Abstract
International marketing strategies are of fundamental importance in the dynamic landscape of global business. This paper broadly assesses Nestle’s international marketing efforts, explicitly focusing on its endeavours in the UK and Bangladesh. Understanding the intricacies of marketing approaches in culturally diverse markets is essential for creating effective global business strategies.
The study begins bordering on Nestle’s global prominence in the consumer goods sector, trailed by a top-to-bottom investigation of its competitive landscape and market share trends. This assessment reaffirms Nestle’s position as an industry leader and highlights its adeptness at flourishing in a remarkably competitive market. The subsequent section delves into the full-scale and miniature factors shaping Nestle’s strategies in the UK and Bangladesh. A point-by-point PESTLE analysis provides intuitions into the complicated elements impacting the marketing landscape in every nation, setting the stage for a comprehensive assessment of Nestle’s miniature climate, including contender strengths and consumer conduct. The analysis further scrutinizes Nestle’s market passage strategies, uncovering the challenges and opportunities experienced during its expansion into these markets. This section sheds light on Nestle’s capacity to adjust to cultural diversity, administrative intricacies, and developing consumer expectations. The STP marketing analysis underscores Nestle’s capability in segmenting and positioning its products effectively, using tools such as perceptual maps to illustrate its strategic prowess.
Lastly, the assessment of Nestle’s marketing mix decisions demonstrates its ability to adjust standardization and adaptation while taking special care of local preferences. This analysis provides significant insights into Nestle’s international marketing success, emphasizing its flexibility, strategic agility, and responsiveness to market dynamics.
International Marketing Evaluation of Nestle in the UK and Bangladesh
In an era characterized by unprecedented connectivity and economic interdependence, the idea of international marketing has turned into a driving force for multinational corporations trying to expand their horizons and outfit the capability of diverse markets. Global marketing is the strategic approach through which businesses tailor their products, services, and promotional efforts to care for different countries’ unique preferences and cultural nuances. This starting segment not just fills in as a preface to our Evaluation of Nestle’s international marketing strategies in the United Kingdom (UK) and Bangladesh yet additionally gives a brief look into the more extensive setting of globalization and its impact on present-day business rehearses. Globalization, described by the disintegration of geological hindrances and the free progression of merchandise, data, and thoughts across borders, shapes the setting against which international marketing flourishes (Keegan & Green, 2017). As organizations like Nestle look past their homegrown shores, they experience a scene where nearby nuances and cultural variety shape consumer behaviour and market elements. In this way, international marketing exemplifies the dexterity to adjust global brands and contributions to reverberate with consumers’ unique necessities and desires in distinct markets.
Brief Outline of Nestle
Nestle, a multinational consumer goods giant founded in 1866, has scratched its global imprint. With a broad portfolio traversing classifications like food, beverages, healthcare, and nutrition, Nestle contacts the existence of billions (Czinkota & Ronkainen, 2013). Its products have become inseparable from quality and taste, laying out Nestle as a household name in various countries. This Evaluation takes an amplifying glass to Nestle’s international marketing strategies, focusing explicitly on its operations in the UK and Bangladesh.
Compelling statistics within the food and beverage sector substantiate Nestlé’s financial prowess. The Nestlé Group’s net profit surged from approximately seven billion Swiss Francs in 2017 to a remarkable 16.9 billion Swiss Francs in 2021. While there was a dip in net profits to 9.3 billion Swiss Francs in 2022, Nestlé’s financial stability remains evident. As one of the globe’s largest food and beverage entities, Nestlé boasts an extensive portfolio encompassing more than 2000 brands distributed across over 180 countries (Onkvisit & Shaw, 2019). This financial data underscores Nestlé’s enduring ability to navigate competitive markets and maintain a significant global presence.
