Introduction
Human resources are the number one asset of any organization. From this perspective, human resource management is critical to the operation and success of organizations. Human resource management involves concepts such as recruitment and selection of employees. This process also involves learning and development as well as performance management. In addition, HRM also involves compensation and benefits to the employees. H.R. data and analytics, as well as Human Resource Information Systems, are the foundations of effective HRM.
All these functions are essential in obtaining and retaining the best talent and building an organization’s human resources. All these aspects create collaboration and engagement, thereby developing strategic human resource management where employees feel engaged and valued and more motivated to participate in an organization’s operations.
In this process, the Strategic Human Resource Management theory presents critical decisions about human resource practices. Integrating employees’ skills and different abilities create the best human capital. Therefore, organizations should make vital decisions with the help of this theory, which promotes effective human resource management and supports better organizational performance (Anwar, G. 2021, 5).
While engaging in practices such as compensation and benefits, learning and development, as well as recruitment and selection, employees should be at the heart of this process. This is because such practices and decisions affect them. As a result, making decisions and promoting practices that are in their best interest go hand in hand with improving the overall performance of organizations.
Analysis of the significance of Strategic Human Resources Management (SHRM)
The primary objective of the SHRM is to ensure that employees’ different abilities and talents are utilized effectively. This process is carried out by identifying the employees’ development needs and responding by providing resources and training to help the employees improve. The intention and goals of the SHRM are to develop programs and policies that align with the company’s business strategy.
Therefore, SHRM is essential as it helps companies achieve their goals and improve the overall performance of the employees. Employees can improve their performance when provided with a conducive working environment. SHRM delivers just that. By having such an environment, employees can improve their productivity. In addition, SHRM enables businesses to save revenue by enhancing productivity and reducing turnover. This process is done by creating compensation and benefits programs that attract and retain existing talent.
As indicated earlier, human resources are the number one asset in any organization. Therefore effective management is vital to such an asset. The function of HRM is to recruit the best talent that the organization needs. In addition, HRM provides also provides a platform for hiring and training these talents (Budhwar, P. 2018, 486).
Consistently, HRM also supports the employees to help them improve their performance and reach their full potential to help the organization achieve its goals and objectives. When an organization achieves its goals and objectives, sit grows even to the next level. In the same spirit, developing the best talent translates into having the bests skills and abilities in employees. An organization with highly skilled and experienced employees develops a competitive advantage over other companies, staying ahead of the competition.
Providing support to the employees involves compensation, benefits, and training and development. When the employees are noticed and recognized by their department for a job well done, they are likelier to perform even better next time. Consistently, this approach has a ripple effect as other employees are more likely to strive to achieve better to get the same recognition and rewards as their colleagues. This way, the organization is expected to improve its performance and output, thereby increasing its profitability.
Extensively, staffing enables organizations to onboard the best employees for different responsibilities. From this perspective, the scope of staffing pays more attention to recruitment, training, and even development of employees within an organization. Like any other organization, Etisalat undergoes the same process (Christopher, N. 2018, 30).
In this regard, the company has the most competitive recruitment process. This is because its recruits and looks for the best talent. Subsequently, the company gets and trains these talents and helps them to achieve their goals and objectives. As a result, the company has improved its performance, thereby attaining its strategic objectives. This performance has also promoted essential stakeholder satisfaction, which is even better for the company.
However, the company’s compensation activities for HRM have had issues before. This is because some of the rewarded employees could have been more deserving. Therefore, HRM should develop a legally binding policy and promote organizational compliance. Legal compliance in such an aspect is vital as it helps the HRM identify and reward the most deserving employee. This is a gap that needs to be filled. The best way to fill the gaps is to develop a policy and a system that scores the employees’ work. The one with the best scores deserves recognition and a reward.
The abovementioned HRM activities, compensation, benefits, learning, and development, among others, help the employees achieve their goals and objectives, including those of the organization.
Over the years, the perception of SHRM has changed to one that aligns the organization with its values, vision, and mission and with the various business objectives and strategies. The emphasis on SHRM is being a strategic and dependable business partner. Additionally, it reflects on utilizing human resources and flexible arrangements to achieve organizational goals. It affects current H.R. issues such as performance appraisal, compensation, benefits, and recruitment and selection. In addition, the SHRM is perceived to emphasize organizational performance, which affects modern HRM, which mainly focuses on individual performance.
Impact of HRM Activities on organizational performance
Practical HRM activities go a long way in improving organizational performance. As indicated earlier, HRM activities and practices include compensation, benefits, and learning and development, among other aspects. These elements are critical to the motivation and satisfaction of employees. For that reason, effective management of such activities greatly influences employee satisfaction and motivation, significantly contributing to organizational performance.
