Recommendation
Glass Lewis issued a C grade to Stantec Inc after conducting a pay-for-performance analysis of its executive salary. The median pays of a set of peer companies chosen using the Glass Lewis technique was lower than the total salary of Stantec Inc named executive officers. The CEO’s pay was also less than that of the CEOs of similar comparable businesses. WSP fared a little worse than its competitors while paying less.
Here are suggestions for Stantec Inc executive compensation in light of this analysis:
- Be open and honest regarding executive compensation procedures, and advise shareholders of pertinent details.
- Only give out one-time prizes in unusual situations or for very outstanding accomplishments.
- Keep front-loaded awards to a minimum to keep CEOs engaged in the long run.
- . Create measures that measure how well the business performs in terms of governance, social, and environmental issues, and tie CEO remuneration to those criteria.
- Take into account raising the CEO’s salary so that it is still performance-based and in line with market rates.
- Give executives full-value awards to encourage the production of long-term value.
- Provide equity incentives based on performance that balance the interests of shareholders and executives.
The Canada Pension Plan Investment Board (CPPIB) is concerned about director compensation practices as an institutional investor. According to Elsayed and Elbardan (2018), CPPIB examines director fees, share ownership, and stock options to make sure they support long-term wealth development, are consistent with the company’s overall pay strategy, and reflect market best practices. To ensure that shareholders can make knowledgeable investment decisions, the organization advocates transparency and disclosure of director salary and share ownership.
Glass Lewis Analysis on Stantec INC
Glass Lewis plays a key role in assisting companies such as Stantec Inc to achieve their financial breakthrough by evaluating the independence, diversity, and experience of a company’s board of directors. Furthermore, it assesses the board’s oversight of risk management and strategic planning. There are many ways that Glass Lewis Analysis benefits companies such as Stantec. First, it offers businesses knowledge of the best methods for board composition, executive compensation, diversity, and risk management. This can assist businesses in bettering their overall governance procedures and bringing them into compliance with stakeholder and investor expectations.
Additionally, based on its research of a company’s governance policies and other elements, Glass Lewis’s research offers unbiased proxy voting recommendations. These suggestions might help businesses comprehend the possible effects of various ideas on their shareholders and take action to allay any worries. Additionally, Glass Lewis Analysis can assist businesses in communicating with investors and other stakeholders. Its research and analysis can assist businesses in comprehending the priorities of their investors and formulating plans to allay their worries. This can enhance a company’s reputation and performance while also assisting it in forging closer bonds with its investors. In a great way, the Glass Lewis Analysis assists businesses in maintaining compliance with pertinent laws governing shareholder meetings and proxy voting. Companies can learn about the needs of various regulations and take action to guarantee that they are meeting these standards with the use of their analytical tools and services.
Glass Lewis analyzed Stantec data of CEO/NEO Compensation,3-Year Averages of CEOs, and peer company 3-Year-NEO and CEO salary comparison with the aid of graphs.
Table 1: CEO/NEO Compensation
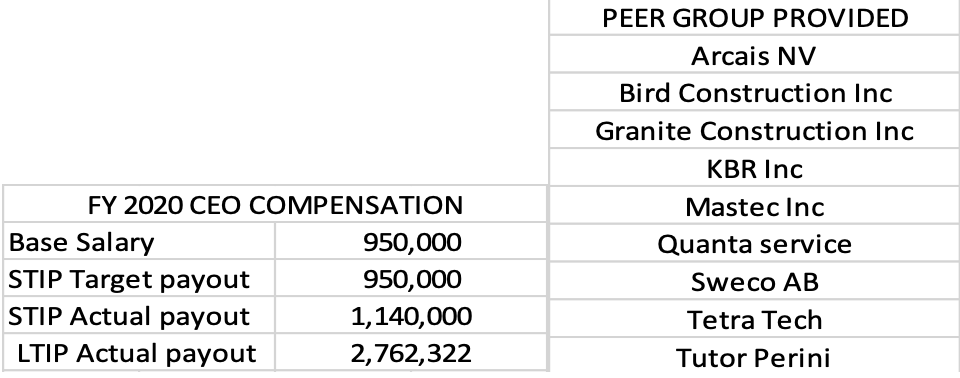
Table 1 showcases the compensation rates of the CEO (Chief Executive Officer) and NEO (Named Executive Officer) in 2020 at Stantec Inc, a company under review. The data reveals that the CEO’s average compensation is greater than the NEOs. Furthermore, the table shows the compensation details of the company’s rivals, a group of companies selected based on Glass Lewis’ peer group methodology. Glass Lewis makes a case-by-case determination as to whether companies have provided for board-level oversight of matters related to human capital management, including issues such as employee diversity, employee engagement, and other related issues. This information aids the comparison of Stantec Inc company compensation rates with its competitors. The peer group data can be used to determine whether Stantec Inc’s compensation rates are favorable in the market or not. If not, the company can apply adjustments to catch up with its peers (Groysberg, 2021).
