In the contemporary workplace, keeping employees has become a crucial problem for businesses all over the globe. Retaining qualified and experienced personnel has become a big problem due to rising talent competition and shifting employee expectations. This essay examines employee retention with a particular emphasis on the contemporary workplace. Employee retention is crucial since it directly affects a firm’s performance, productivity, and stability. Increased recruiting expenses, knowledge loss, and team chemistry may all be the effects of high turnover rates. Therefore, it is crucial for businesses looking to foster a good and stimulating workplace to understand the elements affecting employee retention. The study’s research topic is the major elements influencing employee retention in contemporary workplaces and how businesses can successfully address them. The study aims to pinpoint the elements that affect employee retention, delve into the difficulties businesses confront, and provide tactics for raising retention rates.
The paper will have a section stating the research question and will be followed by an introduction offering background information and stressing the significance and difficulties of employee retention. A thorough assessment of the literature, the study methodology, the analysis of the results, and a discussion of the implications are covered in the following parts. The presentation will finish with suggestions for businesses and lines of inquiry for future studies. This article will provide a better knowledge of employee retention in the contemporary workplace, aiding firms in their efforts to provide a friendly and stimulating work environment that encourages employee loyalty and long-term success.
Research Review
Resource-Based Perspective on Staff Retention
The resource-based view (R.B.V.) hypothesis and its relevance to employee retention are introduced at the outset of the literature study. The R.B.V. places a strong emphasis on how organizational resources might improve retention. It asserts that businesses with valuable, uncommon, and unique resources are better equipped to draw in and keep top people (Barney, 1995). The review will review how the R.B.V. theory offers a framework for comprehending how resources and retention relate.
Analysis of the Effect of Retention Procedures on Human Resource Management
The impact of human asset board (H.R.M.) techniques on worker maintenance is analyzed in this segment. It analyzes a few H.R.M. strategies, for example, recruiting, picking, preparing, and creating workers, as well as their impacts on representative maintenance (S.H.R.M.,
2016). The study will assess how well employee engagement and loyalty are fostered through reward and performance management systems.
The literature study investigates the elements influencing employee retention, such as work-life balance, company culture, and employee engagement. It explores the connection between job happiness and retention, highlighting how contented workers are more inclined to remain with a company. The analysis also examines how organizational culture affects retention, highlighting the need for a supportive and encouraging culture. It also examines how employee engagement and work-life balance might help to increase long-term retention.
Leadership’s Effect on Retaining Staff
The effect of leadership on staff retention is the main topic of this section. It assesses how effective leadership is in fostering teamwork and commitment among workers. The study examines several leadership philosophies and how they affect employee retention and satisfaction (Kadam, 2021). It emphasizes how crucial relationship-building and excellent communication skills are for leaders in encouraging retention.
Age and Gender Variations in Demographics and Retention
The literature review investigates how age and gender differences, in particular, influence employee retention. It examines how various age groups’ incentives and preferences relate to retention. (Van Yperen & Wörtler, 2016) It also examines how gender variations in retention variables, such as work-life balance and possibilities for professional growth, vary.
Review of Pertinent Secondary Materials
This area includes research from academic journals, surveys, and industry reports. Combining up-to-date data with useful insights offers a thorough grasp of employee retention. In order to understand employee opinions on retention reasons and initiatives, the study includes data from surveys. In order to illustrate current trends and best practices in employee retention, it also combines information from industry publications. The part on the literature review provides a thorough study of the ideas and studies done so far on employee retention. By highlighting important elements and practical tactics for successful employee retention in the contemporary workplace, it lays the groundwork for the paper’s future parts. In order to provide readers with a comprehensive grasp of the subject, the study incorporates academic literature, industry reports, and survey data.
