Introduction.
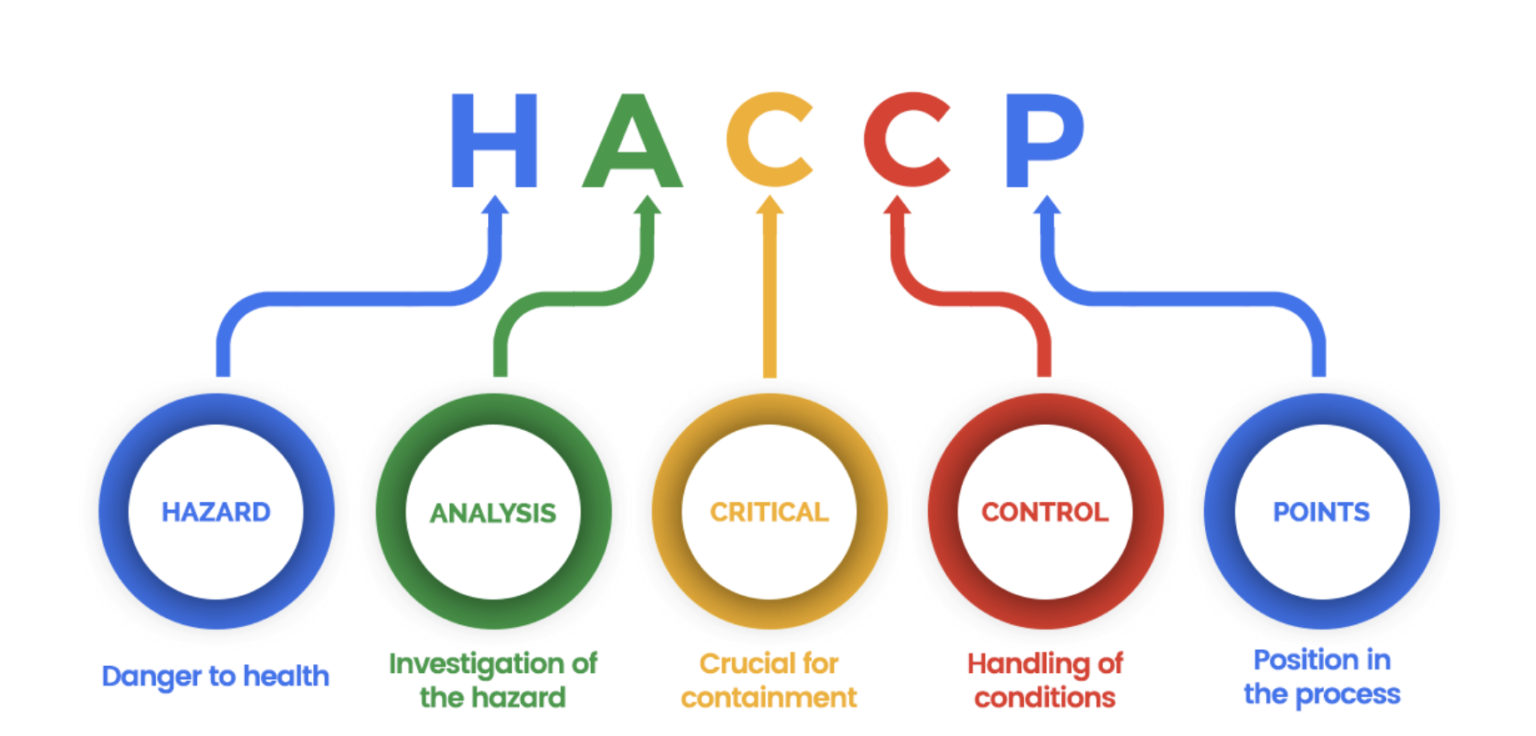
HACCP is a systematic approach to food safety management that aims to identify, evaluate, and control the hazards throughout food production. The primary goal of HACCP is to prevent dangers that could compromise the safety of food products rather than relying solely on end-product testing(Kalisa, n.d.). ISO 9001:2015 year, the qualitative system management standard, concurs that customer satisfaction and improvement are the main principles. Integration of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) within a quality management system like ISO 9001: In 2015, the food security sector experienced a whole new spectrum with the communities, stakeholders, and businesses displaying up-to-date food safety standards and operational excellence. This article examines techniques’ role in strengthening cardinal areas like identifying training needs, documentation and data control, traceability, coordination, and calibration. Summary and usage of the best processes could make a vital focus of the essay because, if integrated, it will become an integral part of robust food safety systems.
