1. INTRODUCTION
1.1 Context
Efficient management and leadership are important elements in accomplishing objectives and sustaining a competitive advantage in any entity. Samimi et al. (2022, p.101353) insist that the management and leadership of an entity play a crucial role in shaping its direction and vision in today’s work climate. Moreover, they provide a persuasive vision that inspires people to work towards achieving these objectives. Furthermore, Piwowar-Sulej and Iqbal (2023, p.134600) agree that the productivity and performance of a company are within the purview of its administration and leadership. Managers enhance efficiency and performance by overseeing day-to-day operations, delegating work, allocating duties, and monitoring progress. Therefore, proficient management approaches are responsible for producing top-notch results and enhancing operational efficiency. Effective leadership and management approaches accelerate the process of managing tasks (Moore and Hanson, 2022, p.452).
Managers and leaders who demonstrate attentiveness towards their staff and include them in decision-making foster a feeling of contentment and responsibility in their positions. The organization would gain advantages by providing regular feedback to staff members, acknowledging their accomplishments, and presenting prospects for career progression. As a result, there would be an increase in revenue, employee loyalty, and retention. Additionally, managers and leaders are responsible for cultivating connections with stakeholders, consumers, and the community. Due to their role as the organization’s spokespersons, they can establish and sustain relationships. They fulfil the requirements of the stakeholders, fostering favourable connections and ensuring long-term viability. The development and success of an organization are largely determined by the leadership and management. Businesses must prioritize the enhancement of their leadership and management skills to survive in today’s competitive business environment.
1.2 Aims
- Critical evaluation of the evolution of 2 traditional leadership theories to a 2023/2024 context
- Critical evaluation of the evolution of 2 traditional management theories to a 2023/2024 context
1.3 Methodology Overview
The research used both qualitative and quantitative analysis. Peer-reviewed articles from Google Scholar and Elsevier were used to access literature on traditional leadership and management theories. Secondary data from literature review and desk research was sourced from scientific publications and journals.
2. CRITICAL EVALUATION OF THE EVOLUTION OF LEADERSHIP AND MANAGEMENT THEORIES
Leadership theories primarily centre on examining leaders’ qualities to elucidate the process and rationale behind selecting individuals for leadership roles. Traditional leadership theories, such as trait theory and behavioural theory, assert that people can improve their leadership skills in various situations (Benmira and Agboola, 2021). On the other hand, management theories entail a collection of concepts that provide the fundamental principles to be followed in the operation of an organization. Rosenberg Hansen and Ferlie (2016, p.12) agree that traditional management theories, such as administrative theory and systems theory, assist organizations in expanding.
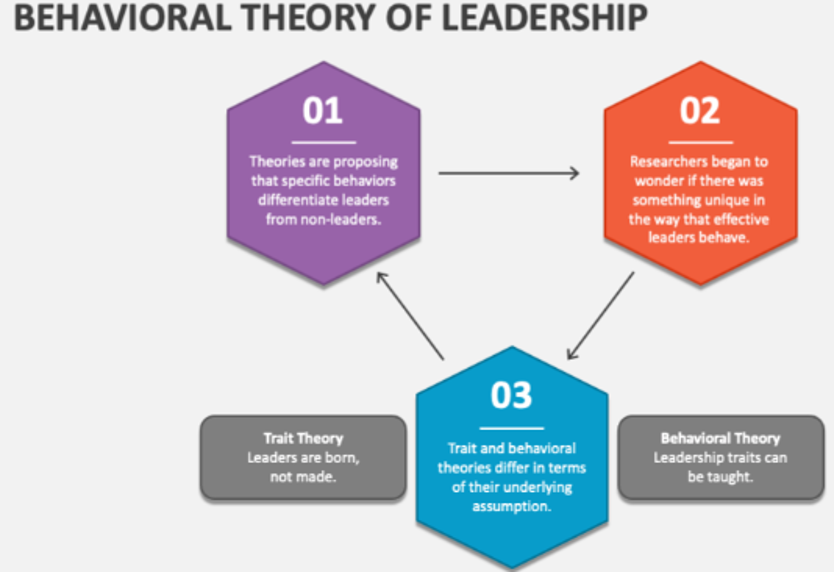
Figure 1: Trait and behavioural theories differ as they evolve.