Methodology
Mixed-Methods Research Approach and Pragmatism Philosophy
This study will use a mixed-methods research methodology to examine employee retention in contemporary workplaces. This strategy integrates qualitative and quantitative methodologies to comprehend the study issue fully. The pragmatism concept served as the foundation for this study since it allowed researchers to choose the best methodologies and data sources to accomplish the study’s goals.
An investigation of the variables affecting staff retention will be done via a survey. The overview will accumulate information on various subjects, including the balance between fun and serious activities, organizational culture, and representative commitment (Brown et al., 2019). A blend of shut finished and questions that could go either way will be utilized to gather quantitative and subjective information. An electronic sample of workers from various companies and backgrounds will get the survey.
Interview and Sample Size Explanation
In-depth interviews will also be done in addition to the survey to understand better workers’ experiences and aspirations concerning retention. Because the interviews will be semi-structured, there will be freedom to examine the participants’ viewpoints (Smajic et al., 2022). Based on their survey replies, a sample of roughly 25 participants will be chosen to guarantee a broad mix of age, gender, and organizational responsibilities. Due to geographical restrictions, the interviews will be performed by video conference.
Secondary Data and Scholarly Journals
In order to enhance the analysis, the study will also use secondary data and scholarly articles. A theoretical framework will be provided, and the conclusions will be supported by a study of pertinent literature on leadership, human resource management techniques, and employee retention (Serra et al., 2018). To learn more about current trends and practices, it will be reviewed reports, surveys, and industry statistics on staff retention.
Justification for The Study’s Limitations and Selected Methodologies
