Executive summary
The study is set to determine the impact of social media on Louis Vuitton’s growth in the British market. People share photos, videos, and information with friends, families, business stakeholders, or desired audiences based on the content shared through social media, proving a powerful tool used in business to convey marketing information. Businesses can advertise their products and services through social media platforms, including Facebook, X, LinkedIn, Telegram, Instagram, TikTok, and WhatsApp channels, which are some of the most used platforms across the globe and can be used to access the international audience. Therefore, the study surveyed 50 participants and employed a multiple-liner regression to determine if social media marketing, customer attraction, and brand power could be used to determine sales. The result proved a positive relationship, hence the need for businesses to embrace social media marketing.
Introduction
The technological advancement that has led to the growth of social media has greatly impacted the marketing industry of all businesses, making a remarkable change in the number of sales (Rana et al., 2020). Today, visiting social media platforms at various times of the day has become a routine and part of life that has attracted over 3.6 billion people across the globe, making it a vital forum in business (De-Roe, 2021). Communication, which is the basis of social media platforms, is also regarded as a great pillar in business (Quesenberry, 2020). The advertising process through social media commences by creating the content to be shared, which should be done with great consideration of the target audience; the content is then shared digitally and facilitated to reach many through promotion. The running advert is then digitally assessed to analyze its performance, which helps improve the results and make the digital marketing strategy effective. Therefore, businesses that aim to increase their production through increased demand for their products and services can never assume the relevance of social media marketing to enjoy its full list of benefits.
Company Background
Louise Vuitton (LV) Company is not an exception for a company that enjoys the benefits since it has strongly embraced the implementation of social media and utilized the opportunity to transform its sales and production margins (Gan, 2022). Louise Vuitton has embraced offering their target audience the ability to have a visual experience of their range of products and create brand awareness to social media users on platforms such as X, Instagram, and Twitter (Grilec, 2020). Louise Vuitton has invested in the digital space to build on the brand’s success in offering fashion and cosmetic commodities making them a dominant player in the digital space through compelling content that engages customers and attracts new target customers. LV, which operates in the luxury goods market, understands the significance of using digital channels to dominate the global market, especially in the British Market (Wu, 2023). The British luxury market is projected to generate approximately $17.20 billion in the year 2024, with an anticipated annual growth rate of 4.005% for the following four years. Luxury fashion is reported to be the largest portion contributing to the success of luxury goods performance in Britain,n with an estimated market volume of $7.34 billion this year (Statista, 2024). Despite global economic challenges, the luxury goods market in Britain has been reported to be booming; and young adults have gained more interest in luxury goods. LouisAmong luxury brands’ products, such as rare Birkin bags, Swiss watches, and 81-year-old whiskies, Louis Vuitton trainers, are among the top goods that have recorded the highest growth in the British market (The Guardian, 2022).
Therefore, the study is set forth to determine social media’s impact on LV’s growth in the British Market by examining the effects on sales, corporate standing, public image, and brand power in the luxury goods market. Based on the literature reviewed by Alar et al. (2023), Bekar and Tümer (2016), Xiao (2023, September 26), and Godey et al. (2016), this study aims to understand the various ways in which social media has influenced LV’s growth trajectory in the British market.
Objectives
The outlined are the primary objectives of the study which define the accomplishments that need to be attained by the end of the study. The objectives used in this study will be employed to guide the methodology and formulate the desired questionnaire used to collect relevant study data. The three research objectives include;
- Find out how many sales LV had due to social media involvement.
- Analyze how social media influences brand power and client attraction in a roundabout way.
- Analyze how LV’s social media marketing affected customers’ opinions and purchases.
Research Questions:
The outlined research questions are based on the previously detailed objectives and will help define the investigation to determine the impact of LV growth in the British market. The research questions based on the research help set clear study boundaries to ensure that only essential entities are considered in the analyses and to remain within the scope of the study. The research questions are;
- What is the effect of LV’s social media UK marketing on the company’s bottom line?
- By strengthening the brand’s reach and drawing in new consumers in the UK, how does social media impact LV’s bottom line in the UK market?
- How do young consumers from the UK view LV’s social media marketing, and how do they impact their purchasing habits?
- Which social media sites do members of the target audience use most often to find out about LV in the UK market?
