Introduction
Karen Hughes stated that the tourism and travel sector is not just a place but a considerable section of a nation’s economy. Marketing a location, also known as destination marketing, is a management process that involves demand-driven research, advertising, and communication activities, emphasizing potential customers from the outside. Its primary objective is to entice visitors, tourists, investors, students at educational institutions, or skilled workers. The tourism sector significantly emphasizes destination marketing as a critical component. It entails promoting a specific location to people interested in visiting it as tourists, with the ultimate goal of persuading them to visit it (Ingrassia et al., 2022). In recent years, there has been an increasing interest in determining the economic impact that destination marketing has on the number of tourists that arrive at a particular location. It entails locating the destination’s most advantageous and competitively enticing assets in the eyes of potential visitors, constructing a narrative out of these assets that distinguish the destination from its rivals, and ensuring that this narrative is carried out consistently throughout all marketing communications for the destination. Even with the relevance of destination marketing, there is a need for more studies on the precise financial impact of destination marketing on visitor arrivals. This research paper addresses the gap by evaluating the relationship between destination marketing and tourism in New York.
Literature review
According to Papatheodorou (2006), an integrated marketing communication approach is paramount for successful destination marketing. He says that to properly market and position a location among the chosen audience, a marketing communication strategy that is both thorough and coordinated is required. The marketing communication plan for a destination should be customized to its unique qualities, such as its location, culture, attraction, and infrastructures, alongside the needs and preferences of the audience visiting the place. For a communication strategy to be successful, it is necessary to consider various aspects, such as the media utilized, the message sent, and the intended consequence. According to Papatheodorou (2006), a destination’s marketing plan succeeds when it includes many stakeholders, including tourist boards, travel agents, hotels, and local businesses. Maintaining a unified brand voice and message across all platforms demands careful planning and constant communication. An all-encompassing plan must consider relevant elements and encourage cooperation amongst relevant parties. This tact allows destination marketers to successfully advertise their locations and develop a memorable brand image.
In addition, Sotiriadis (2020) summarises the research done in the field of tourism destination marketing. The article focuses on the most critical ideas, philosophies, and practices within the industry, and it stresses the need to adopt a strategic and integrated method when approaching destination marketing. When marketing a destination, it is essential to have a solid understanding of the target audience’s demographics and preferences, as well as the roles that branding, communication, and stakeholder collaboration play in sculpting the image and identity of a location. There is a requirement for a marketing mix plan that is both all-encompassing and well-coordinated, and that strategy should involve various communication methods and platforms. A focus must be placed on the significance of adopting a strategic and integrated method of destination marketing and that insights into the most significant difficulties and possibilities connected with this industry be uncovered.
Becken (2002) strongly emphasizes the relevance of destination branding as an essential part of destination marketing. According to the article, destination branding develops a distinctive image and personality for a location to separate it from similar destinations and entice potential visitors. It is essential to take a methodical, step-by-step approach when developing a successful brand for a destination. This includes determining the destination’s unique selling proposition (USP), defining the personality and values of the brand, and developing a brand identity that reflects the distinctive qualities and features specific to the destination. Similarly, the significance of the involvement and engagement of stakeholders in the branding process must be considered. Furthermore, efficient destination branding takes persistence and cooperation among all marketing channels, such as advertising, public relations, and digital media. A well-crafted destination brand can assist in establishing an emotional attachment with prospective visitors, thereby enhancing the visitors’ interest in and engagement with the specific destination.
From a global viewpoint, Pritchard (2011) lays out the many difficulties and potential rewards of destination marketing. They are realizing the significance of cultural variations and tailoring marketing approaches to the requirements of overseas markets. Adapting destination marketing techniques to suit individual foreign markets is a significant concept in the field. Marketing a place requires in-depth familiarity with the targeted demographic and an awareness of the cultural nuances that must be considered while designing campaigns. Not only do people have different languages and cultural norms, but they also have different travel habits and reasons for seeing the world. Destination marketing relies heavily on active participation and cooperation from key stakeholders. Destination marketing is most successful when it includes several parties, such as residents, business owners in the tourist industry, and government organizations. Collaboration and marketing alignment with broader economic, social, and environmental goals may be achieved by establishing partnerships and networks. It is also essential to think about how technology and digital media function in the context of destination marketing. According to Pritchard (2011), the advent of the Internet and social media has completely changed how tourism spots are advertised, allowing for more specific and individualized approaches to promotion. Gathering information about tourists’ habits and likes with technology may help shape advertising campaigns and enhance the trip for those who visit a specific location.
