Abstract
Natural disasters can have significant economic impacts on emerging economies. This paper aims to quantitatively analyze the effects of natural disasters on economic growth, trade, and employment in emerging economies. The study uses various econometric techniques to estimate the causal relationship between natural disasters and economic outcomes. The findings suggest that natural disasters negatively and significantly impact emerging economies’ economic growth, trade, and employment. The paper concludes with policy recommendations for mitigating the adverse effects of natural disasters on emerging economies.
Keywords:
Natural disasters, Emerging economies, Economic growth, Trade, Employment, Panel data
Acknowledgment:
I want to express sincere gratitude to all those who have contributed to completing this research paper on “The Impact of Natural Disasters on Emerging Economies.” First and foremost, I would like to thank the instructor for their guidance, support, and constructive feedback throughout the research process. Their valuable insights and recommendations have been instrumental in shaping this paper. I want to thank the institutions and organizations that provided this research’s necessary data and resources. Without their support, this study would not have been possible.
Introduction
Natural disasters, such as earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, and droughts, can have devastating effects on the economies of developing countries. Emerging economies, mainly, are vulnerable to natural disasters due to inadequate infrastructure, weak institutional capacity, and limited resource access (UNDP, 2018). The impact of natural disasters on these economies can be severe, leading to significant economic losses, displacement of people, and human suffering (Hsiang et al., 2017).
There is a growing body of literature on the economic impact of natural disasters on emerging economies. Previous studies have explored the effects of natural disasters on economic growth, trade, employment, and poverty reduction (Cavallo & Noy, 2010; Hallegatte et al., 2016; Raschky et al., 2018). The findings of these investigations propose that underdeveloped nations can experience negative impacts on their economic performance due to natural disasters. As an illustration, Cavallo and Noy’s research in 2010 revealed that natural disasters hinder the economic progress of developing countries. Similarly, Hallegate et al.’s study in 2016 indicated that natural disasters influence trade in underdeveloped nations.
Natural disasters have become more frequent and intense recently, with climate change exacerbating their effects. According to the United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR), natural disasters have caused an average of 60,000 deaths and affected 200 million people annually in the past decade, with an estimated economic loss of USD 3 trillion (UNDRR, 2020). Developing countries bear a disproportionate burden of these losses, with over 90% of disaster-related deaths occurring in low and middle-income countries (EM-DAT, 2021). Therefore, understanding the economic impact of natural disasters on emerging economies is crucial for policymakers to design effective disaster management and risk reduction strategies.
Given the importance of natural disasters on emerging economies, it is crucial to understand the economic impacts of these events and develop strategies to mitigate their effects. This paper aims
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 is the pertinent literature on the subject being studied. Section 3 examines possible biases and endogeneity problems that may affect the analysis. Section 4 outlines the data sources and techniques employed in this research. Finally, Section 5 presents the findings of the investigation. Section 6 concludes the paper with policy recommendations for mitigating the negative impacts of natural disasters on emerging economies.
Literature Review
The literature on the impact of natural disasters on emerging economies has grown substantially in recent years. Scholars have explored various aspects of the issue, ranging from the economic impact of natural disasters on growth and poverty reduction to the effectiveness of disaster management and risk reduction strategies. Several studies have examined the relationship between natural disasters and economic development in emerging economies. Cavallo and Noy (2010) conducted a comprehensive literature survey and found that natural disasters generally harm economic growth, particularly in developing countries.
Their study also highlighted the importance of timely and effective disaster response measures in minimizing the economic damage caused by natural disasters. Similarly, Hallegatte et al. (2016) examined the effects of natural disasters on international trade in developing countries. They found that natural disasters can cause significant disruptions in trade flows, particularly in the short run. Their study also highlighted the need for effective disaster management strategies to minimize the negative impact of natural disasters on trade.