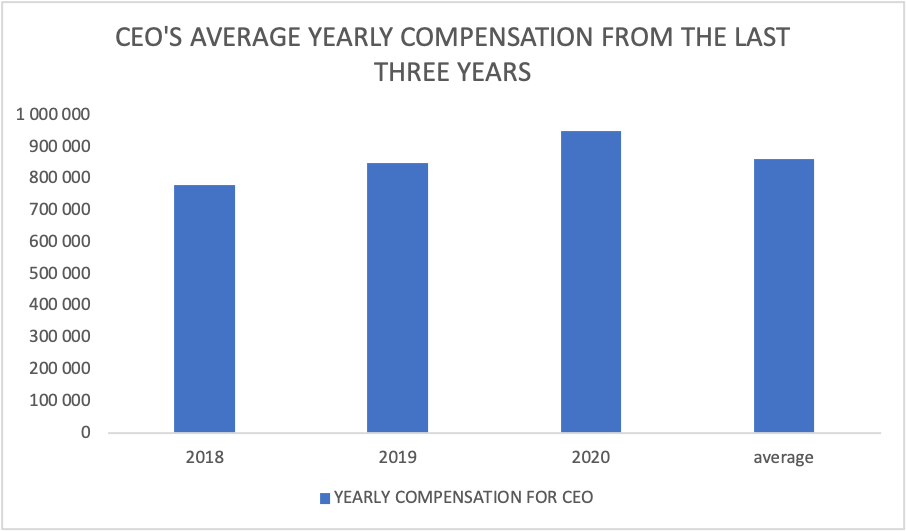
Figure 1: Pay for Performance
Figure 1 displays the 3-year calculated average compensation for the performance of Stantec Inc from the year 2018 to 2020. The data indicate an increase in compensation rates from the last three years. This is one of the efforts to show motivation which in turn increases the company’s revenue (Sammer, 2013).
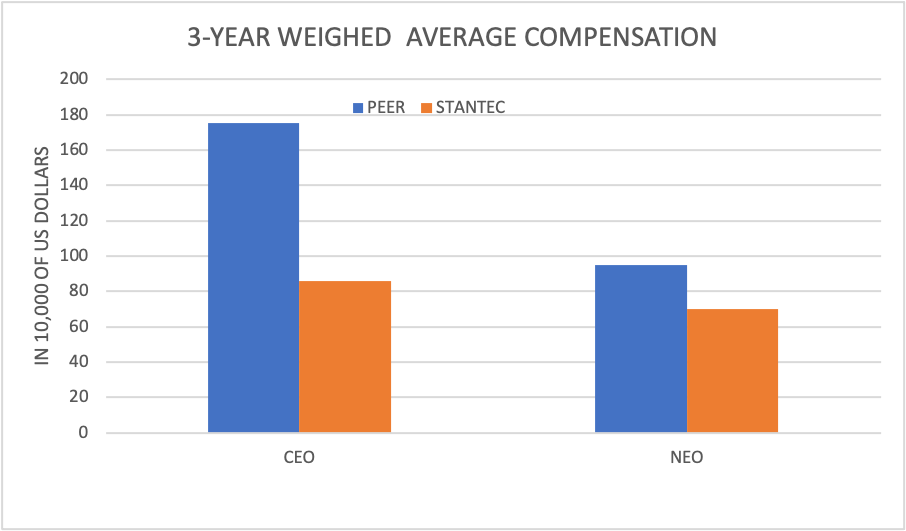
Figure 2: Pay for Performance
Figure 2 shows the weighted average pay for Stantec Inc’s performance during three years. The data reveals that the Peer CEO received greater compensation than the other members of the group, suggesting that this person may have delivered an extraordinary performance for the three years. The success of Stantec Inc compensation policies may be assessed using this data, and any potential for improvement can be found.
