Operational Challenges in Managing Its Global Supply Chain
The Coca-Cola Company is a multinational beverage corporation headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. The company was founded in 1886 by John Pemberton and is best known for its flagship product, Coca-Cola, a carbonated soft drink. The company operates in more than 200 countries and territories and offers more than 500 brands, including Fanta, Sprite, Dasani, and Powerade (Brondoni, 2019). In addition to soft drinks, Coca-Cola produces juice, coffee, tea, and energy drinks. The company is publicly traded and listed on the New York Stock Exchange. The company was incorporated in 1892 as the Coca-Cola Company, and in 1899, the first bottling plant was opened in Chattanooga, Tennessee. The Coca-Cola formula and brand were bought in 1919 by Asa Griggs Candler, who incorporated The Coca-Cola Company. The company is now based in Atlanta, Georgia, and is one of the world’s largest manufacturers and distributors of nonalcoholic beverages.
An operations management issue that the Coca-Cola Company has faced in recent years is supply chain management. The company has a complex global supply chain that involves sourcing raw materials, manufacturing and packaging products, and delivering them to customers (Smith, Xiang, & Medlin, 2021). The company has faced challenges with managing this supply chain effectively, such as unexpected disruptions due to natural disasters and political instability, as well as managing its operations’ environmental and social impact. This has led to increased costs and disruptions in the company’s operations.
Problem Statement
The Coca-Cola Company, one of the world’s largest manufacturers and distributors of nonalcoholic beverages, has recently been experiencing problems with its supply chain. These problems have manifested in delays and shortages of products at various locations, causing customer frustration and disrupting the unit’s operations.
One example of these disruptions is the shortage of popular products due to delays in replenishment. This means that some stores have run out of the products that consumers typically purchase, causing disappointment and inconvenience for customers (Brondoni, 2019). Additionally, unexpected spikes in demand have also caused shortages as the supply chain struggles to keep up with the sudden increase in demand.
These supply chain problems have affected not only the company’s operations but also its reputation. Customers have become frustrated with the need for more availability of their preferred products and may turn to competitors. Furthermore, supply chain disruptions also affect the company’s bottom line as lost sales, customers, and higher costs are all consequences of supply chain problems.
Current Condition
Like many other companies, the Coca-Cola Company faces several supply chain challenges in the UK and EU. One of the main challenges the firm is currently facing is a lack of HGV (heavy goods vehicle) drivers. This shortage of drivers is affecting the company’s ability to transport goods to and from its warehouses and distribution centers, which in turn is causing delays and shortages of products at various locations.
Another challenge the company faces is the increased demand for goods due to e-commerce and home delivery services. This has put pressure on the company’s logistics operations, as it needs help to meet the demands of online shoppers who expect fast and reliable delivery. This has led to a higher demand for transportation and warehouse services, further exacerbating the need for HGV drivers (Feleke, 2022). The root cause of the lack of HGV drivers can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the current economic climate has resulted in a shortage of drivers due to the high demand for goods and services. The unemployment rate is low, and many choose to work in other sectors, such as construction, healthcare, and technology. As a result, the number of available HGV drivers needs to catch up with the demand for logistics services. The job of an HGV driver is becoming increasingly unattractive to many people. The job involves long hours, being away from home for extended periods, and dealing with the pressures of tight delivery schedules. Additionally, the government’s crackdown on illegal immigration has made it difficult for companies to hire drivers outside the EU, further exacerbating the shortage.