Integrating quantitative and qualitative data, the mixed-methods approach thoroughly studies employee retention. This enables the triangulation of results, improving the study’s validity and reliability. While the interviews give in-depth information on workers’ thoughts, the survey offers a comprehensive picture of retention reasons. The theoretical groundwork is strengthened and given a real-world perspective via the incorporation of academic publications and secondary data.
There are certain restrictions on this research, however. First, self-reported data included in the survey and interviews may be biased due to respondents’ responses. Second, the results generalizability may be constrained by the sample size and makeup, which may not accurately reflect the total workforce (Serra et al., 2018). Third, since the research was cross-sectional, it may not have captured changes in retention variables over time. Despite these drawbacks, the technique enables a thorough investigation of employee retention in the contemporary workplace, offering insightful information for businesses and future research projects.
Survey Findings
Summary of Survey Respondents’ and Demographic Data
Members of the survey came from many associations and foundations. The member socioeconomics, including age, orientation, and hierarchical obligations, were accumulated to give an exhaustive image of the review populace. An overview of the survey respondents’ profiles will be provided in this section, showcasing the sample’s variety and representation.
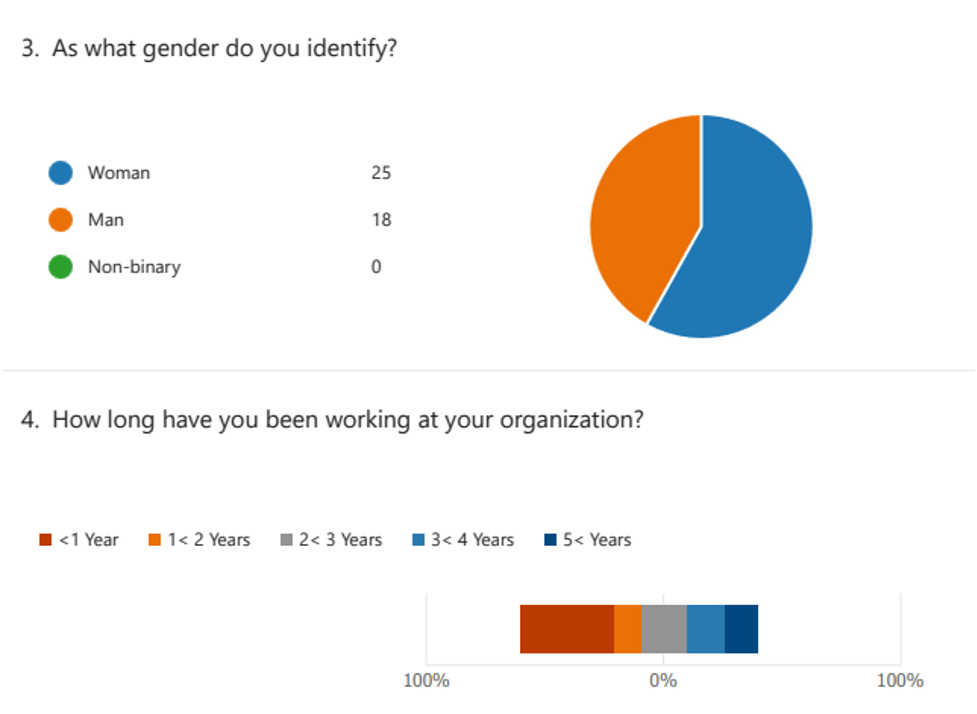
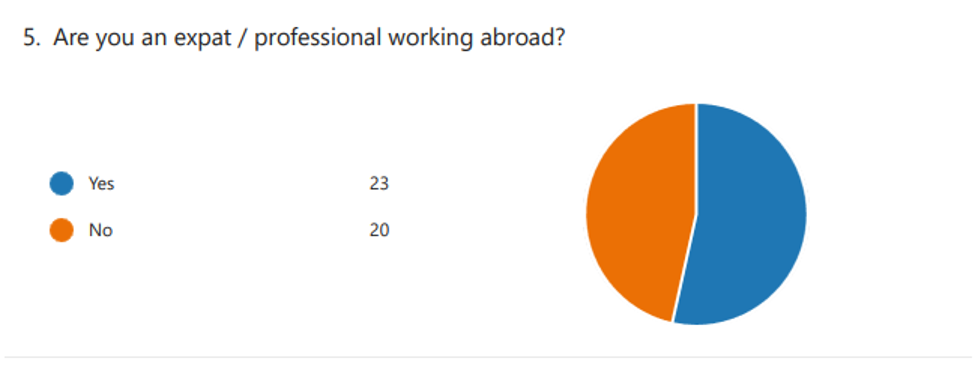
Analysis of Survey Data On the Most Important Variables Affecting Employee Retention
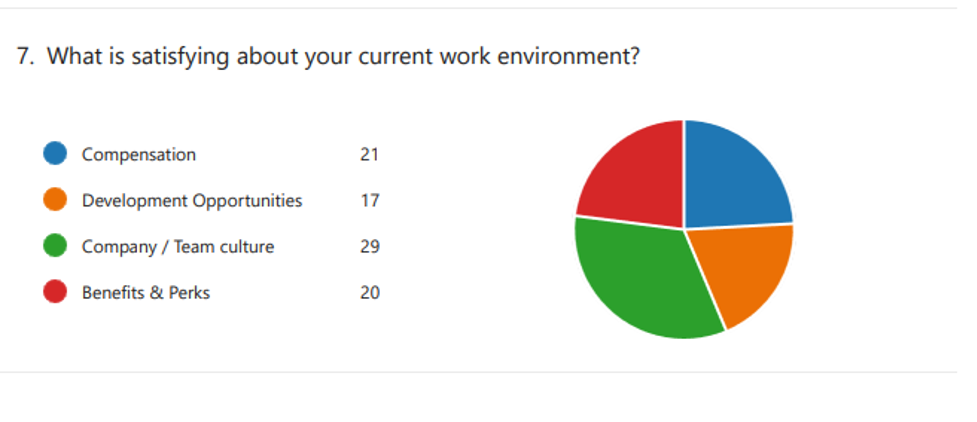
The results of the poll will be examined to determine the primary variables affecting employee retention in the contemporary workplace. This research will examine the respondents’ assessments and comments on employee engagement, work-life balance, company culture, and job satisfaction. It will light the elements influencing workers’ choices to work for their company.
