Introduction
For many organizations, organizational change has become the rule rather than the exception. At various organizational levels, change has been associated with the urge to resign, decreased productivity, absenteeism, and increased healthcare expenditures. At the personal level, change has been found to impact time pressure, job satisfaction, psychological well-being, and stress. Hence, organizational change is correlated with potentially adverse outcomes if not well executed by transformative or charismatic leaders at both organizational and individual levels. Due to the increase in frequency and range of organizational change, it is pertinent to explore leadership styles that may contribute to positive results in organizational change. In this context, the transformational leadership style emerged as a significant factor in driving successful organizational change. Transformational leaders, with their visionary outlook, focus on individual growth, and inspirational communication, can create a profound impact on the whole organization’s change process. As a result, when executing change initiatives, the more managers are transformative and visionary role models, the more employees appraise the change positively during the final phases of change. Therefore, through a review of the literature, this study found that transformational leadership style positively impacts employees’ long-run appraisal to change.
Literature Review
The transformational leadership theory is a popular leadership approach that focuses on the leader’s ability to inspire and transform their adherents or subjects. Rooted strongly in the scholarly work of James MacGregor Burns, the theory opines that transformational leaders elevate their adherent’s Motivation and performance by appealing to higher ethics, ideals, values, and intrinsic motivations(Van Wart,2014). Transformational leaders depict four key elements: idealized influence, where they serve as role models; inspirational Motivation, through articulating a compelling vision; intellectual stimulation, by encouraging creative and critical thinking; and individualized consideration, attending to individual needs and growth. In layman’s language, the theory demonstrates that transformational leaders profoundly impact organizational culture and performance, enabling innovation, collaboration, and a sense of purpose among employees.
A study by Bradley(2020) investigating the relationship between transformational leadership and change management illustrated that transformational leadership is a leadership style in which leaders inspire, encourage, and motivate employees to innovate and initiate change that will help grow and shape the future development of an organization. Through the strength of their vision and their charismatic personality, transformational leaders inspire followers to change expectations, perceptions, and motivations to work towards common goals and objectives. Bradley(2020) further states that organizational change is a demand of the day and the future, as it is needed by the organization to survive in dynamic and competitive world markets. Transformational leaders have the wherewithal and ability to lead change in the organization’s vision, strategy& culture, plus promote innovation in technologies and products.
Nevertheless, Transformational Leadership(TL) has emerged as one of the most feasible and effective leadership approaches, positively contributing to primary outcomes for most organizations in relation to the rapid change of business setting. Transformational leaders motivate their employers to adhere to change strategy and inspire them to accomplish the change objectives beyond expectations through their positive effects on employee trust in them. The motivation and inspiration attributes of transformative leaders are important in improving organizational capability for change since the key changes considerably rely on employees’ competencies, trust, and skills acquired to align with the demands of reforms and innovation. The proposition is supported by the Cao and Le (2022) research that investigated the impacts of transformational leadership(TL) on Organizational Change Capability(OCC) via arbitrating roles of two specific elements of trust in leadership, specifically disclosure-based trust and reliance-based trust. Disclosure-based trust pertains to the openness and transparency depicted by transformational leaders as they are candid in sharing information, intentions, decisions, and implications of organizational change initiatives with their employees. For reliance-based trust, it appertains when leaders fulfill their promises, meet commitments, and depict competence, thus establishing reliability and dependability. The study by Cao and Le(2022) opines that reliance-based trust refers to how transformational leaders’ consistent attributes in executing change initiatives positively impact employees’ trust in the leadership’s capacity to maneuver change effectively. Using empirical data obtained from 376 interviewees in 115 Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises(SMEs) in China, Cao and Le(2022) found positive and enormous impacts of transformative leadership(TL) and elements of employee trust in leadership on Organization Change Capability(OCC). The study demonstrated that disclosure-based trust in transformational leadership has a significant impact on changeability compared to the impacts of reliance-based trust in transformational leadership.
