Sustainability is a crucial aspect of development and growth in modern times, which represents a well-balanced relationship between humans and their environments. It is rooted in finding a balance between environmental, social, and economic sustainability, where all three elements are given equal importance and consideration without disrupting the ability and existence of future generations. Besides preserving the ecosystem and natural resources, sustainability also includes political, ethical, social and economic aspects that influence their use today and in the future (Blowfield, 2013). Such practices are about long-term universal relationships that ensure resources are sustained and passed to future generations.
Major Sustainability Challenges
Sustainability’s most pressing challenges are ecosystem, demographic, and climate change.
- Demographic Changes
Shifts in size and patterns of the population over time as well as wealth and poverty distribution, are some of the demographic changes that significantly impact sustainability. In case of uncertainty, unequal distribution of resources and increased poverty occur, leading to resource depletion and degradation of the environment (Kuhlman & Farrington, 2010).
- Ecosystem
Ecosystem change refers to the variation in Earth’s natural capital over time, affecting Earth’s natural sustainability measures for the survival of future generations.
- Climate Change
Natural variability and human activities may cause changes can cause severe environmental changes making it difficult for natural ecosystems to adapt and survive.
These challenges must be addressed to ensure that the universe can host future generations in a balanced nature that sustainably supports existence. All stakeholders must maintain natural balance in all practices by caring for nature.
Apple Inc. Sustainability Challenges
Apple is a multinational technology company with a strong reputation for innovation, design, and products known for its sleek and user-friendly features. For many years, Apple has faced criticism for making choices that indirectly push consumers to replace their devices instead of repairing or upgrading them. For instance, in 2020, Apple decided to stop including a charger and EarPods with its new iPhone models, a move that sparked controversy among consumers.
This decision was made as the company shifted towards 5G technology, making it more expensive to produce its latest iPhone models. The transition to 5G was crucial in Apple’s search for cost-saving measures, as the components needed for 5G speeds were more costly and complex (Newman, 2022). In recent years, Apple has established itself as a company that prioritizes environmental awareness. It has frequently promoted its initiatives to combat climate change and its commitment to reducing its carbon footprint.
Removing chargers and headphones from Apple’s new iPhone models would increase packaging waste and emissions from separate deliveries. This raised concerns regarding the impact on the carbon footprint of not only Apple but also other companies if consumers purchase these accessories from different vendors. The short-term effects were expected to benefit accessory makers due to the incompatibility between the cable provided with the iPhone 12 and the power blocks of previous models, forcing consumers to purchase new USB-C chargers. On the other hand, the long-term effects of this move on the environment, primarily through the high emission levels, were adverse, raising concerns that resulted in a backlash against apple.
Despite the backlash, Apple continued its plan not to include chargers and EarPods with its new iPhones. Excluding accessories with the new iPhones was an attempt to maintain the phone’s profitability. It was estimated that radio frequency components in the new iPhone 12 would be more costly by more than 30 to 35 per cent compared to earlier models, which translates to a little over 1 per cent increment in the company’s gross profit. (Newman, 2022). The fact that apple was willing to cause huge and long-term climatic and environmental effects for very little was the fueling factor behind the backlash.
How Apple. Inc Are Succeeding in Addressing the Identified Major Sustainability Challenge
Apple has taken strong measures and has been at the forefront of protecting the environment for the future. The company has prioritized reducing its negative climate change impact by utilizing renewable energy sources and increasing the energy efficiency in its products and facilities (Apple’s paper and packaging strategy, 2017). Conservation of precious resources by apple is aimed through more recycling and use of renewable materials. Also, Apple has initiatives for end-of-life product recovery to source functional materials and proper disposal.
The company is also committed to the identification, development and utilization of safer materials in its products and processes. With a goal to shift from a linear model of extraction, use, and disposal to a closed loop, Apple is focused on sourcing recycled materials and returning them to the recycled market, as well as responsible sourcing and regeneration of renewable materials. Apple’s efforts in this area show its dedication to creating not just the best products but the best products for the world.
iPhone 6s to iPhone 7 packaging changes reduced plastic and increased the use of recycled fibre.
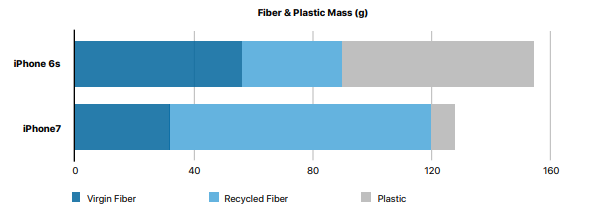
Apple has taken steps to protect the environment by launching a paper and packaging initiative that reduces the use of plastic and increases the use of recycled fiber. This initiative, introduced in 2015, has become a model for positive change, not just within Apple but also beyond. It has prompted the company to rethink its approach to other key materials and explore new ways to create closed-loop supply chains for the finite resources used in its products.