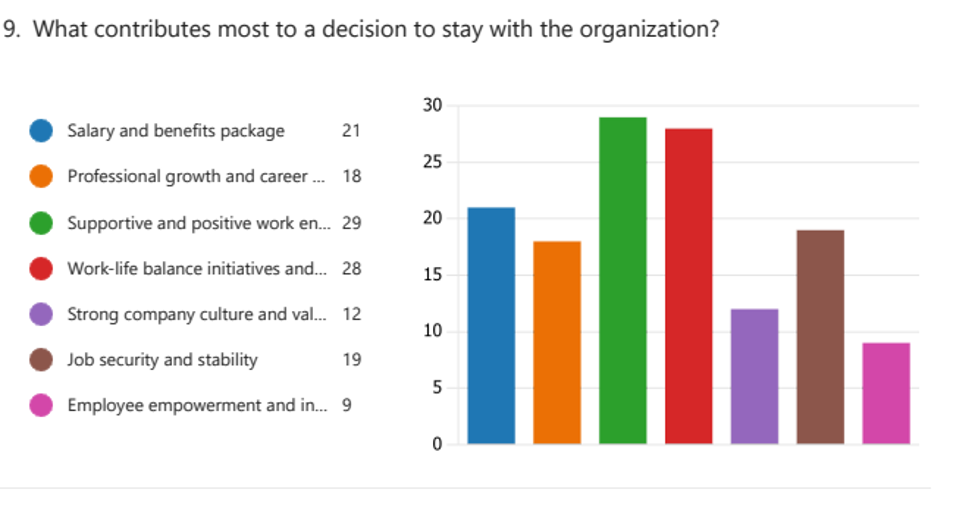
Comparing Retention Variables Based On Age and Gender Variations in The Population
A comparison of retention variables based on demographic variations, such as age and gender, will be done to understand the survey results better. This study will examine if different variables have different weights or effects based on a person’s age or gender. It will highlight any possible differences in retention requirements and preferences across various demographic groupings.
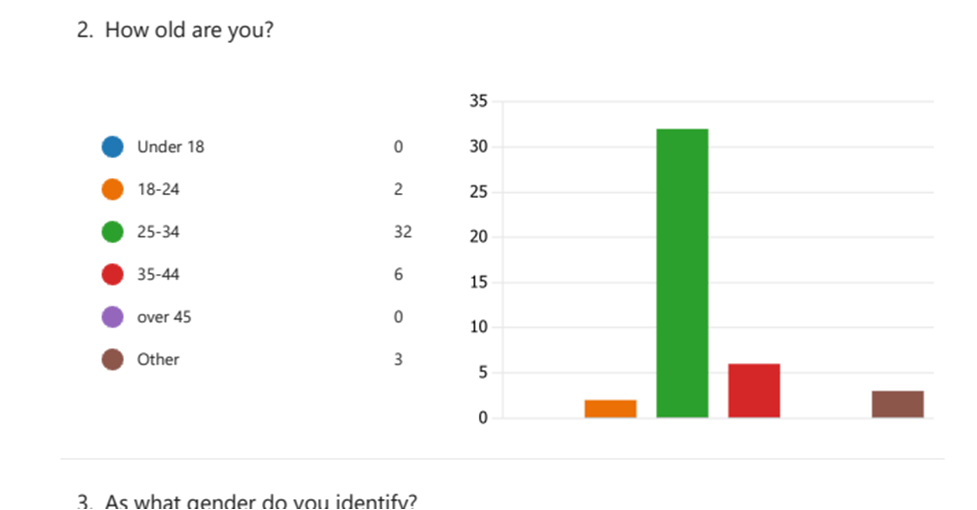
Analyzing How Workers See Leadership’s Contribution to Retention
Employee perceptions of leadership’s contribution to retention were also the subject of survey questions. This section will evaluate the data and provide insights into how workers see the influence of leadership on their choice to remain with the company (Kumar, 2021). It will investigate if staff members think successful leadership techniques, including communication, support, and acknowledgment, help keep them around.