Rationale
Researching how social media affected LV’s expansion in the UK market is important since digital platforms have the potential to revolutionize the way luxury brands interact with their customers and the methods they employ (Appel et al., 2020). To thrive in today’s tech-driven market, luxury firms must master the art of social media marketing and how it affects sales, customer perceptions, and brand image (Vinerean & Opreana, 2019). The study investigates how the complex interplay between traditional luxury marketing tactics and the ever-changing world of social media impacts LV’s bottom line, customer engagement, and brand loyalty. Godey et al. (2016) and Xiao (2023) have shown that social media is increasingly important for promoting high-end cosmetics and apparel. According to their research, the fiercely competitive luxury goods market is particularly vulnerable to the influence of social media on consumer behaviour and brand equity.
Significant of the Study
Understanding how social media affects luxury businesses like LV is vital in a market where digital platforms increasingly influence consumer behaviour and buying decisions (Athwal et al., 2019). The problem is interesting because it examines how social media affects customer brand perception and purchasing decisions in our interconnected society (Park et al., 2020). Moreover, the study is essential for the LV Company to make necessary adjustments based on the study findings.
Literature Review
The analysis of social media advertisement history and development to enhance its effective application can be traced back to 2005 when the first advisement appeared on Facebook. A remarkable adaptation of social media gained significant momentum in 2006 when LinkedIn also reported its first advert as Facebook was entering the mobile space. Analyzing various metrics of how social media has enhanced success for different organizations across industries and sectors is essential for the research to ensure that gaps, trends, opportunities, threats, and strategies are identified for the purpose of application in the luxury goods industry. Therefore, the literature review will commence with the definition of luxury brands and then delve into a study that analyzes the impact of social network marketing on luxurious goods. The study will offer the need to address consumer behaviour and brand equity which will help shed light on consumer engagement.
Definition
Luxury brands were traditionally mistaken for the meaning of offering satisfaction and pleasure to customers owning luxurious products. However, the definition of luxurious goods has transformed and well-understood goods that enhance civilization among customers as it relates to cultural and societal influence. The adaptation of luxurious goods’ positive definition among other factors has led to its growth where it has reported about a 10% annual increase which is above the annual world economy growth rate. Marketing luxurious brands has been linked to its success hence the need to conduct a review on the most effective marketing strategy for these goods.
According to research by MajlesiRad & Haji pour Shoushtari (2020), it was established that digital marketing through social media is the most effective marketing strategy and influences the number of sales and brand identity for luxurious goods. One of the core findings of the roles played by social media sites in marketing luxurious goods is the establishment of effective communication relationships with customers. Therefore, the study was conducted in three various districts in the North of Tehran region where the inhabitants are considered to belong to classes A and B and have much disposable income creating a higher demand for luxurious goods. The study utilized a survey descriptive as a data collection technique which validated the principal component analysis through exploratory factor analysis. The survey aimed to study the tendency to purchase luxury brands of the inhabitants of the well-chosen demographic participants who are proven to prefer luxury products. The collected data was analyzed using the Spearman correlation test and equation modelling technique. Therefore, based on the methodology employed various findings were outlined from the study.
One of the significant findings based on luxurious goods marketing is that the emergence of the Internet has facilitated word-of-mouth marketing. Word-of-mouth marketing is regarded as one of the most ancient marketing strategies across all sectors where consumers exchange information about a product or service based on experience or exposure hence influencing consumer attitude and behavior towards the commodity. The emergence of social interaction sites where people can actively engage in social issues provided a space where word-of-mouth could be facilitated hence the development of online word-of-mouth or electronic word-of-mouth. The active human interaction experienced in social media sites enhances electronic word-of-mouth which leads to the creation of brand value based on the fact that consumers are always interested in hearing from other’s experience on a brand product. Word of mouth in social media marketing has proved to be higher in creditability and relevance by spreading information about the brand to friends and family. Companies can also interact with their customers through the social site through electronic word-of-mouth hence an essential element of a promotion mix. The promotion mix offered by electronic word-of-mouth is essential in facilitating all the phases of purchase for the need of recognition of post-purchase consumer behaviour as shown in Figure 1. Therefore, it is essential to consider previous research on consumer behaviour.
