Introduction
Healthcare is a growing sector, and the management team must understand performance management and reward to ensure the organization operates effectively and efficiently. Performance management and reward are two critical components that play a crucial role in motivating and retaining employees and achieving organizational goals (Manzoor et al., 2021). This briefing paper aims to provide essential knowledge and understanding of performance management and reward for Healthcare on Hand’s management team. It will cover the purpose and components of performance management, factors to consider when managing performance, different performance review methods, key components of an effective total reward system, the relationship between reward and performance, and the reasons for treating employees fairly about pay.
-
Purpose and Components of Performance Management
Performance management is a process of measuring, managing, and improving individual and organizational performance. Its purpose is to ensure that employees are working towards achieving the organization’s objectives. Performance management provides a look into the future by identifying potential problems and minimizing risks. It helps create training strategies and improves clarity in the organization by defining employee roles, leading to increased productivity (Leggat, 2009). It provides a platform for feedback exchange, leading to improved communication and employee satisfaction. Effective performance management also encourages employee recognition and rewards, mentoring to increase performance and employee retention.
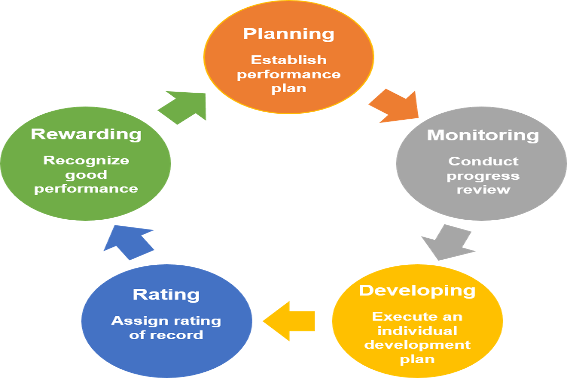
The key components of performance management include;
- Planning
- Monitoring
- Development,
- Rating
- Rewarding
Two critical components of performance management are Development and Rewarding. Development is crucial in performance management since employees need skills and knowledge before working to meet the set goals. Employees need to be trained to meet their future and new goals for higher performance. This component also provides employees with information on how well they are performing and what needs to be improved. Also, it provides employees with guidance, support, and encouragement to improve their performance. Rewarding is important since it is key to motivation and plays a big role in performance. To achieve maximum productivity, employers need to motivate employees through rewards. Its common knowledge that every employee always wants to be recognized for their achievements and efforts. With these rewards, employees can perform highly (Manzoor et al., 2021)
Source; https://www.google.com/url?sa=i&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.doi.gov%2Fpmb%2Fhr%2Fnon-ses-performance-management-toolbox&psig=AOvVaw2KlQEshqPFU3k-9FzMPkeD&ust=1679464082799000&source=images&cd=vfe&ved=0CBEQjhxqFwoTCKing7Op7P0CFQAAAAAdAAAAABAg
-
Factors to Consider When Managing Performance
Several factors need to be considered when managing performance. These include
- Job-related factors include the nature of the job, job requirements, and work processes.
- Organizational factors include the organization’s culture, structure, and leadership style.
- Team factors include teamwork, collaboration, communication, and providing feedback.
- Individual factors include employee motivation, skills, knowledge, and experience.
- Environmental factors include external factors that affect the organization, such as economic conditions and competition.
Two critical factors to consider when managing performance are individual (employee) factors, such as motivation, and Team factors, like providing feedback. Individual factors affect the performance of any organization is affected. Therefore, the individual’s skill, competence, motivation, and commitment are significant while managing performance. Management should be treated as part of the normal process, and its process should fit how work is done. Team factors like collaboration and feedback are elements in employee performance management that often creates controversy concerning cultural context feedback, given different ways of confronting conflict in different cultures, while the discomfort that surrounds critical feedback is more or less universal, leading to many of the problems with appraisal, it may be particularly acute in certain culture (Leggat, 2009)
-
Different methods of performance review
There are several methods for conducting performance reviews, including 360-degree feedback, Assessment centers, and behavioral checklist method. 360-degree feedback. This method is designed to obtain feedback from all angles. It gets feedback from managers, clients, supervisors, peers, and customers. This method is highly important in an organization. 360-degree feedback provides a broader perspective on employee performance and can lead to increased self-awareness, multiple sources of feedback, improved work relationships, team building, and improved customer relationships (Leggat, 2009). However, there are some disadvantages, including the potential for employees to compete against each other, slow feedback delivery, the unreliability of data, and confidentiality issues.
The assessment center method involves testing employees on their social interaction skills and job capabilities and can be used for selection, training, and promotion. It allows candidates to identify their strengths and weaknesses and is considered valid since many experts evaluate the candidate. However, this method takes a lot of work. Self-assessment involves employees evaluating their performance, while peer assessment involves colleagues evaluating each other’s performance.
The behavioral checklist method involves evaluating employees’ behaviors using a checklist with weighted responses. This method focuses on the critical behaviors required in the workplace. Its disadvantage is that it can be costly to implement.