The survey findings’ impact on our knowledge of employee retention in contemporary workplaces will be covered in this section. It will emphasize the most important research results concerning leadership, demographic variations, and retention-influencing variables. The discussion will include information on how businesses might use these results to create retention strategies that work (Kurdi et al., 2020). It will also discuss any contradictions or unexpected findings from the survey results and recommend possible study topics.
The survey results section will include a thorough analysis of the data, offering insightful information on the elements affecting employee retention in contemporary workplaces. The investigation will gain depth via comparisons based on demographic variables, revealing possible changes in retention factors across other populations. The analysis of the survey data will add to the body of research on employee retention and provide useful recommendations for businesses looking to enhance their retention tactics.
Interviews
Interviews and Choosing Participants
A sample of participants was chosen from the survey respondents to participate in the in-depth interview procedure. The selection process was designed to guarantee representation across the age, gender, and organizational positions spectrums. Video conferencing was used for semi-structured interviews, enabling candid and in-depth discussions on workers’ retention experiences and expectations (Kakilla, 2021). With the participants’ permission, the interviews were audio-recorded for precise data analysis.
Experiences and Aspirations of Workers
To learn more about workers’ retention experiences and expectations, the interview data will be presented and examined. Participants will discuss the aspects of their present employment that motivate them to remain with it and their perceptions of company culture, work-life balance, and employee engagement (Kakilla, 2021). The interviews will provide a comprehensive insight into the unique experiences and opinions of the participants via in-depth tales and anecdotes.
A candid examination of the interview replies will be conducted to learn more about how leadership affects employee retention. The examination will examine how participants see professional growth possibilities, support, communication, and other leadership techniques (Tian et al., 2020). The interviews will provide insight into the relationship between strong leadership and workers’ dedication and loyalty to the company. The results will be a great source of information for businesses looking to improve their leadership techniques to increase staff retention.
Combination of Survey Findings with Interview
The interview data will be combined with the survey findings to further our knowledge of retention dynamics in the contemporary workplace. A thorough picture of the variables impacting employee retention will be created by combining the interview information and survey answers. Integrating data sources will allow a more nuanced understanding of the unique experiences recorded in the interviews and the more general trends discovered in the survey (Kalyanamitra et al., 2020). The complexity of employee retention will be better understood due to this all-encompassing strategy, which will also help firms to foster a positive and stimulating workplace.
In-depth interviews will provide a more intimate and nuanced viewpoint on staff retention, complementing the survey results. An in-depth knowledge of the elements that influence workers’ decisions to remain with their present company will be possible due to the analysis of interview data, which will provide insightful information on the employees’ subjective experiences and expectations (Kurdi et al., 2020). The combination of interview data and survey findings will increase knowledge of employee retention dynamics and provide employers with useful information for enhancing retention strategies and cultivating more devoted and engaged employees.
Discussion and Analysis
Critical Assessment of the Survey and Interview Results
The findings from the interviews and the survey will be critically analyzed to determine their overall contribution to our knowledge of employee retention and their validity and reliability. It will be recognized and addressed if the data-gathering procedure has any biases or restrictions. The study will also spot any contradictions or unexpected results and look into possible justifications for them. The survey and interview results will be contrasted and compared to previously published works and ideas on employee retention (Kurdi et al., 2020). This comparison will show where the results agree or disagree, validating and contextualizing the results. It will also provide a chance to spot any gaps or places where further study is required to improve the state of the art in employee retention.
Examining the Effects on Businesses of Developing a Workplace that Focuses on Retention
The research will concentrate on the results’ implications for businesses seeking to establish a work climate that encourages employee retention. We will talk about the main ideas and tactics that came up in the poll and the interviews as they relate to actual use (Kurdi et al., 2020). There will be suggestions on how businesses may boost employee engagement, encourage work-life balance, and improve corporate culture to boost retention rates.