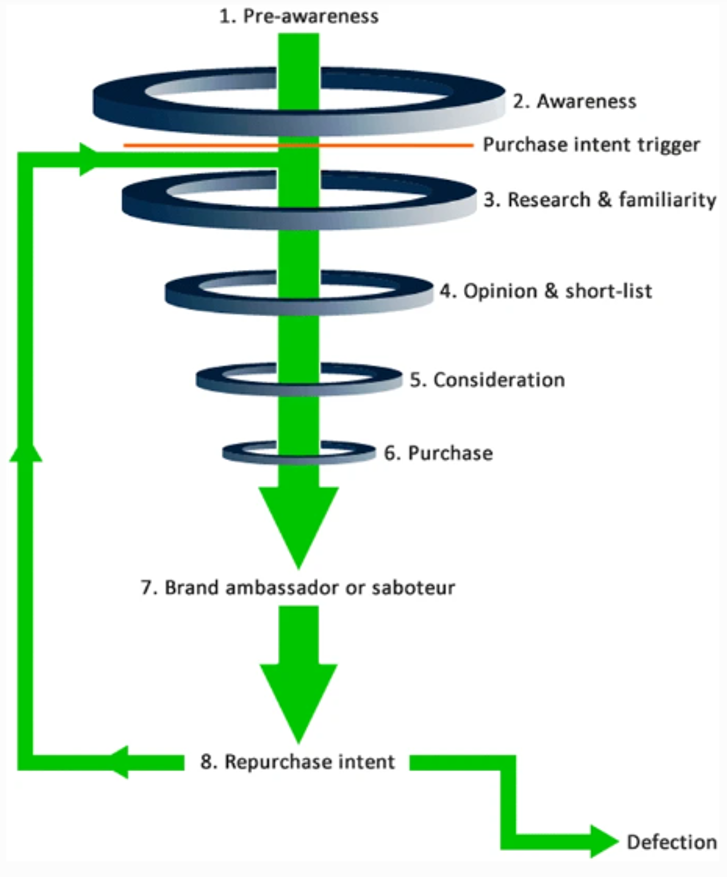
Figure 1. Phases of purchase facilitated by social media marketing.
Consumer Behavior and Brand Equity
According to the study by Godey et al. (2016) on the study of how social media influences consumer behaviour and brand equity by investigating various brands that have dominated the luxurious market, such as LV, Gucci, Christian Dior, Hermes, and Burberry. The study involved a total of 845 participants from four different countries who filled out the survey that was set to identify the consequences of various social media marketing efforts. The studied consequences include customer loyalty, price premium, and brand preference, while the studied efforts include customization, word of mouth, interaction, entertainment, and trendiness.
Entertainment as a marketing effort is a vital component that must be well-addressed. Users go to social media platforms in search of pleasure and enjoyment; hence, adverts through social media should be geared to deliver the same purpose to remain relevant in the social media space (Graciyal & Viswam, 2021). Effective use of social media will also help align with consumer behaviour theories, such as prospect theory, which suggests that consumers make decisions based on risk assessments; hence, the social media advertisement should provide some sense of satisfaction through entertainment (Day et al., 2020). Social media is also a space for interaction where people communicate hence, and it is relevant for businesses to consider the need to maintain constant and effective communication with their clients. The company that desires to use social media for marketing must also design a team of customer care service to assist customers in navigating various challenges in accessing goods and services. The study also highlights the need for trendiness effort, which is described as cover surveillance to remain updated on information about the social environment, knowledge on the products, pre-purchase information to familiarize with the product, and inspiration, which includes following updates on a product. The client uses the four criteria to determine the product on-trend through social media and decides whether or not to make a purchase. Customization is another social media marketing effort that can be used to create success in marketing (Oscarius Yudhi Ari Wijaya et al., 2021). Companies such as Gucci have used the customization opportunity to send personalized messages to clients, which can help customize personalized goods based on the client’s preferred design hence increasing consumer engagement with a particular brand. Therefore, it is essential to also navigate through previous research to identify the effects of consumer brand engagement through social media.
