Introduction:
The airline sector is an essential part of the global economy because it links people and companies all over the world. However, operating an airline is not without its challenges, as companies must navigate a complex web of government regulations and economic restrictions. In addition, airlines must work closely with a range of stakeholders, such as manufacturers, airports, and air traffic management, to ensure safe and efficient operations. This report’s objective is to give a general overview of the principles of airline management, including the political and financial constraints on which airlines must operate and the interactions they have with different stakeholders. By analyzing these key aspects of airline management, this report aims to provide insights into how airlines can optimize their operations and improve their profitability in a highly competitive industry.
A Framework of Stakeholders in the Airline Industry:
As we know, the airline industry operates within a highly interconnected framework that involves various stakeholders, including airports, manufacturers, air traffic management systems, and regulatory institutions (Roungas et al., 2021).
Airlines are the primary players in the industry, responsible for transporting passengers and cargo from one location to another. However, they do not act alone, and they rely on other stakeholders to provide essential services and support.
Airports are one of the most critical stakeholders in the airline industry, providing essential services such as runway access, ground handling, and passenger facilities. Airlines must comply with regulations and guidelines set by competent authorities to ensure safe and efficient operations at airports. Airports also impose fees and charges on airlines for the use of their facilities, which can impact the airlines’ profitability.
Manufacturers are another critical stakeholder in the airline industry, responsible for designing and producing the planes that airlines use to transport passengers and cargo (Cardeal et al., 2020). Manufacturers must comply with regulations and standards set by competent authorities to ensure that their planes are safe and reliable. Airlines must purchase or lease planes from manufacturers, which involves negotiating contracts and ensuring that the planes meet their operational requirements.
The safe and effective movement of air traffic at and around airports is the responsibility of air traffic management systems. These systems involve air traffic control towers, radar systems, and communication networks. Airlines must follow specific procedures and guidelines set by air traffic management systems to ensure that their flights are safe and efficient.
Finally, regulatory institutions and organizations such as the International Air Transport Association (IATA) and the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) set guidelines, standards, and regulations that airlines must follow to ensure safety and efficiency in air transportation (Ateş and KAFALI., 2020). Airlines must comply with these guidelines and regulations to maintain their licenses and certifications.
In summary, airlines operate within a complex framework that involves various stakeholders, each playing a critical role in the industry’s success. Effective collaboration and communication among these stakeholders are essential for ensuring safe, efficient, and profitable airline operations.
Analysis:
The airline industry operates within a complex regulatory framework with many government and economic restrictions. Airlines must comply with regulations and guidelines set by competent authorities to ensure safe and efficient operations. Effective collaboration with stakeholders such as airports, ground handlers, and maintenance organizations is crucial to ensuring high-quality services and operations.
Manufacturers:
When working with manufacturers, airlines should keep in mind that they are purchasing or leasing a product that is essential to their business. Therefore, airlines must ensure that the planes they acquire meet their operational requirements and are safe and reliable. This involves negotiating contracts with the manufacturer, specifying the features and performance characteristics required, and ensuring that the planes are certified by competent authorities. The main operations that appear in this interaction include plane selection, purchase/lease negotiation, and plane delivery and maintenance.
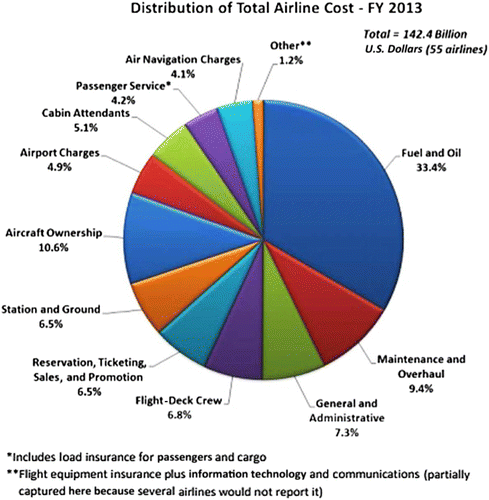
Figure 1: Cost-Estimating Model for Aircraft Maintenance
Source: Google
Airports:
When interacting with airports, airlines must arrange for essential services such as runway access, ground handling, and passenger facilities. Airlines must comply with regulations and guidelines set by competent authorities to ensure safe and efficient operations at airports. Airports also impose fees and charges on airlines for the use of their facilities, which can impact the airlines’ profitability. The main operations that airlines need to arrange with airports include runway access, gate allocation, ground handling services, and passenger facilities.
