Project Execution Plan
Ultimately the project execution plan for hiring a machine to produce goods will be vital in ensuring that there is the alignment of the project resources to the overall scope and magnitude. These will be essential in the attainment of the objectives. In this context, a project execution plan outlines the steps necessary to complete a project. It is an important tool for project managers as it provides a roadmap for executing a project and enables effective communication with stakeholders, team members, and other stakeholders. To this effect, some of the critical elements include the project overview, which is critical in providing the summary of the project, its objectives, and the scope of work. The next element is the project management approach. It is critical because the section outlines the management approach to be used during the project, including the roles and responsibilities of team members, communication plan, risk management plan, quality management plan, and change management plan. The next element is the project schedule. The section includes a detailed project timeline, including major milestones, deliverables, and deadlines. Additionally, it stipulates the resources and the project budget. To this effect, it provides a basis for measuring the success of the project by outlining the objectives, deliverables, and timelines. Overall, a well-constructed PEP is a crucial tool for project managers to ensure the success of their projects.
Project Scope
Correspondingly, project Scope Management involves establishing, verifying, and regulating its scope to ensure it is on track to accomplish its goals. On the other hand, it is also essential because it gives the manager the magnitude of the project and the inherent deliverables, such as the budget, resource requirement, and other deliverables, such as schedules (Mirza et al., 2019). Project deliverables, tasks, schedules, resource requirements, and budgets are part of the scope Methods for managing the scope of project help managers carry out the project’s planning, execution, and monitoring stages more efficiently.
Planning, efficient project management, and careful attention to detail are essential for hiring a machine to produce goods. To this effect Goals and objectives for Hiring a machine to produce goods is a technical part of project management that necessitates fulfilling a set of predetermined objectives through the execution of a predetermined set of actions. Approval of the budget, procurement of the required machine, hiring of an operator, installation of the machine, training of the operator, and manufacturing of items all are within this project’s scope.
Major Tasks Involved in hiring a machine to produce goods
Conversely, the running of the project will require clear tasks to achieve the objectives. In this case, a company decides to produce goods using a machine, and there are several primary tasks involved in the hiring process. These tasks include obtaining the machine, hiring the operator, installing the machine, training the operator, and producing the goods. Each task requires careful planning and execution to ensure that the project runs smoothly and successfully.
Obtaining the Machine
The first step in hiring a machine to produce goods is to obtain the machine. This involves researching and selecting the appropriate machine for the project. The machine should be capable of producing the required goods efficiently and effectively (Althiyabi & Qureshi, 2021). The company should also consider the cost of the machine, including the purchase or rental price, maintenance costs, and operating costs. Once the machine has been selected, the company should negotiate the terms of the agreement with the supplier. It may include the machine’s price, delivery, installation costs, and any warranties or guarantees. The company should also ensure the machine meets all relevant safety standards and regulations.
Hiring the Operator
The next task is to hire an operator for the machine. The operator should have experience operating the specific type of machine and be familiar with its functions and capabilities. The company should advertise the position and screen candidates to ensure they have the necessary qualifications and experience. During the hiring process, the company should also consider the operator’s salary and benefits and their availability and willingness to work. The company should also ensure the operator has all the necessary licenses and certifications to operate the machine safely.
Installing the Machine
Once the machine and operator have been secured, the next task is to install the machine. It involves preparing the site for the machine, including ensuring that the electrical and plumbing systems are in place and that the floor is level and sturdy enough to support the machine’s weight. The supplier may provide installation services, or the company may need to hire a contractor to install the machine. The company should ensure that the installation is completed according to the manufacturer’s specifications and that all safety measures are in place.
Training the Operator
After the machine has been installed, the operator must be trained to use the machine effectively and safely. This training should cover the machine’s functions and capabilities, as well as any safety procedures that need to be followed. The company should ensure that the operator understands how to operate the machine and how to troubleshoot any issues that may arise. The training should be hands-on, allowing the operator to practice using the machine under supervision. The company should also provide ongoing training and support to ensure that the operator remains up-to-date with any new features or upgrades to the machine.
Producing the Goods
The final task is to begin producing the goods. The company should establish production targets and ensure that the operator is working efficiently to meet these targets. The company should also monitor the quality of the goods to ensure that they meet the required standards. The company should maintain regular maintenance and cleaning schedules for the machine to ensure it operates effectively and efficiently. The company should also have contingency plans in place in case of any machine breakdowns or other issues that may affect production. Hiring a machine to produce goods involves several primary tasks, including obtaining the machine, hiring the operator, installing the machine, training the operator, and producing the goods. Each task requires careful planning and execution to ensure the project runs smoothly and successfully. To this effect, by following these steps, the company can produce high-quality goods efficiently and effectively, leading to increased profitability and success.