Consumer Brand Engagement
According to the research on consumer brand engagement in luxury goods by Febrian & Ahluwalia (2021), consumer brand identification and self-expressiveness have a positive impact on the three dimensions of brand engagement utilized in the study. The study focused on cognitive, emotional and behavioural factors as the dimensions of studying consumer brand engagement. However, three various variables including brand identification, self-expressiveness, and consumer involvement were used to analyze their effect on the three dimensions of consumer engagement. Consumer involvement is defined in the study as a measure of the success of social media marketing given that luxury goods consumers need to express themselves in a social space. Therefore, the data collection technique used in the study involved 125 questionnaire respondent who filled out the online survey on their experience of purchasing luxurious goods. Structural equation modeling SmartPls was employed to conduct an empirical study on the collected data hence the analyzed data yielded various findings on the relationship of the three variables to consumer engagement. The findings included a negative impact yielded by consumer involvement while consumer brand identification and self-expressiveness yielded a positive impact on consumer engagement based on the three dimensions of the study; cognitive, emotional, and behavioural aspects of the consumers. Moreover, the study also noted that social media was essential in increasing brand image and loyalty by leveraging the opportunity within the cognitive, emotional, and behavioural aspects of the consumers.
Methodology
The various data collection tools and analysis strategies employed in the study were essential to ensure that the findings and discussion were accurate, precise, and relevant for making valid conclusions and recommendations. The chapter discusses the data collection tools, sampling strategy, research design, and data analysis techniques used to quantify the study’s objectives.
Data Collection Procedure
Using a carefully designed structured questionnaire to gather data across UK residences constituted the study’s only quantitative analysis method. The study used a quantitative method to attain an objective measurement which would allow precise quantification of study variables in numeric, hence the ease of generalizability of findings and efficiency (Mohajan, 2020). The research also used the quantitative research method, which targeted 250 respondents, but due to challenges in accessing the respondents, it was scaled down to 50. The current literature on the effect of social media on the market for high-end items was reviewed in depth before designing the questionnaire. The questionnaire had three main sections, each aiming to solve a research objective. The first section involved questions that helped determine the number of sales made by LV; the second section was based on the influences of social media on brand power and client attraction; while the third section determines how LV’s social media marketing affected customers’ opinions and purchases.
Sampling Strategy
To get a wide range of opinions, this study involved 50 respondents through a survey process to answer the formulated questionnaire. The 50 respondents were selected using a stratified random sampling technique, which was essential to involve respondents from varying ages, genders, preferences, and income levels across different locations (Bhardwaj, 2019).
Data Analysis Technique
The linear Regression Model was used to explore the association between parameters
Sales = β0 + β1Social Media Involvement + β2Brand Power + β3*Customer Attraction + ε
Where,
- Sales represent the dependent variable.
- Social Media Involvement, Brand Power, and Customer Attraction are independent variables.
- β0 represents the intercept.
- β1, β2, and β3 are the coefficients
- ε represents the error term.
The independent variables, Social Media Involvement, Brand Power, and Customer Attraction, were assigned the coefficients β1, β2, and β3, respectively.
An SPSS and Excel statistical software tool was used for data analysis to conduct the regression analysis to help conduct an accurate and timely test, providing information for analysis. The tools were also necessary to generate a graphical presentation of the findings to help give detailed information on the result (Mishra & Alok, 2022).
Results and Analysis
Descriptive Analysis
Among the 50 respondents, only one had never purchased Louis Vuitton products, suggesting that a significant number have purchased one at some point in their lives, which makes the data collected relevant for the study. All the respondents who had bought LV products before confessed to having recommended the product to a friend and marked the LV products as Superior.
The survey result showed that out of the 50 participants that took part in the study, the majority were male, with a count of 27, with a proportion of 54% and 23 women accounting for 46%, as shown in Figure 2. The gender difference or proportion does not influence the analysis, for there was no significant difference.
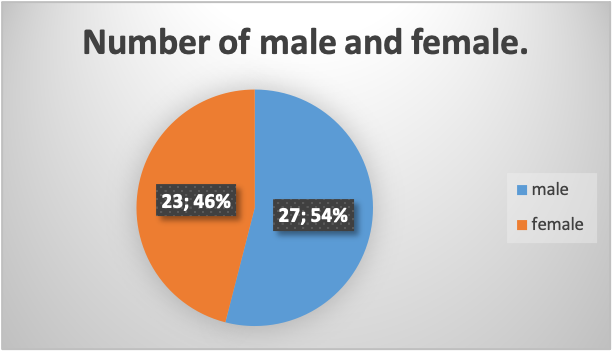
Figure 2. Graph showing the proportion of males and women in the survey.