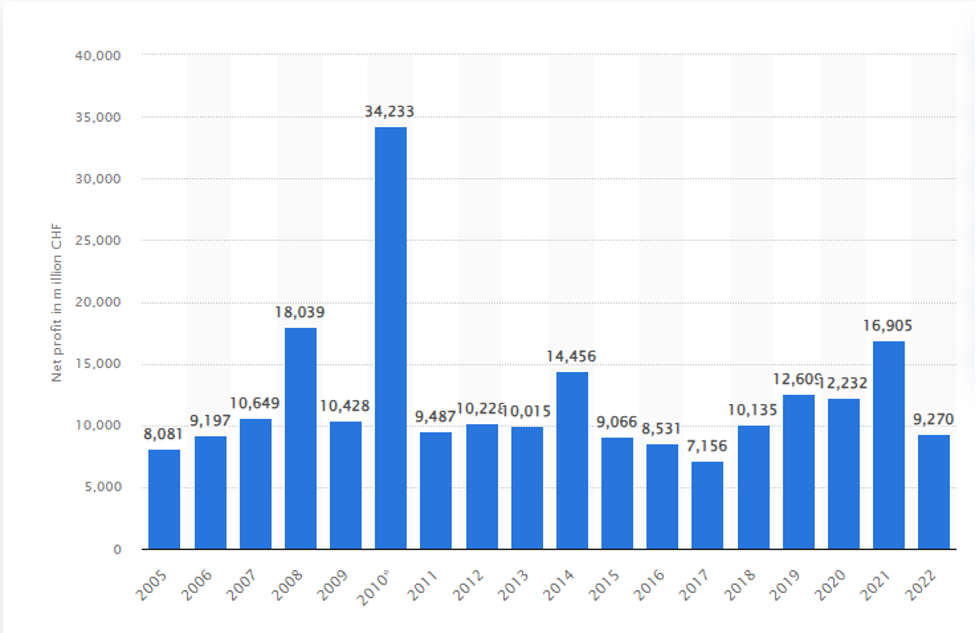
Net profit and financial of the Nestlé Group from 2005 to 2022
Significance of International Marketing for Nestle
Regarding Nestle, international marketing is not only a strategic choice but an imperative. Nestle’s very essence lies in its capacity to comprehend and take special care of the diverse preferences of consumers around the world. International marketing enables Nestle to rise above borders, carrying iconic brands to new shores while exploring the unpredictable woven artwork of cultural preferences, economic incongruities, and administrative systems (Keegan & Green, 2017). Nestle’s prosperity relies on its capacity to blend its global brand identity with the requirement for targeted localization, permitting it to reverberate with the hearts and brains of consumers in every unique market.
Global Profile and Competitors
2.1 Nestle’s global presence and market share
Nestle’s effect on the consumer goods area is likened to an orchestra resounding across the globe. Since its beginning in 1866, Nestle has painstakingly supported a tradition of quality and development that has laid it out as a global force to be reckoned with. In more than 180 countries, Nestle’s inevitable presence highlights its obligation to satisfy various consumer needs. This far-reaching market impression fits with a significant market share, demonstrating Nestle’s capacity to draw in a diverse global crowd reliably. The agreement of its global reach and market share highlights Nestle’s considerable impact on the consumer.
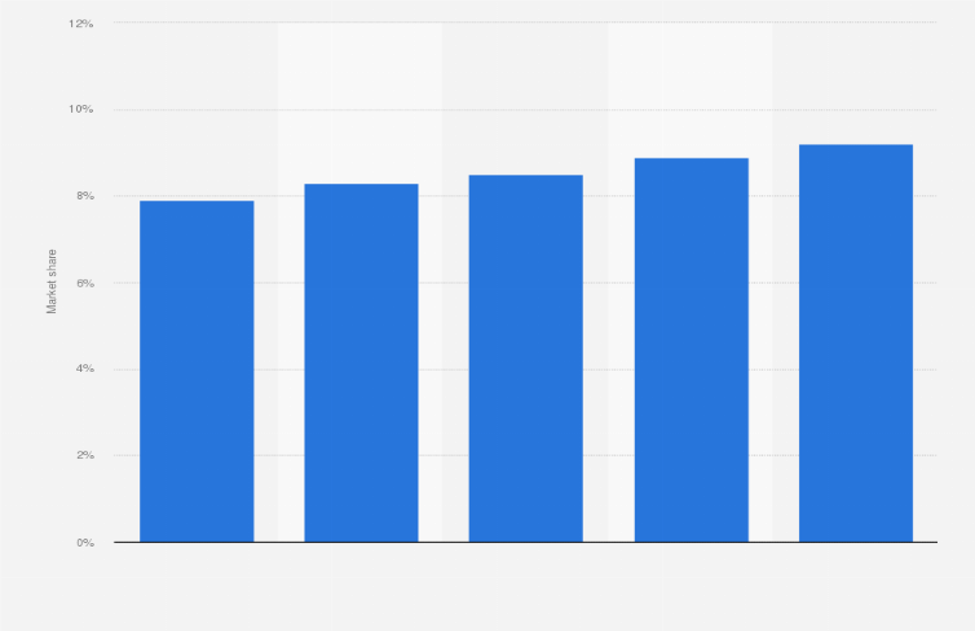
Graph 1: Nestle’s Global Presence and Market Share
2.2 Comparison with crucial competitors
In the field of global consumer goods, the competition is energetic, and Nestle winds up in the organization of industry heavyweights like Mars, Mondelez, and Unilever. This group of four takes part in a many-sided dance of strategy, innovation, and brand resonance, each endeavouring to cut out its speciality in the hearts and households of consumers worldwide. Mars, eminent for its confectionery and pet care products, presents a convincing competitor to Nestle. Mondelez, with its iconic snacks and confectionery, remains a considerable opponent, while Unilever, a conglomerate crossing diverse consumer classes, adds one more layer of intricacy to the competitive scene. Contrasting Nestle and these key opponents discloses an entrancing embroidery of strategic decisions and market positioning (Onkvisit & Shaw, 2019). Nestle’s diverse portfolio, including food, beverages, healthcare, and nutrition, allows it to meet consumer needs. This expansiveness of contributions differentiates Nestle, empowering it to adjust and flourish in other market fragments.