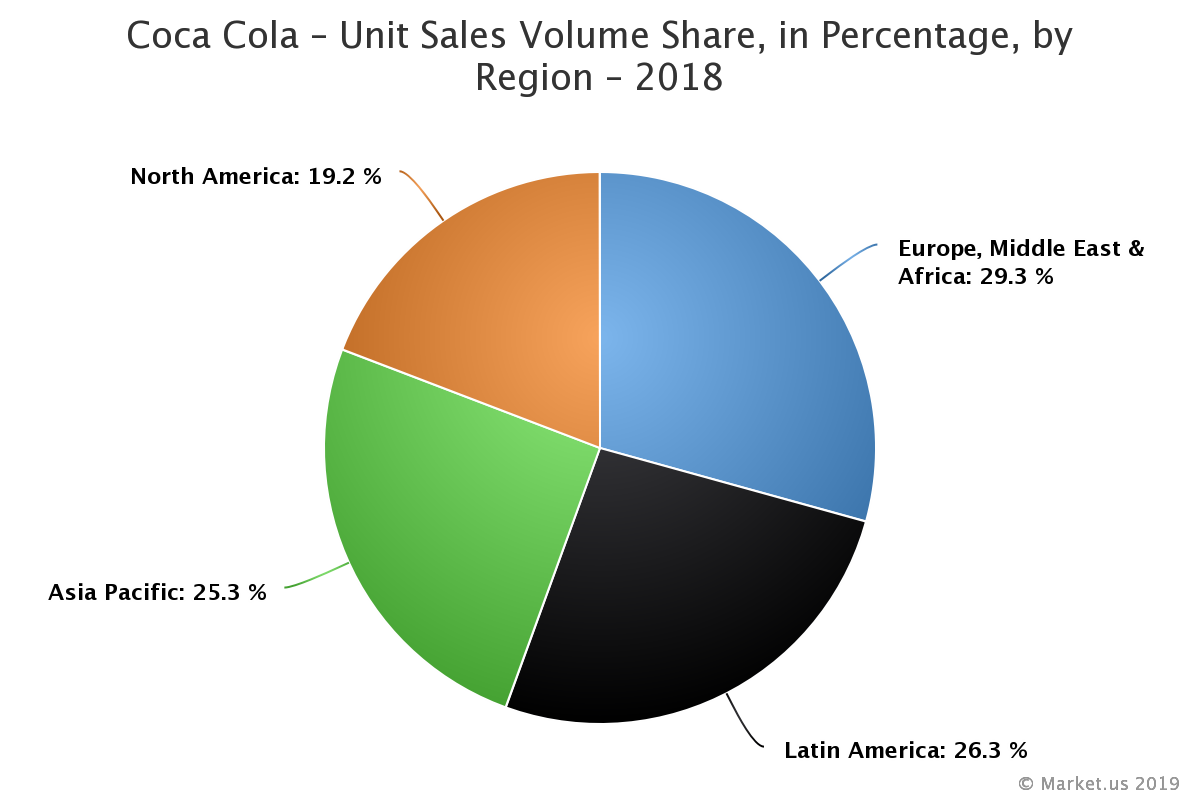
Chart showing Cocacola supply chain performance in different regions
In addition, the company is also facing challenges related to Brexit. The UK’s exit from the EU has resulted in changes to regulations and customs procedures that have made it more difficult and time-consuming to transport goods between the UK and the EU. This has increased the cost of logistics and transportation, which has impacted the company’s bottom line.
Furthermore, the company is also experiencing challenges related to sustainability. The company’s goal is to reduce its carbon footprint. However, this is a challenging task when it comes to logistics. The company is looking for ways to reduce its dependence on fossil fuels, for example, by using alternative fuels, electric vehicles, and other sustainable transportation options (Bwakea, 2020). This requires significant investments, new infrastructure, and technology, which poses a significant challenge to the company.
Analysis Of The Effects Of The Current Condition
If changes are not made to address the current supply chain challenges the Coca-Cola unit faces, the company may experience several negative consequences.
Firstly, the company may see a decline in sales and revenue due to delays and shortages of products at various locations. This is caused by a lack of HGV drivers, which affects the company’s ability to transport goods to and from its warehouses and distribution centers. When products are unavailable to customers, they will turn to competitors, resulting in lost sales for the company.
Secondly, the company may experience a decline in customer satisfaction and loyalty. Customers become frustrated when products are unavailable and may look for alternatives. This can lead to a loss of repeat customers and a decrease in brand loyalty. The company may also see increased negative online reviews and social media mentions as customers voice their disappointment.