The participants represented Different age groups, with the majority being 18-25 years, accounting for 44% of the total respondents’ population, followed by 35-50 years, as shown in Figure 3. The distribution of ages also was evenly spread, suggesting that it could have no or minimal effect on the analysis of the study.
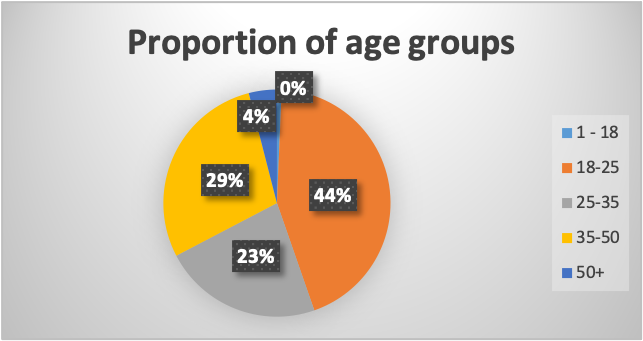
Figure 3. A pie chart showing the proportion of respondents based on age group.
The annual household income of the participants slightly differed as the majority of the participants earned between £ 50,000 – £ 75, 000 accounting for 17 participants. The subsequent group with a higher frequency was the £ 25,000 – £ 50, 000 which had 13 individuals while 5 participants earned more than £ 100,000 yearly. Only 1 participant earned less than £ 10,000 while 8 participants earned between £ 10,000 – £ 25, 000 as shown in Figure 4. The witnessed distribution signifies that the majority have an average or above-average income. Significant annual income is essential for determining the amount of disposable income which can be used to purchase luxurious products.
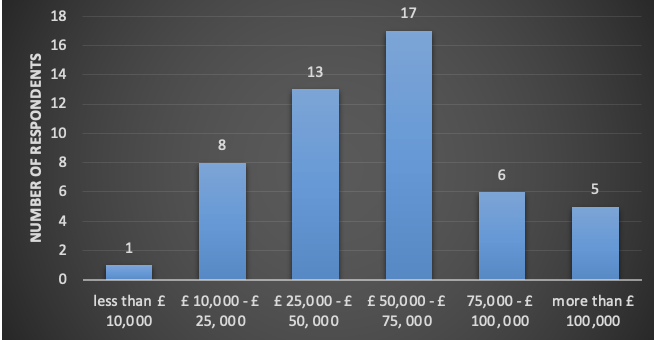
Figure 4. A bar graph showing the distribution of annual household income of the participants.
According to the survey, it was evident that among the participants, there was no significant difference in the most desired social media platform. However, Facebook had a slightly higher preference, followed closely by TikTok, then Instagram and X followed, as shown in Figure 5. Despite LinkedIn’s slightly lower number, the bar graph suggests that all the listed social media platforms were relevant for marketing.
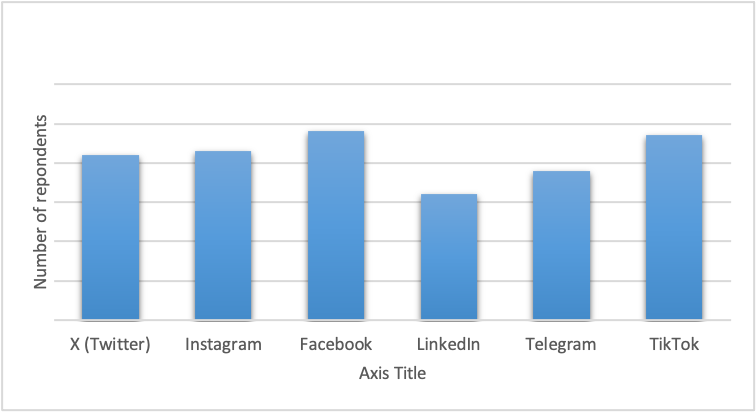
Figure 5. A bar graph comparing participant’s most desired social media platforms.