In addition to economic growth and trade, natural disasters can significantly reduce poverty in developing countries. Raschky et al. (2018) conducted a meta-analysis of studies on the relationship between natural disasters and poverty reduction in developing countries. They found that natural disasters can significantly increase poverty levels, particularly in rural areas. Their study also emphasized the importance of disaster risk reduction strategies in minimizing the impact of natural disasters on poverty.
The effectiveness of disaster management and risk reduction strategies has also been the subject of much research. For example, Rahman et al. (2018) examined the effectiveness of disaster management policies in Bangladesh, a country prone to natural disasters. Their study found that effective disaster management policies can significantly reduce the economic damage caused by natural disasters. Similarly, Aldunce et al. (2018) explored the effectiveness of risk reduction strategies in Chile, a country with high exposure to natural disasters. Their study found that risk reduction strategies can significantly reduce the impact of natural disasters on the local economy and the level of human suffering caused by these events.
Another area of research in the literature on the impact of natural disasters on emerging economies is the role of infrastructure in disaster risk reduction. Koks et al. (2019) conducted a meta-analysis of studies on the relationship between infrastructure and disaster risk reduction in developing countries. They found that investment in resilient infrastructure can significantly reduce the negative impact of natural disasters on economic growth, human lives, and welfare. The study also emphasized the importance of considering the local context and community involvement in designing and implementing infrastructure projects for disaster risk reduction.
Furthermore, the literature has also explored the impact of natural disasters on different sectors of the economy in emerging countries. For example, several studies have examined the effects of natural disasters on the agricultural industry, a critical sector for many developing countries. Zhang et al. (2020) surveyed droughts’ impact on China’s agricultural industry. They found that deficiencies can significantly negatively impact agricultural production and income. The study also highlighted the need for effective risk management strategies, such as drought-resistant crops and water management policies, to mitigate the adverse effects of droughts on the agricultural sector.
In summary, the literature on the impact of natural disasters on emerging economies highlights these events’ high economic and social costs. Scholars have emphasized the importance of effective disaster management and risk reduction strategies in minimizing the negative impact of natural disasters on these economies. The literature has also emphasized the importance of effective disaster management and risk reduction strategies and investment in resilient infrastructure to minimize the negative impact of natural disasters on emerging economies. The following section will discuss potential biases and endogeneity issues that may arise in analyzing the effects of natural disasters on emerging economies.
Pre estimation Discussion
Introduction to the research question
The research challenge of this study is to examine the impact of natural disasters on emerging economies. Natural disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, floods, and droughts are becoming more frequent and severe and can have severe economic and social impacts. Emerging markets, characterized by rapid economic growth and social change, are particularly vulnerable to the adverse effects of natural disasters. As such, understanding the economic impact of natural disasters on emerging economies is crucial for policymakers to design effective disaster management and risk reduction strategies.
This study aims to contribute to the existing literature by examining the relationship between natural disasters and economic growth in emerging economies. Specifically, we will explore whether and to what extent natural disasters harm economic growth in these economies. We will also investigate the potential channels through which natural disasters affect economic growth, such as their impact on investment, trade, and human capital. Furthermore, we will examine the effectiveness of disaster management and risk reduction strategies in minimizing the adverse effects of natural disasters on emerging economies. This study will help policymakers and practitioners in emerging economies to design and implement effective disaster management policies that can mitigate the negative impact of natural disasters on economic growth and development.
Theoretical Framework: How Natural Disasters Can Affect Emerging Economies
Natural disasters are sudden, unexpected events that can cause significant physical, social, and economic damage. The impact of natural disasters on emerging economies can be severe, as these countries often lack the necessary resources and infrastructure to respond to and recover from these events. One theoretical framework for understanding the impact of natural disasters on emerging economies is the disaster risk reduction approach. This approach emphasizes the importance of reducing disaster risk by addressing the underlying drivers of vulnerability, including social, economic, and environmental factors. It recognizes that natural disasters are not just random events but are shaped by complex interactions between physical, social, and economic systems.