Additionally, employee trust in transformative leadership plays a crucial role in change initiatives due to the vulnerability and uncertainties inherent in the procedures of implementing new ideas and change strategies. Trust depicts the level of confidence that an individual has in another’s skills, competence, and commitment to act in an ethical, predictable, and fair way. Van Wart(2014) opines that the trust of organizational leaders is the employee’s willingness to acknowledge and accept vulnerability based on the positive expectations of the leader’s intentions. As a result, employee-leadership trust occupies the central role of promoting the processing of sharing information, new ideas, and the relationship between leaders and employees for pursuing change initiatives and innovation. A study by Harms and Crede(2010) indicated a positive correlation between TL and trust in leadership since transformative leaders are good role models and mentors who enable emotions and a culture of trustworthiness. Harms and Crede(2010) further indicated that if employees have knowledge of TL attributes in their leaders, they will exhibit a higher degree of trust in their leadership. Employees’ trust in their leaders positively impacts organizational change since the effectiveness of OCC is positively related to the levels of employees’ trust in their leaders and colleagues in an organizational setup. Similarly, suppose employees have high levels of trust in their transformative leadership and organization. In that case, they will have greater determination and commitment to obey and effectively implement the change for organizational development.
Findings
Impacts of Transformational Leadership Style on Organizational Change Initiatives
A literature review of past scholarly articles was the main methodology applied in determining the effects of transformational leadership on organizational change plans. The review indicated that transformational leadership is a dynamic leadership approach characterized by leaders who empower and motivate their employees to achieve excellent outcomes by appealing to their ideals, ethics, and intrinsic motivations. Transformational leadership is based on moral ethics and defined by its four main elements, referred to as the 4I’s of Transformational leadership, that is, idealized Influence, inspirational Motivation, intellectual stimulation, and individual consideration, which play a crucial role in fostering organizational change. Through idealized influence, the leaders serve as ethical role models, guiding employees with integrity and enabling alignment with organizational change goals. Inspirational Motivation characterizes enthusiasm and commitment by openly communicating a compelling vision of radication change and innovation. The element of intellectual stimulation is crucial as it encourages creative problem-solving and innovative thinking, which are important for navigating the problems of change. Lastly, the attribute of individual consideration in transformative leadership fosters leader-employee trust and growth, enabling leaders to address employees’ unique needs and concerns during change, consequently developing an environment where transformation is accepted and pursued with unity and confidence.
Also, the review of the literature found that TL positively affects employee engagement during firms’ change through the mediating responsibilities of valence and trust in leadership, thus enabling organizations to initiate and implement change plans. Transformative leaders openly communicate their vision for the future and depict charismatic attributes that align with employees’ expectations. Through open communication, consistent behavior, and cations and transparency, transformational leaders create an environment of disclosure-based trust, where employees feel knowledgeable and valued. This development of trust encourages employees to accept change as they believe in the transparency and sincerity of leadership intentions, thus contributing to organizational transformations with absolute commitment and confidence. This finding aligns with Lei et al.(2019), that rationalized that using the TL style aids managers in creating a collaborative environment that is beneficial for promoting the employee’s trust in leadership, therefore making it effective for organizations to successfully implement changes. Also, the finding is in tandem with Islam et al.(2021) study that inference that TL, directly and indirectly, affects employee engagement during firms’ change through the mediating responsibilities of valence and trust in leadership. Therefore, the findings of this study that TL positively impacts employee trust in leadership, consequently enabling the change capability of organizations, are justified as depicted in the conceptual framework below.