The determination of how social media influences brand power and client attraction also showed that various aspects of LV’s social media content had almost the same extent of attraction. Customer review and visual appeal scored higher in both 12 preferences each, suggesting that the two proved to be more effective methods to capitalize in social media advertisements as shown in Figure 6. The high scores in customer reviews and visual appeal, which are features of social media marketing, prove that the company should consider capitalizing on social media opportunities while marketing the brand. Exclusive offers were the least, with only seven preferences, which suggested that LV’s clients were not focused on offers, for they could comfortably afford the products. However, the limitation to the result in this category might have been slightly influenced by the majority of young respondents.
>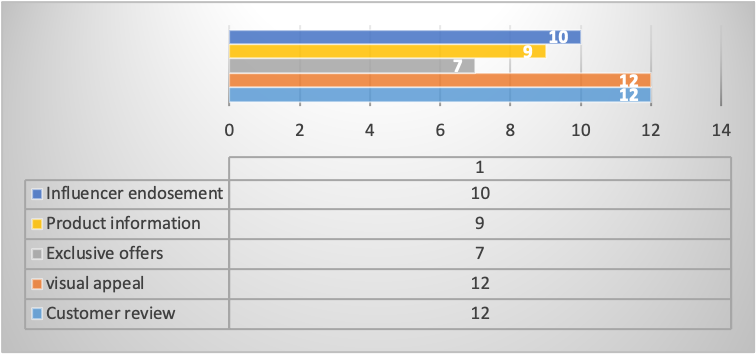
Figure 6. LV’s client attraction marketing option.
Regression Analysis
The regression analysis was based on finding the relationship between the three independent variables, which include; (social media involvement, brand power, and customer attraction); and the dependable variable sales. The linear regression model for the study was;
Sales = β0 + β1Social Media Involvement + β2Brand Power + β3*Customer Attraction + ε
Based on the findings from analyzing the data from the 50 respondents, it was established that there is a strong positive correlation between the independent and dependent variables justified by the 0.97 score of multiple R. The relationship suggests that social media advertisement positively affects the amount of sales. The Adjusted R Square of the study also scored high at 94%, suggesting a better fit of the regression model to the data, which was also supported by a low standard error value. The ANOVA assessment shows a higher F-statistics score and a lower p-value, suggesting strong evidence against the null hypothesis, as shown in Figure 7.
Therefore, the linear regression model based on the study is;
Sales = -0.213 + 0.381*Social Media Involvement + 0.333*Brand Power + 0.396*Customer Attraction + ε
The intercept at -0.213 represents the expected sales when all other independent variables are at zero. However, the intercept, which is less than (p-value>0.05), shows that it is not statistically significant.
All the independent variables had positive coefficients, suggesting that higher levels of the variables translate to higher sales. Therefore, LV should consider embracing social media marketing for higher sales.
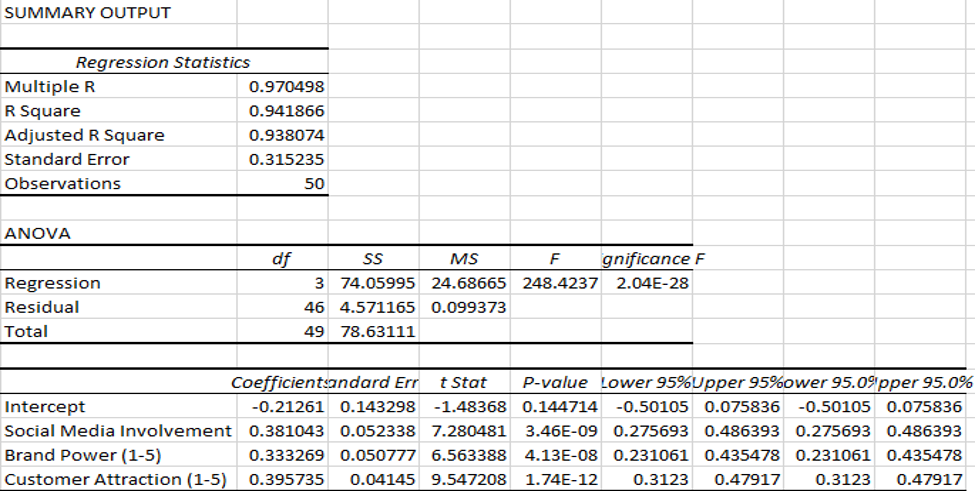
Figure 7. Figure of multiple regression analysis result.