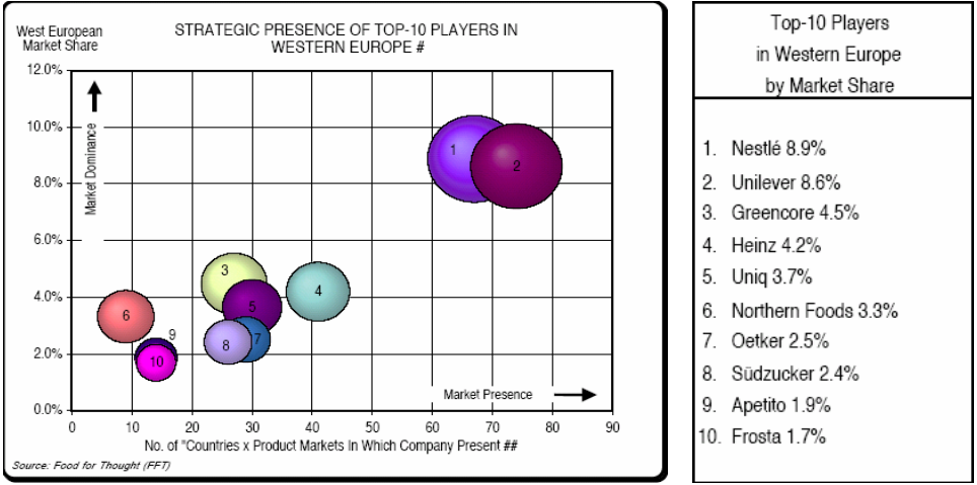
Diagram 2: Market Divide Examination Between Nestle and Competitors
Market dynamics, consumer preferences, and brand dependability further characterize the competitive account. Nestle’s capacity to reverberate with consumers across markets demonstrates its global brand bid and confined adaptation (CastelarHost, 2016). The diverse competencies of every player, combined with their unique product contributions, make a dynamic biological system where innovation, marketing strategies, and consumer commitment decide achievement.
Marketing Environment Overview
3.1 Macro Environment Analysis of the UK and Bangladesh
The macro environment of the UK market, dissected through the PESTLE structure, gives bits of knowledge into the outer factors moulding Nestle’s operations. Political solidness, economic pointers, cultural qualities, mechanical progressions, lawful systems, and environmental worries all impact Nestle’s marketing choices in the UK.
PESTLE Analysis for the UK Market:
| Factor | Situation | Impact on the UK Market |
| Political | The UK maintains political stability with a well-established democratic governance system.
Trade relationships are maintained, promoting international business collaboration. Brexit implications have led to economic and trade uncertainties. |
Creates a favourable environment for domestic and foreign investments, leading to economic growth.
– Encourages business expansion and development due to consistent regulatory policies. – Brexit-related changes influence trade dynamics and require adaptive business strategies. |
| Economic | The UK economy is characterized by its diverse and dynamic nature, comprising finance, technology, and manufacturing industries.
The UK has a robust GDP and favourable fiscal policies promoting business growth. |
– Attracts global companies and investors due to a stable economic climate and various growth sectors.
– Provides ample opportunities for innovation and entrepreneurship across diverse industries. |
| Sociocultural | The UK is home to a multicultural society with a
blend of ethnicities and cultural backgrounds. Evolving consumer preferences are witnessed as younger generations exhibit distinct behaviours. The culture values sustainability and ethical practices, influencing market demand. |
– Offers a diverse consumer base, allowing businesses to tailor products and services to specific segments.
– Niche markets and subcultures provide opportunities for specialized products and marketing approaches. – Companies embracing sustainability and ethical practices gain a competitive edge and meet consumer expectations. |
| Technological | The UK boasts advanced technology infrastructure,
fostering digital transformation. High-speed internet and widespread digital connectivity offer opportunities for businesses to engage with consumers through digital platforms. The tech sector is rapidly growing, attracting investments and talent. |
– Technological advancements facilitate seamless connectivity and data sharing, enhancing business operations.