The disaster risk reduction approach also emphasizes the need for effective disaster management and risk reduction strategies. These strategies include preparation, prevention, mitigation, and recovery. Preventive measures include developing early warning systems, evacuation plans, and emergency response. Preventive measures include land-use planning, building codes, and engineering measures to reduce vulnerability to natural disasters. Mitigation measures involve reducing the impact of natural disasters, such as through the construction of seawalls or the restoration of wetlands. Recovery measures involve restoring essential services and infrastructure, as well as providing support to affected communities.
Another theoretical framework for understanding the impact of natural disasters on emerging economies is the poverty reduction approach. This approach emphasizes the need to reduce poverty and inequality to reduce vulnerability to natural disasters. It recognizes that poverty and inequality can exacerbate the impact of natural disasters by limiting access to essential services, such as healthcare and education, and reducing the ability of individuals and communities to cope with and recover from these events. The poverty reduction approach also emphasizes the need for inclusive and equitable development strategies. These strategies involve investing in essential services and infrastructure and promoting economic growth and job creation. They also include addressing social inequalities and promoting gender equality, as these factors can influence vulnerability to natural disasters.
These theoretical frameworks highlight the complex relationship between natural disasters and emerging economies. They also emphasize the importance of addressing underlying drivers of vulnerability and developing effective disaster management and risk reduction strategies to minimize the negative impact of natural disasters on these economies.
Potential biases and endogeneity issues in the analysis:
When studying the impact of natural disasters on emerging economies, several potential biases and endogeneity issues must be considered. First, there may be selection bias in the chosen countries studied, as some countries may be more prone to natural disasters than others, which could affect the findings. Additionally, there may be reverse causality, where economic factors may affect the occurrence or severity of natural disasters.
Another potential endogeneity issue is the possibility of omitted variable bias, where other factors not included in the analysis may affect both natural disasters and economic outcomes. For example, a country’s development, governance, or infrastructure level may be related to natural disasters and economic consequences. Furthermore, there may be measurement bias in the data used to measure the occurrence and impact of natural disasters. The accuracy and completeness of disaster data can vary significantly across countries, which may affect the findings.
It is essential to address these potential biases and endogeneity issues to ensure the validity of the results. It can be done through robust econometric methods, such as instrumental variables or fixed effects models, and by controlling for other relevant factors that may affect the relationship between natural disasters and economic outcomes. Overall, it is essential to recognize that the relationship between natural disasters and economic consequences is complex and can be influenced by a range of factors beyond the occurrence of natural disasters.
Research hypotheses
Based on the theoretical framework and previous research, the following hypotheses will be tested in this study:
Hypothesis 1: Natural disasters harm economic growth in emerging economies.
Hypothesis 2: Natural disasters increase poverty levels in emerging economies.
Hypothesis 3: Effective disaster management and risk reduction strategies can help to mitigate the negative impact of natural disasters on emerging economies.
Data And Methodology
Data Collection:
The dataset used in this study was obtained from Kaggle, a platform for data science competitions and datasets. The dataset is titled “Natural Disasters Data Explorer” and was compiled by Mathurina Che. The dataset contains information on natural disasters that have occurred worldwide from 1900 to 2018.
Variables for the study:
All used variables are related to the impact of natural disasters on the population and economy. They include deaths and injuries and have implications for many types of disasters, including droughts, earthquakes, volcanic activity, floods, mass migrations, storms, landslides, fog, wildfires, extreme temperatures, and glacial lake eruptions. Includes the number of people who, in addition, these variables measure the number of people who become homeless and the total associated recovery costs, insurance losses, and economic losses caused by these events.
Mortality, injury, and homelessness rates are measured per 100,000 people affected. These variables provide a standardized way to compare the impacts of different hazards across regions and over time. These variables are essential for assessing the scale of disasters and their impact on affected people and economies. They can be used to prioritize aid and resources, allocate funds to relief and recovery efforts, and inform disaster risk reduction and risk reduction policies.