Therefore, the effect of LV’s social media UK marketing has proved to be enhanced with the ability to offer clients the opportunity to review products and the appealing nature of the products ‘ visuals as they are presented on the social media platform. Social media enhances and strengthens the brand’s reach and draws in new consumers in the British market by making the products easily accessible for clients in remote areas without stores through digital purchases and technical assistance, hence quick product deliveries (Silvia, 2019). The young consumers, who constitute the majority of the respondents in the research, have a positive perception towards social media and are active users of the platform; hence, they have been motivated by the advert, ts making them develop the urge to make purchases and recommend the products to friends. Facebook and TikTok were the most used social media platforms preferred by the respondents, hence the need for the company to capitalize on them. Instagram and X (Twitter) also recorded a significantly higher number of users, which can never be assumed when choosing the social media platform for marketing.
Conclusion
The paper has focused on the importance of social media marketing of luxurious goods and specifically analyzed the Louise Vuitton Company’s growth in British. Based on previous studies, the literature reviews first showed that social media is effective in increasing brand sales and has been confirmed by the analysis, which has proved the same with a strong positive relationship. Social media marketing is also essential in enhancing other variables like customer attraction and brand power that increase sales. For instance, a one-unit increase in brand power is associated with a 0.333 increase in sales, while a one-unit increase in customer attraction is associated with a 0.396 increase in sales, hence proving to be vital aspects that need to be considered. One of the factors that needs to be considered in social media marketing for its effective operation is enhanced customer engagement. Therefore, future research should consider investigating the challenges faced in marketing using social media platforms and how LV and other companies in Britain and other parts of the world can navigate through the challenges.
References
Alar Kolk, By, & Kolk, A. (2023, March 19). Louis Vuitton: Mastering the art of luxury brand marketing. EpiProdux Blog. https://epiprodux.com/blog/louis-vuitton-mastering-the-art-of-luxury-brand-marketing/
Appel, G., Grewal, L., Hadi, R., & Stephen, A. T. (2020). The future of social media in marketing. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 48(1), 79-95.
Athwal, N., Istanbulluoglu, D., & McCormack, S. E. (2019). The allure of luxury brands’ social media activities: a uses and gratifications perspective. Information Technology & People, 32(3), 603-626.
Bekar, G., &Tümer, M. (2016, January 1). Impacts of luxury fashion brand’s social media marketing on purchase intention in Turkey: A comparative study on Louis Vuitton and Chanel. DSpace Home. http://i-rep.emu.edu.tr:8080/jspui/handle/11129/4556
Bhardwaj, P. (2019). Types of sampling in research. Journal of Primary Care Specialties, 5(3), 157-163.
Cheung, M. L., Pires, G. D., & Rosenberger III, P. J. (2019). Developing a conceptual model for examining social media marketing effects on brand awareness and brand image. International Journal of Economics and Business Research, 17(3), 243-261.
Day, S., Godsell, J., Masi, D., & Zhang, W. (2020). Predicting consumer adoption of branded subscription services: A prospect theory perspective. Business Strategy and the Environment, 29(3), 1310-1330.
Derakhshan, A., & Beigy, H. (2019). Sentiment analysis on stock social media for stock price movement prediction. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 85, 569-578.
De-Roe, S. (2021) How Capitalism Has Caused the Western World to Re-Define the Snapshot Introduction With over 3.6 billion users on social networking sites (Statista, 2021), it seems natural that uploading the snapshot1 into cyberspace is par for the course, one of millions entering a digital.
Di Domenico, G., Sit, J., Ishizaka, A., & Nunan, D. (2021). Fake news, social media and marketing: A systematic review. Journal of Business Research, 124, 329-341.
Febrian, A., & Ahluwalia, L. (2021). Investigating The Antecedents of Consumer Brand Engagement to Luxury Brands on Social Media. Indonesian Journal of Business and Entrepreneurship (IJBE), 7(3), 245-245.
Furui, Y. (2021). Analysis of Marketing Strategy of Luxury Brand under the Context of New Media: Taking Gucci as An Example. J. Econ. Bus. Manag., 9.
Gan, Y. (2022). Luxury Marketing in the Age of Network Traffic: Taking Louis Vuitton as an Example. Frontiers in Business, Economics and Management, 5(2), 18–21.