Strategic Recommendations That Apple Inc. Should Implement in The Next Decade
Apple can work towards improving energy efficiency in its operations, such as reducing energy use in its stores, offices, and data centres. The company can also consider implementing energy-efficient technologies, such as LED lighting and energy-efficient HVAC systems. Combating climate change is still a top priority for Apple, and they are taking action to demonstrate their commitment. In order to make its supply chain carbon neutral, Apple should aim to maintain a strong partnership with its suppliers. This can involve working together to reduce carbon emissions through improved energy efficiency, reducing waste, and transitioning to renewable energy sources (Beddewela, 2019). In addition, Apple can help its suppliers to assess their carbon footprint, establish carbon reduction targets, and provide the necessary support and resources. The company may also consider implementing a carbon pricing program or investing in carbon offset projects to reduce its carbon footprint further. By collaborating with its suppliers, Apple can help reduce the environmental impact of its supply chain while also achieving its sustainability objectives. This approach will also enhance Apple’s reputation as a leader in sustainable business practices and earn it positive recognition from its customers, stakeholders, and the wider public.
To achieve the top spot in the market as the most highly regarded brand by consumers, Apple needs to reinforce its distinctive approach to sustainable growth by prioritizing customer service and enhancing the customer experience (Beddewela, 2019). Apple should aim to maximize profits for its stakeholders while also emphasizing customer satisfaction through introducing new products and implementing a product differentiation strategy. This will guarantee long-term sustainable growth for the company.
Redesigning production practices and processes is another strategy that Apple needs to ensure sustainable development. Securing the availability of essential limited resources and reducing excessive waste are also central to Apple’s environmental approach (Spence & Bourlakis, 2009). Therefore, Apple needs to broaden its repair services globally through official retail locations and authorized distributors to make repairs more easily accessible and convenient. It should establish recycling centres to promote trade-in and buyback programs, provide extended software support for its macOS and iOS products, and integrate these services and initiatives into its marketing efforts.
Apple’s refurbishing program represents an additional source of revenue. The company will collect old devices through a sales and after-sales strategy and refurbish them for resale. These refurbished products can generate substantial sales and provide benefits for the environment through reduced waste and consumers through more accessible and affordable access to Apple products. Refurbishing also creates new market and sales opportunities for the company. Not only does this corporate social responsibility initiative help safeguard and preserve the environment, but it can also give the company a competitive edge, making it a crucial component of its business strategy. A strong emphasis on sustainability will enable the company to effectively overcome and tackle current and future environmental challenges.
It should be noted that the implementation of the initiatives and strategies discussed above comes with financial costs. Adherents of the conventional approach to corporate social responsibility contend that businesses should concentrate exclusively on profit-driven strategies (Maignan et al., 2005). Nonetheless, for Apple and other companies that have established and executed their sustainability strategies, investing in environmentally-friendly innovation can yield positive outcomes, particularly when aligned with the organization’s mid-term to long-term mission and vision.
In conclusion, it is recommended that Apple prioritize and reinforce its sustainability strategy. This includes expanding repair services, enhancing product security and availability, implementing a refurbishing program, and integrating sustainability initiatives into its marketing efforts. These initiatives align with the company’s commitment to environmental protection and provide a competitive advantage and new market opportunities. Although these efforts may be associated with costs, the long-term benefits to both the company and the environment make it a worthwhile investment. It is recommended that Apple continue to lead by example in its approach to sustainability, demonstrating its dedication to both financial success and social responsibility.
References
Apple. (2022, October 25). Apple calls on the global supply chain to decarbonize by 2030. Apple. https://www.apple.com/newsroom/2022/10/apple-calls-on-global-supply-chain-to-decarbonize-by-2030/
Apple’s paper and packaging strategy. (2017). Apple.com. https://www.apple.com/environment/pdf/Packaging_and_Forestry_September_2017.pdf
Beddewela, E. (2019). Managing corporate community responsibility in multinational corporations: Resolving institutional duality. Long Range Planning, 52(6), 101911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lrp.2019.101911
Blowfield, M. (2013). Business and Sustainability. Oxford University Press.
Calma, J. (2020, October 16). Apple ditching chargers saves costs but not the planet. The Verge. https://www.theverge.com/2020/10/16/21519466/apple-iphone-12-chargers-airpods-greenhouse-gas-emissions-e-waste
Inside. (2021, March 16). Apple’s charger decision – good or bad for the environment? Inside.com. https://features.inside.com/apple-chargers-iphone-carbon-emissions-ewaste/
Kuhlman, J. W., & Farrington, J. (2010). What is sustainability? Sustainability (Vol. 2).
Maignan, I., Ferrell, O. C., & Ferrell, L. (2005). A stakeholder model for implementing social responsibility in marketing. European Journal of Marketing, 39(9/10), 956–977. https://doi.org/10.1108/03090560510610662
Newman, L. (2022, October 2). Apple isn’t as green as it pretends to be: Here’s why. MUO. https://www.makeuseof.com/apple-isnt-as-green-as-it-pretends-to-be/
Pineda, M. E. (2021, June 15). Environmental strategy of Apple: Key sustainability initiatives. Profolus. https://www.profolus.com/topics/environmental-strategy-of-apple-key-sustainability-initiatives/
Spence, L., & Bourlakis, M. (2009). The evolution from corporate social responsibility to supply chain responsibility: The case of Waitrose. Supply Chain Management. An International Journal, 14(4), 291–302.
 write
write