Risk Identification
Identification of the Two Risks
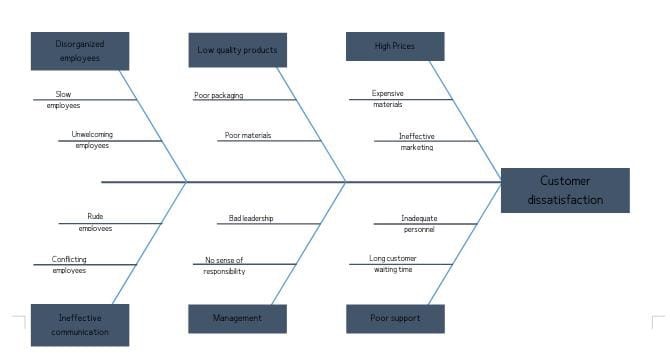
Customer dissatisfaction is the first risk and problem that the life science organization in the dynamic and competitive business environment. Since customers are the main contributors to an organization’s success, growth, and development, the life science organization is preparing for its exit strategy due to losing customers. Therefore, customer dissatisfaction might have been triggered by the following reasons according to the subject matter. First, the organization might not have been keeping customer promises. For example, if customers requested some products which were missing, the company might have delayed the fast delivery of these demanding goods and services. Failure to keep these promises contributes to a loss of customer trust and an increase in complaints. Hence, the customers choose to switch to potential competitors offering similar services and keeping promises. Second, the organization might have a poor customer service department that does not serve customers according to their specific tastes and preferences. In this context, the employees in this department have been poorly trained because of long waiting and service time. Poor customer services contribute to poor resolving of customer problems and high levels of complaints and dissatisfaction (Boadi et al., 2018). Third, the employees might be rude and harsh while serving customers. Employee rudeness and harshness play a significant role in facilitating an unfavorable workplace and ineffective communication. For example, employees with inadequate communication skills do not maintain eye contact when communicating with customers, which contributes to poor customer service quality. These unwelcoming employees and staff also reduce customers’ purchasing power and willingness to buy various goods and services. Finally, the life science organization might have offered low-quality products and relatively high costs, leading to a bad customer experience. High costs and poor quality products drive away customers who join other potential organizations that offer high-quality services based on specific customer tastes and preferences. Hence, this main risk is well-illustrated in the fishbone diagram below.
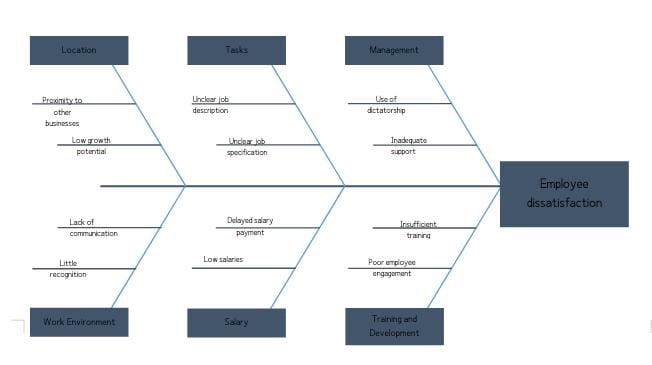
Employee dissatisfaction is the second risk the life science organization might face in the competitive business and market environment. The dissatisfaction might have been brought about due to the following reasons. First, the company might have underpaying employees considering they are working towards attaining specific goals and objectives and improving productivity and performance. Poor remuneration programs and delayed payments are the main contributors that demotivate and reduce employee morale. The employees also fail to pay their bills due to inadequate and delayed salaries, leading to dissatisfaction. Second, bad management is another reason that might have led to employee dissatisfaction in life science organizations. For example, unsupportive and dictatorial bosses and managers create an unfavorable working environment. Bad management is brought by poor leadership skills, experience, and knowledge and plays a significant role in contributing to employee dissatisfaction. (Kim and de Dear, 2019). Third, the company might have little room for future professional growth and development. For example, if employees detect no future job growth prospects, they leave the organization. Therefore, this is the main reason that made the company experience high levels of employee attrition. Finally, the organization might have experienced poor communication and workplace relationships (Alyammahi et al., 2020). Ideally, employees like working with each other in teams to perform specific roles and responsibilities according to the job specification and description stipulations. However, when these descriptions and specifications are unclear, employees lose morale and seek other organizations where they can communicate well and establish mutual workplace relationships. Thus, the risk is shown in the fishbone diagram below.
