The general production schedule is a way to assist producers in determining what products and quantities to produce during specific periods. Master Production schedule work as they direct the production process in terms of what is made and what materials are purchased. The main production schedule in the third master of production schedule decides which products will be manufactured and when. Completed materials bill products specify the required raw materials integrated with the current inventory data to create a material requirement plan for raw material purchases (Bagheri, Demartini, Arezza, Tonelli, Pacella, & Papadia 2022). The general production schedule is the basis for sales and manufacturing communications. While sales and production use the main production schedule as a contract, sales can provide valid order commitments. Rules do not set the main production schedule. Parliamentarians are flexible plans that can be adjusted as demand or changes in capacity.
Main production schedules often do crucial planning work as part of a fully integrated ERP system, supplying precise distribution and demand data and projections to help you create correct and timely production plans. Developers meet their production objectives while lowering expenses. Shopping main production schedule also factors in the plant’s output capacity in their estimations. The material requirement plan begins after production orders have been analyzed and approved and purchase orders can be generated. The main production schedule also protects against resource scarcity, snafus planning, and improper resource allocation.
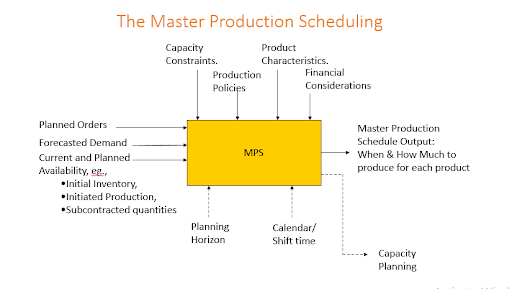
Typically, software develops a master production schedule, which requires only minor manual adjustments to achieve the company goals. Master production scheduling collects a lot of data about current and expected needs, lists, production time, and resource capacity. The general production planning program deals primarily with planning, lists, and other aspects of production control. This includes understanding what needs to be produced according to demand and when these products should be made according to the materials’ deadlines and capabilities or availabilities.
Explain the development of each element of the Master Production Schedule
The preparation of Greenville’s main production schedule follows a general planning process in the production process is an s representative of the production schedule in charts and descriptions. Demonstrates a general strategy based on specific products or designs for which priority can be given. The main production schedule for the completed products is created using available planning. The main goal of the material requirement plan is to turn those schedules into procurement and production orders for the entire facility (Amaranti, Muhammad & Septandri, 2020). The material planning system also indicates material requirements and capabilities for each workplace. To distinguish it from a more complex mechanism known as manufacturing resource planning or the MRP-II, this system is often called MRP –I. We will review the concept of the MRP-I first and then show how it applies to the MRP-II system.
A simple production component analysis, as shown, is the best way to present MRP-I. The artwork is called a product design tree, and the product is a toy circus car. It is important to note that the finished vehicle consists of a wheel axle sub-assembly. The amount of each small part required in the whole collection is displayed in parenthesis.
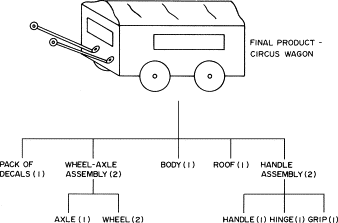
MRP-I also requires lead time values for each component, the completed product’s main production schedule, and the product structure tree. Lead time is when it takes to produce a certain amount of parts. Assume that the final assembly of the toy wagon takes one day, while the wheel axis takes two days to assemble, the wheels take two days to make, and it takes two days to repair. Assume the main schedule requires 500 wagons. As a result, at least five days before the wagons are completed, 200 wheels must be scheduled for production. More wheels may not be needed if there are already wheels assemblies of the wheel axles in hand. When calculating the need for each component, the system must consider the computational part.
Manufacturing resource planning or MRP-II is a system that combines MRP-I, marketing, and financial plans and a factory model to create a strategic planning tool. MRP-II can explore different levels of resources and market strategies regarding manufacturing and economic feasibility. The future demand for various products is estimated using hypothetical market strategies. The MRP-I system uses these demand estimates to determine corresponding needs in different workplaces. Constrains and the ability to not work can be determined using a factory model. Production capacity can be adjusted as needed, and new simulations can be implemented. The financial system is used to estimate the dollar’s impact on a hypothetical market strategy as soon as a reasonable level of potential is reached. The most cost-effective manufacturing resource plan can be developed this way.
Timely or JIT is a simple philosophy that aims to have the right amount of material available at the right time. The goal is to carry only what is essential in the calculation. Several things must happen for JIT to work. For a week at a time, production rates must remain the same. Quality must be unique so that the scrap or recycling does not cause delays. Machines must be arranged so that the work moves quickly from one to another. Preventative maintenance must be done regularly to ensure that the devices are not damaged. Installation tools must be redesigned to swiftly complete to switch from one location to another.
Identify how the new owners can benefit from the master production schedule provided in comparison to your team’s previous performance.
The main production schedule is a detailed schedule for a specific period. It considers consumer needs, capacity planning, material flow, and inventory planning when making manufacturing. The main production schedule is typically created using software and manual adjustments from planners and schedulers. While production planning software considers consumer needs and demands, master production scheduling software also finds the entire manufacturing operations capabilities and constraints. A master production schedule is an excellent solution for businesses looking to synchronize their operations and improve efficiency. The main production schedule has become critical for many manufacturing operations, as its benefits increase efficiency and profits.
