From Earth, the moon looks different as it moves around the Earth. As it moves, the shape looks like a crescent, then a circle, and then back to a crescent. As the moon moves around the Earth, the shape changes ( Guo et al.,2018). The observer looks at different parts of the moon’s surface that are lit up each day. When the moon goes through its phases, it shows up in a lot of different places. In every month, the moon goes through all of its different stages.
A lot of sunlight that is reflected from Earth to the moon makes only a small part of the moon visible. This makes the rest of the moon only visible in very weak detail. Because the rest of the moon is facing Earth, this is why. It moves west each night.

An Earth-based person may see more of the sun’s rays each night because the line moves. “Half moon”: People call it that when they see half of a full moon after seven days( Guo et al.,2018). During the synodic month, “first quarter” refers to that part of the time. Soon, the moon will be on the other side of Earth from the sun. People can now see every single bright side.
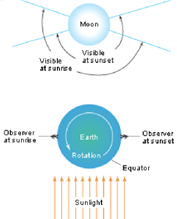
An observer’s daily movement in position relative to the moon causes diurnal libration. Consider a person at the equator of the Earth during a full moon. As the Earth circles from west to east, the spectator sees the moon rise on the eastern horizon and set on the western horizon. During this time, the observer’s viewpoint varies by around 7,900 miles (12,700 kilometers) in reference to the moon. As a result, the moon seems to rotate westward. The observer may see the western edge of the near side as the moon rises in the east. This is because the moon is dropping to the western horizon. Moon’s eccentric orbit causes longitude liberations.
Cirrus clouds may be seen from a height of 18,000 feet in the sky. Because of its capacity to reflect light, this kind of cloud is famed for producing spectacular sunsets and sunrises. Cirrus clouds, which are among the highest in the sky, tend to shine more brightly during golden hour.
At night, when the sky becomes crimson, it’s a lot of fun to sail because you get to see some magnificent sunsets. However, what distinguishes certain sunsets from the others?
As the sun sets, the sky transforms into a kaleidoscope of red, orange, and pink. When the sun goes down, the sky becomes red. The stronger the tones, the better in terms of color.
Because of a scientific phenomenon known as “light scattering,” as the sun sets, the colors we perceive seem to change or stay the same. Lasers cause particles in the atmosphere to disperse and change direction.At sunrise and sunset, the sun’s rays have an easier time penetrating Earth’s atmosphere because it is lower on the horizon. As it travels through the atmosphere, the sun disperses an increasing amount of particles.
During sunset, the sky becomes scarlet, and the air is filled with moisture and dust particles. Because it has the longest wavelength of any hue in the visible spectrum, we name it red. Because of this, we have come to this conclusion(Ye et al., 2018). The fact that they’ve been deconstructed makes them difficult to see. Colors such as blue serve as a good illustration. For the same reasons, the sky stays clear all day. The shorter wavelengths of blue light make it more broadly diffused than other colors. Due to the changing seasons, sunsets become more beautiful throughout the year. NOAA says fall and winter in the eastern United States are the best seasons to see sunsets.
References
Guo, H., Liu, G., & Ding, Y. (2018). Moon-based Earth observation: Scientific concept and potential applications. International Journal of Digital Earth, 11(6), 546-557.
Ye, H., Guo, H., Liu, G., & Ren, Y. (2018). Observation scope and spatial coverage analysis for earth observation from a Moon-based platform. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 39(18), 5809-5833.
 write
write