Anxiety disorder is a mental health problem characterized by feelings of fear, worry, and anxiety that are strong enough to disrupt a person’s normal functioning and activities. It is characterized by uncontrollable and persistent worry that is associated with multiple unpleasant psychological effects (Gomez et al., 2018). An anxiety disorder differs from normal feelings of anxiousness or nervousness and involves extreme fear and anxiety
Neurobiological Basis of Anxiety Disorders
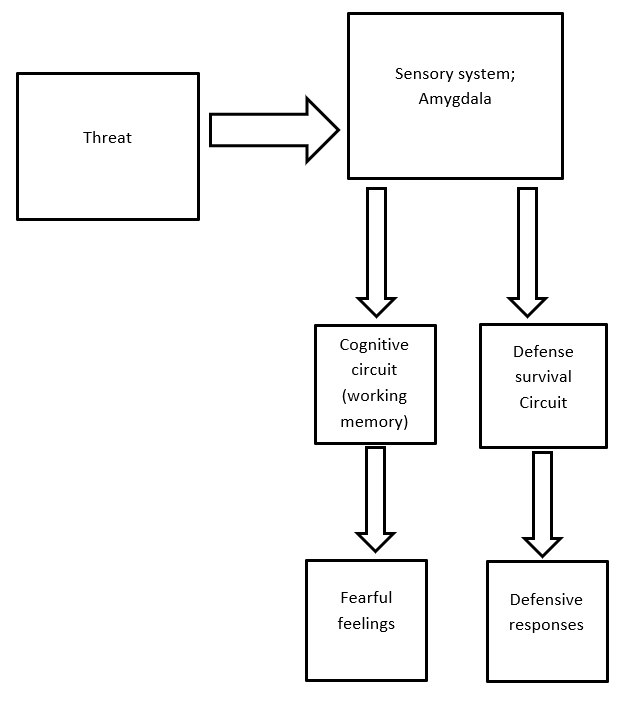
The neurology of anxiety involves changes in the neural systems involved in coordinating defensive responses. Symptoms of the disorder result from a disruption in the balance of activities in the brain’s emotional centers. The amygdala is part of the brain responsible for acquiring, responding, and expressing fear conditioning and is consistently activated in anxiety-provoking situations (Holzschneider & Mulert, 2022). It is situated in the medial temporal lobe and has thirteen nuclei, with three of them, central nuclei, lateral amygdala (LA), and basal amygdala (BA), being involved in fear reception and response. Fear stimuli received by the sensory thalamus are transmitted to the lateral amygdala and then moved to the central nuclei. The basal amygdala also acts as a link between the central nucleus and the lateral amygdala. Signals are sent from the prefrontal cortex, insula, and sensory cortex to the lateral amygdala. From there, information projects to the effector sites in the brain stem and the hypothalamus, consequently producing behavioral and autonomic manifestations of the acute fear response. It should be noted that the lateral amygdala is responsible for plasticity and memory consolidation in fear conditioning. Lesions or disruptions of the lateral or central amygdala can disrupt the acquisition of fear and the long-term contextual fear memory and responses.
It is necessary to note that in addition to the functioning of the brain regions, there are various neurotransmitters that provide communication between the regions. Increased activities in emotion processing for individuals with anxiety disorder results from increased excitatory neurotransmission by glutamate or decreased inhibitory signaling by GABA. Also, the anti-depressant and anxiolytic properties of drugs used in treating anxiety disorder have implicated the presence of dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine in the pathogenesis of the disorder.
Concept Map of the Neurology of Anxiety Disorder
Classes of Medication for the Treatment of Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorder can be treated/reduced using various classes of medication, including benzodiazepines (BZs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
They are a first-line medication for treating anxiety. They work by inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin, thus availing more serotonin to the brain and increasing serotonin activity, consequently improving anxiety and mood. According to Gomez et al. (2018), randomized controlled trials have indicated the efficiency of SSRIs in treating anxiety disorder. They are, however, associated with various side effects, including gastrointestinal disturbances, sleep difficulties, headaches, nausea, jittering, and dizziness (Gomez et al., 2018).
Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs)
They are a first-line medication for the treatment of anxiety. They ease anxiety by affecting the neurotransmitters used for communication between brain cells. They inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine, consequently causing an increase in neurotransmission by increasing the availability of extracellular concentrations of serotonin and norepinephrine. They are associated with various side effects, including gastrointestinal disturbances, sleep difficulties, headaches, nausea, jittering, and dizziness (Gomez et al., 2018).
Benzodiazepines (BZs)
They are a class of sedative drugs. They work by enhancing the binding of GABA neurotransmitters at different GABA receptors across the central nervous system. This consequently strengthens the effects of GABA neurotransmitters, thus promoting relaxation and reduced brain activity. According to Balon et al. (2018), the effectiveness of BZs in relieving the symptoms of anxiety has been well documented. BZs are associated with various side effects, including headache, confusion, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, tremor, respiratory arrest, and respiratory depression (Bounds & Nelson, 2021).
Recommended Medication and Education
Mary presents various signs, including irrational fears and extreme worry. Benzodiazepines (BZs) would be effective in treating her situation. Compared to serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, Benzodiazepines are more tolerable and have a rapid onset of effects. Alprazolam, particularly would be more effective for the treatment. Bounds and Nelson (2021) state that alprazolam is particularly indicated for treating anxiety disorders, and its effectiveness has been reported.
However, it is essential to note that despite their effectiveness in treating anxiety disorder, BZs are associated with various side effects. For example, the patient may experience headaches, confusion, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, tremor, respiratory arrest, and respiratory depression. Additionally, if not properly managed, they can result in over-sedation, psychomotor incoordination, and cognitive impairment (Gomez et al., 2018). However, BZs do not always cause adverse effects if used well, and people find them highly effective and tolerable. It is also important to note that benzodiazepines may inhibit respiratory drive; thus, careful monitoring of all vitals, especially respiratory rate and blood pressure is necessary upon administration (Bounds & Nelson, 2021). Proper use of the medication and appropriate monitoring is thus advised to enhance their effectiveness.
Evaluation of Efficacy
With the goal being to control the anxiety disorder symptoms and manage them to prevent relapse, the efficacy of the medication can be determined using the symptoms presented by the patient during/ after drug use and the quality of their mental life. According to Balon and Starcevic (2020), the efficacy of Benzodiazepines in treating anxiety disorder is seen in their effectiveness in reducing the symptoms and their ability to calm down patients. In this case, Mary has irrational fears of people breaking into her house, thus repeatedly checking her locks and extreme worry of contracting disease, causing her to wash her hands until they are dry and cracking. If the drugs administered have high efficacy, Mary can manage her fear and worry, and her quality of life and work will improve or get back to normal. On the other side, if the medication has low efficacy, the levels of worry and fear will continue to be extreme, and the quality of her mental life will not improve or may worsen.
References
Balon, R., & Starcevic, V. (2020). Role of benzodiazepines in anxiety disorders. Anxiety Disorders: Rethinking and Understanding Recent Discoveries, 367-388. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-981-32-9705-0_20
Balon, R., Rafanelli, C., & Sonino, N. (2018). Benzodiazepines. Psychotherapy and psychosomatics, 87(6), 327-330. https://www.jstor.org/stable/48516350
Bounds, C. G., & Nelson, V. L. (2021). Benzodiazepines. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470159/
Gomez, A. F., Barthel, A. L., & Hofmann, S. G. (2018). Comparing the efficacy of benzodiazepines and serotonergic anti-depressants for adults with generalized anxiety disorder: A meta-analytic review. Expert opinion on pharmacotherapy, 19(8), 883-894. https://doi.org/10.1080/14656566.2018.1472767
Holzschneider, K., & Mulert, C. (2022). Neuroimaging in anxiety disorders. Dialogues in clinical neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.31887/DCNS.2011.13.4/kholzschneider
 write
write