Objectives and deliverables of the project
Concurrently, using a machine to produce goods will increase output and production efficiency. The project seeks to streamline manufacturing and boost productivity by adding new machinery. The company might experience an increase in sales and market share. The initiative hopes to reduce manufacturing costs through process optimization (Vanhoucke, 2019). When a new piece of equipment is added to a production line, the team in charge of that line can better identify and address inefficiencies, reducing costs. To accomplish this, optimize the time it takes to make a product, the time it takes to process an order, and the quantity of raw materials wasted.
Some of the deliverables of the project are:
The main goal of the project is to buy and install a new piece of equipment that is required for the production process. The project also needs to hire an experienced operator. Operator training will be the next component. It will be essential because the success of the products produced will depend on the human capital. The project’s objective is to guarantee that the operator is aware of all pertinent safety protocols and industry best practices, as well as how to handle the new equipment properly. Before the new machine can be put into service, the project team must test and commission it to ensure it is in good working order (Autor, 2020). To improve productivity and workflow, the project requires integrating the new equipment into the current manufacturing process. Keeping tabs on a project’s production output, costs, and efficiency indicators is a great way to keep track of and evaluate its development.
Project schedule
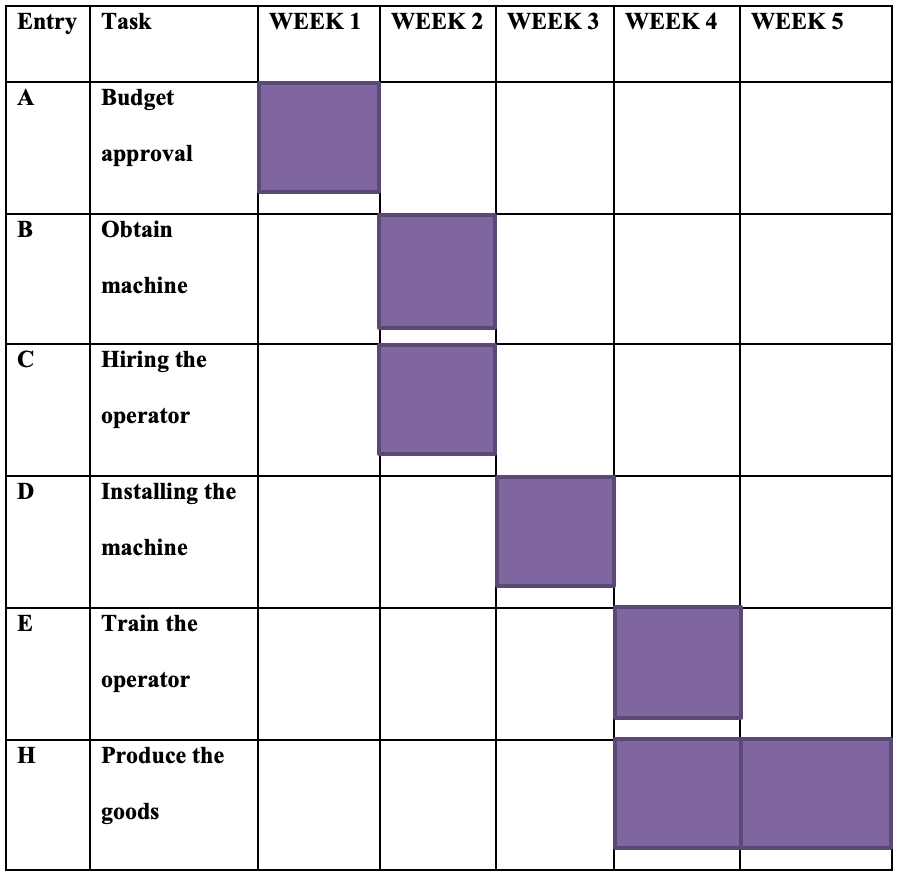
Project shareholders
Ultimately, stakeholders are vital in supporting the product to achieve the set deliverables. In this case, it is vital to tap into the stakeholder perception, and the inherent involvement in the various stages. In this context, the focus of the stakeholders is on the project results in this case hiring of a machine to produce goods. The project’s success will be determined by the identification and manage the expectations of all stakeholders. Effective stakeholder management includes engaging stakeholders early in the project, keeping them informed of project developments and changes, and resolving any problems that may arise.
The project shareholders include:
In any project, there are several key stakeholders who are accountable for different aspects of the project’s success. Understanding the role of each stakeholder is critical for ensuring that the project’s goals are met, and the project is completed according to the needs of all involved parties. Let’s discuss each stakeholder’s role in more detail.
The project’s sponsor is the person or organization that provides funding for the project and has the final say over significant project choices. They are responsible for ensuring that the project meets the organization’s strategic goals and objectives. The sponsor provides the financial resources necessary for the project’s success and has the ultimate decision-making authority over the project’s direction, budget, and resource allocation.