Source: ISO Global
Integrating HACCP within ISO 9001:2015
Integrating HACCP within The new Board Law ISO 9001, effective from 2015, regulates food safety and quality into health security. The visible connection between the hazard analysis and control measure, which is HACCP’s actual description, and the broader quality management system, which is ISO 9001, avoids counter-productivity. This way, replication in work is minimized, and improving the entity’s overall effectivenesstegration of these into the central system where both food safety and overall quality are handled aims at harmonious continuity using the same organizational employees (Sacchetti, 2022). Overall, integrating HACCP within ISO 9001: While 2015 concentrates on food safety, it is also working to increase its operational efficiency.
HACCP principles complement ISO 9001: Consequently, we will enhance our food safety by 2015 through a specialized approach that covers particularly food hazards and risk management. While ISO 9001 provides a description of quality management in general, HACCP provides a systematic procedure to assess, define, and control the critical hazards related to food safety (Chen et al., 2019). HACCP expounds preventive measures that focus on continuous improvement within an organization. Therefore, the parties involved can mitigate risks and boost product quality. By adopting HACCP principles, this ISO 9001 organization will set up effective food safety procedures, thus achieving increased conformity with regulatory norms and customer satisfaction (Purwanto et al., 2020). Such integration allows for a complete quality management strategy where food safety gets built organically and continuously into all the organizational systems and processes designed to make food products safer and the organization more efficient.
Areas where ISO 9001 can strengthen HACCP
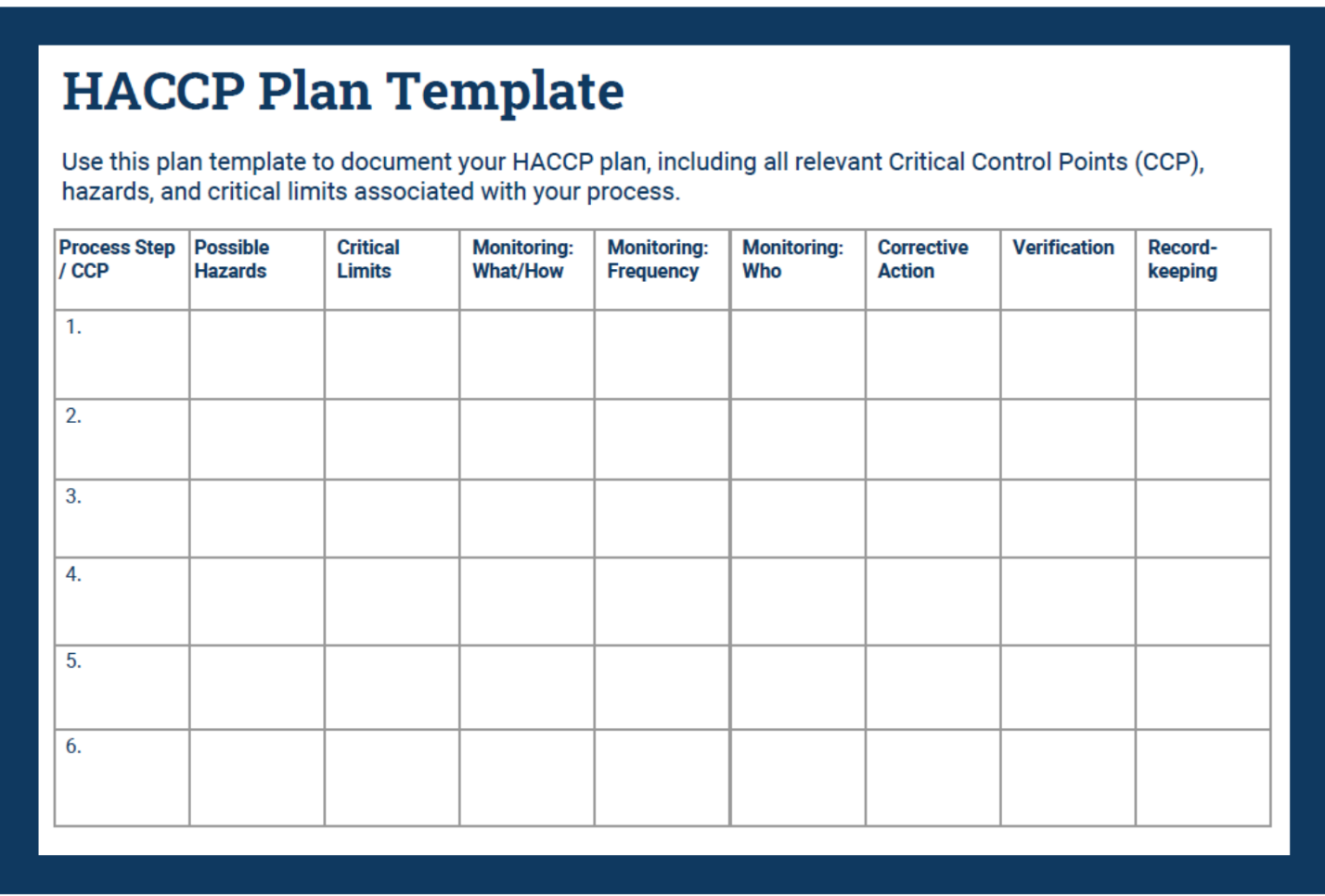
Document and data control
ISO 9001:2015 imposes powerful document control specifications to obtain the quality management system’s (QMS’s) efficiency. This refers to having processes that cover the formation, review and approval, release, and revisions of these documents. Papers consist of documents such as policies, procedures, work instructions, and record-keeping as a part of QMS activity. Each document shall have its unique identifier following the strict version control guidelines to avoid misuse of outdated documents. Periodic reviews mean that documents are current, truthful, and consistent with the operation and direction of the organization. Moreover, the security of records is also necessary to prove compliance and show the performance of the QMS.
