An overview of the concept
Project Management Institute (PMI) is a non-profit organization aiming to promote the best project management practices. PMI was established to address the increasing demands of the project management industry. It recognizes that project management methods and techniques are continually evolving, especially in software projects. PMI published the Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) to promote consistency and uniformity in the field. PMBOK is a recognized standard for project management and serves as a comprehensive guide for managing projects effectively (Jolley, 2021). The organization produces and promotes this Guide, a benchmark for project management professionals.
Projects are typically non-permanent, meaning they have a defined start and finish date, fixed scope and resources. They are also considered unique endeavours, as they are not part of an organization’s regular operations but rather a set of organized actions to achieve a specific goal. Project teams often include individuals who do not typically work together, such as employees from different companies or countries. Examples of projects include creating software to improve company operations, building bridges or structures, disaster recovery efforts, and expanding sales to new regional markets. These projects must be managed effectively to achieve successful outcomes, including staying within budget and completing them on time.
In summary, PMI is an organization that promotes best practices in project management by providing guidance and resources through PMBOK. Its goal is to make the field consistent, comprehensive and straightforward. A project is a temporary and unique effort with a defined start and end date and a specific goal, which must be managed effectively to achieve desired outcomes within budget and schedule.
Ten PMI Standard Project Management
- Project management is a complex process involving coordinating various aspects of a project to achieve its goals. One crucial aspect of project management is integration management, which involves creating a scope statement, project charter, and strategy for leading, managing, tracking and controlling changes to the project (Jolley, 2021).
- Another critical aspect of project management is scope management, which involves breaking the project into smaller components and maintaining them through a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS). This process includes preparation, identification, development, verification, and control of the WBS.
- Managing the project schedule is also crucial, as projects have a specific start and end date, and it is essential to keep the project on schedule and within budget. This involves definition, duration, sequencing, estimating resources, scheduling, and monitoring the schedule.
- Cost management is also an essential aspect of project management as it involves controlling the project’s cost by planning resources, budgeting, forecasting costs and controlling the expense.
- Quality management is also an essential aspect of project management; it ensures the deliverables meet the performance and project expectations by implementing quality assurance, planning and control.
- Managing human resources is an essential aspect of project management; it involves recruiting, planning and building a project team, monitoring their performance and keeping them on track.
- Communication management is also vital in project management; it requires effective communication planning, performance reporting, information distribution, and stakeholder management to ensure the stakeholders are informed about the project’s progress and outcome.
- Risk management is a critical aspect of project management; it involves identifying potential risks, analyzing their likelihood and impact, and taking steps to mitigate or avoid them. It is important to have risk planning, recognition, response planning, analysis, tracking, and control as critical components to manage the risk.
- Procurement management involves managing the purchase and contracting strategies, buyers’ responses and choices, contract management, and contract termination. It is crucial to select and maintain vendors throughout the life cycle of a project.
- Stakeholder management is a crucial part of project management; it involves recognizing stakeholders early on in the project, assessing their level of interest and power to affect the project, and managing their interactions and relationships with the project.
In summary, project management is a complex process involving many different aspects that must be coordinated to achieve the project’s goals. These aspects include integration management, scope management, schedule management, cost management, quality management, human resource management, communication management, risk management, procurement management, and stakeholder management. Each of these aspects plays a crucial role in ensuring the project’s success.
GANNT Chart
The representation of project timelines using GANTT charts is a common practice in project management. American mechanical engineer and management consultant Henry Gantt invented them in the 1910s to show how a project was progressing over time (Pellerin & Perrier, 2019). The activities, resources, and general progress of a project are planned, scheduled, and monitored using Gantt charts. A GANTT chart shows a project’s timetable clearly and visually. It displays each job’s beginning and ending dates and interdependencies (Pellerin & Perrier, 2019). Project managers and team members can easily comprehend the project timeline and see any possible problems or delays. Project timelines are frequently communicated to sponsors and stakeholders using Gantt charts.
Typically, a GANTT chart has the following significant components:
- The project’s tasks are listed from left to right in this document.
- Each task’s start and finish times are shown by horizontal bars on a timeline.
- The arrows linking one job to another reflect the interdependence between those tasks.
