monczka et al., 2015). This enables organizations to take preemptive measures, such as changing inventory levels or manufacturing plans, to solve these issues.
Monitoring and control in real-time is a third way big data and analytics may help firms improve supply chain management. Using sensors, RFID tags, and other technologies, businesses may collect real-time data about their operations and use analytics to identify and resolve problems in real-time (Accenture, 2015). This may enable firms to make rapid course corrections, such as rerouting shipments or modifying production schedules, to prevent delays or quality issues.
Several studies have demonstrated big data and analytics’ potential supply chain management benefits. For instance, according to a McKinsey & Company study (2016), organizations can save up to 15 percent on prices and 20 percent on inventory when they employ big data and analytics to enhance supply chain visibility and decision-making. Businesses that utilize big data and analytics to manage their supply networks can reduce order-to-delivery cycle times by up to 20 percent and enhance supply chain efficiency by up to 25 percent, according to a different Accenture study.
In conclusion, logistics and supply chain management are essential components of modern business operations, and managing complex supply chains provides significant challenges for companies. With greater visibility, predictive insights, and real-time monitoring and control, the emergence of big data and analytics provides businesses with a significant opportunity to enhance their supply chain management strategies. Big data and analytics can aid in the success of enterprises.
Aim & Objectives
The project aims to investigate the impacts of big data and analytics in logistics and supply chain management and to develop a case study demonstrating the potential benefits for a real-world company. The objectives are to:
Conduct a literature review to identify key concepts and trends in big data and analytics for logistics and supply chain management.
Analyze the impacts of big data and analytics on supply chain visibility, agility, and efficiency.
Develop a case study illustrating the potential benefits of big data and analytics for a real-world company.
Evaluate the limitations and challenges of implementing big data and analytics in logistics and supply chain management.
Work program
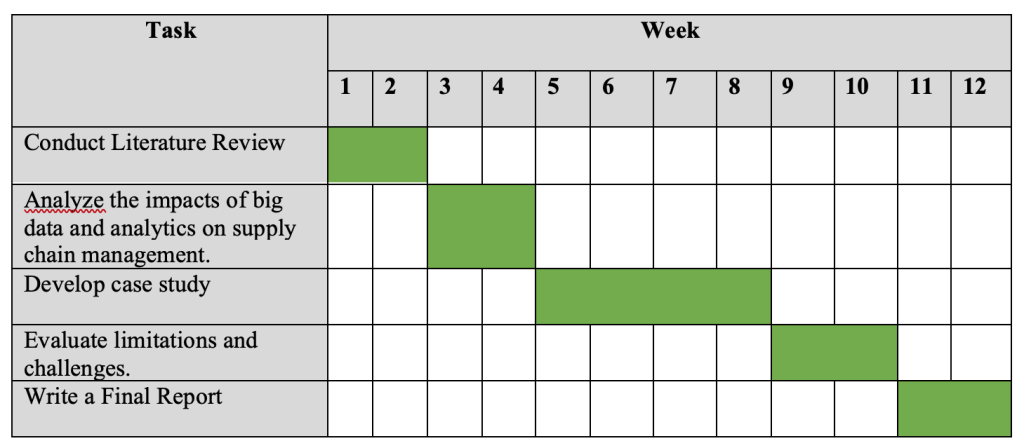
The 12-week project will investigate the implications of big data and analytics on logistics and supply chain management. The project will be broken into several milestones, each with its objectives.
During weeks 1 and 2, I will conduct a comprehensive review of the relevant academic literature, serving as the first milestone. The literature review will be vital for establishing a firm foundation for the project and identifying the significant themes and trends that can be used to guide the subsequent phases of the project.
Over the course of the third and fourth weeks, I will investigate the effects of big data and analytics on supply chain management. The results of the literature review will serve as the foundation for this analysis, which will identify the potential benefits and challenges of incorporating these technologies into supply chain management.
In weeks 5 through 8, I will develop a case study to illustrate the effects of big data and analytics on supply chain management. The case study will involve collaboration with a real-world firm to comprehend how these technologies have been deployed, the problems they have encountered, and the effects this has had on their supply chain performance. The case study will be vital for providing real-world insights into the benefits and challenges of using big data and analytics in different supply chain settings.
In weeks nine and ten, I will evaluate the disadvantages and complexities of implementing big data and analytics in supply chain management. This review will identify potential hurdles to successful implementation and guide how to overcome them.