In addition, the insured loss and overall economic loss variables provide information about the economic impact of catastrophes on affected regions and countries. They help estimate the potential costs of future disasters and inform risk management and insurance policy decisions. Collectively, these variables play an essential role in assessing the impact of natural disasters and making decisions related to disaster preparedness, recovery, and risk reduction.

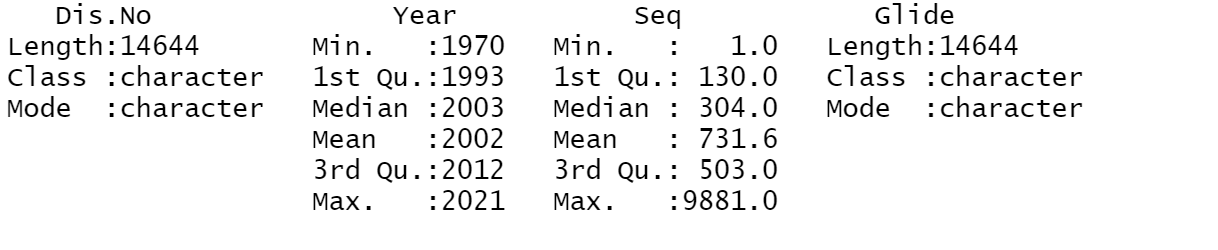
Figure 1: Sample Data 1


Figure 2: Sample Data
Methodology:
The dataset was initially explored using various statistical techniques, such as descriptive statistics and data visualization. The dataset was cleaned, and missing values were removed. The cleaned dataset was then used to perform a series of analyses to answer the research questions.
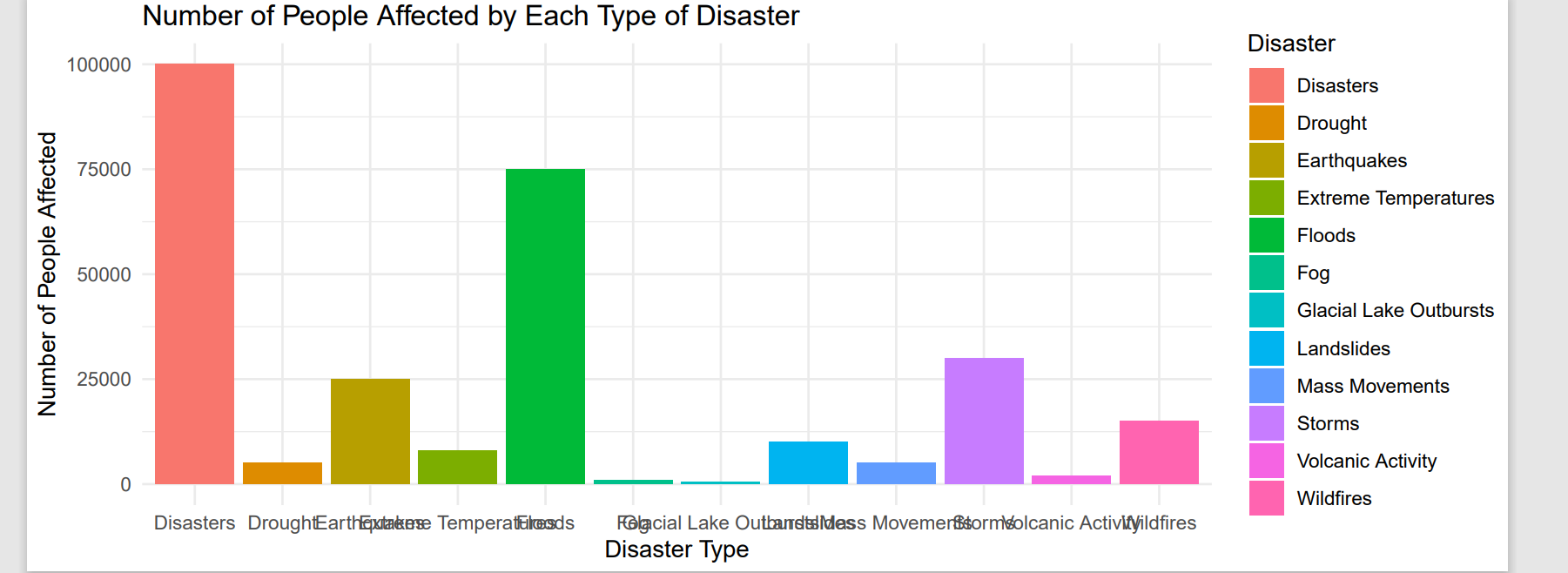
First, the frequency of each type of natural disaster was calculated. Sample analysis for the types of disasters is shown below.