Document and data control under ISO 9001:2015 is a structured framework that can highly assist HACCP implementation by managing important documents concerning food safety. For example, hazard analysis reports, the critical control point (CCP) monitoring records, and corrective action procedures are equally important in implementing HACCP (Motarjemi & Warren, 2023). By adhering to ISO 9001 in 2015, organizations need to adopt the document control requirements so that these documents are adequately managed, updated, and accessible to the relevant personnel (Tendero, 2023). The system promotes effective communication, uniformity in procedures, and compliance with food safety regulations along the production procedure.
The establishment of specific document control principles that are common with HACCP can help in achieving the goals of food safety management. Thus, for instance, hazard analysis reports describe hazards associated with the product stages of manufacture and the control measures that prevent risks. These evaluations pass quality control and acceptance to ascertain their accuracy and efficiency. Also, the CCP monitoring records include the critical control point observations and actions taken as corrections, which would recapitulate the enforced safety measures (Wallace & Motarjemi, 2023). By integrating these procedures within ISO 9001:2015 document control guidelines, organizations shall be able to have an efficient and seamless HACCP implementation. They will have a systematic framework to control food safety documentation while striving to improve food safety practices continuously.
Source: safe site
Identification of training needs.
ISO 9001:2015 gives detailed works associated with human resource training to achieve quality management (QMS) operation competence. The organizations should determine the skills required for employees performing operations that affect the final result and effective QMS implementation (Chiarini et al., 2020). Training programs must touch upon these competency aspects, ensuring that employees taking up roles will have the knowledge, skills, and abilities. Worksheets, tests, and trainee records should be preserved to show trainees’ training outcomes and expertise.
To put HACCP into practice and professionally, training should be given thorough priority to the personnel so that everybody knows their role and rightful place in pursuits of food safety. Well-prepared staff know the whole array of food safety principles and methods, how to pinpoint hazardous processes, outline the critical control points (CCPs), and show actions to be taken if things go wrong (Kartano, 2023). It develops vigilance for possible risk factors and brings a practical approach towards risk mitigation activities, improving the food safety culture within the organization.
HACCP implementation training programs must address all the issues related to food safety management, starting with HACCP principles, hazard analysis techniques, CCP checks, and corrective actions. Workers who deal with kitchens and food processing lines are usually instructed in safe sanitation rules, allergen management, and hygiene guidelines. Supervisors and managers may be trained on the process of the HACCP plan development, implementation, and verification while specialized in these. These training programs aim to have them designed to reflect the staff’s specific job roles and responsibilities to acquire the relevant competencies in implementing and maintaining the HACCP system (Disanto et al., 2021). Experimental exercises, case studies, and assessments can be incorporated for reinforcement of learning and demonstration of acquired competency. Moreover, training should be repeated periodically to update employees on fast-changing rules, ordinances, and new hygienic requirements, ensuring the whole system’s longevity.
Traceability.
ISO 9001: 2015 institutions traceability onto the products and materials tracked over the whole supply chain. This means that traceability should include not only procedural activities for identifying and recording products but also batch information about the goods processed, inputs, production dates, and distribution records. Traceability mechanisms facilitate the capability of an organization to follow the products during their journey from the receipt of raw materials to the delivery to the customers. Hence, prompt identification and resolution of quality issues and product recall.