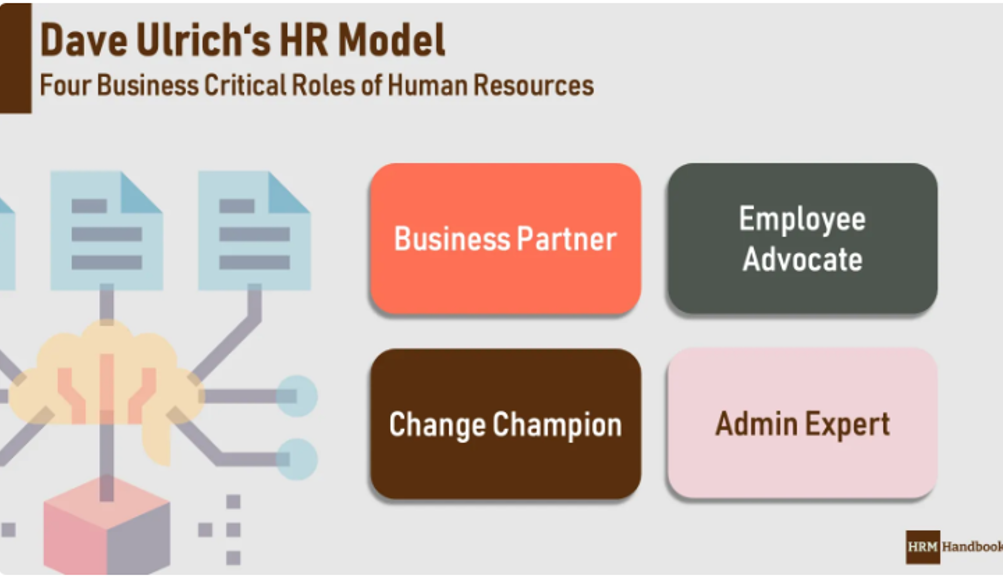
Dave Ulrich’s H.R. model has developed various strategies for H.R. professionals, such as focusing on activities that contribute to organizational success instead of just administrative tasks. With the guidance of the H.R. professional, such approaches enable employees to contribute to organizational performance (Shaalan, L. 2022, 240).
In addition, the same model advocates for increased collaboration between H.R. professionals and employees toward achieving overall organizational objectives and strategy. The model also suggests the development of new competencies which enable H.R. professionals to build diverse sets of abilities and skills, such as strategic thinking and financial acumen, among the employees to promote organizational performance. See the model in Appendix I.
Extensively, HRM activities can enhance the performance of organizations by increasing the level of commitment and motivation among employees. In addition, these practices develop a psychological contract with the employees, which enables them to work towards achieving the goals and objectives of the organization.
Consistently, these HRM activities enhance employees’ skills and abilities, creating a rich skills base that promotes organizational performance. Finally, these activities offer employees extended roles to optimize their skills and abilities, boosting their experience and the organization’s performance.
Extensively, HRM practices enhance organizational effectiveness by promoting profitable experiences for employees. For instance, employees can get to the orientation programs of organizations which enable them to learn about the organizations together with its goals and values, increasing organizational performance. Overall these activities foster excellent organizational development. Increased organizational performance enables organizations to move from one level to the next, promoting more excellent organizational development.
Leadership Styles and Practices in Organizations
Contingency theory of leadership
This theory is called situational leadership theory and proposes that different leadership styles suit different situations. In this leadership theory, the company’s leaders must assume their leadership style based on their condition. This approach to leadership increases effectiveness and innovation. This theory enables different leaders to adapt to various needs and become versatile. In addition, it also makes their transition from one level to another more manageable and gives them the required knowledge and skills to face different situations.
This theory can be used to promote organizational development at Etisalat Telecommunication Company. In this regard, it can help different leaders in the organization respond appropriately to different situations and have the necessary knowledge and skills to tackle problems they might face on the way (Demir, A.2018, 175).
Transformational leadership theory
This theory asserts that leaders should share a good relationship with their team members. Such leaders significantly influence their teams and improve their focus on achieving the goals and objectives of the organizations through inspiration and influence. These leaders also ensure that their teams’ objectives are aligned with that of the organization to avoid discrepancies.
Leaders at Etisalat Company can adopt the principles of this theory to promote organizational development. By building a good relationship with their team members, these leaders are more likely to inspire and positively influence the performance of each team member and hence that of that organization.