Godey, B., Manthiou, A., Pederzoli, D., Rokka, J., Aiello, G., Donvito, R., & Singh, R. (2016). Social media marketing efforts of luxury brands: Influence on Brand Equity and consumer behaviour. Journal of Business Research, 69(12), 5833–5841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.04.181
Graciyal, D. G., & Viswam, D. (2021). Social media and emotional well-being: the pursuit of happiness or pleasure. Asia Pacific Media Educator, 31(1), 99-115.
Grilec, A., Vukusic, D., & Dujic, D. (2020). Communication strategies of luxury brands during the COVID-19 crisis. Economic and Social Development: Book of Proceedings, 281-290.
Jia, W., & Ran, H. (2021, December). The Analysis of Brand Co-Branding Strategy. In 2021 3rd International Conference on Economic Management and Cultural Industry (ICEMCI 2021) (pp. 1567-1574). Atlantis Press.
Macarthy, A. (2021). 500 social media marketing tips: essential advice, hints and strategy for business: Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest, Google+, YouTube, Instagram, LinkedIn, and more.
MajlesiRad, Z., & Haji pour Shoushtari, A. H. (2020). Analysis of the impact of social network sites and eWOM marketing, considering the reinforcing dimensions of the concept of luxury, on the tendency toward luxury brands. Future Business Journal, 6(1), 1-19.
Mishra, S. B., & Alok, S. (2022). Handbook of research methodology.
Mohajan, H. K. (2020). Quantitative research: A successful investigation in natural and social sciences. Journal of Economic Development, Environment and People, 9(4), 50-79.
Mohr, I. (2013). The impact of social media on the fashion industry. Journal of applied business and economics, 15(2), 17–22.
Momot, R., Belavina, E., & Girotra, K. (2020). The use and value of social information in the selective selling of exclusive products. Management Science, 66(6), 2610-2627.
Oscarius Yudhi Ari Wijaya, A. P., Sulistiyani, S., Pudjowati, J., Kartikawati, T. S., Kurniasih, N., & Purwanto, A. (2021). The role of social media marketing, entertainment, customization, trendiness, interaction and word-of-mouth on purchase intention: An empirical study from Indonesian smartphone consumption. International Journal of Data and Network Science, 5(3), 231-238.
Park, M., Im, H., & Kim, H. Y. (2020). “You are too friendly!” The negative effects of social media marketing on value perceptions of luxury fashion brands. Journal of Business Research, 117, 529-542.
Quesenberry, K. A. (2020). Social media strategy: Marketing, advertising, and public relations in the consumer revolution. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers.
Rana, N. P., Slade, E. L., Sahu, G. P., Kizgin, H., Singh, N., Dey, B., … & Dwivedi, Y. K. (2020). Digital and social media marketing. Springer.
Shin, D., & Darpy, D. (2020). Rating, review and reputation: how to unlock the hidden value of luxury consumers from digital commerce? Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 35(10), 1553-1561.
Silvia, S. (2019). The importance of social media and digital marketing to attract millennials’ behaviour as a consumer. Marketing, 4(2), 7-10.
Statista. (2024). Luxury Goods – United Kingdom: Statista market forecast. https://www.statista.com/outlook/cmo/luxury-goods/united-kingdom#:~:text=The%20United%20Kingdom’s%20Luxury%20Goods, US%247.39bn%20in%202024.
The Guardian. (2022, November). Luxury goods boom in Britain as super-rich youngsters buck the recession. https://www.theguardian.com/business/2022/nov/20/luxury-goods-boom-in-britain-as-the-young-rich-and-mortgage-free-buck-the-recession
Tuten, T. L. (2023). Social media marketing. Sage Publications Limited.
Vinerean, S., & Opreana, A. (2019). Social media marketing efforts of luxury brands on Instagram. Expert Journal of Marketing, 7(2).
Wu, X. (2023). Louis Vuitton’s Strategies for Enhancing Customers’ Engagement on Instagram and Weibo. Media and Intercultural Communication: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 1(2), 61–73.
Xiao, J. (2023, September 26). The Role of Social Media in Purchasing Luxury Goods – Taking Louis Vuitton as an Example. Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Economic Development and Business Culture (ICEDBC 2023) | Atlantis Press. https://www.atlantis-press.com/proceedings/icedbc-23
 write
write