The project manager is accountable for directing the team’s work and ensuring that it is completed according to the project’s goals and the needs of all parties involved. They are responsible for managing the project’s scope, budget, timeline, and resources, and for communicating with stakeholders. The project manager must ensure that the project is delivered on time, within budget, and to the satisfaction of all involved parties.
Members of the project team are accountable for carrying out the project’s activities and ensuring that the project’s goals are met. They are responsible for executing the tasks and activities outlined in the project plan, as well as reporting on their progress to the project manager. The team members must work collaboratively to ensure that the project is delivered according to the established standards and timelines.
Customers are the people or organizations that stand to gain from the project’s results, such as the upgraded products manufactured by the new machinery. They are the ultimate beneficiaries of the project and are often the reason the project is being undertaken. Customers may provide input into the project’s requirements, goals, and objectives, and are responsible for providing feedback on the project’s results.
Suppliers are the people or organizations that provide goods or services to the project, such as the new machine’s maker. They are an essential part of the project’s success, as they provide the resources and expertise necessary for the project’s completion. Suppliers must deliver their goods and services on time and within the project’s specifications, ensuring that the project stays on track and within budget.
Compliance with applicable norms and standards, such as those about the new machine’s safety, is supervised by regulators. Regulators are responsible for ensuring that the project complies with all relevant laws and regulations, including safety, environmental, and other regulatory requirements. Regulators must work closely with the project team to ensure that the project is delivered safely, and that all necessary permits and approvals are obtained.
Employees are the people who work for the company and may be affected by the project’s results, such as when manufacturing methods are altered, or a new operator is hired. They are often the ones responsible for executing the project’s tasks, and may be affected by changes to the project’s scope or timeline. Employees must be kept informed of the project’s progress and any changes that may affect their work, to ensure that they can adjust their work accordingly.
Project budget
A project budget is a financial plan that outlines the estimated costs required to complete a project. It typically includes the cost of resources, such as labor, materials, equipment, and any other expenses associated with the project. A well-planned project budget helps to ensure that the project is completed within its financial constraints and allows for effective cost management. It is important to create a realistic budget that accounts for potential risks, such as unforeseen expenses or changes in scope. The budget should be regularly reviewed and updated throughout the project to ensure that it remains on track and any necessary adjustments can be made.
| TASK | COST |
| Budget approval | $3500 |
| Obtain machine | $50,000 |
| Hiring the operator | $3000 |
| Installing the machine | $2000 |
| Train the operator | $1000 |
| Produce the goods | $4000 |
Project planning and monitoring of the project
The quality assurance and monitoring is vital to achieve the deliverables. In this case, it is vital to note that every process will be monitored. Monitoring and control of project progress is a critical component of project monitoring. This involves tracking project milestones, identifying delays and deviations from the project plan, and taking corrective action to keep the project on track. Effective monitoring and control of project progress require regular project status updates, monitoring of key performance indicators (KPIs), and tracking of project risks.
Management of project risks is another crucial stage in project planning and monitoring. Risk management involves identifying potential risks to the project, assessing their impact and likelihood, and developing strategies to mitigate or avoid them. Effective risk management requires a comprehensive understanding of project risks and a proactive approach to risk mitigation. Risk management should be an ongoing process throughout the project lifecycle, with regular risk assessments and updates to the risk management plan
Conclusion
In conclusion, a new machine’s hiring is crucial to the project’s overall strategy. It will be necessary to provide extensive information on specifics such as the machinery that will be needed, its estimated cost, and the timetable for its acquisition and integration into the overall project plan. The primary objective of the project is to acquire and set up a brand-new piece of machinery that is necessary for the production procedure. Additionally, a skilled operator needs to be hired for the project. The following element will be operator training. It will be crucial because human capital will determine how well the products are made. The project’s goal is to ensure that the operator is knowledgeable about all relevant safety procedures and industry best practices. understanding the role of each stakeholder is critical for ensuring the success of any project. Each stakeholder has a unique set of responsibilities and must work together collaboratively to ensure that the project is completed according to the established goals and objectives. By understanding each stakeholder’s role, the project team can work more effectively to deliver a successful project that meets the needs of all involved parties.
Reference
Althiyabi, T., & Qureshi, R. (2021). Predefined project scope changes and its causes for Project Success. International Journal of Software Engineering & Applications, 12(3), 45–56. https://doi.org/10.5121/ijsea.2021.12304
Autor, D. (2020). The “task approach” to Labor Markets: An overview. https://doi.org/10.3386/w18711
Mirza, M. N., Pourzolfaghar, Z., & Shahnazari, M. (2019). Significance of scope in Project Success. Procedia Technology, 9, 722–729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.protcy.2013.12.080
Vanhoucke, M. (2019). Resource-Constrained Project Scheduling. Project Management with Dynamic Scheduling, 107–137. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-25175-7_7
 write
write