One of the essential advantages of a significant production schedule is its communication tool between manufacturing and other companies. The main production schedule results provide a brief overview of all production plans allowing everyone in the organization to see the production schedule. Another significant advantage of a master production schedule is that it aids in the prioritization of supply chain requirements by analyzing all requirements and determining what must be completed first. Effective prioritization will improve and maintain supplier relationships through real-time demand and on-time delivery; effective prioritization will help enhance and maintain supplier relationships, ultimately combating any other supply chain inefficiencies.
In terms of efficiency and timely delivery, maintaining a consistent production flow is essential for manufacturing operations. By analyzing your production version and finding any possible constraints or other constraints, you can use the primary production schedule process to streamline it. This will allow you to make the most of your resources and deliver your products on time (Dewiyana et al., 2021). The main production schedule can help you provide accurate start-up quotes to customers by explaining what will be provided and how much capacity is available to produce additional products. Accepting orders that cannot be fulfilled within the allotted time will help prevent you from insisting on manufacturing departments.
The intended manufacturing schedule of final goods or product alternatives is the main production schedule. Material requirements management systems, for example, use it as part of their production planning system. It’s a remark about output, not about the market demand. The main production schedule, in other words, is not projections; however, sales forecasts are an integral part of the primary production schedule calculation process. Represents the company’s production plans based on models, numbers, and delivery dates (Serrano-Ruiz, Mula & Poler, 2021). It focuses on demand forecasting, overall production plan, backlash, material availability, and capacity. Ideally, demand management activities in the arms Company (Such as forecasting, order entry, pledging, etc.) should be closely monitored by the primary production schedule from time to time. The main production schedule focuses on capacity constraints and serves as the main link between marketing and production.
Prior advantages of the Master Production scheduling
Can help to smooth the demand signal – Many signals of customer needs will have peaks and paths in demand, which can lead developers to plan and negligence issues. The main production schedule has the advantage of separating customer needs from what is being made, allowing the size of the group to be adjusted to improve the manufacturing process (Zhang et al., 2022). When demand is particularly distorted (i.e., peaks and pools), this can be very helpful in creating a consistent production rhythm (by taking advantage of smaller batch sizes and faster installation times), which can go through the distribution stream.
Protects lead time and helps book future deliveries- Many organizations complain that requirements are loaded within the initial period. For example, if a part takes 100 days to repair, it does not make sense to accept customer needs to be sent within 50 days when there is no stock. You will have problems before you even start the manufacturing process. This can lead to panic among employees, causing existing priorities to become confusing. Although various methods prevent this, the main production schedule can be particularly effective because manufacturing is driven by a production schedule rather than customer requirements. This helps the company maintain its lead and helps to plan in determining when the needs of future customers will be well-supported by-product production.
Helps the supply chain prioritize requirements – With a regular timetable, the supply chain team, particularly the procurement department, can convey goals and needs more effectively. One of the significant issues that many manufacturing companies face when changing customer preferences is that the supply chain is being restructured according to the week’s problem. It is not surprising that suppliers respond well to predictable, streamlined needs; when demand is unpredictable, missing delivery (of what is planned) is standard, not to mention the negative impact on relationships with suppliers struggling to conform to what is needed.
Helps stabilize production- The preliminary production schedule should be evaluated as part of a formal business process that includes all key stakeholders. They frequently require chief approval before being incorporated into the manufacturing resource planning system or sent to production. SIOP standard inspections are commonly used to produce production schedules (Kesen et al., 2022). Because major production schedules usually do not allow for debt planning where errors occur and the product is not designed as planned, these products are restructured until the most appropriate time.
Acts as a single communication tool to the business – One of the essential features of the Main production schedule is that it serves as a central communication hub for the company’s manufacturing planning. The main production schedule is usually provided by the material requirements plans systems regardless of the source; it must be presented in an easily understandable format that can be used throughout the business.
Conclusion
Another feature of the preliminary production schedule is that it generally includes a planning window during which no changes are made to the plans. The first six weeks of the program, for example, might be regarded as unique. This allows producers to focus on the tasks ahead of them without worrying about setting priorities again. Additions to this set period are possible but are usually well-controlled. Despite the difficulties of implementing the preliminary production schedule, there are significant and tangible benefits, as with any business process. Manufacturing equipment can cause damage to the supply chain if waves of manufacturing demand are not adequately managed, resulting in prioritization, overcrowding, and UN explained depression in the relationships of major suppliers.
References
Bagheri, F., Demartini, M., Arezza, A., Tonelli, F., Pacella, M., & Papadia, G. (2022). An Agent-Based Approach for Make-To-Order Master Production Scheduling. Processes, 10(5), 921.
Serrano-Ruiz, J. C., Mula, J., & Poler, R. (2021). Smart Master Production Schedule for the Supply Chain: A Conceptual Framework. Computers, 10(12), 156.
Permana, S., Andriani, M., & Dewiyana, D. (2021). Production Capacity Requirements Planning Using the Capacity Method Requirement Planning. International Journal of Engineering, Science and Information Technology, 1(4), 36-40.
Zhu, B., Zhang, Y., Ding, K., Chan, F. T., Hui, J., & Zhang, F. (2022). Lot-sizing decisions for material requirements planning with hybrid uncertainties in a smart factory. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 51, 101527.
Yağmur, E., & Kesen, S. E. (2022). Bi-objective coordinated production and transportation scheduling problem with sustainability: formulation and solution approaches. International Journal of Production Research, 1-22.
Amaranti, R., Muhammad, C. R., & Septandri, M. V. (2020, April). Determining the changes in the Master Production Schedule (MPS) at the company with Make to Stock (MTS) and Make to Order (MTO) strategies. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 830, No. 4, p. 042003). IOP Publishing.
 write
write