– Drives innovation in various industries, leading to new products, services, and business models. – Creates a tech-savvy consumer base, demanding seamless digital experiences and personalized interactions. |
| Legal | The UK operates under stringent regulatory frameworks encompassing consumer protection, competition, and data privacy.
The legal system provides mechanisms for dispute resolution and business contracts. |
– Shapes business practices, ensuring fair competition and market transparency.
– Challenges businesses to maintain compliance with complex regulations, leading to effective governance. – Shapes business practices, ensuring fair competition and market transparency. |
| Environmental | Environmental awareness is prominent, driving
sustainability efforts in various industries. Green initiatives encourage energy-efficient practices and responsible waste management. |
– Companies adopting sustainable practices receive positive recognition and enhance brand image.
– Consumer preferences shift towards eco-friendly products and services, driving market demand. |
PESTLE Analysis for the Bangladesh Market:
| Factor | Situation | Impact on the Bangladesh Market |
| Political | Political stability prevails, encouraging foreign investments and trade collaborations. Government initiatives promote foreign investment and economic growth. | – Attracts foreign investments and fosters business growth.
– Provides a conducive environment for business expansion. |
| Economic | Bangladesh is an emerging market with a growing middle class and increasing disposable income. | – Presents opportunities for business growth and expansion. |
| Sociocultural | Cultural solid values and close-knit communities define societal norms and preferences.
Traditional consumption habits are deeply rooted, influencing consumer choices. |
– Shapes consumer behaviour and influences purchasing trends.
– Niche markets cater to specific cultural preferences, allowing tailored product offerings. |
| Technological | A growing tech sector, increased internet penetration, and mobile phone usage.
E-commerce platforms and digital payment systems are on the rise. |
– Digital transformation allows businesses to engage with consumers through online platforms.
– Enhances consumer connectivity and accessibility. |
| Legal | The legal landscape is evolving to accommodate foreign investment and business growth.
Investment incentives and trade agreements are being established to attract foreign businesses. |
– Facilitates foreign investment through regulatory changes.
– Offers a more conducive environment for international companies. |
| Environmental | Climate concerns are mounting, urging businesses to adopt eco-friendly practices.
Natural resource challenges, such as water scarcity and pollution, require attention. Environmental regulations are evolving to address sustainability challenges. |
– Encourages businesses to adopt sustainable practices and contribute to environmental conservation.
– Consumer preferences shift towards environmentally friendly products, influencing market trends. – Regulatory changes impact production processes and sourcing of materials. |
3.2 Micro Environment Analysis
Competitors in the UK and Bangladesh (strengths & weaknesses)
Nestle competes with the UK’s prestigious giants like Mars, Mondelez, and Unilever. These competitors gloat about deep-rooted brands, broad circulation organizations, and a global presence. Mars, known for its confectionery products, benefits areas of strength from dependability and imaginative marketing efforts. Mondelez, with brands like Cadbury, leverages its legacy and diverse product range. Unilever’s obligation to maintainability reverberates with environmentally conscious consumers. However, Nestle’s competitors might experience moves in adjusting to developing consumer preferences, especially the shift towards better and more supportable choices. Also, Brexit-related exchange intricacies present likely interruptions to supply chains.
In Bangladesh, Nestle competes with nearby players like PRAN and multinational corporations like Unilever. Neighbourhood organizations figure out nearby consumer preferences and have effective conveyance organizations. Nonetheless, they might confront restrictions regarding mechanical progressions and international brand acknowledgement. Multinational competitors leverage global assets yet need to adjust to neighbourhood cultural nuances. With its perceived brand, diverse product portfolio, and innovation abilities, Nestle is strategically set up to take special care of the two markets’ developing requests. It can leverage its global capacity to make products custom-made to neighbourhood tastes while tending to rising well-being and manageability trends.
Statistical evidence of market share and performance
Nestle has reliably kept a significant market share across numerous product classes in the UK. For example, Nestle’s KitKat and Air brands are well-known decisions among consumers in the confectionery portion, adding to a critical market presence. Nestle’s market share in Bangladesh has consistently developed, mirroring the rising interest in quality consumer goods. Nestle’s interest in the dairy portion, including products like NIDO and Nestle Milkpak, has built up some forward movement among neighbourhood consumers (Jain, 2020). This demonstrates Nestle’s capacity to take advantage of the nation’s expanding working class and changing utilization designs. These insights underline Nestle’s ability to adjust its product contributions to align with neighbourhood preferences and care for diverse market fragments. Nestle’s obligation to innovation, quality, and understanding consumer trends upgrades its competitive advantage in the two markets.