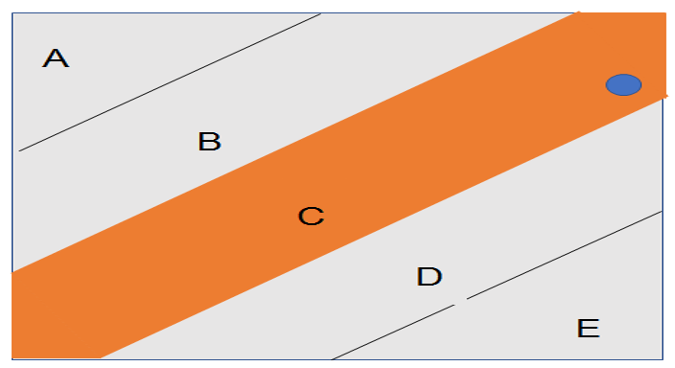
Figure 3: FY 2020 Pay for Performance Grade (NEO)
The performance rating for a company’s named executive officers (NEOs) in 2020 is shown in Figure 3. The data reveals that, on an A to E scale, the NEOs obtained a grade of C, which is lower than their grade from the previous year. This data can be used to evaluate the management team’s performance and pinpoint areas for development.
Table 3: 3-Year Averages of CEOs
| Group | Salary | Stock Awards | Short Tem | Compensation |
| Arcadis NV | 963841 | 4601140 | 1607042 | 8449253 |
| Bird Construction Inc. | 1064647 | 5116667 | – | 8680999 |
| Granite Construction Inc. | 1128240 | 4064692 | – | 636000 |
| KBR Inc | 1040310 | 2655012 | – | 8476154 |
| Mastec Inc. | 1300284 | 6504381 | – | 80201 |
| Quanta Services, Inc. | 982597 | – | 1205450 | 183469 |
| SNC-Lavalin Group, Inc | 1353042 | 11166734 | – | 56584 |
| Stuart Olson Inc. | 1110513 | 3992286 | – | 92265 |
| Sweco AB | 1121960 | – | 1084128 | 98130 |
| Tetra Tech Inc. | 959626 | – | – | 102199 |
The average salary for CEOs is shown in Table 3, which shows that Mater Inc pays its CEOs much more than comparable businesses. The table also reveals that all groups pay CEO remuneration, although only three groups receive short-term incentives. According to this information, CGI might be putting more of an emphasis on rewarding its top executives with hefty compensation packages that include bonuses and other incentives. This strategy could be used to recruit and keep top executives who are crucial to the success of the business. When analyzing compensation methods, it’s critical to keep in mind that additional variables, including industry, firm size, and performance, might have an impact on executive pay.
CPPIB Analysis
The Canada Pension Plan Investment Board (CPPIB) is among the largest pension funds in the world. As of June 30th, 2012, CPPIB was reported to own approximately 3.4 million shares representing 3.9% of Stantec Inc’s total shares, making it one of its largest shareholders. CPPIB’s investment in Stantec Inc company is its strategy of investments in companies with strong growth and potential. Moreover, CPPIB strategically identifies well-organized companies with a highly competitive market advantage. They furthermore identify companies operating in attractive markets (Riviere Lemmel, 2021). Stantec In’s performance in the engineering consultancy field led to the attraction of CPPIB due to the favorable conditions of their profile. Several factors such as social, environmental, and governance are considered in making CPPIB’s decisions regarding investments. Stantec Inc ensures its business practices are in line with CPPIB’s values to minimize the risk of losing its investors. Therefore, CPPIB’s step of investing in Stantec Inc is a major boost in the company’s operation and long-term relation projects (Boustani & Pallavicini, 2019). As a step of ensuring maximum profits, The CPPIB their policies are adhered to by Stantec Inc.
Director Compensation
Director Compensation: CPPIB, being one of the major investors in Stantec Inc plays the role of evaluating the director compensation practices to ensure maximum cooperation with the company’s overall compensation policy (Williams, 2020). One of the policies includes reviewing the formation and components of director compensation and the pay level compared to its rivals.
Director Share Ownership: The CPPIB encourages directors to maintain equity in their companies to match their interests with those of their investors. Furthermore, the institution may need to carry out an evaluation concerning the level of director share ownership. The ownership of shares by CPPIB’s directors is encouraged in several ways:
First, Stock Ownership Guidelines have been instituted to ensure it happens through automation. There is minimum stock ownership set for directors. According to these provisions, each director must own a minimum amount of business stock equal to five times their yearly salary.