Furthermore, given the complexity and fluidity of the area, Fyall, Garrod, and Tosun’s (2007) paradigm for future study in destination marketing is timely and vital. The authors claim that knowing how internal and external elements interact to build a place’s image and attraction to potential tourists is essential for efficient destination marketing. A framework is required that considers the destination product, the marketing mix, and the destination setting while promoting a destination. The natural and cultural resources, infrastructure, and services that make up a destination are only some of the physical aspects of the destination product dimension. Advertising, public relations, and sales promotions are all part of the marketing communication methods that may be utilized to spread the word about the holiday spot, which make up one part of the marketing mix. The destination context considers the role of stakeholders and cooperation in destination marketing and the more extensive social, cultural, economic, and political variables that define a destination’s image and desirability. Destination marketers must keep up with the ever-evolving tastes of the tourist industry and adjust their marketing tactics appropriately. However, they must also take a holistic and integrated strategy considering the connections between each framework’s components.
Moreover, the article by Tran and Rudolf (2022) comprehensively assesses the literature on social media applications in tourist destination branding. The authors investigate the impact of social media platforms on the promotion of travel destinations, the creation of brand awareness, and the formation of travellers’ impressions of the places they visit. Because of its ability to sway visitors’ choices, the rising significance of social media in the tourism sector is vital. This is because of the potential that it has to affect the decision-making process of tourists. It is now only possible to successfully sell a place by extensively using social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and YouTube. Tourism organizations and destination marketing companies use these platforms more often to communicate with travellers and promote their locations. Because visitors can now share their experiences and views with an audience worldwide, the conventional top-down strategy for marketing holiday destinations has shifted due to the rise of social media.
Pike and Page’s (2014) narrative review of the literature on DMOs and destination marketing is thorough. By examining the fundamental themes and concepts in the literature, the authors want to better understand the theoretical and practical elements of destination marketing. DMOs are well-recognized in this setting for their contributions to tourist marketing and the enhancement of destination attractiveness. Teamwork and partnerships between several parties are essential for a successful destination marketing campaign. A thriving destination marketing campaign often results from collaborative efforts among DMOs, governments, commercial sector organizations, and local communities. Working together as partners has several benefits for the tourist industry, including better alignment of interests, improved product and service quality, and promotion of a destination’s appeal. With the proliferation of smartphones and other digital devices, DMOs increasingly turn to digital technology to advertise their destinations to visitors. DMOs must adjust to these shifts by creating digital marketing models that use digital media’s potential.
Bunghez (2020) investigates the connection between tour operators’ advertising tactics and the tourism business’s long-term health. While travel agents are the primary focus of the research, the results may be applied to destination marketing as a whole. Sustainable tourism businesses promote their services by highlighting the destination’s natural and cultural features and the agency’s commitment to social responsibility and ethical business practices. This data supports the idea that destination marketing campaigns highlighting eco-friendliness and social responsibility are likelier to entice visitors with similar beliefs. Successful customer acquisition is often associated with digital marketing channels, including social media, email marketing, and search engine optimization (SEO). Digital marketing campaigns for tourist destinations are equally efficient in reaching potential customers. There is a correlation between a travel agency’s level of client happiness and loyalty and the extent to which it allows for personalized holiday packages and experiences. In light of these findings, destination marketing campaigns that emphasize the unique and individual opportunities available at a particular location are more likely to lure visitors and establish a favourable reputation.
Research design and methodology
A quantitative research approach was utilized for the study, which entailed gathering and examining various numerical data. The quantitative research entailed surveys from New York through the analysis of surveys from the companies and data presented by the state articles. The research covered companies like New York City Tourism + Conventions and New York City Guide and the contribution of tourists to New York. The visitors who have already been to New York City have commended the functioning and operations of destination marketing through their impressions of the marketing methods employed by New York agencies. In addition, the survey, through questionnaires from New York City Tourism + Conventions and New York City Guide managers and New York policymakers, provided data about the destination marketing strategies that have been put into action.
