CHAPTER THREE: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 Introduction
This study examines the Factors to Reduce Production Wastages in The Automotive Industry. The research technique portion is crucial to correctly understanding the study objectives and data collection and analysis. This chapter describes the methodology and framework the study used to look at the factors that affect manufacturing waste in the automobile sector, with a particular emphasis on overproduction and over-rejection.
Our research’s conceptual framework is based on the understanding that these factors are crucial to the automobile sector. Overproduction has a substantial influence on inventory management, production rate optimization, and production costs. The generation of excessive inventory characterizes it. Conversely, Over rejection, which arises from components being disqualified for quality-related reasons, results in production losses and calls for attention to quality control procedures, staff involvement, and training.
The study carried out a thorough literature evaluation to make sure the framework was adequate and relevant. Roslin et al., Nawanir et al., and Brönnimann are among the authors who have added to the discussion of our Dependent Variable (DV) – Lean Manufacturing Profit and Independent Variables (IVs) – Over Production and Over-rejection. The importance of these characteristics and how they affect the automotive industry’s profitability, efficiency, and waste reduction have been clarified by these researchers.
A structured online survey questionnaire, strict sampling procedures, and data analysis using statistical tests are all part of the research design. Through pilot testing, the study intends to confirm the reliability of the questionnaire. The study plan will align with our goals and hypotheses, guaranteeing that the information gathered will provide insightful information on the variables affecting production waste in the automotive sector.
3.2 Research Design
To guarantee that the study is methodologically sound and in line with the research objectives, research design plays a crucial role in directing the entire research process. It serves as a roadmap, outlining the study’s organizational structure and the techniques used for data collection and analysis (Motiani & Kulkarni, 2021). A well-designed research study improves the validity and dependability of the results and makes it possible for researchers to come to meaningful conclusions and offer well-informed advice.
The first step in the research is to determine the study’s variables, Over-production, and Over-rejection based on the proposal. These factors were chosen with care since they have a significant influence on manufacturing waste in the car sector. While over-rejection results in production losses and calls for attention to quality control procedures, employee engagement, and training, overproduction impacts inventory management, production rate optimization, and costs (Wale, 2023).
The proposal’s research framework, which focused on the unique problems the automobile industry faced, was highly pertinent to our investigation. After an extensive literature analysis, the study determined the main problems with over-production and Over-rejection. The literature emphasized how these factors negatively impact profitability, production efficiency, and the sustainability of the sector as a whole. This architecture was chosen to ensure the relevance and applicability of our research by providing a thorough grasp of the difficulties faced by the automobile industry (Falcone, 2020).
The study’s survey questions were gathered using a thorough questionnaire according to the found variables. The purpose of the questions was to ascertain the participants’ opinions on Overproduction and Over-rejection, encompassing topics such as inventory control, quality assurance, and staff involvement. Google Forms was used to structure the questionnaire, making data gathering and distribution simple.
A group of respondents was chosen for the pilot survey in order to evaluate the efficacy and clarity of the questionnaire. Basic descriptive statistics were used to analyze the data from the pilot survey in order to find any questions or areas of uncertainty in the questionnaire. This feedback was very helpful in improving the survey questions and making sure they were precise, succinct, and in line with the goals of the study.
After the survey is over, SPSS software will be used to analyze the data that was gathered statistically. To summarise the data, descriptive statistics like mean and standard deviation will be used. The survey data will be analyzed using inferential statistics, such as regression analysis and ANOVA, to examine correlations between variables and derive significant findings.
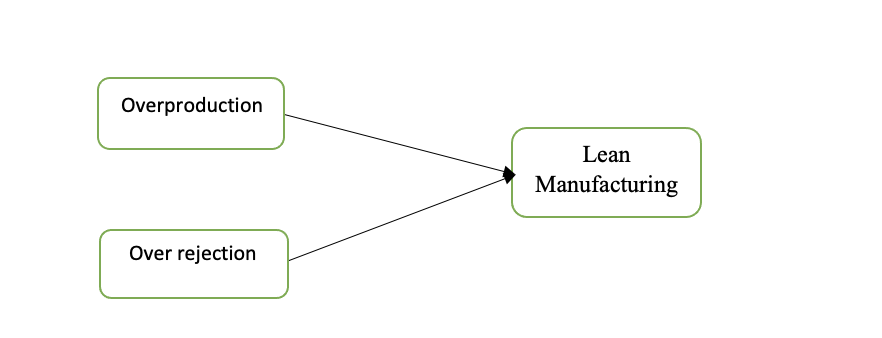
Figure1: Conceptual framework
This study’s research framework shows the dependent variables to be lean manufacturing, and the independent variables are over-production and over-rejection. It provides for a structured representation that directs the investigation of variables impacting production wastes in the automotive sector. The framework considers essential factors and how they are related to one another, shedding light on how these factors affect profitability, production efficiency, and the sustainability of the sector as a whole. It acts as a thorough map that makes it easier to conduct a methodical examination of the complexity of the automotive industry and its difficulties with waste reduction.