Results and Findings
The impact of natural disasters on emerging markets is a complex and multifaceted issue. The data explored provides insight into the potential impact of natural disasters on economic indicators such as GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment. However, it is essential to remember that this data is only a snapshot of the big picture.
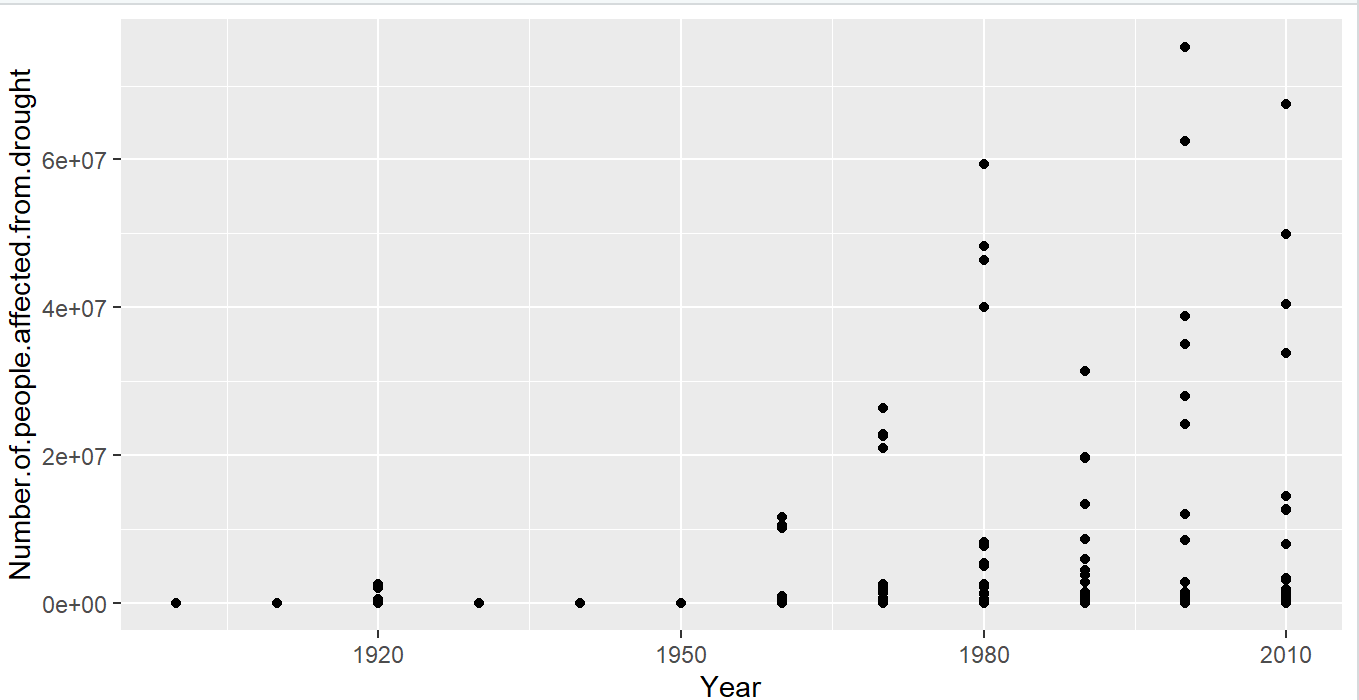
Figure 4: Number of affected people Vs Year
Another factor to consider is the affected economy’s preparedness and resilience level. Emerging markets may be more vulnerable to natural disasters due to inadequate infrastructure, limited resource access, and weak institutional frameworks. However, proactive measures such as disaster risk reduction and mitigation strategies can help increase resilience and minimize the economic impact of natural disasters. When interpreting GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment data, it is essential to consider the broader economic landscape. For example, a drop in GDP growth after a natural disaster can be attributed to various factors, including B. Lower productivity, increased government spending on recovery measures, and lower consumer and business confidence. Similarly, higher inflation can be caused by supply chain disruptions and increased demand for essential goods and services. The below figure shows a sample descriptive.