Air Traffic Management:
Air traffic management (ATM) systems are responsible for ensuring the safe and efficient flow of air traffic in and around airports (Pratama et al., 2020). ATC is mainly responsible for providing pilots with information and instructions to ensure safe flight operations. Airlines must follow specific procedures and guidelines set by ATC to ensure that their flights are safe and efficient. These procedures include flight planning, communication with ATC, and following specific flight paths and altitudes.
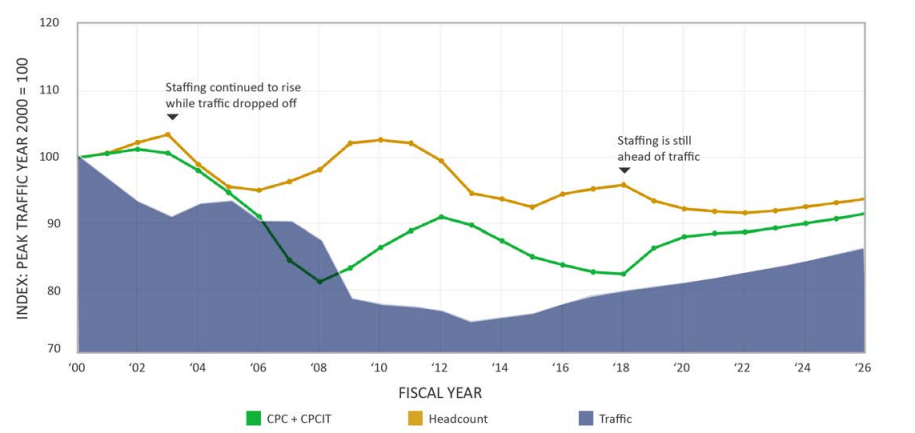
Figure2: Air traffic controller plan 2017-2026
Source: Google
Institutions, Governments & Regulatory Organisations:
Various organizations and regulatory institutions affect airline companies in terms of regulations, including the International Air Transport Association (IATA), the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), and the European Aviation Safety Agency (EASA). Airlines are affected by regulations in terms of safety standards, operational procedures, and licensing requirements. Airlines can participate in the regulatory process by providing feedback and input to these organizations, which can influence future regulations.
Government and Economic Restrictions:
Airlines operate within a highly regulated industry, with many government and economic restrictions. Governments regulate airline safety, security, and environmental impact, among other things. They also impose taxes, fees, and other charges on airlines, which can impact their profitability. Economic factors such as fuel prices, currency exchange rates, and global events such as pandemics can also affect the airline industry. Airlines must comply with regulations and guidelines set by competent authorities to ensure safe and efficient operations.
Structures and Activities Mandated by Competent Authorities:
Competent authorities, including government bodies and regulatory institutions, mandate structures and activities that airlines must comply with. For example, airlines must maintain certain safety and security standards, provide training for their employees, and comply with licensing and certification requirements. Airlines must also follow specific operational procedures, such as those related to takeoff, landing, and communication with ATC systems. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in penalties, fines, or even revocation of licenses.
Relationships Between Different Airline Stakeholders:
Airlines have relationships with many stakeholders, including airports, ground handlers, maintenance organizations, and others. These stakeholders provide essential services such as runway access, ground handling, and maintenance of planes. Effective collaboration with these stakeholders is crucial for airlines to ensure safe and efficient operations. Airlines must negotiate contracts with these stakeholders and comply with regulations and guidelines set by competent authorities to ensure these services are provided at a high level of quality.