Research Objectives
- To identify the factors of overproduction that significantly influence Lean Manufacturing.
- To identify the factors of over-rejection that significantly influence Lean Manufacturing.
Research Questions
- What are the over-production factors that influence Lean Manufacturing?
- What are the Over Rejection factors that influence Lean Manufacturing? `
3.3 Population of the Study
Working adults in the corporate sector of Malaysia’s automobile industry make up the study’s population. The target audience comprises persons currently employed in various roles within Malaysia’s business environment and taking keen consideration on a range of years of experience. Because it directly relates to the topic of the examination of the factors influencing production wastes in the automotive sector, this demographic selection is essential to the research.
The purpose of the survey is to gather the varied viewpoints of business professionals who are knowledgeable about the inner workings of the sector, as well as its problems and possible solutions, to ensure that the study findings are solid. Representative of the complex dynamics of the industry, the study plans to collect a wide range of insights and experiences from respondents in all departments and job categories.
The study will expedite the distribution of Google Forms survey forms to reach about 100 respondents. Owing to temporal and procedural limitations, the surveys will be sent digitally through email. The information gathered from the responses will be carefully combined and examined to offer a thorough grasp of the variables affecting production waste in the automobile sector.
3.4 Sampling Technique(s)
The study will mainly use a sample group of the population to enhance the collection of data for the survey. The sample population consists of Working adults in the corporate sector of Malaysia’s automobile industry, which comprise the study’s population. Purposive sampling, a non-probability sampling methodology used in our study, enables us to deliberately choose particular individuals depending on their applicability to the goals of the investigation. This sampling strategy allows the researcher to specifically target people who have insightful knowledge and relevant experience about our two variables of choice, over-production, and over-rejection, which makes it especially appropriate for our study of the factors impacting production wastes in the automotive sector (Khan, 2020).
Purposive sampling gives the ability to choose people for the study deliberately. The study concentrates on those actively involved in the automotive sector, such as suppliers, employees, and managers. The study makes sure that the sample includes people who have firsthand knowledge of the difficulties and problems associated with overproduction and over-rejection by selecting participants from these particular groups.
The study will gather information through purposive sampling that is highly pertinent to the study goals and can offer insightful information about the variables affecting production wastes in the automobile sector. This methodology improves the validity and relevance of the results to the opportunities and real-world issues the industry faces.
3.5 Method and Procedure(s) for Data Collection
The research’s methodology and data-gathering processes follow a structured approach to guarantee a thorough investigation of the variables impacting production wastes in the automotive sector, particularly overproduction and over-rejection.
The study used a survey-based approach and a Google Forms-distributed online questionnaire. The carefully designed questionnaire addresses inventory management, production rate optimization, production expenses, quality control methods, and staff engagement, among other aspects of overproduction and overrejection. Using a self-administered structured questionnaire, data was gathered according to the survey’s parameters. Five sections comprise the questionnaires, and each section has characteristics rated using a five-point Likert scale (1 being strongly disagree, and 5 being strongly agree).
In order to reach the targeted sample of management experts, suppliers, and employees in the automotive industry, the survey link is electronically distributed via email. Purposive sampling is used to choose the respondents, guaranteeing that we get a range of viewpoints from influential industry players.
The study carried out a pilot test with a subset of respondents in order to improve the validity and reliability of our questionnaire. By incorporating input from the pilot test, the study can improve the survey questions and make them more relevant and transparent. This iterative approach ensures the usefulness of the questionnaire in eliciting insightful responses from our participantsThis iterative approach ensures the usefulness of the questionnaire in eliciting insightful responses from our participants.
Following the survey, statistical tools like SPSS will be used to analyze the data gathered. The replies will be summarised using descriptive statistics, such as mean, standard deviation, and frequencies. To investigate correlations between variables and derive meaningful inferences from the data, inferential statistical techniques such as ANOVA and regression analysis will be utilized.
3.6 Validation of the Questionnaire
In order to validate our questionnaire, a critical pilot test including 30 samples was carried out. Before starting the main data-gathering procedure, this pilot test evaluated the survey questions’ precision, efficacy, and dependability.
Selected people were requested to fill out the questionnaire in the pilot test, which replicated the survey’s settings. Like our target market, the respondents were drawn from the automotive industry and represented the management, supplier, and worker segments. Their varied vocations and origins allowed them to record a variety of viewpoints. The Pilot test results are provided below;
Table 1 Pilot Test Results
| No. | Variable | No of Questions | Sample size | Cronbach’s Alpha |
| 1. | Pilot-DV +IDV1 + IDV2 (Overall) | 18 | 30 | 0.903 |
| 2. | Pilot- DV | 6 | 30 | 0.836 |
| 3. | Pilot- IDV1 | 6 | 30 | 0.804 |
| 4. | Pilot- IDV2 | 6 | 30 | 0.901 |
The findings of the pilot test, which are displayed in Table 3.1, offer essential information about the validity and coherence of our survey questions. To guarantee that the survey items are trustworthy and precisely measure the intended structures, a high degree of internal consistency is essential. Cronbach’s Alpha readings in this range that are near to or more than 0.70 are typically regarded as acceptable.