Source: (Collidu, 2024).
2.1 Evolution of Traditional Leadership Theories
2.1.1 Trait Theory
Hunt and Fedynich (2019, p.23) note that the trait theory came into play in the early 1900s. The primary objective of this theory was to ascertain the human attributes and characteristics that contribute to a leader’s effectiveness. This viewpoint asserts that leaders are distinguished from non-leaders by possessing qualities such as confidence, intellect, and drive. The idea of cultural intelligence, which refers to the ability of organizations to adapt and thrive in different cultural contexts, has been influenced by several environmental factors. Nawaz and Khan (2016, p.2) explain that an effective leader must possess attributes pertinent to the requirements of the circumstance they are tasked with leading. Conversely, the trait leadership theory has faced criticism for its excessive focus on human characteristics while neglecting the significance of contextual influences. The theory focuses on the specific qualities associated with future leaders. The characteristic leadership style identifies a successful leader by considering the individual’s mental qualities, attitudes, and talents.
The concept of seeing leadership through the lens of individual leaders is founded on the assumption that certain characteristics contribute to consistent patterns. During the early 1990s, leaders were differentiated from non-leaders by their distinct physical and psychological characteristics, which separated them from the general population. These criteria considered physical traits such as stature, cognitive abilities, efficiency, charm, and self-confidence. Spector (2016, p. 253) argues that given the close connection between the Great Man hypothesis and trait theory, it is crucial to examine the Great Man hypothesis, which asserts that leaders inherently possess the requisite qualities and abilities. The Great Man Theory insists that leaders are not made but possess inherent qualities from birth. They distinguish themselves from other industry specialists via their expertise, self-assurance, and adeptness in interpersonal communication. These leaders are renowned for their audacious early career moves and are well-positioned for upward mobility within the corporate hierarchy.
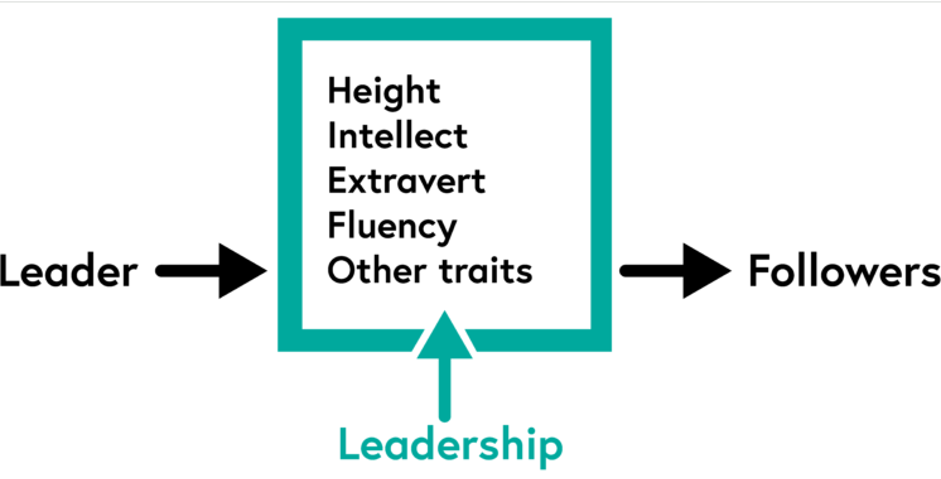
Figure 2: Specific qualities and characteristics make a leader.
2.1.2 Behavioral Theory
Meuser et al. (2016, p.1375) highlight that behavioural theory emerged as a viable alternative to cover the gaps in trait theory. Successful leadership in this situation requires diverse abilities, including technical, interpersonal, and intellectual talents. Conceptual skills entail the aptitude for generating ideas essential for a firm’s management, while interpersonal skills pertain to the ability to interact well with others. Technical skills refer to the practical knowledge and expertise required for certain tasks or procedures.