Consumer behaviour in the UK and Bangladesh markets
In the UK, consumer behaviour is described by an elevated spotlight on well-being and health. There is a developing interest in products that offer nutritional advantages, comfort, and moral obtaining. Consumers are progressively looking for straightforwardness in marking and maintainability rehearses. The pattern towards web-based business and internet shopping has additionally impacted buying behaviours.
In Bangladesh, consumer behaviour is moulded by cultural qualities, reasonableness, and quality. Consumers focus on fundamental things, and reasonableness frequently offsets brand unwaveringness. Conventional utilization propensities and solid cultural ties impact preferences, with families continually pursuing aggregate buy choices (Jain, 2020). The quick take-up of computerized innovation has prompted expanded internet-based exploration and shopping, especially among metropolitan consumers. Nestle’s outcome in the two markets depends on its capacity to expect and answer these consumer behaviours. By offering products that align with well-being and health trends, tending to moderation concerns, and drawing in consumers through computerized stages, Nestle can catch market offers and encourage brand dedication.
Evaluation and Entry Analysis
Nestle’s approach to entering each market
In the UK, Nestle embraced a market entrance strategy to leverage its current brand acknowledgement and diverse product portfolio. Nestle guaranteed a quick entry into the market by zeroing in on existing products like KitKat and Nescafé and fitting them to neighbourhood preferences. Moreover, strategic coalitions with wholesalers and retailers worked with effective conveyance, upgrading its market presence. Conversely, Nestle’s approach in Bangladesh included a market improvement strategy (Kotler & Armstrong, 2017). Perceiving the capability of a developing market, Nestle presented a scope of products customized to the nearby sense of taste while sticking to reasonable requirements. Coordinated efforts with nearby providers and merchants empowered Nestle to lay out significant areas of strength in the market and expand its arrival at past metropolitan places.
Challenges and opportunities faced during market entry
During market entry in the UK, Nestle confronted difficulties connected with extraordinary competition from laid-out players and changing consumer preferences towards better choices. The immersed market expected Nestle to develop and differentiate its contributions to stick out. Be that as it may, the open door lay in the UK’s well-off consumer base and its receptiveness to exploring different avenues regarding new products, which permitted Nestle to present effective varieties and gain by advancing trends.
In Bangladesh, Nestle experienced difficulties with cultural adaptation, moderation concerns, and a profoundly competitive neighbourhood market. Adjusting products to suit nearby tastes while keeping up with quality represented a test; however, it likewise introduced an open door to exhibit Nestle’s obligation to understand and embrace cultural variety. The developing working class and expanding extra cash offered a promising open door for Nestle to take advantage of a market with critical growth potential (Kotler & Armstrong, 2017). Nestle’s strategic entry into the UK and Bangladesh markets highlights its capacity to fit its approach to diverse market conditions.
STP Marketing Analysis
5.1 Segmentation and Targeting Definition
Segmentation includes dividing a diverse market into distinct groups in light of shared qualities, ways of behaving, or needs, permitting organizations like Nestlé to tailor methodologies for explicit client portions. Targeting involves choosing these fragments and centring marketing efforts to address their extraordinary inclinations proficiently. The positioning includes creating a convincing picture or value proposition that separates Nestlé’s contributions to purchasers. Product adaptation, then again, alludes to changing products to align with local tastes, guidelines, and inclinations in different markets, guaranteeing they reverberate with diverse audiences.
Segmentation Criteria Used by Nestle
Consistently comprehending consumers’ diverse necessities and preferences supports Nestle’s segmentation strategy. Nestle utilizes a complex approach in the UK market, considering both segment and psychographic factors. Demographically, Nestle targets different age gatherings, perceiving that the nutritional prerequisites of newborn children contrast from those of grown-ups or seniors. Besides, pay levels assume a segmentation part, as Nestle tailors premium contributions for higher-pay fragments looking for a guilty pleasure. Psychographically, Nestle dives into a way of life considerations. Well-being-cognizant consumers looking for nutritious decisions structure one section, while people esteem comfort and, in a hurry, utilization comprises another (Doole & Lowe, 2016).
Targeting Strategies Employed (e.g., Concentrated, Differentiated, Undifferentiated)
Nestle’s focus on strategies represents its skill in adjusting market needs with customized approaches. Nestle focuses on a differentiated strategy in the UK market to catch consumer preferences’ complexities. This includes creating distinct marketing drives and product contributions for different fragments. For example, Nestle takes exceptional care of the well-being of conscious consumers looking for nutritional worth by advancing its cereal brands and speaking to espresso aficionados with its exceptional Nescafé line. This approach empowers Nestle to amplify market share by tending to diverse consumer wants. Conversely, in the unique scene of the Bangladesh market, Nestle utilizes a concentrated focus on strategy (Doole & Lowe, 2016). Perceiving the thriving working class as a crucial growth driver, Nestle focuses on gathering their developing requirements.