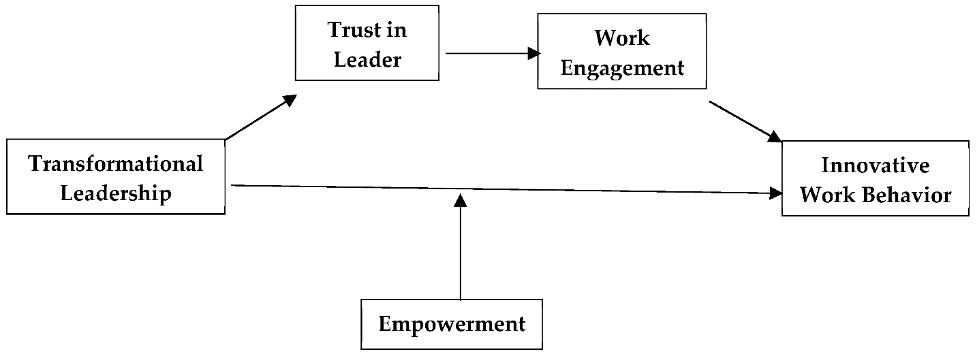
The conceptual framework indicates how transformational leadership facilitates trust in an organization’s leaders, thus creating work engagement and innovative work actions and behavior. Work engagement is based on trust, making employees attached to the organization in a persistent condition. This study indicates that trust is an important predictor of various organization-aimed changes and behaviors, including creativity and innovation, commitment to changes, and loyalty. The layman’s explanation for this is that trust typical among transformational leaders enables employees to focus on their current roles as they dedicate their energy, effort, and time to performing their duties efficiently instead of protecting themselves by engaging in lobbying and ingratiation typical in transactional leadership styles. Therefore, this study found that greater trust in transformative leaders provides more time and energy for employees to focus, accept, and integrate organizational changes in their daily roles.
Still, this study found that TL serves as s catalyst in enabling organizational change by instigating a paradigm shift in the norms and values of employees. As in, transformative leadership arouses the intellectual thinking that motivates employees to explore unconventional solutions and align their commitments with the organizational change visions. The finding is supported by the Van Wart(2014) study that concluded that through modeling expected behaviors, transformational leaders facilitate the development of employees’ problem-solving abilities, nurturing independent decision-making, and improving intellectual prowess. Additionally, the transformational leadership style involves essential components such as Motivation, problem-solving, and performance assessment, all of which are important in developing and exposing employees to innovative behaviors that foster organizational change.
Conclusion and Future Research
Conclusively, this research on the impacts of transformational leadership style on organizational change plans underscores the critical role that this leadership approach cultivates in a conducive environment for organizational changes in dynamic and competitive world markets. The four elements of transformational leadership, that is, – Idealized Influence, Inspirational Motivation, Intellectual Stimulation, and Individual Consideration – contribute to fostering higher trust levels among employees. Inspirational Motivation strengthens trust by communicating a persuasive vision that aligns with employees’ aspirations and values, stimulating a shared sense of purpose. Intellectual stimulation enables employees to think creatively, instilling trust in their competencies and promoting a collaborative environment where innovative solutions are embraced. Therefore, This bedrock of trust leads to increased employee acceptance and execution of organizational changes, as they believe in leadership intentions and view change initiatives as credible and beneficial discourses. This study recommends future research on the spill-over impacts of employee trust on broader organizational outcomes beyond change plans, as it could uncover the complex implications of cultivating trust through transformational leadership.
References
Bradley, R. (2020). Reviewing Transformational Leadership and Change Management in the United States of America. Journal of Human Resource & Leadership, 4(6), 56–65. Retrieved from https://stratfordjournals.org/journals/index.php/journal-of-human-resource/article/view/689
Cao, T. T., & Le, P. B. (2022). Impacts of transformational leadership on organizational change capability: a two-path mediating role of trust in leadership. European Journal of Management and Business Economics.
Holten, A. L., & Brenner, S. O. (2015). Leadership style and the process of organizational change. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 36(1), 2-16.
Harms, P. D., & Credé, M. (2010). Emotional intelligence and transformational and transactional leadership: A meta-analysis. Journal of Leadership & Organizational Studies, 17(1), 5-17.
Islam, M.N., Furuoka, F. and Idris, A. (2021), “Employee engagement and organizational change initiatives: does transformational leadership, valence, and trust make a difference?”, Global Business and Organizational Excellence, Vol. 40 No. 3, pp. 50-62.
Lei, H., Phouvong, S. and Le, P.B. (2019), “How to foster an innovative culture and capable champions for Chinese firms: an empirical research,” Chinese Management Studies, Vol. 13 No. 1, pp. 51-69.
Van Wart, M. (2014). Dynamics of leadership in public service: Theory and practice. Routledge.
 write
write