Introduction
Organizational planning entails the drafting of the day-to-day operations of businesses. This often ranges from the simple aspects of determining the organization’s principal reason for existence to designing sophisticated elements such as the organizational goals and the fundamental business activities. Organizational planning helps to attain a business firm’s set goals and objectives (Ahmad & Ahmad, 2019). Setting priorities, concentrating energy and resources, bolstering operations, ensuring that workers and other stakeholders are working toward common targets, establishing agreement around intended outcomes and results, and evaluating and adjusting the organization’s direction in response to a changing environment are all examples of organizational management activities that involve planning (Fernandez et al., 2019). This specific kind of planning aids the organization is concentrating on a specified set of goals and enables them to modify those goals in response to the environment. Guidelines for strategic planning should be followed. A company must be prepared for success for a corporate strategy to be successful. However, the company must still be ready to participate in a quick win even when there are strong reasons to do so.
The attainment of organizational goals depends greatly on aligning departmental plans to overall strategic plans and business operations goals (Ghonim & Khashan, 2020). This, in turn, relies on the planning techniques that the organization employs. The first step towards this alignment entails bringing all employees at all departmental levels and other stakeholders to cooperate and work towards achieving the common goals. These stakeholders should be involved in planning to ensure that all the requisite intellectual inputs are effectively utilized. The move will ensure that all departments have all the required resources to help attain their departmental goals for the company’s interest. The goals set in the plan should be realistic and measurable. The planners should effectively communicate the plan to all the employees for effective execution. Once the plan has been made, the organizational leaders should embark on the action plan through the contributory process. This involves determining the organization’s readiness to execute the plan, establishing a strategic planning schedule, and collecting supportive review information to help further managerial decision-making. The organization then sets the plan and ensures effective monitoring and control to reduce errors.
Determining key performance indicators for effective monitoring and control follows the execution of the organizational plan (Carter, 2019). Several indicators can be used to determine the effectiveness of the plan. These include the degree of engagement by the employees, the energy, and the skills they put towards the plan. The managers can also determine the success of their plan through aspects such as the number of new contracts signed, the average sales, and the profitability made by the organization since the implementation of the plan. These measures are always critical for enabling the managers to develop new ideas for strengthening their weak areas and maintaining their proficiencies.
The Business Planning Process
Setting goals is the initial stage of company planning (Argenti, 2018). This generally entails formulating the primary objectives and goals that the business desires to set within a specific time frame. It is a crucial portion because, without a clearly defined aim, the organization would run without a clear sense of direction, which might cause it to lose focus along the road. After identifying goals, the planning premises are developed, where the plans are created, and any underlying circumstances are specified. At this point, the environment and any limitations are evaluated to determine the effective techniques for achieving the goals.
The second step involves the creation of the operation plans for the company. The process is often accompanied by conducting research in the market to determine the possible challenges that may be faced and the effective ways to overcome them. The company’s scope and aims should be reflected in the operation plans. They should consider several factors, including infrastructure, market competitiveness, and many other things that might be crucial to ensuring the company achieves a competitive edge. The integration of plans is the last phase. To ensure that the plans can complement one another, it is crucial to ensure that they have been appropriately balanced. The individuals carrying out the plans should get clear communication about them. Additionally, it is critical to periodically examine the strategies to ensure they remain relevant to industry changes.
The managers should then conduct a pilot study to determine the operation ability of the plans. This will be critically followed by the execution of the plan, with a clear directive on the roles of each stakeholder (Ahmad & Ahmad, 2018). Having leaders at each level of the execution with a clear direction and role of the employees will be fundamental in enhancing the success of the business plan. Through the pilot study, the managers will have a clear framework for going about their plan and determining all the required resources for the plans.
The next step entails the execution of the business plan. This is usually coupled with the monitoring and evaluation of the processes. The managers will devise techniques to measure the plan’s success after a given period. The plan’s success will significantly be measured by the achievement of the set objectives and the overall result of the firm’s performance. If the firm fails to succeed, the managers often re-evaluate the plans and processes to identify the areas that should be worked on in the preceding planning processes.
Components of a Business Plan, Technology Plan, and Marketing Plan
Components of a Business Plan
- A business plan should have an executive summary. This summary highlights the topics the business plan will address and offers a broad document overview. This enables the managers to fully understand the business strategy before getting to the main parts of the business plan.
- A business description and structure follow the executive summary. This section provides a comprehensive description of the business, the goals, the target market, and other relevant services.
- The next part involves market analysis and strategy. The plan should give a detailed account of the marketing research, the relevant information on the challenges to be expected, and other information. The market analysis incorporates information on the target market’s geographical location, the target audience’s needs, and how the needs will be met through sales and targeted profits.
- A business plan should also have a management and organization description, financial projection, and needs. The section covers details on the business management and organization strategy. The section may introduce the company’s leaders with their qualifications and responsibilities within the business.
- The section may include human resources requirements and the business’s legal structure.
- The financial projections are also vital in showcasing the financial resources needed to execute the plan with effective apportionments.
Technology Plan
The technology plan describes the technologies to be applied in executing the business plan (Sahai & Singh, 2021). A strategic technology strategy first evaluates the organization’s technical strengths and limitations to integrate technology with how a company intends to do business. Businesses have specialized procedures, guidelines, policies, and workflows that contribute to the value of the enterprise as a whole. The success of the business is a result of it. A strategic technology strategy outlines ways to integrate and automate those elements that make the business unique.
Marketing Plan
The marketing plan analyzes the target market, providing all the requisite demographic information (Katsikeas & Zeriti, 2019). This includes the examination of the size, structure, and movement of the population, their habits, likes, and income brackets. The section then outlines the positioning, competitive analysis, and budgeting. This helps to establish the identity of the products and services and the techniques through which the sales will be attained.