Interpersonal skills include the ability to interact and cooperate with others effectively. This approach investigates the degree to which a leader can cultivate empathy and trust among their followers. Leadership aims to foster a sense of shared commitment among all organization members towards the overall prosperity of the firm, achieved via effective organization and explicit delineation of duties that need to be completed. The overwhelming majority of individuals in positions of power in our society are either democratic or supportive of democracy. Employers acknowledge and praise employees who exceed their expectations, while those who fail to reach these standards are subject to disciplinary measures.
2.2 Evolution of Traditional Management Theories
2.2.1 Systems Theory
Jackson (2016) uses the systems thinking approach to assert that organizations are intricate systems impacted by a wide array of interconnected elements. The system theory underscores the need to adopt a holistic approach to management while also highlighting the interconnections among the many components within an organization (Morgeson, Mitchell, and Liu, 2015, p.522). For example, the expansion of large-scale organizations and the accelerating rate of societal changes have played a crucial role in the evolution of systems theory. The idea of organization based on systems was formally formulated in the 1950s (Lewis, 2016, p. 126). The idea gained prominence in management and organization studies as a departure from the conventional perspective of organizations as mechanistic entities. Recognizing that organizations are complex systems made up of interrelated subsystems was highlighted. In today’s society, understanding enterprises’ behaviour, adaptation, and evolution requires a grasp of systems thinking. This paradigm facilitates understanding the many links and interdependencies inside organizations, aiding managers in efficiently managing and resolving the challenges these operations face.
System theory offers a systematic framework for understanding management and organizations, facilitating the analysis and evaluation of complex situations. This phrase highlights the mutual reliance and interconnection of all internal components inside an organization and their relationships with the external world. Managers who engage in this practice have more proficiency in making judgments by considering the whole perspective. It promotes the perspective of managers to consider the whole system and the interrelationships among its many components. The evaluation of the system’s overall performance is based on the systems approach framework rather than only concentrating on the success of each particular component. It facilitates the integration of system principles across different levels within the firm rather than only prioritizing the aims and efficiency of specific departments. The systems approach posits that choices and actions made in one sector of the company will affect other divisions within the business. This encompasses a strategy that acknowledges the interdependence between an organization and its environment (Teece, 2018, p.361).
2.2.2 Administrative Theory
Bishop (2015.p.341) credits Henri Fayol as the pioneer in expanding the administrative theory of management. Work groups and functional divisions were established to operationalize the concept, each responsible for managing certain tasks. These activities contribute to the organization’s progress towards its goals by assisting in completing more significant tasks. The company used a hierarchical framework to enhance operational effectiveness. Rosenbloom (2016, p. 78) explains the primary emphasis of administrative theory is in the realm of management principles and the roles performed by managers. This idea was developed in response to the need for efficient organizational structures and the fast-growing economy. Frederickson et al. (2018) delineate the fundamental administrative tasks as organizing, planning, commanding, coordinating, and regulating. Therefore, this argument significantly impacted the development of contemporary management styles and served as the foundation for efficient management methodologies.
The division of labour facilitates specialization within an organization. Individuals may enhance their productivity by acquiring proficiency in a certain set of jobs, hence expanding their skill set. In addition, managers must be able to give instructions; nevertheless, this power entails the obligation of ensuring that the assigned tasks are executed. Subordinates are required to fully comply with orders given by their superiors (Chiu and Hung, 2022, p.399). Managers must possess the capacity to enforce discipline by administering punishment. In today’s world, all departments and workgroups adhere to a unified plan to synchronize their actions. A single supervisor should be responsible for overseeing the work activities. Typically, the priorities of the department, business, and organization take precedence over the individual interests of its members. Depending on the company’s characteristics and the workforce’s talents, decision-making should be decentralized, allowing people to make choices, or centralized, with management making all decisions. Raczkowski (2016) insists that a hierarchical structure must be established in the reporting system, whereby workers are positioned as subordinate to supervisors. The degree of authority increases with each successive tier in the organizational hierarchy. It is crucial always to possess a thorough understanding of the organizational structure. Explicit and well-defined standards and rules govern the work environment and its associated duties today.