Between weeks 11 and 12, I will complete the final report summarizing the project’s key findings. The report will provide practical recommendations for firms desiring to integrate big data and analytics into their supply chain operations, as well as a summary of the case study findings, literature review, and assessment of restrictions and hurdles.
This 12-week project will investigate the effects of big data and analytics on logistics and supply chain management, with unique milestones for each phase. Before analyzing the implications of big data and analytics on supply chain management, creating a case study, assessing its strengths and shortcomings, and writing the final report, a comprehensive literature review will be undertaken. The project will provide detailed evaluations of the potential benefits and challenges of deploying big data and analytics in various supply chain scenarios and fundamental recommendations for organizations wishing to implement these technologies in their operations.
Deliverables
The following will be the key deliverables of the project:
Literature Review: This report’s literature study will present a comprehensive analysis of the academic literature on the implications of big data and analytics on logistics and supply chain management. This paper will analyze the current state of the research on this topic and identify essential themes and recurrent trends.
Case Study: In this research, one or more real-world case studies of companies utilizing big data and analytics in supply chain operations will be investigated in depth. The report will detail the organization’s specific challenges and their effects on supply chain efficiency. This article will also examine the benefits and drawbacks of utilizing big data and analytics in various supply chain scenarios.
The Final Report: This report will include recommendations for firms desiring to integrate big data and analytics into their supply chain operations and a summary of the significant findings from the literature review and case study report. The article will highlight these technologies’ potential benefits and challenges and guide the most effective implementation tactics.
Each of these deliverables will be critical for understanding the effects of big data and analytics on logistics and supply chain management. The literature review report will provide a comprehensive understanding of the current status of research on the topic and identify any gaps that need to be filled. The case study report will provide genuine examples of how firms have effectively used these technologies and their implications on supply chain efficiency. The project’s final report will synthesize the findings of the two reports and provide organizations with suggestions for integrating big data and analytics into their supply chain operations.
This study’s findings will be helpful for both industry workers and academics and researchers. The conclusions and recommendations offered in the last chapter of the project report can aid organizations in better comprehending the potential benefits and challenges of integrating big data and analytics into their supply chain operations and in building successful implementation plans. Overall, the project’s results will contribute to the knowledge of the effects of big data and analytics in logistics and supply chain management and provide scholars and industry professionals with valuable information.
Resources
For the intention of conducting a compelling analysis of the effects of big data and analytics on logistics and supply chain management, it will be indispensable to have access to relevant academic literature and case studies. It will be necessary to have access to critical academic publications, business papers, and books to maintain awareness of recent advancements and best practices in the field. Additionally, having access to case studies that demonstrate how other businesses improved the efficiency of their supply chains through big data and analytics will be a helpful resource.
Along with academic research and case studies, it is necessary to consider data from a real-world organization to have a comprehensive understanding of the effects that big data and analytics have on the management of logistical processes and supply chains. This type of data may reveal, among other things, information regarding client demand, production schedules, transportation routes, and stock levels. This knowledge will be of the utmost use if it is obtained from a company that has already integrated big data and analytics into its supply chain operations, as this will demonstrate the full extent to which these technologies have been applied.
Tools and techniques such as online databases and search engines, data analysis software, and communication platforms to link up with businesses for data exchange will be needed to access the necessary resources. Costs may also be associated with hiring experts to evaluate the data or subscribing to specialized academic journals.
Due to the volume of information and material that will need to be accessed and evaluated, this project will necessitate a significant investment of time and effort. However, these funds are essential to ensure that the project produces valuable information about the effects of big data and analytics on logistics and supply chain management.
Beneficiaries
To undertake a compelling analysis of the implications of big data and analytics on logistics and supply chain management, it will be essential to have access to relevant academic literature and case studies. Accessing relevant academic journals, business papers, and books will be essential to stay current on industry trends and best practices. In addition, it will be essential to have access to case studies that illustrate how other businesses have utilized big data and analytics to improve the efficiency of their supply chains.
The effects of big data and analytics on logistics and supply chain management can only be adequately comprehended by adding data from a real business to academic research and case studies. Such data could provide information regarding client demand, production schedules, transportation routes, and inventory levels, among other things. This information is most beneficial if it comes from a company that has already adopted big data and analytics into its supply chain procedures. This will demonstrate their genuine impact.