Best Practices for the Creation of a Business Plan
Creating an inclusive planning process is the first step toward ensuring that the business plan aligns with the organizational goals. This is achieved by including all the business leaders from the early stages of preparing the business plan. The aspect will ensure that all leaders have input into the plan, effectively attaining the organizational goals. An effective business plan should also prioritize communication. Maintaining transparency with all the organizational leaders will enable the firm to attain its objectives. The business organization should then assign roles to the various stakeholders to ensure that the tasks are effectively executed. This entails the identification of the sales team and other parties that will be directly involved in executing the business plan. Through this technique, the organization will stand a high chance of successfully rolling out the business plan.
Business Planning Model
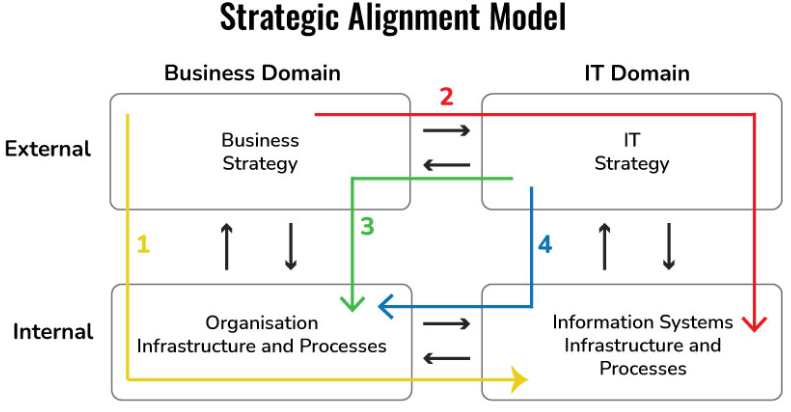
A strategic planning model explains how an organization develops a plan to put its strategy into practice to enhance operations and more effectively achieve its objectives (Bhattacharya, 2018). The business model that will best fit the organization is the alignment model. This model comprises two parts; the strategic fit and the functional integration. The model aligns a business and its IT strategies, which are crucial in attaining organizational goals. The models allow the managers to identify the key goals of the organization and the subsequent requisite steps towards achieving these goals. Among the factors established by the alignment model include; the financial performance of the company, the most effective financial resources for achieving organizational goals, the performance of stakeholders and service offered to customers, the efficiency of the internal organizational processes and the organization’s capacity.
How the Planning Process Applies to Business Support Functions for Leadership
Business planning ensures that an organization’s leaders have an effective framework for achieving the firm’s goals. Through planning, the leaders will have a clear path on what to do at every stage of the execution of the plan, as well as the techniques to overcome the challenges that may arise in the business’s course. The planning process also ensures that the organization has sufficient technological equipment for executing the business plan and reliable marketing and sales team to enhance the sale of goods and services. Planning will also have the marketing team employing the best strategies to attract customers for the goods and services since the planning provides crucial information on the target market.
Reference
Ahmad, I., & Ahmad, S. B. (2019). The mediation effect of strategic planning on the relationship between business skills and firm’s performance: Evidence from medium enterprises in Punjab, Pakistan. Opción: Revista de Ciencias Humanas y Sociales, (24), 746-778. https://dialnet.unirioja.es/descarga/articulo/8155778.pdf
Argenti, J. (2018). Your organization: What is it for?: challenging traditional organizational aims. Routledge. https://www.taylorfrancis.com/books/mono/10.4324/9781351258609/organization-john-argenti
Bhattacharya, P. (2018). Aligning enterprise systems capabilities with business strategy: An extension of the strategic alignment model (SAM) using enterprise architecture. Procedia computer science, 138, 655-662.
Carter, N. (2019). Performance Indicators:‘backseat driving or ‘hands-off control? 1. In Management of Health Care (pp. 243-250). Routledge. https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9780429450242-24/performance-indicators-backseat-driving-hands-control-1-neil-carter
Fernandez, M. E., Ruiter, R. A., Markham, C. M., & Kok, G. (2019). Intervention mapping: theory-and evidence-based health promotion program planning: perspective and examples. Frontiers in Public Health, 7, 209. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2019.00209/full
Ghonim, M. A., Khashaba, N. M., Al-Najaar, H. M., & Khashan, M. A. (2020). Strategic alignment and its impact on decision effectiveness: a comprehensive model. International Journal of Emerging Markets. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/IJOEM-04-2020-0364/full/html?casa_token=mAi26DfDmlEAAAAA:ZhRrvtb0fkjBBoZjeCwzJKr3jNiUUXi8ZDSkIah8IHsflxdE2wUZWOwvTXrx7T6i7jF6zAYHAhSGZBuO3bJhWEdhbt2XO2aj2hdTIbzF4-dM0u7ATXFN
Katsikeas, C., Leonidou, L., & Zeriti, A. (2019). Revisiting international marketing strategy in a digital era: Opportunities, challenges, and research directions. International Marketing Review. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/IMR-02-2019-0080/full/html?casa_token=0iM-dinQpmoAAAAA:g6TeCrvZdwgkdKUu40sPdvrcIvzRKME2gkVJu62orOCpQydAms7EYn6gHAcFEDEW65qqIrRsSuaHRZSk1qiEzN0GnM0fQPBawI5AIqI8n03oXZTwCU6Q
Sahai, S., Goel, R., Bajaj, P., & Singh, G. (2021). IoT and Its Role in Performance Enhancement in Business Organizations. Integration of Cloud Computing with the Internet of Things: Foundations, Analytics, and Applications, 183-196. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/9781119769323.ch11
 write
write