Product Adaptation
Nestlé’s international success is established in its adeptness at tailoring products to suit diverse markets’ unique demands and cultural preferences. In the UK, Nestlé has meticulously responded to the prospering pattern of health-consciousness. The organization has embraced product adaptation by reducing sugar content and consolidating organic ingredients in alignment with the increasing demand for healthier options. This strategy resonates with the health-conscious consumer base pervasive in the district, showcasing Nestlé’s responsiveness to local trends. Conversely, Nestlé’s product adaptation strategy in the Bangladesh market is described by cultural sensitivity and customization. Perceiving the local populace’s solid cultural ties and customary consumption habits, Nestlé has presented localized variations of its products. These adaptations consolidate conventional flavours and ingredients that hold significance for Bangladeshi consumers. By understanding and caring for local preferences, Nestlé fosters a more profound association with consumers, improving brand reliability and market infiltration.
Nestlé’s proactive way of dealing with product adaptation across various markets demonstrates its obligation to understand every locale’s unique intricacies. This astute strategy enables the organization to position itself, offering products that address consumer issues and align with their cultural and lifestyle choices. The custom-fitted product offerings underscore Nestlé’s prowess in exploring international markets and catching diverse consumer segments
5.2 Positioning with Perceptual Map
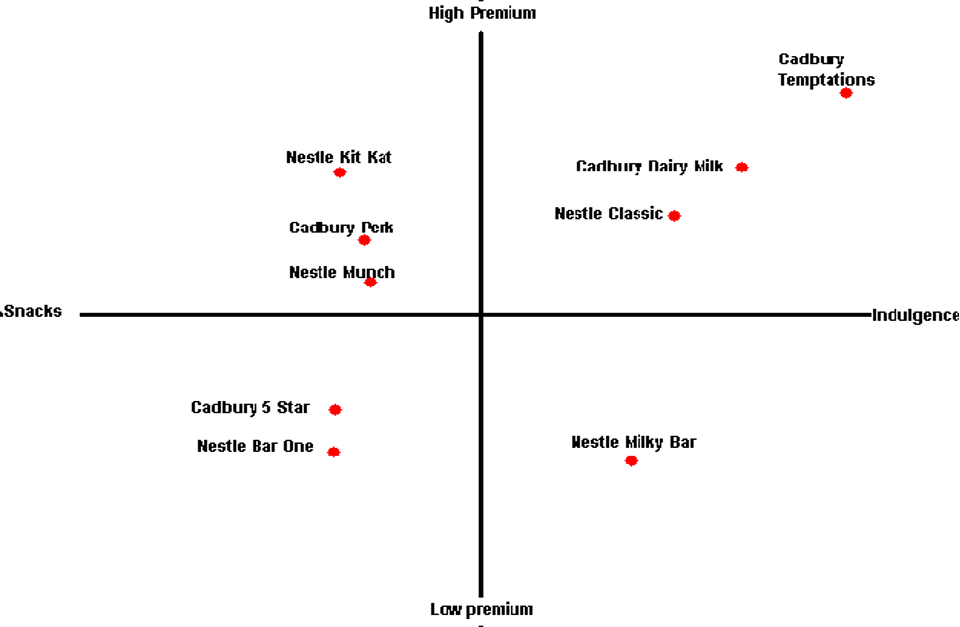
Creation and Use of Perceptual Maps for Positioning:
Nestle strategically utilizes perceptual maps as vital visual instruments that comprehensively comprehend its product positioning inside the competitive scene. These maps graphically address consumer discernments by planning key ascribes or aspects that impact buying choices. In the UK market, Nestle’s perceptual guide grandstands a careful balance between comfort and quality. By plotting its products along aspects like taste, comfort, and value, Nestle acquires significant experiences into how consumers see its contributions compared with competitors. The utilization of perceptual maps goes past representation; it directs Nestle’s positioning choices. The guide recognizes holes in the market, empowering Nestle to plan products that consume unique spaces and take care of explicit consumer needs (Czinkota & Ronkainen, 2013). This strategic approach engages Nestle to make convincing marketing messages and special offers that reverberate with interest groups.
How Nestle Differentiates Its Products in Each Market:
Nestle’s adeptness in product differentiation is exemplified through its strategic utilization of perceptual maps to fit its contributions to the unique requests of each market. In the UK, Nestle succeeds in differentiating its products by strategically positioning them inside the perceptual guide. The guide uncovers how Nestle cuts a distinctive speciality by underlining the cooperative energy between comfort and quality (Jain, 2020). This approach reverberates with UK consumers looking for magnificent treats and time-proficient answers for their quick-moving lives. By distinguishing this vacant space, Nestle makes a convincing and differentiated positioning that separates it from competitors. In the Bangladesh market, Nestle utilizes perceptual maps to direct its differentiation strategy.