Second, Equity-Based Compensation. In the form of deferred share units (DSUs) or restricted share units (RSUs), CPPIB pays its directors equity-based compensation. These units are given to directors on an annual basis, and their value is determined by the share price of the company.
Another way the Canada Pension Plan Investment Board encourages direct share ownership is through Share Purchase Plans. CPPIB provides its directors with a share purchase scheme so they can buy business stock. Directors may buy shares under this plan at a discount to the market value.
In equal measure, the board uses Shareholder Alignment Program. Directors are required by this shareholder alignment scheme to hold onto their CPPIB shares until they retire. The directors’ interests and the shareholders of the company are more closely aligned thanks to this initiative.
Consideration of Director Stock Options: CPPIB considers the use of director stock options. This is a strategy to ensure that they are aligned with the director’s interests and with those of shareholders. This strategy promotes long-term value creation for the company (Williams, 2020). Reviewing the exercise price, overall equity-based compensation structure, and vesting period are among the widely used strategies within the direct stock options. Concerning its role, it has a massive role and its obligations tie it to the future of these directors. It achieves this in several ways:
First, the board ensures that its leadership is of top service and elegance for only then can meaningful progress be realized. The CPPIB board of directors is made up of seasoned experts from various professions who have expertise in risk management, governance, and finance. By doing this, the board is given the tools necessary to make decisions that are in keeping with the investment goals of the CPPIB. To add to that, the CPPIB has a clear investment policy. Its investing objectives, risk management techniques, and ethical and environmental criteria are all clearly stated in its investment policy (Gray, 2005). This policy is consistently examined and revised to make sure it is consistent with the CPPIB’s overarching goals.
Elsewhere, the CPPIB has installed performance metrics to keep track of progress. To evaluate the effectiveness of its investments and make sure that its goals are being realized, it employs a variety of performance measurements. The board of directors periodically examines these measures to make sure they remain pertinent and in line with the CPPIB’s investment goals (Sarney & Preneta, 2001). Lastly, CPPIB utilizes reporting as its main tool to evaluate its presence and impact on those it serves. It regularly updates the board of directors on the success of its investments and risk management tactics. The board will be fully informed and able to make choices that are in line with the investment goals of the CPPIB thanks to this information.
Disclosure of Director Compensation and Share Ownership: CPPIB ensures transparency and disclosure of director compensation and share ownership to assist shareholders in accessing all relevant information in investment decisions (Roller, 2019). This can be archived through the encouragement of companies to provide clear and comprehensive information in their statements and annual reports. To achieve full disclosure of the compensation figures and other particulars, the CPPIB has a range of methods to ensure this result materializes.
First, the board has a disclosure policy enshrined in its board laws. This Disclosure Policy specifies the kinds of information that must be published, such as director salary and share ownership. The policy specifies who is in charge of making disclosures, as well as when and how they should be made. Second, the board has a set of corporate governance guidelines. To provide guidance on the best practices for corporate governance, including director salary and share ownership, it has published Corporate Governance Guidelines. The rules are intended to encourage accountability and openness and to guarantee that the CPPIB upholds strict ethical standards. In the same vein, the board also emphasizes and practices full disclosure of transactions and operations.
The CPPIB complies with every provision and regulation that defines its existence. It is governed by several securities rules and regulations, including those relating to disclosure. To ensure compliance with these criteria, particularly those about director compensation and share ownership, the CPPIB has policies and procedures in place (Ambachtsheer, 2021). Lastly, the CPPIB emphasizes oversight. It is in charge of regulating the organization’s operations, including ensuring that disclosure laws are followed. The Audit Committee, which is in charge of monitoring financial reporting and disclosure, is one of the committees that the Board established to oversee particular facets of the CPPIB’s operations.
Executive Compensation
Executive compensation is a crucial component of Stantec Inc’s corporate governance practices. The organization’s chief remuneration program aims to attract and retain top talent while aligning leaders’ benefits with investors’ interests (Zhou et al., 2021). The Board of Directors Compensation Committee annually evaluates and approves the program. The executive compensation plan of WSP Global consists of both fixed and variable components. The majority of CEO compensation is connected to performance-based rewards like stock options and long-term incentive programs. Additionally, the program includes clawback clauses that, under certain conditions, allow the company to recoup executive income. Stantec Inc provides a thorough disclosure of all material information in its annual proxy statement, which shareholders and the general public can access.