Accessing essential resources will require using tools and technology, such as internet databases and search engines, data analysis software, and communication platforms to connect with enterprises for data exchange. Additionally, there may be expenses involved with employing specialists to assess the data or subscribing to specialized academic journals.
This project will require significant time and effort due to the amount of information and materials that must be accessible and reviewed. However, these monies are necessary to ensure that the project produces meaningful knowledge regarding the implications of big data and analytics on logistics and supply chain management.
Risks/Hazards
The proposed study to explore the impact of big data and analytics on logistics and supply chain management is fraught with several possible threats and risks that must be mitigated. Access to confidential information represents one of the most significant potential dangers. To complete the case study, the researchers will require access to data collected from a real-world organization. On the other hand, the organization might be wary of disclosing its confidential information to outside parties because doing so might expose it to legal and reputational dangers. The researchers will need to explicitly agree with the corporation regarding the ownership of the data, how the data will be used, and how it will be kept confidential to mitigate this risk. In addition, the researchers will be responsible for ensuring that the data is protected from illegal access and is not disclosed to any third parties.
Ethical problems regarding the privacy and confidentiality of data present another possible risk (Del Giudice et al., 2021). The terms “big data” and “analytics” refer to the process of collecting and analyzing enormous volumes of data, which may include disclosing personally identifiable information. The researchers will need to ensure that the data is gathered and processed ethically, in compliance with the applicable rules and regulations pertaining to the privacy of data. They will additionally be responsible for ensuring that the data is anonymized and that the privacy of individuals is preserved. In addition, the researchers will be responsible for ensuring that the findings of the project are presented in a manner that does not violate the confidentiality of the organization or any of the persons who were part of the project.
In conclusion, the project that is being proposed to investigate the effects of big data and analytics on logistics and supply chain management presents the possibility of dangers and hazards connected to the availability of data and the protection of personal information. The researchers must make specific agreements with the corporation regarding the ownership of the data, how the data will be used, and how the data will be kept confidential to reduce these risks. In addition, they will be responsible for ensuring that the data is gathered and processed ethically, in line with the applicable rules and regulations regarding data protection. The researchers will be able to guarantee that the study will be carried out in a safe, secure, and ethical manner if they follow these measures.
Work plan
References
Accenture. (2015). Accenture global operations mega trends survey: big data analytics. Accenture Strategy.
Del Giudice, M., Chierici, R., Mazzucchelli, A. and Fiano, F., 2021. Supply chain management in the circular economy era: the moderating effect of big data. The International Journal of Logistics Management, 32(2), pp.337-356.
Fosso Wamba, S., Gunasekaran, A., Papadopoulos, T. and Ngai, E., 2018. Big data analytics in logistics and supply chain management. The International Journal of Logistics Management, 29(2), pp.478-484.
McKinsey & Company. (2016). Supply chain 4.0: How leading companies are digitizing their global supply chains. McKinsey & Company.
Monczka, R. M., Handfield, R. B., Guinipero, L. C., & Patterson, J. L. (2015). Purchasing and supply chain management. Cengage Learning.
Oncioiu, I., Bunget, O.C., Türkeș, M.C., Căpușneanu, S., Topor, D.I., Tamaș, A.S., Rakoș, I.S. and Hint, M.Ș., 2019. The impact of big data analytics on company performance in supply chain management. Sustainability, 11(18), p.4864.
Raman, S., Patwa, N., Niranjan, I., Ranjan, U., Moorthy, K. and Mehta, A., 2018. Impact of big data on supply chain management. International Journal of Logistics Research and Applications, 21(6), pp.579-596.
Raut, R.D., Yadav, V.S., Cheikhrouhou, N., Narwane, V.S. & Narkhede, B.E. (2021). Big data analytics: Implementation challenges in Indian manufacturing supply chains. Computers in Industry, 125, p.103368.
Schniederjans, M. J., & Ozcan, F. (2016). Big data in supply chain management. Journal of Business Logistics, 37(1), 16-22.
Wang, X., & Wang, Q. (2016). The impact of big data on supply chain management: A conceptual framework. International Journal of Production Economics, 176, 86-97.
Zarnic, R., Rajcic, V. and Vodopivec, B., 2017. Data Collection for Estimation of Resilience of Cultural Heritage Assets. Mixed Reality and Gamification for Cultural Heritage, pp.291-312.
 write
write