Identification of the Main Cause and Ancillary Causes of the Two Risks
The main cause of customer dissatisfaction is low-quality products. Since customers seek to get the best from organizations to satisfy specific tastes and preferences, life science organizations might have supplied low-quality products and services to customers, which led to dissatisfaction. Therefore, product and service quality should be the main drivers of maintaining customers as key players in an organization’s success. The low-quality products contributed to high cases of employee attrition and turnover rates. It also played an essential role in reducing the company’s market share and sales volumes. Low-quality products caused the company to lose its competitive advantage in the competitive and dynamic business environment and decreased financial performance and productivity. The other ancillary causes of customer dissatisfaction include high prices, disorganized employees, ineffective communication, management problems, and poor support. The sub-causes are also illustrated clearly in the fishbone diagram.
The main cause of employee dissatisfaction is poor management in the organization. Since management is the key determiner of organizational success, growth, and development, employees are dissatisfied when they work with dictatorial and unsupportive top leaders. In this context, employees feel lost and unrecognized when working in such an unfavorable environment. For example, dictatorial leaders do not listen to employees concerning serious customer problems and challenges. These unwelcoming leaders think they are the final when making decisions and solving organizational problems. They do not encourage dialogue and effective and efficient communication skills, leading to a loss of morale and vigor to offer high-quality customer services. The other ancillary causes include an unfavorable working environment, low and delayed salaries, poor employee training and development, unclear tasks, and a non-strategic business location.
Risk Evaluation
Evaluation and Justification of the Probability and Impact of the Two Risks
The probability and impact of the two main risks are described using the chart below.
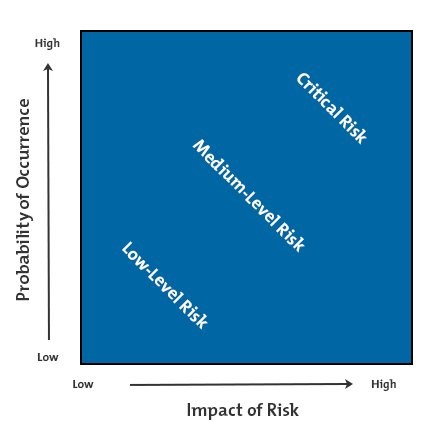
Since the life science organization experienced employee attrition and needs acquisition, customer dissatisfaction has a high impact on risk and a high probability of occurrence (Vitomir, 2021). In this context, employee dissatisfaction is a serious risk that causes loss of customers and a decrease in market share and sales volume. Since customers are the key players in the organization’s success, they are the ones triggering high attrition due to a lack of profitable business operations and activities. According to the performance of the life science organization, it should be acquired by Johnson & Johnson because it does not have customers, and employees are leaving and recording little or no profits. Therefore, the risk has a high impact and probability of occurrence because customers are the determinants of organizational growth and development.
On the other hand, employee dissatisfaction has a high probability of occurrence and a high impact of risk because an organization cannot run its operations and activities without employees. According to the case study, most employees leave the organization due to poor working conditions and lack of recognition. The high cases of employee attrition suggest that the organization is not motivating and addressing serious problems facing employees. For example, low and delayed payments and poor and unsupportive management increase employee stress and struggle in the organization. Hence, that is why many employees are leaving the organization and joining other potential companies offering better working terms and conditions.
Risk Mitigation
Customer dissatisfaction can be mitigated by offering a stringent customer experience in the workplace. Organizations should set a specific day to discuss main issues concerning customer experiences and issues. For example, they can decide to have customer experience programs and operations every Tuesday to engage customers and offer feedback about their main issues (Ling and Soon, 2019). These programs will allow customers to be part and parcel of the organization and work towards increasing their buying patterns. They also assist organizations in offering high-quality products according to specific customers’ tastes and preferences.
On the other hand, employee dissatisfaction can be mitigated by proper motivation, training, and development. In this context, employees should be provided with financial and non-financial benefits to improve motivation and increase morale. They should also be equipped with the required skills and knowledge to perform specific roles and responsibilities. For example, organizations should initiate training and development programs and procedures to work according to stipulations of job descriptions and specifications.
References
Boadi, P. O., Guoxin, L., Sai, A. A., & Karikari, A. F. (2018). Customer dissatisfaction and unfavorable word of mouth. Human Systems Management, 37(4), 445-451.
Kim, J., & de Dear, R. (2019). Employee satisfaction and the quality of workplace environment. In Organizational Behaviour and the Physical Environment (pp. 96-112). Routledge.
Alyammahi, A., Alshurideh, M., Kurdi, B. A., & Salloum, S. A. (2020, October). The impacts of communication ethics on workplace decision making and productivity. In International conference on advanced intelligent systems and informatics (pp. 488-500). Springer, Cham.
Ling, Y. L., & Soon, G. L. H. (2019). Feedback environment in the workplace: Implications for intrinsic motivation. Asian Journal of Social Science Research, 2(1), 1-10.
Vitomir, G. M. (2021). The importance of risk evaluation in the business operations of the company from the aspect of top management decision-making. Baština, (55), 343-352.
 write
write