Abstract
This paper is on Cost Benefit Analysis (CBA) of Immaculate Medical Center (IMC). To plan for changes, IMC is using the cost-benefit analysis. The purpose of the CBA is to predict whether planned changes in the operations at the Hospital are cost-effective. If the cost outweighs the benefits, the project should not be undertaken. Otherwise, if the benefits are more, the project should be conducted. According to Porreca (2020), the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) guides healthcare system administrators in calculating the value of healthcare projects. It provides direction to healthcare system managers on estimating the value of healthcare. The reason for undertaking the project is to come up with new ways of operations at the organizations to better the services offered. A recent survey at the facility identified weaknesses in the processes, like long waiting times and medical errors, which need to be corrected. The predicted project cost is calculated against the benefits likely to be obtained using an M.S. spreadsheet program. The results over five years noted that the benefits far outweigh the cost. Therefore the project will be undertaken. (National Center for Health Statistics, 2018).
Justification
Healthcare organizations are governed by regulations that administrators should always seek to comply with whenever they intend to undertake a project. The rules ensure the avoidance of penalties and help improve service delivery. Healthcare companies can use cost-benefit analysis (CBA) to assess the practicality of integrating new regulatory frameworks into their existing infrastructure. Therefore, CBA will aid in determining whether or not integrating the Immaculate Medical Center’s regulatory compliance framework for managing healthcare quality risk is economically feasible.
The focus of Stakeholders for CBA
Patients, Providers (healthcare professionals and organizations), Funders, and Policymakers are the main stakeholders in the healthcare system. The media, the scientific community, the regulators, and the manufacturers of medical equipment and drugs all play an essential role. As a Missouri hospital, Immaculate Medical Center is subject to the rules and regulations of the HHS. The HHS divisions work toward a common goal: better patient care, healthier medical professionals, and more effective healthcare organizations. The Department of Health and Human Services recognizes that accounting for benefits and costs that are difficult to quantify is required for economic feasibility studies associated with implementing regulatory systems (National Center for Health Statistics, 2018). Therefore, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) sets recommendations for an economic feasibility study of regulatory frameworks on the healthcare sector, which include calculation of maintenance, operating, administrative, and capital expenses.
All the people who have a stake in how a healthcare organization operates should be among the critical stakeholders evaluated throughout the adoption of the regulatory framework. The patients, the insurers, the suppliers, and anybody else involved. It is up to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services to establish rules and guidelines. To oversee the industry’s policy execution, the department collaborates with IMC. Collecting information from stakeholders, including providers, funders, and patients, is the first step in crafting an effective policy. Politicians decide who may practice medicine and who can pay for medical services. Functioned significantly during the health care quality risk regulation framework. Stakeholders include non-governmental organizations (NGOs) that contribute independently to the health care system. The funders are considered when establishing the regulatory framework since they provide the necessary financial resources. Insurance firms fall under the category of “payers” since they stand to gain from a well-executed policy.
Value Proposition for Change Management
Management of change entails the following four steps:
Organizational Change Readiness: To seek and effectively execute change, a company has to be ready on both the practical and cultural levels. Make cultural preparations before operations (Ratana et al., 2020).
Develop a strategy for getting there: Managers are responsible for creating a comprehensive and practical strategy for implementing change once the company is ready to do so. The strategy needs to describe: goals, KPIs, Stakeholders, Team, and the Project Scope (Ratana et al., 2020).
Make the Required Changes: Once the strategy has been drafted, all that remains is to implement the steps outlined in it in order to bring about the intended change. This may necessitate changes to the company’s structure, strategy, processes, procedures, employee habits, or other elements, depending on the specifics of the enterprise. method of ions (Ratana et al., 2020).
New Methods: Once a change initiative has been implemented, it is the responsibility of transformation managers to ensure that the company does not return to what it was before. This is paramount when implementing company culture, strategy, or operations changes. As a result of not having a plan, employees may resort to “old ways of doing things,”, especially during the transition period (Ratana et al., 2020).
Immaculate Medical Center’s administration will be able to calculate the financial performance indicators needed to undertake an impact assessment of the framework adoption, thanks to the CBA’s concept of a microeconomic approach. This concept demonstrates the tradeoffs inherent in devoting healthcare resources like EHRs and human labour to one function rather than another. Considering their highest practical or productive usefulness is thus essential when determining the value of medical resources. The second factor that HHS considers is consumer sovereignty when deciding how much money will be allocated for assistance. The concept calls for healthcare finance managers to separate the cost of transfers from the actual resources used.