-
Key components (financial and non-financial) that are required to achieve an effective total reward system
A total reward system is an all-inclusive approach to employee compensation involving monetary and non-monetary rewards. It encompasses more than fixed pay and benefits and considers intangible rewards like personal growth opportunities, job satisfaction, and a supportive work environment. A total reward approach aims to create a work atmosphere that meets employees’ requirements and encourages them to go beyond their usual work output. By combining various reward elements to complement and reinforce each other, total reward strategies can promote internal consistency and alignment with overall business goals (Armstrong, 2007).
A total reward system includes five key components. The first is base pay, which refers to the fixed salary or wages an employee earns based on job responsibilities, skills, and experience. The second component is contingent pay, which includes bonuses, commissions, and other variable forms of payment based on performance. Employee benefits are also important and can include health insurance, retirement plans, and other perks. Learning and development opportunities are the fourth component, including training and professional development. Finally, work experience, which includes the overall work environment, culture, and relationships between employees and managers, is also crucial. A positive work experience can lead to job satisfaction and engagement, while a negative experience can decrease productivity and turnover (Armstrong, 2007).
Reward systems offer several benefits, such as increasing productivity, eliminating the need for close supervision, and reducing employee turnover. However, increased costs and complexity are the main disadvantages of these systems.
-
The relationship between reward and performance and the links to motivation. (AC 5.2),
Maslow’s theory, developed by Abraham Maslow, argues that human needs are arranged in a hierarchical order, with physiological needs at the bottom and self-actualization needs at the top. The theory suggests that unfulfilled needs motivate behavior, and higher-level needs can only emerge once lower-level needs are met. Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory, on the other hand, developed by Frederick Herzberg, posits that job satisfaction and dissatisfaction are influenced by two types of factors, hygiene and motivator factors. Hygiene factors are necessary to maintain a reasonable level of satisfaction, and their absence leads to dissatisfaction. In contrast, motivator factors are inherent to the job and lead to higher satisfaction levels. According to Herzberg, an effective reward system must address hygiene and motivator factors to enhance employee motivation and performance (Surbhi, 2020).
The relationship between reward, performance, and motivation is complex. While rewards can increase motivation and improve performance, they need to be designed to meet employees’ specific needs and preferences (Johns et al., 2015). For example, monetary rewards may be effective for meeting lower-level needs. Non-monetary rewards may be more effective for addressing higher-level needs such as recognition and growth opportunities. Additionally, rewards must be tied to performance and achievement to motivate employees effectively.
Paying higher salaries to employees doesn’t necessarily lead to better performance. Money is important to prevent dissatisfaction, but more is needed to motivate employees. Job satisfaction, work-life balance, and growth opportunities are equally important for motivating employees and enhancing performance.
-
The relationship between reward and performance and the links to motivation
Treating employees fairly in terms of pay has numerous benefits for employees and employers. Firstly, it can attract and retain skilled and talented employees. Secondly, fair pay can increase employee motivation, engagement, and productivity. In addition, it can promote a positive organizational culture, leading to employee loyalty, collaboration, and commitment to the organization’s goals. This positive work environment can ultimately positively impact the organization’s overall performance. Many firms are beginning to offer more perks to employees to create a more employee-friendly culture (Fauver et al., 2018). However, it is important to consider whether this behavior aligns with maximizing shareholder value. Studies have shown that firms with a more employee-friendly culture, providing benefits, training, and equal opportunities for advancement, have higher valuations. Therefore, treating employees fairly in terms of payment can benefit employees and employers, ultimately contributing to the organization’s success.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, this briefing paper has provided the essential knowledge and understanding of performance management and reward for the Healthcare on Hand management team. It covers the purpose and components of performance management, factors to consider when managing performance, different performance review methods, key components of an effective total reward system, the relationship between reward and performance, and the reasons for treating employees fairly about pay. By understanding these concepts, the management team can improve their performance management strategies and design and implement an effective total reward system that aligns with the organization’s goals and objectives. This will ultimately result in increased employee productivity, job satisfaction, and reduced employee turnover, leading to overall success for the organization.
Reference
Armstrong, M. (2007). A Handbook of Employee Reward, 2nd ed, Kogan Page, London
Fauver, L., McDonald, M. B., & Taboada, A. G. (2018). Does it pay to treat employees well? International evidence on the value of employee-friendly culture. Journal of Corporate Finance, 50, 84-108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcorpfin.2018.02.003
Johns, R., Robinson, J., O’Leary, P. and Plimmer, G., (2015). Managing Employee Performance & Reward: Concepts, Practices, Strategies. Cambridge University Press.
Leggat, S. G. (2009). A Guide to Performance Management for the Health Information Manager. Health Information Management: Journal of the Health Information Management Association of Australia, 38(3), 11-17. DOI: 10.1177/183335830903800303.
Manzoor, F, Wei, L & Asif, M. (2021). Intrinsic Rewards and Employee’S Performance With the Mediating Mechanism of Employee’S Motivation. Frontiers in Psychology, vol. 12, https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.563070.
Surbhi S. (2020). Difference between Maslow and Herzberg’s Theories of Motivation [Online]. https://keydifferences.com/difference-between-maslow-and-herzberg-theories-of-motivation.html
 write
write