At the current organization, employees tend to perform better when they are rewarded. Subsequently, the best leadership style for Etisalat would be transactional leadership. In this style, leaders of different departments will recognize and reward employees that record exemplary performance. However, when these employees fail, they will get an official expression of disapproval from the same leaders. However, this disapproval is limited to the employees’ situation and performance. This limitation does not punish the process of trying to offer solutions to problems, as it discourages innovations.
Implementation of change in an organization
Among the various factors that drive organizational change include growth opportunities. This is no surprise in the modern digital marketplace. The digital economy has revealed various growth opportunities, such as new markets, innovative products, and contemporary business practices and processes. Combining these factors leads to growth opportunities that drive organizational change (Lewis, L. 2019, 410).
Consistently, competitive pressure is another driver of organizational change. Most people in organizations resist change; they only embrace it when they have to. However, competitive pressure is one of the most significant elements that push people to change. Additionally, the shift in culture in organizations is another driver of organizational change. Typically, cultural shits in organizations occur naturally. When they occur, they demand processes and modern workflows which promote organizational change.
Extensively there are various change management models. Lewin’s change management model is one of those. This model divides change into multiple steps—Unfreeze, the preparation stage. Evolution is the implementation phase, and refreezing is the stage where the drivers of change avoid returning to the old ways. In addition, the McKinsey 7-S model breaks down differences into seven steps involving the strategy and structure, business processes and systems, as well as the manner of work, staff, and the team’s skills.
On the other hand, Kotter’s change management theory focuses on the people that drive change and their psychology. According to the idea, these people should develop a sense of urgency which is aimed at motivating the people. In addition, the driver of change should carry a strategic vision and communicate effectively during the transition process to ensure that every team member has the idea and keeps up the momentum throughout the process.
To create an effective change management plan, various steps should be followed; they include defining the change and aligning it to the business goals. Secondly, the change driver should determine the impact of the people affected by the change and an effective communication strategy. In addition, the change driver should offer practical training, execute a support structure, and measure the change process (Rasool, S. 2019, 1010).
To communicate the implementation of change to organizational stakeholders, the driver of change should communicate the vision and share it honestly and regularly. In addition, the change driver should communicate through modeling and engagement with the team players.
Finally, the change driver should build a culture of change and train the team leaders first. This way, the change process will have minimal hurdles and eventually prevail against the resistance. In addition, the change driver should resolve any conflict experienced among the team members quickly and effectively to promote the change process. Finally, the change driver should have passion for the change and the process of change.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the primary objective of the SHRM is to ensure that employees’ different abilities and talents are utilized effectively. This process is carried out by identifying the employees’ development needs and responding by providing resources and training to help the employees improve. The intention and goals of the SHRM are to develop programs and policies that align with the company’s business strategy.
However, this process can only be effective with deliberate HRM activities that promote organizational performance. In addition, various leadership styles must be developed to make this process seamless. Conclusively, organizational performance is driven by change. The change process has challenges, as most people resist it and only embrace it when they have to. However, to promote this process, the change driver should develop a positive culture towards change and the process of change, solve any conflict that might be experienced among the team members as quickly as possible and effectively, and speak passionately about the change process.
References
Anwar, G. and Abdullah, N.N., 2021. The impact of Human resource management practice on Organizational performance. International Journal of Engineering, Business, and Management (IJEBM), 5.
Budhwar, P. and Mellahi, K., 2018. HRM in the Middle East. In Handbook of Research on Comparative Human Resource Management (pp. 487-499). Edward Elgar Publishing.
Christopher, N., 2019. The effectiveness of HRM policies and practices. International journal of social sciences, 2(1), pp.24-32.
Demir, A. and Budur, T., 2019. Roles of leadership styles in corporate social responsibility to non-governmental organizations (NGOs). International Journal of Social Sciences & Educational Studies, 5(4), pp.174-183.
Lewis, L., 2019. Organizational change. In Origins and traditions of corporate communication (pp. 406-423). Routledge.
Rasool, S.F., Samma, M., Wang, M., Zhao, Y. and Zhang, Y., 2019. How human resource management practices translate into sustainable organizational performance: the mediating role of product, process and knowledge innovation. Psychology research and behavior management, pp.1009-1025.
Shaalan, L.A.A.B., Elsaid, A.M. and Aboul-Ela, G.M.B.E., 2022. Knowledge management processes and strategic human resources management: Creating competitive advantage through employee innovation behavior. The Business & Management Review, 13(2), pp.237-245.
Appendix
Appendix I: Dave Ulrich’s H.R. model table
 write
write