The completion of a change effort is no guarantee of the success of the initiative itself. Hence it is essential to review progress and analyze results periodically. Leaders in an organization can learn more about the success or failure of a change initiative by performing a “project post mortem” (an analysis and assessment of the initiative’s results). Moreover, it may provide helpful information and lessons for guiding future efforts to effect change (Ratana et al., 2020).
Immaculate Medical Center’s administration will be able to calculate the financial performance indicators needed to undertake an impact assessment of the framework adoption, thanks to the CBA’s concept of a microeconomic approach. This concept demonstrates the tradeoffs inherent in devoting healthcare resources like EHRs and human labour to one function rather than another. Considering their highest practical or productive usefulness is thus essential when determining the value of medical resources. The second factor that HHS considers is consumer sovereignty when deciding how much money will be allocated for assistance. The concept calls for healthcare finance managers to separate the cost of transfers from the actual resources used.
Quality Improvement Strategies
IMC’s leadership has carefully considered the options available to them as they assess the potential of their new risk regulatory compliance framework. Management notes that it is simple to put a price tag on the price of complying with regulations. Compliance with regulations can have many positive effects on a healthcare system, but it can be challenging for administrators to put a price tag on them. Patients’ health and happiness are essential aspects of healthcare benefits, and happiness is a non-market benefit. Fortunately for the administration, the CBA framework uses several economic ideas that make dollar-value measurement of health benefits possible.
The gradual approach is a CBA idea that will help Immaculate Hospital’s management predict how adopting the regulatory compliance framework would affect the Hospital’s bottom line. The advantages and disadvantages of adopting the framework in terms of money, time, and resources are factored into the gradual approach. Financial managers can use CBA and the social discounting process to produce cash flow estimates for 20 years. Utilizing the discounted net present value, management may evaluate the future advantages and costs of adopting the framework.
Cost-Benefit Analysis and Assumptions
The management of IMC will distribute benefits to the stakeholders as follows:
Patients’ benefits
A lower mortality rate is one of the many health advantages of implementing a compliance framework. The quality of life and the patient’s sense of self-reliance, competence, and confidence improve. New treatment procedures are expected to be adopted by management due to their positive effect on life expectancy. In addition, having easy access to high-quality medical treatment boosts people’s well-being. Patient service delays will be reduced, and patients will be happier overall. (Ananthapavan, et al., 2021).
Employee Benefits
Employee benefits from implementing a regulatory compliance framework include happier workers and better working circumstances. Improvements in job safety, as seen by fewer incidents of occupational injuries, are another perk. Employees will benefit from a higher level of knowledge and competence thanks to chances for training and research.
Costs
The costs will be:
Monetary: infrastructure: Infrastructure building, training, more experienced workers, and regulatory compliance expenses. Money will also be required to buy computers and supervisors.
Non-Monetary Costs: Expenses incurred by healthcare providers as a result of staff members’ resistance to and difficulty adjusting to change throughout service. This partly stems from the fact that people tend to resist changes. Another factor to consider is that internal resistance has slowed the adoption process of new frameworks and technologies.
Benefits to the Hospital
Monetary
- Increased profits
- Increased efficiency
- Reduction of wastage
Non-monetary
- Successful recruitment
- retention, and motivation of employees
- decreased rates of infections and medical mistakes; enhanced patient safety
- Cost reduction due to improved data analysis
Relationship to Vision, Mission, and Values
IMC’s Mission is to provide a healthy setting for patients to heal while also boosting community well-being. Quality patient care is another area of emphasis at IMC. Adopting the regulatory framework is consistent with the goals of IMC since it will lead to better healthcare for everyone.
IMC’s Vision is to become the top Hospital in the world, a position that would make it attractive to medical professionals and patients worldwide. Additionally, the system prioritizes the happiness of both patients and staff, which has led to a rise in both groups. Given that its primary objective is to boost customer and worker happiness, the system aligns with IMC’s general goals.
Internal and External Benchmarks
IMC will use a benchmarking tool to compare its performance to other variables. Benchmarking procedures include assessing best practices and standards, identifying weak points, and evaluating evidence-based procedures. Adoption includes health care quality, patient satisfaction, and service prices, among benchmarking indicators that will be used to assess the efficacy of the regulatory framework. IMC will be able to identify issues by adopting a regulatory framework and implementing improvement plans thanks to the benchmarking operation. IMC may suggest the creation of new benchmarks at any point throughout the execution of the regulatory framework if new tactics are used. IMC can assess whether new benchmarks have been reached through progress measurement. To ensure that adopting a new regulatory framework enhances healthcare organizations’ internal and external performance, IMC will adopt two benchmarking methodologies, including internal and external (Blili & Hancox, 2022). There is a notable increase in medical errors at the Hospital. A reason for some of the errors is overworking by the medical personnel. More personnel will be employed to ease the burden. Automation will be employed in the departments to make the work quicker and more efficient. The Hospital seeks to ensure that they comply with the regulations governing the operations of health centres. The project aims to make the medical centre afloat amidst rising competition from upcoming facilities in the area.