Discussion of the Interactions Between Variables Affecting Retention, Demographic Disparities, and Leadership
The interaction between leadership, demographic variances (such as age and gender), and the identified retention variables will be discussed in this section. The investigation will examine how good leadership practices affect retention outcomes for various demographic groups (Tenney, 2023). It will also cover methods for adjusting retention efforts to suit the various demands of workers and consider possible variances in retention variables depending on demographic characteristics.
The analysis and discussion part will critically assess the survey and interview results, placing them within the body of knowledge on employee retention. It will highlight the practical consequences of the results for employers and provide suggestions for developing a retention-focused work environment (Tenney, 2023). In order to increase retention rates and encourage long-term commitment, businesses need to handle their workers’ individual needs and expectations successfully. This interaction between leadership, demographic variations, and retention variables will be examined.
Recommendations
Suggestions for Measures to Increase Employee Retention in Light of Research Results
In light of the study’s results, several measures might be suggested to enhance employee retention in a contemporary workplace. These tactics include promoting work-life balance initiatives, creating a positive organizational culture, enhancing job satisfaction by offering meaningful work and career development opportunities, and boosting employee engagement through successful communication and recognition initiatives. These tactics must be customized to the company’s and its personnel’s unique requirements and preferences.
In order to successfully deploy retention techniques, leadership is essential. Leaders must emphasize fostering a healthy work environment, open and honest communication, support and mentoring, and employee involvement. Leaders should be responsible for creating and promoting retention-focused programs while coordinating them with the organization’s values and objectives. Additionally, they should pay attention to employee feedback and grievances and resolve problems that can influence retention. Organizations may foster a culture that appreciates and supports workers and improve retention rates by taking leadership duties seriously.
Alignment of Advice with Study Findings, Interview Data, And Conceptual Framework
The survey results, interview findings, and the study’s theoretical framework should all be considered when making recommendations. They have to consider the determined elements affecting retention, the function of leadership, and the effect of demographic variations. To ensure that the suggestions are relevant to and applicable to the population under study, they should be based on the unique insights and patterns found in the data analysis. Organizations may be confident in the suggestions’ efficacy and potential to increase employee retention by matching them to the study results.
The study’s conclusions and insights should serve as a roadmap for boosting employee retention in a contemporary workplace. Organizations may develop a supportive and stimulating work environment by implementing initiatives that address employee engagement, organizational culture, work-life balance, and job satisfaction. Furthermore, acknowledging the leadership duties involved in implementing these tactics will guarantee their success. Organizations may create focused and efficient retention strategies that address the varied demands of their workforce and promote long-term employee happiness and loyalty by coordinating the suggestions with the survey data, interview findings, and theoretical framework.
Conclusion
This research on employee retention in a contemporary workplace has shed important light on the variables that affect retention, the function of leadership, and the effect of demographic variations. The consequences of the review and meetings exhibited the worth of organization culture, the balance between fun and serious activities, and worker commitment in holding representatives. Powerful administration methods have likewise been demonstrated to empower representatives’ devotion and faithfulness. The research also showed that demographic variables like age and gender might impact employee retention rates.
The study’s conclusions have significant ramifications for businesses and H.R. professionals. Organizations may use the identified retention criteria as a guide when establishing initiatives to build a workplace prioritizing retention. H.R. professionals may be essential in implementing policies that boost employee engagement, advance work-life balance, and improve business culture. The report also underscores the need for firms to engage in leadership development programs and the significance of strong leadership in promoting employee retention.