One way the company communicates with shareholders about executive compensation concerns is through the annual advisory vote on executive remuneration. The goal of WSP World Wide’s chief remuneration program is to reward execution and align leaders’ interests with those of investors.
Information on Share Ownership and Senior Executive Compensation: An important practice that gives shareholders and investors transparency and accountability is the disclosure of senior executive pay and stock ownership. Companies that have their shares listed for public trading are required to provide executive salaries in their financial reporting (Wang et al., 2021). This declaration provides information on senior executives’ wages, bonuses, stock options, and other kinds of compensation.
Value-based pay plans are a type of incentive program that enables businesses to give employees ownership or value in the company. These programs give employees a stake in the company’s success and frequently aid in attracting and keeping top personnel. Equity-based compensation programs include things like options, restricted stock units, and grants of shares based on performance. Businesses can use these strategies to make sure that employee interests are in line with corporate objectives like fostering innovation or hitting particular financial targets.
Senior executives who own stock in the company they work for are said to engage in executive share ownership. As executives will gain from the success of the company by appreciating their shares, this method is frequently utilized to align their interests with those of shareholders. Executives may be inspired to accomplish long-term goals and objectives by ownership of company stock. Organizational share ownership might help companies keep their best employees since CEOs who own stock in the business may be less likely to quit for better possibilities.
In the business sector, loans to management and directors are contentious. Some businesses permit CEOs to borrow money from the business, while others forbid it. Loans to management and directors are a source of worry since they may lead to conflicts of interest and cast doubt on the executives’ moral character (Huang et al., 2018). Companies can be concerned that these loans could be utilized unethically or to manipulate stock prices. To address these issues, several businesses have put policies in place that forbid lending to managers and directors.
Companies may recoup executive salary through recoupment plans, also known as clawback policies, in specific situations, such as when the Executive commits malfeasance or the company’s financial performance deteriorates. Recoupment plans aim to increase accountability and bring together the interests of shareholders and executives (Saville & Muscat, 2021). Executives are motivated to operate in the firm’s best interests and refrain from activities that could hurt it by linking executive compensation to company performance. Recoupment procedures can also aid in regaining the trust of shareholders in businesses that have endured financial setbacks or moral transgressions.
Reference
Ambachtsheer, K. (2021). The Canadian pension model: Past, present, and future. The Journal of Portfolio Management, 47(5).
Boustani, M. and Pallavicini, S., 2019. Deposits and termination:’CPPIB Credit Investments Inc v Ren’and’Budiyanto v KPI 6 Pty Ltd’. AUSTRALIAN PROPERTY LAW BULLETIN, 34(1).
Elsayed, N. and Elbardan, H., 2018. Investigating the associations between executive compensation and firm performance: Agency theory or tournament theory. Journal of Applied Accounting Research.
Gray, T. (2005). Dual-class share structures and best practices in corporate governance.
Groysberg, B. (2021, January 1). Compensation Packages That Drive Performance. Harvard Business Review. https://hbr.org/2021/01/compensation-packages-that-actually-drive-performance
Riviere Lemmel, C., 2021. What is the impact of Private Equity Funds on LBO value creation? (Master’s thesis, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya).
Roller, S., 2019. Pension and state funds dominating biomedical R&D investment: fiduciary duty and public health. Globalization and health, 15, pp.1-11.
Sammer, J. M. (2013, May 21). Updating Salary Structure: When, Why, and How? SHRM; SHRM. https://www.shrm.org/ResourcesAndTools/hr-topics/compensation/Pages/Updating-Salary-Structure.aspx
Sarney, M., & Preneta, A. M. (2001). The Canada Pension Plan’s experience with investing its portfolio in equities. Soc. Sec. Bull.
Saville, S. and Muscat, P., 2021. Alternative assets insights. Taxation in Australia, 55(9), pp.484-486.
Williams, C. (2020). ‘Troubling Incrementalism’: Is the Canadian Pension Plan Fund Doing Enough to Advance the Transition to a Low-Carbon Economy?
Zhou, B., Li, YM, Sun, FC and Zhou, Z.G., (2021). Executive compensation incentives, risk level, and corporate innovation. Emerging Markets Review, 47, p.100798.
 write
write