- The project’s total timetable, shown as a horizontal line spanning the project’s duration
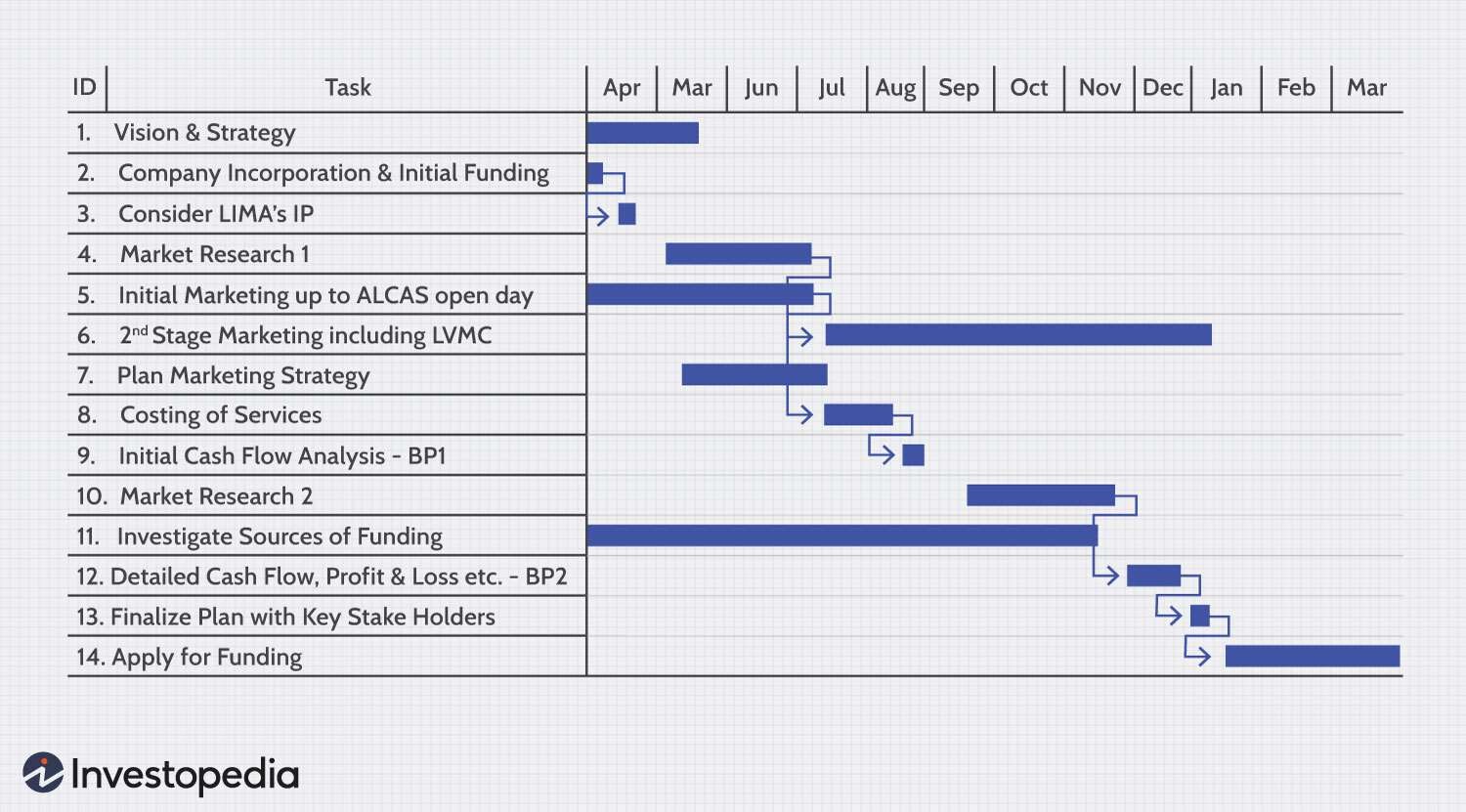
Figure: Example of a GANNT Chart (Grant, 2023)
Important Terms
The project management strategy is strongly tied to scope management, a crucial component of project management. Instead of existing as a separate document, the scope management plan frequently becomes part of the overall project management strategy.
Gathering technical specifications, which entails obtaining detailed information about the finished good or service being given, is a critical aspect of scope management. The project’s goals and deliverables are better-defined thanks to this method.
Another crucial component of scope management is the scope declaration. It is often expressed as a phrase or a list of bullet points and serves as a clear, succinct explanation of the project’s goals and limitations. The scope statement, which outlines the project’s objectives and constraints, is crucial for lowering project risks.
The monitoring and control of deliverables is another crucial component of scope management. This entails ensuring that the created deliverables adhere to the project’s specifications and are formally authorized by the receiver. This process is distinct from the requirements collecting and planning phases and often occurs within the controlling and tracking process group.
Finally, keeping an eye on the scope statement during the project is critical. The project’s scope may need to be modified as it moves forward in light of the budget and other considerations. This can include reducing the project’s goals or deliverables to ensure the project’s success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, scope management is a crucial component of project management that entails establishing the project’s objectives and parameters, compiling technical requirements, monitoring deliveries, and regulating the scope statement. It is crucial to coordinate it with the project management strategy and ensure scope management is adaptable to risks, progress, and budget. Guarantee that the deliverables satisfy the project’s criteria entails monitoring and regulating them, and the scope statement should be updated as the project progresses.
References
Jolley, S. M. (2021). Project Management Core Competencies Perceived as Elements of Project Success (Doctoral dissertation, Capella University).
Pellerin, R., & Perrier, N. (2019). A review of methods, techniques and tools for project planning and control. International Journal of Production Research, 57(7), 2160-2178.
Grant, M. (Accessed 2023)). Gantt charting: Definition, benefits, and how they are used. Investopedia. https://www.investopedia.com/terms/g/gantt-chart.asp
 write
write