1.0 Introduction
Maple Leaf Foods is an iconic brand within the Canadian food industry and stands synonymous with Canada’s one-century commitment to providing people with healthy, great-tasting proteins. Firmly entrenched in Canada’s cultural and culinary landscapes is a company rooted in a rich heritage, married with innovation and a forward-thinking vision towards sustainability in the protein production sector.
From its Mississauga, Ontario base, Maple Leaf Foods works with an unwavering commitment to be the “most sustainable protein company on earth.” That is more than a goal painted on a wall somewhere. It lives and breathes in the operations of the company. At Maple Leaf Foods, history has always been contemporary, in a continuous change of taste, preference, and value to respond to consumers with quality, nutrition, and ethics in everything they do since 1917 (Maple Leaf Foods, 2023). Indeed, the company has spanned perfectly through changes in the food industry landscape while remaining anchored on an offering that represents many types of meat products within different dietary diversities and ethical considerations.
Canada is the largest market for Maple Leaf Foods, with sales of C$4.7 billion posted in 2022 (Oatman, 2023). Underpinning this financial success is the strong workforce of 13,500 team members supported by an expansive foot of operations supported by 27 manufacturing facilities across Canada. Second, the company is having impacts beyond the national border. Significant business deals have been made in the U.S., Mexico, and various markets of Asia, and it shows a food company worldwide. Maple Leaf Foods is considered one of Canada’s leading producers of prepared meats and poultry. It is one of the leaders in North America’s Raised Without Antibiotics (RWA) poultry and pork segment, offering private-label products to leading retailers and food service customers from coast to coast in Canada.
Thus, the major stakeholders for Maple Leaf Foods in the business include the employees, shareholders, suppliers, customers, and the community from which they draw their working strength. Sustainability and the practice of humankind have become increasingly recognizable by consumers, improving their lives and welfare. In the relentless focus, these values are aligned with consumer values and, combined with strategy-driven continuous improvement and innovation, propel Maple Leaf Foods to a leadership position in the Canadian food industry and one of the critical players in the global marketplace.
Eight Leadership Values give Maple Leaf Foods the journey of integrity to guide corporate and personal decisions and actions at every level. This guarantees a values-based culture through a transparent and accountable corporate governance structure that guarantees Maple Leaf Foods remains relevant to the food industry for generations.
2. Case Report
2.1 Stakeholder Analysis
Customers and Consumers: Their key concern is ensuring access to safe, high-quality, sustainable protein products. This aligns directly with Maple Leaf Foods’ commitments to food safety, considering they have never posted a single failing, either in meeting Food Safety Incident Rate (FSIR) targets or Quality Incident Rate (QIR) targets. Additionally, to minimize animal antibiotic use, pork operations at the company have reduced their application by 99.1% since 2014 (Mapleleaffoods.com, 2023). This perfectly complies with the customers’ needs to make a healthier and more responsibly produced food product.
Employees and team members: These represent a significant stakeholder group in the internal category with interests directed toward job security, career development, and a working environment that is safe and inclusive. Inclusion and Advancement are the focus areas within the comprehensive Diversity and Inclusion Blueprint of Maple Leaf Foods. Moreover, the recognition for contributions in mental health at work only highlights the importance that both team trainers and execs share toward the employees’ well-being.
Communities: Based in Canada and operating in different regions, local communities will play an indispensable role. This aligns with the company’s target of working towards halving food insecurity in the community by 2030 through the Maple Leaf Centre for Food Security. By so doing, it shows the company has committed to good community well-being. Their involvement in health food products donated in Canada and the U.S., plus the support for UNICEF by companies, thus reflecting their reflection of social welfare and community development to the bone.
Investors and Shareholders: Financial stakeholders interested in knowing the company’s financial performance and its sustainability initiatives that drive long-term value. As evident from its first Integrated Report, Maple Leaf Foods’ approach to integrating sustainability into business strategy reveals that the company is very open and responsible, attracting investor interest towards sustainable and responsible business practices.
Suppliers and Partners: Just like we have, we expect our suppliers and partners to hold their operations to the highest sustainability and ethical production standards at Maple Leaf Foods. We would expect standards as high from our suppliers and partners as we do from ourselves in animal welfare, the environment, and social responsibility. Its animal care improvements—the transition of the system to the Advanced Open Sow Housing system and the massive reduction in the use of antibiotics—are good instances of such expectations and portray the impact of those expectations on supply-chain practices.
2.2 VRIO Analysis
Maple Leaf Foods’ strategic resources and capabilities can be assessed through the VRIO framework. As defined by Bruin (2019), it evaluates the Value, Rarity, Imitability, and Organization of a company’s assets to determine potential competitive advantages.