The overall results for the dependent and the independent variables exhibited an excellent Cronbach’s Alpha of 0.903. The 18 questions have a good internal consistency score (above 0.70), indicating the reliability of the DV, IDV1, and IDV2 questions about overproduction and over-rejection.
Each of the particular groups also demonstrated acceptable internal consistency on its own. The six-question DV pilot test produced a Cronbach’s Alpha of 0.836, indicating a trustworthy way to measure the dependent variable. Similarly, Cronbach’s Alpha values of 0.804 and 0.901 were shown by IDV1 and IDV2, both of which had six questions. These findings further support the dependability of the questions within the independent variables.
3.7 Research Ethics
The research is fundamentally based on ethical considerations, which direct each stage of the investigation to protect participants’ rights and welfare and maintain the validity of the research process. The study is done by the highest ethical standards and the guidelines provided by the framework for research excellence.
Informed Consent and Participant Information: Before beginning the survey, participants are given thorough and unambiguous information about the research goal, how they will be involved, and how their answers will be handled (Husband, 2020). Every participant provides their express agreement, which emphasizes their voluntary involvement and their freedom to leave the study at any time without incurring any fees.
Data Security and Privacy: The study handles participant data with the highest care to guarantee security and privacy. Participant anonymity is maintained by maintaining the confidentiality of personal identifiers (Miyachi & Mackey, 2021). The gathered data is safely stored on password-protected computers, with access restricted to authorized researchers only. The information will not be shared with or revealed to uninvited parties; it will only be used for this study.
Minimizing Harm: The study has taken great care to ensure that our survey questions are non-intrusive and sensitive to minimize any potential discomfort or harm participants may experience (Li et al., 2022). The questions are designed to extract data relevant to the study goals without upsetting or hurting the respondents.
Respect for Participants: The study values each participant’s contributions and treats them with respect and dignity throughout the research process. The study values their insights and ensures that its conclusions fairly and accurately represent their points of view.
Integrity and Objectivity: Honesty, objectivity, and integrity serve as the guiding principles for the study. The meticulous and impartial data analysis and interpretation processes employed guarantee the validity and dependability of our study findings.
Community Impact: By tackling essential issues, the study aims to have a constructive influence on the automotive sector. The study is dedicated to ethically disseminating our research findings so that the industry and the general public may profit from the knowledge created.
The research keeps the confidence of the participants and the general public by adhering to these ethical guidelines. The study is committed to conducting our research with integrity, ensuring that our conclusions respect the highest ethical standards and significantly advance our knowledge of the variables driving production waste in the automotive sector.
3.8 Summary
The efficiency, sustainability, and competitiveness of the automobile industry could be significantly impacted by the findings of our study on the variables influencing production wastes, with a focus on overproduction and over-rejection.
The goal of the study is to offer valuable insights and suggestions for waste reduction and enhanced manufacturing processes by methodically examining these critical concerns. In addition to helping industry experts, the research findings will educate legislators and regulators on the prospects and difficulties facing the automobile industry.
The research is a critical first step in improving lean manufacturing practices, cutting waste, and increasing profitability in a quickly changing industry where efficiency and resource utilization are critical. As the study moves on, we hope that the findings will provide valuable strategies to deal with the problems of overproduction and over-rejection, promoting long-term expansion and competitiveness in the Malaysian automotive sector.
References
Falcone, P. M. (2020). Environmental regulation and green investments: The role of green finance. International Journal of Green Economics, 14(2), 159-173. https://www.inderscienceonline.com/doi/abs/10.1504/IJGE.2020.109735
Husband, G. (2020). Ethical data collection and recognizing the impact of semi-structured interviews on research respondents. Education Sciences, 10(8), 206. https://www.mdpi.com/2227-7102/10/8/206
Khan, N. (2020). Critical review of sampling techniques in the research process in the world. Available at SSRN 3572336. https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3572336
Li, F., Chen, C. H., Lee, C. H., & Feng, S. (2022). Artificial intelligence-enabled non-intrusive vigilance assessment approach to reducing traffic controller’s human errors. Knowledge-Based Systems, 239, 108047. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0950705121011369
Miyachi, K., & Mackey, T. K. (2021). hOCBS: A privacy-preserving blockchain framework for healthcare data leveraging an on-chain and off-chain system design. Information Processing & Management, 58(3), 102535. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0306457321000431
Motiani, N. N., & Kulkarni, A. (2021). Leadership role in implementing Lean Six Sigma–a cross case analysis of KPO/BPO service organizations. International Journal of Innovation Science, 13(3), 249-267. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/IJIS-09-2020-0159/full/html
Wale, A. (2023). The Effect of Manufacturing Wastes on Operational Performances of Bottled Water Manufacturing Industries: The Case of Asku PLC (Doctoral dissertation, ST. MARY’S UNIVERSITY). http://repository.smuc.edu.et/handle/123456789/7790
 write
write