For HACCP and food safety management, traceability is essential when addressing the need to track and manage possible risks of food-borne hazards. Traceability systems encompass the prompt and thorough retrieval of contaminated or unsafe products from the market to prevent the spread of food safety-related hazards (Wilson, 2021). Thus, by tracing products up to their source, organizations can quickly identify the magnitude of a problem, find lot numbers for affected items, and address the problem to prevent future adverse effects on consumers.
Examples of traceability systems that meet both ISO 9001:2015 HACCP plans and GMP require electronic data tracking systems and barcode tracking systems. Thanks to these systems, companies can take and save product information at each step of the production procedure, from the raw material intake to the shipped final product. By integrating traceability data with HACCP documentation, such as hazard analysis reports and CCP monitoring records, organizations can establish a comprehensive traceability system that ensures compliance with both ISO 9001: Current update includes revision of 2015 and HACCP standards (Ijabadeniyi & Olagunju, 2023). Also, RFID (Radio et al.) tags and blockchains are examples of advanced systems for improving traceability with real-time visibility of product movement and keeping the record in the form of an unalterable record. Such integrated traceability systems meet regulatory standards and make proactive risk management more effective and faulty reactions to food safety incidents more efficient.
Calibration.
ISO 9001: According to this item, in 2015, a specific calibration requirement was established to control and ensure the accuracy and reliable measurement and monitoring equipment used in quality control activities. Enterprises must create a calibration of the equipment, which relates to the variability of a product and the quality system. Calibration activities need to be planned at given time sets using certified standards, and notes on calibration are to be kept (Wittler et al., 2021). The objective is to guarantee that measuring devices do not surpass the admissible accuracy parameters, resulting in the trustworthiness of the measurement outcomes and high quality of goods.
Source: Super scientific direct.
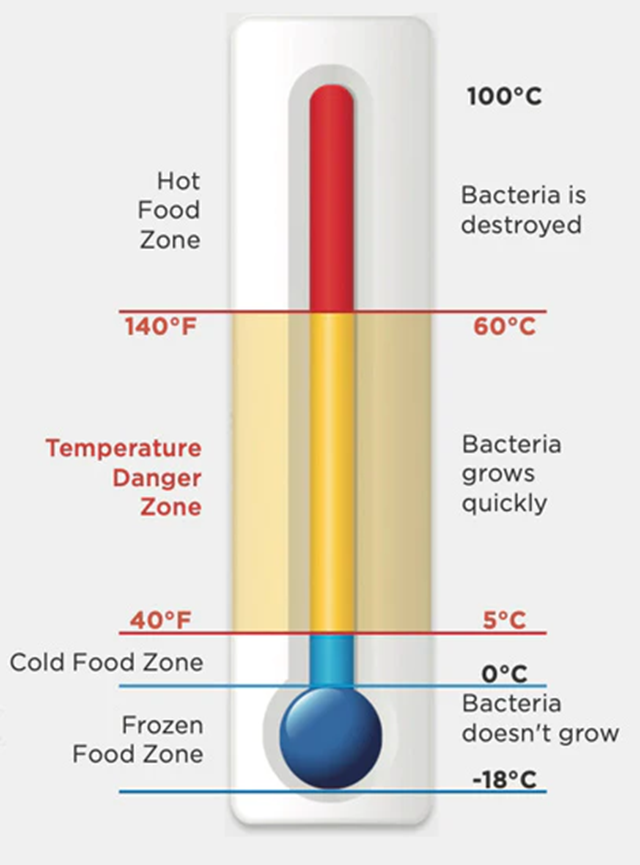
In this context, calibration of the CCP monitoring equipment is cardinal for ensuring the efficacy of HACCP. Therefore, the exact content measurement and monitoring of CCPs like temperature, pH, and pressure are significant for controlling food safety hazards. Calibration ensures that the monitoring devices read correctly before a deviation is detected from a critical limit; thus, preventive actions are likely to follow, reducing the risks of food safety issues. One example is the calibration of thermometers, which check the cooking temperatures and refrigeration units to ensure that food is being cooked or stored at the correct temperatures.
Particular calibration practices applied to HACCP may comprise verification before and after use, calibration against known standards, and adjustments in case of necessity. For instance, pH meters are used for monitoring the acidity levels in food products; calibration of such meters should be done using buffer solutions of known pH values. Incidentally, the thermometers used to check the cooking temperature should also be calibrated for accuracy using a certified standard thermometer. Through calibration practices, HACCP procedures are integrated into the organizations’ processes, which ensures measurement data reliability, the maintenance of food safety standards, and the risk mitigation associated with inaccurate monitoring of critical control points.