Marketing Mix Decision for UK and Bangladesh
6.1 Product and Service Standardization & Adaptation
Products adapted to meet local requirements
Nestle’s approach to product adaptation is attached to its obligation to fit contributions to each market’s unique requirements and preferences. In the UK, where well-being awareness wins, Nestle has proficiently adjusted its product portfolio to take special care of the rising interest in better choices. This incorporates decreasing sugar content, presenting natural fixings, and zeroing in on nutritional advantages. By tending to pervasive well-being trends, Nestle secures itself as a brand that lines up with consumer prosperity, in this way improving its market presence.
In Bangladesh, Nestle perceives the significance of reasonableness and cultural arrangement. This drives the adaptation of products to match nearby tastes and fundamental economic factors. Nestle presents flavours and piece measures that resound with Bangladeshi consumers, making areas of strength for an association and positioning itself as a brand that comprehends and takes exceptional care of their preferences. By lining up with nearby culinary customs, Nestle catches the sense of taste and shows cultural awareness, further hardening its market position. Nestle’s strategic product adaptations show its ability to understand diverse consumer scenes and capacity to tailor contributions reverberate with the well-being cognizant UK market and the culturally rich market in Bangladesh.
Standardized products across markets and benefits
While Nestle embraces adaptation to take care of nearby nuances, it strategically utilizes product standardization to leverage global brand value and operational Effectiveness. Iconic brands like KitKat feature Nestle’s capacity to keep up with reliable bundling and branding across markets, benefiting from the acknowledgement and trust these brands have earned worldwide. Standardization offers several advantages, including smoothed-out production processes, economies of scale, and a durable global brand picture (Hollensen, 2019). Using normalized products, Nestle can accomplish cost reserve funds, create a compelling store network for executives, and diminish intricacies in marketing and circulation.
Evaluation of product strategies in each market
The outcome of product strategies fluctuates by market. In the UK, Nestle’s adaptation to well-being trends aligns with consumer requests, adding to market entrance. In Bangladesh, restricted transformations make more grounded consumer associations, helping brand reliability. Notwithstanding, careful Evaluation is crucial for working out harmony among adaptation and standardization, guaranteeing ideal market fit.
6.2 Pricing Strategies Comparison & Evaluation
Pricing approaches in the UK and Bangladesh
Nestle’s evaluating strategies mirror a sharp comprehension of the economic and cultural settings of the UK and Bangladesh markets. In the UK, a developed and competitive market, Nestle utilizes a worth-based estimating approach. This strategy adjusts product estimating with the apparent worth and quality they deal with well-being-conscious consumers. By positioning its products as premium and zeroing in on their advantages, Nestle lays out an evaluating structure that legitimizes its top-notch position in the market. Conversely, Nestle uses an expense-based estimating strategy in Bangladesh, a developing market with shifting pay levels. This approach considers neighbourhood economic circumstances and guarantees moderation for a more extensive consumer base. By setting costs that resound with the buying force of the nearby populace, Nestle improves openness and broadens its market reach (Hollensen, 2019). These distinct evaluating approaches exhibit Nestle’s capacity to fit strategies as per market elements, guaranteeing competitive estimating that resounds with the consumer attitude in both the UK and Bangladesh markets.
Factors influencing pricing decisions in each market
Market-explicit factors complicatedly mould Nestle’s valuing choices in the UK and Bangladesh. In an exceptionally competitive and mature market in the UK, elements, for example, consumer discernments, brand positioning, and winning well-being trends, impact valuing. Nestle considers the exceptional picture it has developed and adjusts costs to its well-being-centred products’ apparent worth and quality (Hollensen, 2019). Also, market competition requires evaluating strategies that manage fluctuating consumer portions while keeping up with profitability. Conversely, Bangladesh’s valuing scene is portrayed by diverse pay levels and a developing working class.
Effectiveness and challenges of pricing strategies
In the UK, esteem-based valuing improves Nestle’s top-notch picture, reinforcing profitability. Challenges include potential moderation worries for specific fragments. In Bangladesh, cost-based estimating increments openness yet may affect apparent worth (Doole & Lowe, 2016). Finding some harmony between reasonableness and premium quality remains a test.
6.3 Distribution Strategies Comparison & Evaluation
Distribution channels used in the UK and Bangladesh
In the UK, Nestle leverages diverse appropriation channels, including supermarkets, general stores, and online stages. In Bangladesh, customary retail and more modest outlets overwhelm appropriation because of framework requirements.