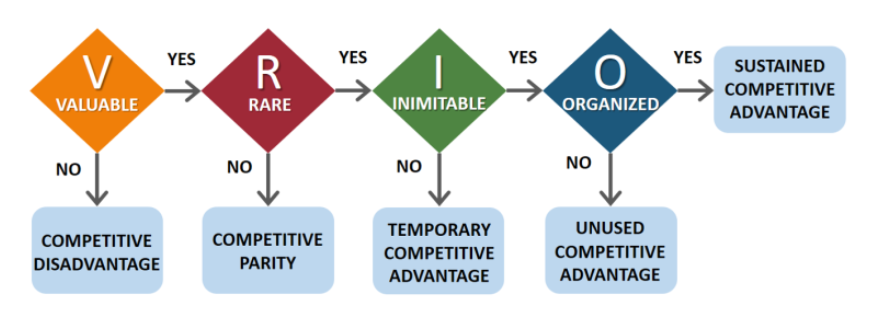
Source: (Bruin, 2019)
Value
Maple Leaf Foods provides value as follows: “We will continue to strengthen our focus on sustainability, safety, and quality.” For example, the focus is on their aspiration of being the most sustainable protein company on earth, further exemplifying their company’s focus on environmental sustainability, such as carbon neutrality and reduction of packaging waste. Besides gaining the consumers ‘ trust and loyalty, their advanced food safety measures reflect a value in surpassing FSIR (Food et al.) and Quality Incident Rate (QIR) targets.
Figure 2:Maple Leaf Foods Key Achievements and Vales
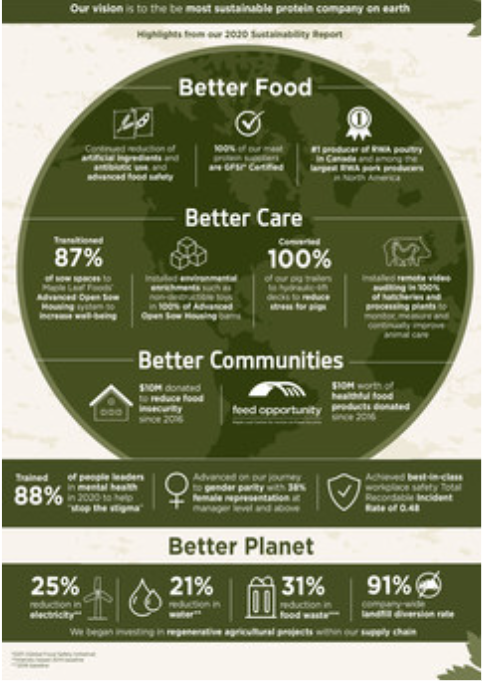
Source: (Mapleleaffoods.com, 2021)
Rarity
Maple Leaf’s commitment to sustainability and animal welfare practices is rare in the industry. Sh shining examples are their investment in being the first major carbon-neutral food company and the material reduction of antibiotics used across their hog production operations—reducing it from 2014 by 99.1%—. These initiatives are not joint among large food producers, giving Maple Leaf a distinctive edge in the market.
Figure 3: Reduction in Antibiotic Use in Maple Leaf Foods
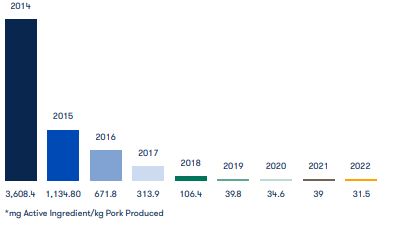
Source: (Mapleleaffoods.com, 2023)
Imitability
Therefore, Maple Leaf Foods has the most robust sustainability and safety practices that have been difficult for competitors to match, given its considerable investment and time to implement the measure. They also have the latest state-of-the-art facilities, such as the London Poultry plant, which just opened. They show an investment in leading technology and processes that optimize animal welfare and food safety. These form part and parcel of an entrenched safety and sustainability culture, making it difficult for competitors to copy them in the short term or on the cheap.
Organization
Therefore, Maple Leaf Foods is a well-structured organization that uses the resources and capacities demonstrated through its strategic focus on sustainability, safety, and quality integrated from the top to the bottom. Its strategic evolution towards a value-adding meat product, even extending to plant-based proteins, speaks volumes of very strategic company management in tune with the times and core company values, but likewise with a keen eagle eye on market trends and consumer demands. It aligns the Maple Leaf Centre for Food Security with organizational capability and various awards for workplace mental health in effectively aligning corporate social responsibility with business operations.
2.3 PESTEL Analysis
The macro-environment embraced by Maple Leaf Foods is dynamic and replete with the influence of varied external forces. A PESTEL analysis describes the various factors—political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal—that impact the operations and strategy of the company.
Political Factors
Political stability is a critical factor that affects Maple Leaf Foods in the markets it operates in. These markets’ local governments dominate decision-making processes, policy formulation, and regulation, particularly in Canada. This would mean that with possible changes in governments from time to time, the company will have to face a growing regulatory environment due to environmental factors and shifting policies. Further, international trade agreements play a significant role in global regulation compliance with the guidelines set by the World Trade Organization.
Economic Factors
It sums up consumer disposable income, inflation, and labour market conditions among the leading Canadian and global economic conditions that affect Leaf Foods. This has been eased by the fact that the company has taken advantage of the skilled workforce in Canada; hence, it allows it to improve its services and make it possible to explore international markets. The company’s performance was critically linked to the behaviour of consumer spending and economic cycles in Canada; hence, there was a need for financial strategic planning.