Conclusion.
Integrating Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) within a quality management system like ISO 9001: year 2015 is a tool for auditing food safety protocols, which include but are not limited to inspection, monitoring tests, and analysis protocols. Document and data management should be necessary to control all essential documents like Hazard Analysis Reports and CCP Monitoring Records, thus reducing errors and ensuring compliance. Training after identifying training needs means the staff are well aware of their roles in keeping food safe, as the case of Jamie McDonald’s training program shows how the company pays importance to food safety. Traceability, like Nestle’s systems, enables rapid tracing and removal of products at issue in case of contamination. Calibration or Tyson Foods calibration principles guarantee accuracy in status-quo control in critical areas. In the end, HACCP system integration tends to improve document control, training, traceability, and calibration activities, which results in improved food safety management and consumer confidence in food products.
References.
Chen, H., Liu, S., Chen, Y., Chen, C., Yang, H. and Chen, Y. (2019). Food safety management systems based on ISO 22000:2018 hazard analysis methodology compared to ISO 22000:2005. Accreditation and Quality Assurance, 25(1), pp.23–37. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00769-019-01409-
Chiarini, A., Castellani, P., Rossato, C. and Cobelli, N. (2020). Quality management internal auditing in small and medium-sized companies: an exploratory study on factors significantly improving quality performance. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, pp.1–21. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/14783363.2020.1776101
Purwanto, A., Asbari, M. and Santoso, P.B. (2020). Effect of Integrated Management System of ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 22000:2018 Implementation To Packaging Industries Quality Performance at Banten Indonesia. Jurnal Ilmiah MEA (Manajemen, Ekonomi, & Akuntansi), [online] 4(1), pp.17–29. doi: https://doi.org/10.31955/mea.vol4.iss1.pp17-31
Tendero, E.J. (2023). Implementing ISO 9001:2015 in Local Government: Controversies and Options. [online] Social Science Research Network. doi: https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4511285
Wallace, C.A. and Motarjemi, Y. (2023). Chapter 45 – Incident Management and Root Cause Analysis. [online] ScienceDirect. Available at:
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128200131000401
Wilson, S. (2021). The ASQ Certified Food Safety and Quality Auditor Handbook. [online] Google Books. Quality Press. Available at: https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=Igg1EAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=Traceability+systems+encompass+the+prompt+and+thorough+retrieval+of+contaminated+or+other+unsafe+products+from+the+market+to+prevent+the+spread+of+any+food+safety-related+hazards&ots=Nu1HTdAZpD&sig=jP-Rn4mTR8dvT7wXPM89dIyuGFM
Ijabadeniyi, O.A. and Olagunju, O.F. (2023). Food Safety and Toxicology: Present and Future Perspectives. [online] Google Books. Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG. Available at:
https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=EajpEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA243&dq=By+integrating+traceability+data+with+HACCP+documentation
Disanto, C., Celano, G., Dambrosio, A., Quaglia, N.C., Bozzo, G., Tritto, A. and Celano, G.V. (2021). Food safety in collective catering: knowledge, attitudes and correct application of GHP/GMP knowledge among foodservice workers. Italian Journal of Food Safety, 9(4). doi: https://doi.org/10.4081/ijfs.2020.8453
Kalisa, S. (n.d.). The Significance of Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point (HACCP) System to Promotion of Food Safety at Hôtel Des Mille Collines-Kigali -Rwanda. [online] Available at: https://johat.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/5
Kartano, A. (2023). Utilization of HACCP to Find Critical Logistics Control Points in the Restaurant. [online] Available at:
https://www.theseus.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/801690/Johansson_Robert.pdf?sequence=2
Motarjemi, Y. and Warren, B.R. (2023). Chapter 36 – Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point System (HACCP). [online] ScienceDirect. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128200131000176
Sacchetti, S. (2022). Prosocial Organizational Capabilities in the Work-Integration Social Enterprise. VOLUNTAS: International Journal of Voluntary and Nonprofit Organizations. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11266-022-00523-1
Wittler, N., Roy, F., Pack, K., Werninghaus, M., Anurag Saha Roy, Egger, D., Filipp, S., Wilhelm, F.K. and Shai Machnes (2021). Integrated Tool Set for Control, Calibration, and Characterization of Quantum Devices Applied to Superconducting Qubits. Physical review applied, 15(3). doi: https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevapplied.15.034080
 write
write