2.3 Key Emerging Social, Economic, Technical, and Environmental Context and Drivers Likely To Inform and Influence the Development of New Leadership and Management Theories
The contemporary management and leadership theories in the 21st century provide a valuable understanding of how social, economic, technical, and environmental frameworks have progressed.
2.3.1 Shifts in the Operational Dynamics of the Work Environment
With the market’s growth, several ideas have gained popularity in an attempt to address problems caused by shifting management, leadership and labour dynamics. Scott (2022) notes that the workforce may have seen an increase in diversity, with workers from many generations and locations actively engaged. Managers and leaders are adopting inclusive and adaptable tactics into their work due to the diversity. Developing novel theories might aid in accomplishing this objective. Therefore, the development of theories is prioritizing cross-cultural leadership and cultural integration.
2.3.2 Corporate Social Responsibility and Evolving Employee Demands
Businesses are transitioning their attention from escalating social and environmental concerns to a more ethical and sustainable approach to doing business. Leaders and managers incorporate social responsibility and environmentally sensitive practices into their company operations. The economic and social aspects of sustainability and corporate social responsibility are propelling the emergence of novel theories in management and leadership to tackle urgent challenges in enterprises. The theories address concerns such as stakeholder management, sustainable leadership, and moral decision-making. Contemporary workers seek meaningful employment to harmonize their professional commitments with personal development prospects. To recruit and keep skilled individuals in this particular circumstance, managers and leaders must understand the evolving demands and requirements of their employees.
2.3.3 Globalization and Market Unpredictability
Globalization has led to increased interconnectivity in economic activities, resulting in an unstable corporate environment. Steger et al. (2023) note how the market’s volatility is prompting the development of novel theories to tackle challenges such as decision-making in multinational contexts, adaptive leadership and management, and uncertain circumstances. Globalization modifies the norms that organizations follow, thereby leading to a transformation in the skills and capabilities of its executives (Dickson, 2023, p.48). Moreover, the phenomenon of globalization compels managers to develop comprehensive globalization strategies to turn their organizations into internationally competitive entities. Leaders and managers must cultivate the skills to supervise international organizations, negotiate intricate geopolitical landscapes, and adapt to ever-changing market situations. Consequently, new ideas are being developed to give them direction on doing business in the global economy.
3. CONCLUSION
The paper critically evaluates the evolution of traditional leadership and management theories to a 2023/2024 context. The evolution is impacted by socio-economic, technical and environmental drivers. The concepts have been significantly shaped by a variety of social scenarios. Moreover, the historical progression of leadership theories demonstrates a change from focusing on individual attributes to emphasizing actions and inspiring leadership. This transition encompasses the movement from trait theories to behavioural theories and transformational theories. Similarly, the focus on efficiency, managerial responsibilities, and holistic thinking is seen in the evolution of management theories, ranging from scientific management to administrative and systems theories. The focus of these new theories will mostly be on effectively managing a workforce that is varied in terms of demographics, including aspects such as sustainability, navigating the global market, and satisfying the expectations of employees. Some of the newer concepts in the field of management and leadership theory include servant leadership, ethical leadership, true leadership, and adaptive leadership. The emergence of new theories of leadership and management is attributed to the changing work dynamics, characterized by a varied workforce including individuals from all generations and cultures, as well as other socioeconomic and technical reasons. Consequently, there is a need for novel concepts that are pertinent to cultural intelligence. In addition, the original concepts would attract innovative and flexible leadership philosophies that would guarantee leaders change their communication and decision-making processes accordingly.