Conclusion
The leadership at IMC will work hard to implement a regulatory compliance structure that lives up to the high requirements required by the United States Department of HSS. The enhanced services will benefit the Hospital, the employees, and the patients. More people will use the service since it has been enhanced, increasing revenue. No costs associated with noncompliance will occur. Employees will be more satisfied, and patients will receive good services. On calculation, the benefits are found to be $ 1,350,000.00. The project is, therefore, viable. It should be undertaken.
References
Ananthapavan, J., Moodie, M., Milat, A., Veerman, L., Whittaker, E., & Carter, R. (2021). A cost-benefit analysis framework for preventive health interventions to aid decision-making in Australian governments. Health Research Policy and Systems, 19(1), 1–23. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12961-021-00796-w
Blili-Hamelin, B., & Hancox-Li, L. (2022). Making Intelligence: Ethics, I.Q., and ML Benchmarks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.00692. https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.00692
National Center for Health Statistics (U.S. (2018). Health, United States, 2017: With Special Feature on Mortality [Internet]. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30702833/
Porreca, A. (2020). Assessing Diversity and Inclusion in the Context of the U.S. Federal Department of Health and Human Services. Decision Making in Social Sciences: Between Traditions and Innovations (pp. 411–421). Springer, Cham. https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&as_sdt=0%2C5&as_ylo=2018&q=The+United+States+Department+of+Health+and+Human+Services+&btnG=#d=gs_cit&t=1665437342885&u=%2Fscholar%3Fq%3Dinfo%3AIxfereQ0TUEJ%3Ascholar.google.com%2F%26output%3Dcite%26scirp%3D1%26hl%3Den:~:text=Porreca%2C%20A.%20(2020).%20Assessing%20Diversity%20and%20Inclusion%20in%20the%20Context%20of%20the%20US%20Federal%20Department%20of%20Health%20and%20Human%20Services.%20In%20Decision%20Making%20in%20Social%20Sciences%3A%20Between%20Traditions%20and%20Innovations%20(pp.%20411%2D421).%20Springer%2C%20Cham.
Ratana, S., Raksmey, C., & Danut, D. (2020). CONCEPTUALIZING A FRAMEWORK: A CRITICAL REVIEW OF THE DEVELOPMENT OF CHANGE MANAGEMENT THEORIES. Studies in Business & Economics, 15(2). https://magazines.ulbsibiu.ro/eccsf/RePEc/blg/journl/15215som.pdf
Appendix
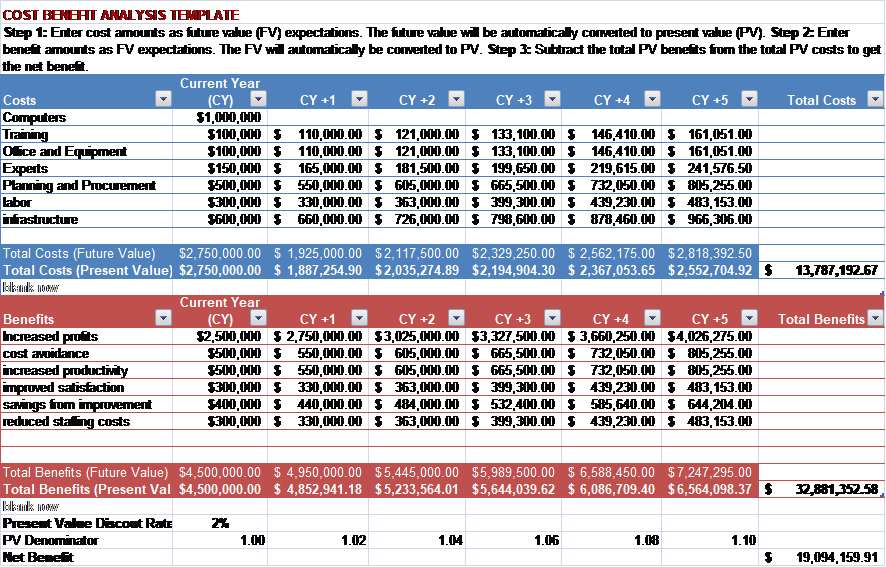
Assumptions
The assumption is that all the other factors will be the same as before. The increase in the benefits is also assumed to be only contributed by the management change and not any other factor. The cost and benefits increase by 10% each year. The cost of buying computers is only in the first year.
 write
write