Social Factors
Maple Leaf Foods reacts to social trends and consumer preferences due to rising health and safety demand, the new need for access to essential services, and changing leisure interests. Demographic trends favour the growing population; therefore, opportunities would be presented to diversify the product range to fit consumers’ growing tastes and preferences.
Technological Factors
The technological revolution has redefined the way business is done in the Food Processing sector, and the reverberation has been felt at Maple Leaf Foods through changes in customer service innovation, supply chain disruptions, and changes in production costs. Commitment to research and development and adaption to new technologies is critical for the company to remain competitive and respond to the pace of changing technologies.
Environmental Factors
Social and environmental responsibilities are core elements of Mofle Leaf Foods’ operations. Government regulations, customer activism, and global accords, like the Paris Climate Agreement, are some external pressures continually increasing for the company. These drive Maple Leaf Foods to invest in renewable technologies, waste management, and sustainability practices to reduce environmental impact.
Legal Factors
The environment within which Maple Leaf Foods works is complex, with requirements of the law on health and safety, intellectual rights of employment, and protection of intellectual property rights for innovators, to mention just a few within the Canadian context. Requirements of this law are at the centre stage of their pursuit to maintain their operations and food safety while at the same time protecting their innovations.
2.4 SWOT analysis
Strengths vs. Weaknesses
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
| Strong brand reputation: Maple Leaf Foods is recognized for its high-quality food products, contributing to a solid reputation among consumers (Ramirez, 2023). | Dependence on the Canadian market: The company’s heavy reliance on it makes it vulnerable to local economic fluctuations and consumer spending patterns. |
| Diverse product portfolio: Offers a wide range of food products, including deli meats, bacon, poultry, and plant-based protein alternatives, catering to different customer preferences. | Limited global presence: Despite some international operations, Maple Leaf Foods’ global footprint is relatively small compared to its competitors, potentially limiting growth opportunities (Ramirez, 2023). |
| Commitment to sustainability: Has set ambitious targets to reduce its environmental footprint, invested in renewable energy, waste reduction, and sustainable packaging. |
Opportunities vs. Threats
| Opportunities | Threats |
| Growing demand for plant-based protein: The rising popularity of plant-based diets presents a significant opportunity for Maple Leaf Foods to expand its offerings. | Intense competition: Faces competition from both established companies and new entrants, which could threaten its market share and profitability. |
| Expansion into emerging markets: Opportunities to diversify its revenue streams and expand its customer base by entering emerging markets in Asia and Latin America (Ramirez, 2023). | Fluctuating commodity prices: Relies on various commodities for production, making it susceptible to price fluctuations that can affect profitability. |
| Partnerships and acquisitions: Can form strategic partnerships or acquire companies that align with its values, providing access to new technologies, distribution channels, and market insights. | |
| Sustainability and ethical sourcing: The increasing consumer demand for sustainable and ethically sourced products aligns with Maple Leaf Foods’ commitments and can be leveraged to attract environmentally conscious customers. |
3 Conclusion
with such a long history, nearly a century-long, and strong sustainability commitment, merged with a robust portfolio of products, Maple Leaf Foods has become one of the pivotal and most vital actors in the Canadian food industry, and through this, one of the most pivotal on the worldwide stage. In the meantime, the VRIO and PESTEL analyses will establish its competitive advantages on points such as brand reputation and sustainability commitment and point out the challenges and market opportunities that some dynamics and consumer trends bring. A SWOT analysis further delimits the internal strengths and weaknesses of the external opportunities and threats. Leverage its strengths and opportunities while addressing weaknesses and mitigating threats will be imperative for Maple Leaf Foods as it charts its strategic course in pursuit of sustainability for growth in the vision to be the most sustainable protein company on earth as it continues making inroads on the ever-evolving food industry landscape.
References
Bruin, L. de. (2019, November 20). VRIO Framework EXPLAINED with EXAMPLES | B2U. B2U – Business-To-You.com. https://www.business-to-you.com/vrio-from-firm-resources-to-competitive-advantage/
Maple Leaf Foods. (2023). Maple Leaf Foods | Raise the Good in Food. Www.mapleleaffoods.com. https://www.mapleleaffoods.com/
Mapleleaffoods.com. (2021, July 6). Maple Leaf Foods Releases 2020 Sustainability Report – Maple Leaf Foods. Maple Leaf Foods. https://www.mapleleaffoods.com/news/maple-leaf-foods-releases-2020-sustainability-report/
Mapleleaffoods.com. (2023, May 9). 2022 integrated report on environmental sustainability. Maple Leaf Foods. https://www.mapleleaffoods.com/stories/2022-integrated-report-sustainability/
Oatman, R. (2023, October 5). Maple Leaf details sustainability and business strategy successes. | MEAT+POULTRY. Www.meatpoultry.com. https://www.meatpoultry.com/articles/28443-maple-leaf-details-sustainability-business-strategy-successes
Ramirez, M. (2023, April 17). Maple Leaf Foods: Business Model, SWOT Analysis, and Competitors 2023 – PitchGrade. Pitchgrade.com. https://pitchgrade.com/companies/maple-leaf-foods
 write
write