Statistical procedures such as correlation analysis and regression analysis were utilized in the process of analyzing the data that was obtained. The research investigated the connection between marketing a location, the number of visitors who visit that place, and the economic effect on the growth of their respective regions. To boost the accuracy of the research results, integrate various data types in the analysis, save time, and a host of other benefits, the research critically considered the benefits of Big Data and Deep Learning algorithms. This research by Liu et al. (2020) bridges the literature on picture extraction and machine learning on the one hand and the brand literature on the other to extract information from various articles and government articles. It presents a strategy to access the system brands and market intelligence and aggregates consumer-generated photos. Natural language processing, sometimes known as NLP, is a computer science subfield that describes how computers recognize, interpret, and reproduce the structures of natural languages. The fields of mathematics and computer science are inextricably intertwined with linguistics. Natural language processing (NLP) is typically understood to be a subfield of both artificial intelligence and language. As a result, a thorough knowledge of the viewpoints of both domestic and foreign visitors on the branding of New York City may be achieved via social media.
Findings and implications
The research revealed insightful new knowledge on the economic influence that destination marketing has on the number of visitors. The research identified the marketing tactics that are the most effective in drawing visitors to New York City and gave recommendations for destination managers and policymakers on how to enhance their efforts to advertise the area. New York City Tourism + Conventions and New York City Guide are two marketing destination agencies that have remained relevant and successful because of the use of the Internet to advertise their services. In addition, New York City Tourism + Conventions has succeeded by adhering to its mission of maximizing travel and tourism opportunities all through New York while building economic success and spreading the dynamic image of New York City worldwide.
In the financial year ending in June 2020, New York City Tourism + Conventions had contract funds at $21.2 million from $20.9 million in 2019 (NYC & Company, n.d). After Covid 19 and doing away with the restrictions, destination marketing is expected to experience tremendous success, improving the city’s economic growth. New York City Guide, according to recent data presented by the United States Travel Association, direct spending on travel in the United States reached $1.2 trillion in 2022, which was in line with levels seen prior to the epidemic as a result of the economic footprint of $2.6 trillion (Wolff, 2023). Hotel bookings stood at 98% of their pre-pandemic levels, and airline ticket sales achieved an all-time high by increasing by 22% yearly to set a new record. The hospitality industry led the city’s growth, but New York City still needs more people to be hired to keep up with the tourist demand.
More than 376,800 jobs (or approximately 10 per cent of total private sector employment) depend on the tourist industry in New York City (DiNapoli, 2021). Hospitality and transportation form the sector’s backbone, a dynamic ecology of attractions, including performances, events, shopping, and dining.
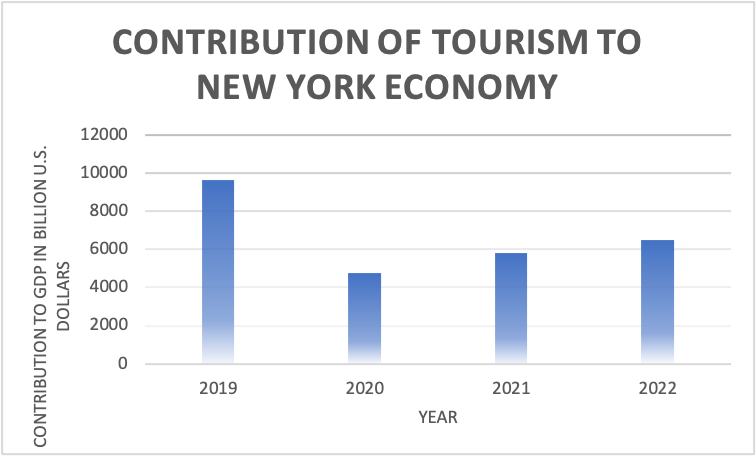
Graph showing the contribution of tourism to the New York economy from the year 2019 to 2022
The vital signs of an industry may be gauged by looking at visitor numbers and tourist expenditures. The number of tourists that visited New York City in 2020 fell by 67% from the record high of $86.6 million in 2019, while their expenditure fell by 73% to $47.4 billion due to the Covid-19 epidemic (DiNapoli, 2021). In 2019, as defined by OSC, the tourist business accounted for a record 283,200 jobs, 7.2% of private sector employment, and 4.5% of private sector incomes. This was a 35% increase from 2009 levels, higher than the overall 30% increase in private-sector employment. According to OSC projections, employment in 2020 dropped to 194,200, a decrease of 31.4% (or 89,000 jobs) and the lowest level since 2004 (DiNapoli, 2021). In 2019, 53.5% of the state’s total tourist jobs were in the City of New York, which explains the impact of destination marketing on the city. The study’s findings stress the value of cooperation among tourist sector players. Many parties, such as local companies, tour operators, travel agencies, and destination managers, must all work together for a destination’s marketing campaign to succeed.