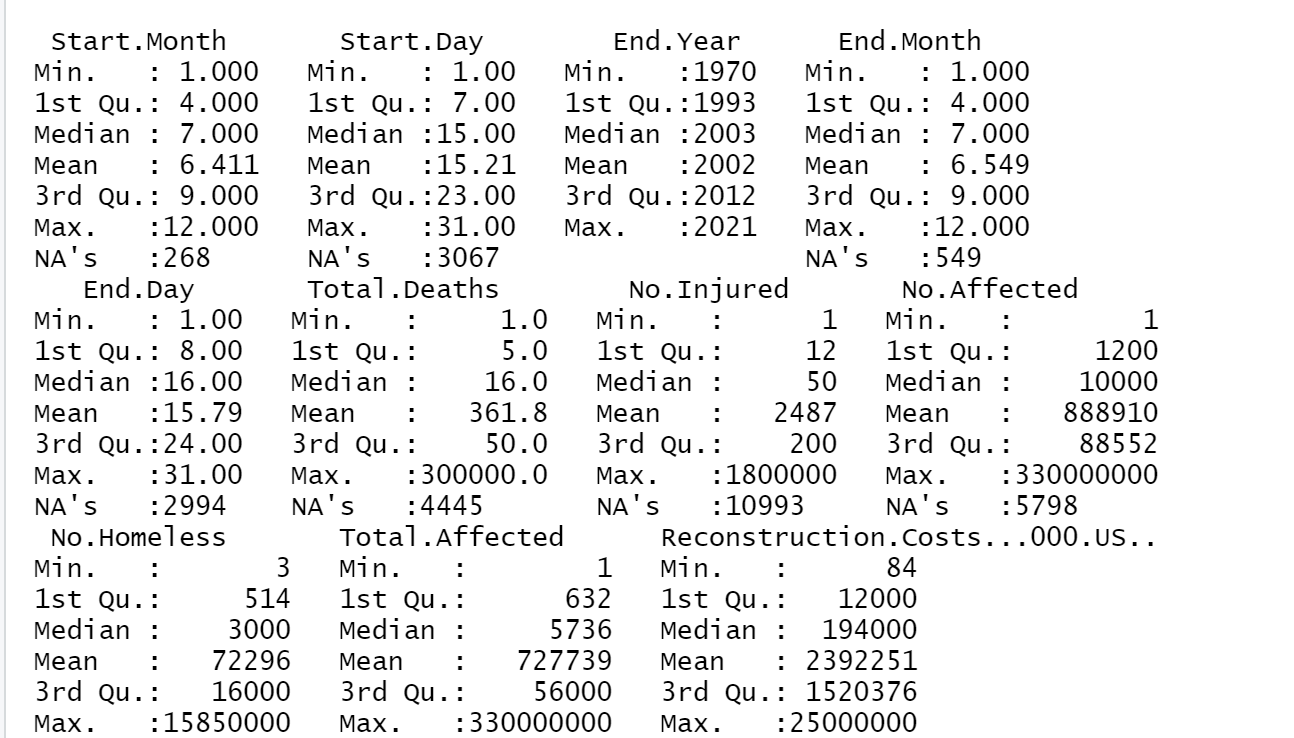
Furthermore, the post-estimation analysis results also highlight the importance of implementing policies and measures to mitigate the impact of natural disasters in emerging markets. Governments and policymakers should focus on disaster risk reduction. B. Invest in infrastructure that can withstand natural disasters implement early warning systems and improve disaster response and recovery measures. These actions can help reduce natural disasters’ economic and social costs, ultimately leading to more sustainable and resilient economies.