How Nestle manages distribution challenges in each market
In the UK, Nestle’s high-level coordinated operations upgrade productivity and meet diverse consumer needs. In Bangladesh, Nestle puts resources into last-mile dissemination and organizations to defeat framework restrictions, guaranteeing boundless product accessibility.
Efficiency and Effectiveness of distribution strategies
The UK benefits from consistent appropriation, improving market reach and consumer availability. In Bangladesh, dissemination challenges require progressing adaptation and venture. Nestle’s strategic conveyance efforts add to market infiltration and brand perceivability.
6.4 Promotional Mix Comparison & Evaluation
Promotional tactics employed in the UK and Bangladesh
Nestle tailors promotional strategies to each market’s cultural setting (Schneiderova, 2010). In the UK, advanced and web-based entertainment crusades draw in educated consumers. In Bangladesh, conventional media and local area commitment reverberate with neighbourhood preferences.
Cultural considerations in promotional efforts
Nestle’s missions underline well-being awareness and maintainability in the UK, aligning with cultural trends. Cultural awareness is vital in Bangladesh, underlining family esteems and shared encounters.
Success and limitations of the promotional mix in each market
In the UK, computerized advancements yield commitment and brand devotion, yet protection concerns present difficulties. In Bangladesh, people group commitment cultivates brand trust, albeit restricted computerized admittance might upset reach.
Conclusion
This analysis has made several vital discoveries regarding Nestle’s international marketing attempts in the UK and Bangladesh markets. The Evaluation featured Nestle’s proficiency in exploring the multifaceted global marketing scene, fitting its strategies to line up with diverse market attributes, and leveraging both adaptation and standardization approaches to guarantee resonance with neighbourhood consumers. Nestle’s obligation to product adaptation because of well-being trends in the UK and cultural preferences in Bangladesh features its capacity to address unique market requests.
Nestle’s international marketing achievement is highlighted by its capacity to keep severe strength areas for a brand identity while remaining sensitive to neighbourhood market complexities. The organization’s double spotlight on product adaptation and standardization has empowered it to find harmony between global consistency and neighbourhood importance. Diverse market entry strategies, focusing on approaches, and positioning strategies mirror Nestle’s capacity to fit its efforts to different cultural and economic scenes. Nonetheless, specific difficulties, like estimating elements and consumer behaviour varieties, accentuate the requirement for constant refinement. While Nestle has exhibited momentous outcomes in international marketing, there are regions for expected improvement. Initially, a more profound investigation of cultural shades and consumer behaviour can give experiences to more exact segmentation and focusing on. Second, further research on imaginative conveyance could support openness in the two markets. Third, nonstop checking of evaluating strategies and acclimations to line up with developing economic circumstances can enhance market competitiveness.
References
Alfimohammad. (2012). Competitive Advantage and Value Chain Nestle. Retrieved from https://alfimohammad.wordpress.com/2012/11/22/caompetitive-advantage-and-valuechain-nestle/
Best, D. (2011). In the Spotlight: Comparing Nestle, Danone and Unilever. Just-food. Retrieved from http://www.just-food.com/analysis/comparing-nestle-danone-andunilever_id114355.aspx
CastelarHost. (2016). Nestlé LC1. Retrieved from http://articles.castelarhost.com/nestle_competitive_strategy.htm Morning Star. (2016). Nester SA ADR. Retrieved from http://financials.morningstar.com/competitors/industry-peer.action?t=NSRGY
Czinkota, M. R., & Ronkainen, I. A. (2013). International marketing (10th ed.). Cengage Learning.
Doole, I., & Lowe, R. (2016). International marketing strategy: Analysis, development and implementation (7th ed.). Cengage Learning. https://images.template.net/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/09212256/international-marketing-plan-template.pdf
Hollensen, S. (2019). Global marketing: A decision-oriented approach (8th ed.). Pearson. https://portal.findresearcher.sdu.dk/en/publications/global-marketing-a-decision-oriented-approach-with-a-special-indi
Jain, S. C. (2020). International marketing (7th ed.). Cengage Learning. https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/978-3-030-33588-5.pdf
Keegan, W. J., & Green, M. C. (2017). Global marketing (9th ed.). Pearson.
Kotler, P., & Armstrong, G. (2017). Principles of marketing (17th ed.). Pearson.
Nestlé (2016). Strategy. Retrieved from http://www.nestle.com/aboutus/
Onkvisit, S., & Shaw, J. J. (2019). International marketing: Strategy and theory (7th ed.). Routledge. https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=4248443
Schneiderova, K. (2010). Strategic Analysis of Nestlé and Its Competitor Kraft Foods. Retrieved from http://media0.webgarden.cz/files/media0:510a4fec84d42.pdf.upl/Nestl%C3%A9+%26+ Kraft+Foods+(International+Business+Strategy).pdf
 write
write