An increase in the number of tourists that visit a location may lead to an increase in the amount of money spent, the number of jobs created, and the amount of tax income collected, all of which can be beneficial to the community’s cultural landmarks, natural beauty, and regional food, which might pique a traveller’s interest in a potential holiday spot and encourage them to book a trip there as in the case of New York City. If destination managers and politicians understand these motives better, they will be better equipped to craft marketing tactics that align with their target audience’s interests and preferences.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this study provided critical analysis to fill a vacuum in existing research on the economic influence that destination marketing has on the number of visitors it attracts. In this study, a quantitative research approach was taken, and the data gathered through secondary sources, interviews, and surveys from New York City Tourism + Conventions and New York City Guide indicated the massive impact of destination marketing on New York City’s GDP. The research identified the marketing strategies like proper advertisements of the places and the organizations and excellent customer service through well-laid plans and mission as the most effective in luring tourists to the destination. Additionally, the research recommended that government officials and managers of destination marketing organizations should work together to form policies that create desirable conditions for the success of tourism. The results of this study had significant repercussions for the tourism sector and led to a better understanding of the link between destination marketing and the number of tourists who visit New York City and other locations.
References
Becken, S. (2002). Destination branding: Creating a unique destination proposition. New Zealand Tourism Research Institute, University of Otago.
Bunghez, C. L. (2020). Marketing strategies of travel agencies: A quantitative approach. Sustainability, 12(24), 10660.
DiNapoli, T. P. (2021, April). The tourism industry in New York City. Office of the New York State Comptroller. Retrieved April 28, 2023, from https://www.osc.state.ny.us/reports/osdc/tourism-industry-new-york-city
Fyall, A., Garrod, B., & Tosun, C. (2007). Destination marketing: A framework for future research. In Progress in tourism marketing (pp. 75-86). Routledge.
Ingrassia, M., Bellia, C., Giurdanella, C., Columba, P., & Chironi, S. (2022). Digital influencers, food and tourism—A new open innovation model for businesses in the Ho. Re. Ca. Sector. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 8(1), 50.
Liu, L., Dzyabura, D., & Mizik, N. (2020). Visual listening in Extracting brand image portrayed on social media. Marketing Science, 39(4), 669-686.
NYC & Company. (n.d.). NYC & Company Annual Report 2020 – 2021. Retrieved from https://indd.adobe.com/view/3e235017-4549-4a3a-af52-171d9b95094e?cid=NYCEM_MEM_AnnualReport_20210324&cid=NYCEM_MEM_TourismRecovery45_20210325
Papatheodorou, A. (2006). Destination marketing: An integrated marketing communication approach. Tourism: An International Multidisciplinary Journal of Tourism, 1(1), 9–25.
Pike, S., & Page, S. J. (2014). Destination Marketing Organizations and destination marketing: A narrative analysis of the literature. Tourism management, pp. 41, 202–227.
Pritchard, A. (2011). Destination marketing: An international perspective. In R. V. D. Berg, M. M. Sigala, & J. V. Eijgelaar (Eds.), Advances in tourism marketing research: An international perspective (pp. 93–112). Emerald Group Publishing Limited.
Sotiriadis, M. (2020). Tourism destination marketing: academic knowledge. Encyclopedia, 1(1), 42-56.
Tran, N. L., & Rudolf, W. (2022). Social Media and Destination Branding in Tourism: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Sustainability, 14(20), 13528.
Wolff, E. (2023, March 20). NYC Tourism 2023. New York City Guide. Retrieved April 28, 2023, from https://www.cityguideny.com/article/summer-tourism-data-nyc-2022
 write
write