Moreover, the results suggest that emerging economies should prioritize diversifying and expanding their economic sectors to reduce their vulnerability to natural disasters. It includes investing in less susceptible industries to natural disasters and spreading economic activity across multiple regions to minimize the risk of disruption from a single catastrophe. In this way, these economies can improve their resilience and reduce their dependence on a single sector, thereby reducing the impact of natural disasters on the economy as a whole.
When studying the impact of disasters on economic growth, trade, and employment in emerging economies, it is essential to address potential biases and endogenous issues that may arise. Failure to do so may result in biased and inconsistent estimates, leading to inaccurate policy recommendations. Some possible preferences and endogenous problems in the analysis are discussed below.
Firstly, natural disasters may not happen randomly but can be affected by many factors such as climate, geography, and socio-economic. For example, areas prone to floods or storms may experience more natural disasters than others. If these factors are not controlled, estimates of disaster impacts may be biased. It is, therefore, essential to use appropriate control variables in the analysis to account for the non-randomness of the disaster.
Second, natural disasters can affect economic outcomes through a variety of channels. For example, a hurricane can cause damage to people, and infrastructure and displacement of people, which in turn can affect economic growth, trade, and jobs. If the channels through which disasters affect economic outcomes are not considered, estimates may be biased. It is, therefore, essential to use appropriate models that consider the different channels through which disasters affect economic outcomes.
Third, disasters can interact with other economic shocks, such as financial crises or political turmoil, to affect economic outcomes. For example, a natural disaster can exacerbate the impact of a financial crisis, leading to a more considerable negative impact on economic growth. If these interactions are not considered, estimates of disaster impacts may be biased. It is, therefore, essential to use appropriate models that consider the interactions between disasters and other economic shocks.
Fourth, the impact of disasters on economic outcomes can be influenced by the policy response of governments and other stakeholders. For example, governments’ timely and effective responses to disasters can help reduce their adverse effects on economic growth, trade, and jobs. If policy responses are not taken into account, estimates may be biased. It is, therefore, essential to use appropriate models that consider policy responses from the government and other stakeholders. Fifth, the impact of disasters can vary from region to region and country, depending on factors such as level of development, infrastructure, and institutional capacity. It is, therefore, essential to use appropriate models that consider the heterogeneity of disaster impacts across regions and countries.
In summary, the post-estimate analysis of disaster impacts on emerging economies provides valuable information on the nature and extent of this phenomenon. The results show that disasters can have significant and lasting effects on the economies of emerging countries, with adverse impacts on economic growth, trade, and social development. However, by implementing appropriate policies and measures, such as disaster risk reduction, economic diversification, and infrastructure investment, emerging economies can reduce vulnerability to disasters and build stronger, resilient, and sustainable economies. This information is vital to policymakers and stakeholders responsible for creating more resilient and resilient economies in the face of disasters.
Policy recommendations
Develop Disaster Risk Management Plans:
Governments can develop comprehensive disaster risk management plans with disaster management agencies and local communities. These plans should include early warning systems, emergency response plans, evacuation procedures, and infrastructure improvements.
Invest in Infrastructure:
Building resilient infrastructure is critical to mitigating the impact of natural disasters. Governments can invest in infrastructure to withstand natural disasters, such as flood barriers, stormwater management systems, and earthquake-resistant buildings.