Future studies in employee retention should keep probing the nuanced dynamics of retention in a workplace that is changing quickly. The knowledge of employee experiences and expectations would be furthered and richened by using the specific interview data from this research. It would enable a more thorough investigation of how leadership, demographic variations, and retention issues interact. The findings of the interviews may be incorporated into future research to provide a more comprehensive and nuanced perspective on employee retention, resulting in improved organizational policies and practices to increase employee happiness, engagement, and long-term commitment.
The main determinants of retention, the function of leadership, and the significance of demographic disparities have all been clarified by this research on employee retention in a contemporary workplace. The ramifications for businesses and H.R. professionals are substantial because they provide practical advice on developing a work environment that encourages employee engagement and pleasure. To further improve the knowledge of employee retention dynamics and contribute to the creation of successful retention strategies, future research should expand on these findings and include specific interview results.
References
Barney, J.B. (1995). Looking inside for competitive advantage | Academy of Management … Available at: https://journals.aom.org/doi/abs/10.5465/ame.1995.9512032192
Brown, A. R., Walters, J. E., & Jones, A. E. (2019). Pathways to Retention: Job Satisfaction, Burnout, & Organizational Commitment among Social Workers. Journal of Evidence-Based Social Work, 16(6), 577–594. https://doi.org/10.1080/26408066.2019.1658006
Kadam, R. et al. (2021) “Predicting organizational citizenship behavior in a multicultural environment: The role of Cultural Intelligence and cultural distance,” International Journal of Cross-Cultural Management, 21(3), pp. 602–624. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1177/14705958211051510.
Kakilla , C. (2021). Strengths and Weaknesses of Semi-Structured Interviews in Qualitative Research: A Critical Essay. Strengths and Weaknesses of Semi-Structured Interviews in Qualitative Research: A Critical Essay, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202106.0491.v1
Kalyanamitra, P., Saengchai, S., & Jermsittiparsert, K. (2020). Impact of Training Facilities, Benefits and Compensation, and Performance Appraisal on the A Job Satisfaction. Systematic Review Pharmacy, 11(3), 2020. https://doi.org/10.5530/srp.2020.3.19
Kurdi, B. A., Alshurideh, M., & Afaishat, T. A. (2020). Employee retention and organizational performance: Evidence from banking industry. Management Science Letters, 10(16), 3981–3990. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.msl.2020.7.011
Serra, F. A. R., Martins, F. S., & Cunha, J. A. C. da. (2018). Secondary Data in Research – Uses and Opportunities. Revista Ibero Americana de Estratégia, 17(4), 01–04. https://doi.org/10.5585/%20ijsm.v17i4.2723
Smajic, E., Avdic, D., Pasic, A., Prcic, A., & Stancic, M. (2022). Mixed Methodology of Scientific Research in Healthcare. Acta Informatica Medica, 30(1), 57. https://doi.org/10.5455/aim.2022.30.57-60
S.H.R.M., S.H.R.M. (2016) Shrm Benchmarking Report: $4,129 average cost-per-hire, S.H.R.M. S.H.R.M. Available at: https://www.shrm.org/hr-today/news/hrnews/pages/shrm-benchmarking-report-$4,100-average-cost-per-hire.aspx
Tian, H., Iqbal, S., Akhtar, S., Qalati, S. A., Anwar, F., & Khan, M. A. S. (2020). The Impact of Transformational Leadership on Employee Retention: Mediation and Moderation Through Organizational Citizenship Behavior and Communication. Frontiers in Psychology, 11(3). Frontiers in. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00314
Tenney, M. (2023). What are the challenges leaders face in finding and retaining great employees? – business leadership today, Business Leadership Today – The resource for leaders working to build and sustain world-class teams and organizations in today’s business environment. Available at: https://businessleadershiptoday.com/what-are-the-challenges-leaders-face
Van Yperen, N. W., & Wörtler, B. (2016). Blended Working and the Employability of Older Workers, Retirement Timing, and Bridge Employment. Work, Aging and Retirement, 3(1), 102–108. https://doi.org/10.1093/workar/waw036
 write
write