Maintenance Organizations and Ground Handlers:
Maintenance organizations and ground handlers are essential stakeholders in airline operations (Dožić, 2019). Maintenance organizations provide essential maintenance services to ensure planes are safe and reliable for flight. Ground handlers are responsible for a range of services, including baggage handling, fueling, and catering. Airlines must negotiate contracts with these stakeholders and ensure compliance with regulations and guidelines set by competent authorities. Failure to do so can result in disruptions to flight operations and reduced profitability.
Understanding the Connections between Stakeholders and Airline Companies:
The analysis of the stakeholders in the airline industry provides a clear understanding of the connection between these stakeholders and airline companies. Each stakeholder plays a critical role in the operations and success of airlines, and airlines must consider the operations and procedures of each stakeholder in order to operate effectively.
For example, airlines must work closely with manufacturers to ensure the design, production, and delivery of reliable and safe aircraft. They must also consider technological advancements that may improve their efficiency and performance. Similarly, airlines must arrange a range of operations with airports, including ground handling services, passenger handling services, and fuel services, and must comply with various restrictions on airport operations.
Air traffic management is also critical to the operations of airline companies, as they are responsible for managing the flow of air traffic and ensuring safe and efficient operations. Airlines must comply with air traffic control instructions and procedures and must also consider the impact of weather conditions and airspace restrictions on their operations (Budd and Ison, 2020).
Institutions, governments, and regulatory bodies also play a significant role in the airline industry. They set regulations and standards for the industry, covering a wide range of topics such as safety, security, and environmental impact. Airlines must comply with these regulations and may also participate in industry associations and advocacy groups to influence policy and regulation.
In summary, the analysis of the stakeholders in the airline industry highlights the critical connections between these stakeholders and airline companies. By understanding these connections and considering the operations and procedures of each stakeholder, airline companies can develop effective strategies to optimize their operations and improve their overall performance.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the airline industry operates within a complex web of government and economic restrictions, including regulations set by competent authorities. Airline companies must also work closely with various stakeholders, such as manufacturers, airports, and air traffic management, to ensure efficient and safe operations. The relationships between these stakeholders are critical to the success of the airline industry, as each party plays a key role in the management of airlines. By analyzing the different aspects of airline management, including cost analysis, airport fees, on-time performance, and safety incidents, airlines can make informed decisions and implement effective strategies to optimize their operations and improve their bottom line. It is essential for airlines to maintain strong relationships with their stakeholders and stay abreast of the latest industry trends and developments to remain competitive in a constantly evolving market.
References:
Ateş, S.S. and KAFALI, H., 2020. Personnel Licencing in Aviation Authorities: An Implementation in Faculty of Aeronautics and Astronautics of Eskisehir Technical University. Journal of Aviation, 4(1), pp.103-114.
Budd, L. and Ison, S. eds., 2020. Air transport management: an international perspective. Routledge.
Cardeal, G., Höse, K., Ribeiro, I. and Götze, U., 2020. Sustainable business models–canvas for sustainability, evaluation method, and their application to additive manufacturing in aircraft maintenance. Sustainability, 12(21), p.9130.
Dožić, S., 2019. Multi-criteria decision-making methods: Application in the aviation industry. Journal of Air Transport Management, 79, p.101683.
Pratama, M.D.Y., Yassi, A.H. and Machmoed, H.A., 2020, October. Code-switching applied by air traffic controllers in air navigation services. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science (Vol. 575, No. 1, p. 012170). IOP Publishing.
Roungas, B., Raghothama, J., Baena, M., Ros, O.G.C., Alcolea, R. and Herranz, R., 2021, December. Technology adoption in air traffic management: a combination of agent-based modeling with behavioral economics. In 2021 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC) (pp. 1-12). IEEE.
 write
write