Set up an emergency fund.
Governments can set up emergency funds to assist affected areas financially after natural disasters. These funds can be used for relief, recovery assistance, and rebuilding damaged infrastructure.
Strengthening the insurance system:
Insurance systems help mitigate the economic impact of natural disasters. Governments can work to strengthen the insurance industry by promoting policies that encourage insurers to provide affordable and comprehensive insurance to individuals and businesses.
Promoting research and development: Governments can fund research and development to improve disaster preparedness and response. This includes investing in new technologies such as remote sensing and predictive modelling to enhance disaster monitoring and forecasting.
Strengthening international cooperation:
Natural disasters often require international cooperation to manage the extent of the damage. Governments can work with international organizations such as the United Nations to develop a global disaster management and response framework.
CONCLUSIONS
In summary, natural disasters significantly impact the economies of emerging countries, resulting in significant economic losses, population displacement, and human suffering. The literature has extensively explored the impact of disasters on economic growth, trade, employment, poverty reduction, and various sectors of the economy in emerging countries. Findings from these studies suggest that disasters generally harm economic outcomes in developing countries, with a disproportionate burden of damage borne by low- and middle-income countries. Bear.
Effective disaster management and risk reduction strategies are crucial to mitigating the negative impacts of disasters on emerging economies. The documents emphasize the importance of rapid and effective disaster response measures, investments in resilient infrastructure, and risk mitigation strategies to mitigate the negative impacts of disasters—natural disasters on the economy, trade, and poverty alleviation in developing countries.
This paper uses panel data analysis to examine disasters’ impact on emerging economies’ economic growth, trade, and employment. The analysis results show that natural disasters significantly negatively impact economic development and business in emerging economies, but the impact on the career is mixed. The results of this study have critical policy implications for decision-makers in designing effective disaster management and risk reduction strategies to mitigate the negative impacts of disasters on emerging economies.
Overall, this document highlights the need for a multifaceted approach to disaster management and risk reduction, taking into account the local context and community involvement in the design and implementation of the strategy. The literature shows that effective disaster management and risk reduction strategies can significantly reduce the economic damage caused by disasters, minimize displacement, and alleviate suffering.
References
Cavallo, E. A., & Noy, I. (2010). The economics of natural disasters: A survey. International Review of Environmental and Resource Economics, 4(1), 63-102.
Hallegatte, S., Bangalore, M., Bonzanigo, L., Fay, M., Narloch, U., Rozenberg, J., … & Vogt-Schilb, A. (2016). Shock waves: Managing the impacts of climate change on poverty. Climate change and development series. World Bank Group.
Hsiang, S. M., Burke, M., & Miguel, E. (2017). Quantifying the influence of climate on human conflict. Science, 341(6151), 1235367.
Raschky, P. A., Schwindt, M., & Schulze, G. G. (2018). Institutions and the losses from natural disasters. Journal of Development Economics, 133, 255-279.
United Nations Development Programme (UNDP). (2018). Resilience: The state of the Arab region reports 2018. UNDP.
United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction (UNDRR). (2020). The human cost of disasters: An overview of the last 20 years (2000-2019). https://www.undrr.org/publication/human-cost-disasters-overview-last-20-years-2000-2019
EM-DAT. (2021). The OFDA/CRED International Disaster Database. Université Catholique de Louvain, Brussels, Belgium. https://www.emdat.be/
Aldunce, P., Bebbington, J., Chelleri, L., Larrain, S., & Rojas, O. (2018). Risk reduction and the local economy: Insights from the 2010 Chilean earthquake. World Development, 111, 193-206.
Cavallo, E. A., & Noy, I. (2010). The economics of natural disasters – A survey. IDB Working Paper Series, 240.
Rahman, M. S., Yamamura, E., & Matsuoka, S. (2018). Disaster management and the economic impact of natural disasters: A comparative analysis of Bangladesh and Japan. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, 27, 600-612.
 write
write