In today’s world, managers must possess the necessary skills to address the challenges arising from the adoption of new systems. In this particular instance, the act of formulating new ideas would tackle these concerns. Additionally, workers are seeking better employment opportunities. As a consequence of the shift in employee expectations, novel theories in management and leadership have developed. In addition, with the increasing prevalence of environmentally conscious activities, firms are compelled to adopt more sustainable practices and take responsibility for the social and environmental impacts of their operations. The new leadership theories address the concepts of ethical behaviour and sustainable leadership in this context, whereas the emergence of globalization and volatile markets has significantly influenced the generation of innovative ideas in leadership and management. Consequently, new ideas are being developed to assist leaders and managers in effectively adapting to a competitive and ever-evolving world.
References
Benmira, S. and Agboola, M., 2021. Evolution of leadership theory. BMJ Leader, pp.leader-2020.
Bishop, S., 2015. Theories of organizational behavior and leadership. Philosophies and theories for advanced nursing practice, pp.339-354.
Chiu, T.C. and Hung, Y., 2022. Impacts of leader humility between authority and trustworthiness on compliance: Tests of three-way interaction. Psychological Reports, 125(1), pp.398-421.
Collidu 2024. Behavioral Theory of Leadership. [online] www.collidu.com. Available at: https://www.collidu.com/presentation-behavioral-theory-of-leadership (Accessed: 19 January 2024).
Cyert, R. and March, J., 2015. Behavioral theory of the firm. In Organizational Behavior 2 (pp. 60-77). Routledge.
Dickson, R.K., 2023. The Changing Paradigm of Leadership in A 21st Century Global Business Environment. IISTE-European Journal of Business and Management, 15(14), pp.46-56.
Frederickson, H.G., Smith, K.B., Larimer, C. and Licari, M.J., 2018. The public administration theory primer. Routledge.
Güttel, W.H. and Kratochvil, R., 2023. Leadership efficacy: Roles, style & priori tization. Successful in turbulent times. Leadership, change management and ambidexterity. Baden-Baden.
Hunt, T. and Fedynich, L., 2019. Leadership: Past, present, and future: An evolution of an idea. Journal of Arts and Humanities, 8(2), pp.22-26.
Jackson, M.C., 2016. Systems thinking: Creative holism for managers. John Wiley & Sons, Inc..
Lewis, P., 2016. Systems, structural properties and levels of organisation: the influence of Ludwig von Bertalanffy on the work of FA Hayek. In Research in the History of Economic Thought and Methodology (pp. 125-159). Emerald Group Publishing Limited.
Meuser, J.D., Gardner, W.L., Dinh, J.E., Hu, J., Liden, R.C. and Lord, R.G., 2016. A network analysis of leadership theory: The infancy of integration. Journal of management, 42(5), pp.1374-1403.
Moore, J.R. and Hanson, W., 2022. Improving leader effectiveness: impact on employee engagement and retention. Journal of Management Development, 41(7/8), pp.450-468.
Morgeson, F.P., Mitchell, T.R. and Liu, D., 2015. Event system theory: An event-oriented approach to the organizational sciences. Academy of Management Review, 40(4), pp.515-537.
Nawaz, Z.A.K.D.A. and Khan, I., 2016. Leadership theories and styles: A literature review. Leadership, 16(1), pp.1-7.
Piwowar-Sulej, K. and Iqbal, Q., 2023. Leadership styles and sustainable performance: A systematic literature review. Journal of Cleaner Production, 382, p.134600.
Raczkowski, K., 2016. Public management theory and practice. Springer.
Rosenberg Hansen, J. and Ferlie, E., 2016. Applying strategic management theories in public sector organizations: Developing a typology. Public Management Review, 18(1), pp.1-19.
Rosenbloom, D.H., 2016. 3a. Public administrative theory and the separation of powers. In The constitutional school of American public administration (pp. 78-94). Routledge.
Scott, A.J., 2022. Metropolis: From the division of labor to urban form. Univ of California Press.
Spector, B.A., 2016. Carlyle, Freud, and the great man theory more fully considered. Leadership, 12(2), pp.250-260.
Steger, M.B., Benedikter, R., Pechlaner, H. and Kofler, I., 2023. Globalization. University of California Press.
Teece, D.J., 2018. Dynamic capabilities as (workable) management systems theory. Journal of Management & Organization, 24(3), pp.359-368.
 write
write