Thirdly, the company may experience an increase in logistics and transportation costs. The lack of HGV drivers may lead to higher costs for temporary drivers, overtime pay, and other expenses associated with finding replacement drivers (Bos, 2022). Additionally, the company may also see an increase in fuel costs due to delays and detours caused by a lack of drivers. When drivers are unavailable, the company must find temporary drivers or hire additional staff to manage the increased workload. This can result in an increase in staff costs, including salaries, benefits, and training expenses.
Furthermore, the company may need to pay overtime or provide additional incentives to attract and retain drivers, which can also add to the costs. Rescheduling deliveries is another administrative task that can arise from a lack of HGV drivers. When drivers are unavailable, the company must reschedule deliveries to ensure that products reach customers on time. This can require additional staff resources and lead to increased costs for the company. Dealing with customer complaints is another administrative task that can arise from supply chain challenges. When products are unavailable or delivery times are delayed, customers may become frustrated and contact the company to voice their complaints. This can require additional staff resources to handle these complaints, leading to increased costs.
Fourthly, the company may experience an increase in inventory holding costs. Delays in replenishment and unexpected spikes in demand can lead to a build-up of inventory in warehouses and distribution centers. This can result in additional costs for storage and insurance.
Lastly, the company may experience an increase in administrative costs. The lack of HGV drivers may lead to more paperwork and administrative tasks, such as finding replacement drivers, rescheduling deliveries, and dealing with customer complaints. This can increase staff costs and other expenses associated with managing these additional tasks (Sangode & Metre, 2019). suppose changes must be made to address the Coca-Cola unit’s current supply chain challenges. In that case, the company may experience several negative consequences, including a decline in sales and revenue, a decline in customer satisfaction and loyalty, an increase in logistics and transportation costs, and an increase in inventory holding costs and administrative costs. To avoid these negative consequences, the company needs to take a comprehensive approach, examining all aspects of the supply chain and identifying areas for improvement.
Gap Issues
Gap issues refer to the discrepancies or differences between what a company intends to achieve and what it achieves in terms of service or product delivery. In the context of the current supply chain challenges the Coca-Cola Company faces, gap issues can arise in several areas, which can negatively impact efficiency in services or products.
Service delivery. The company intends to provide fast and reliable delivery of products to customers. However, the lack of HGV drivers and other supply chain challenges result in delays and shortages of products at various locations. This leads to disappointed customers who do not receive their orders on time, leading to a gap between the company’s intentions and performance.
Secondly, gap issues can arise in terms of product availability. The company may intend to have a wide variety of products available to customers at all times, but the supply chain challenges result in shortages of products at specific locations (Rajeev, Pati, & Padhi, 2019). This causes a gap between the company’s intentions and performance, as customers need help finding the products they want to purchase.
Product quality. The company intends to deliver high-quality products to customers. However, supply chain challenges cause replenishment delays, resulting in products sitting in warehouses or distribution centers for extended periods. This leads to a gap between the company’s intentions and its performance, as end customers receive products past their expiration date or damaged during transit.
Cost efficiency. Coca-cola company intends to keep costs low while providing quality products and services. However, distribution challenges lead to higher logistics and transportation costs, increased inventory holding costs, and increased administrative costs. The challenge results in a gap between the company’s intentions and its actual performance since it cannot maintain the same level of profitability it had intended.
The gap issues about efficiency in service or products arise due to the current supply chain challenges the Coca-Cola Company faces. These gap issues include discrepancies in service delivery, product availability, quality, and cost efficiency (Sodhi & Tang, 2021). To address these issues and achieve efficiencies in service or products, the company should take a comprehensive approach, examining all aspects of the supply chain and identifying areas for improvement.
Changes For Improving The Condition
Based on the information provided in this chat, several changes can be made to improve the current business condition of the Coca-Cola Company’s supply chain. One fundamental change can be made to address the lack of HGV drivers. This can be done by investing in new technology that can help to reduce the dependency on human drivers and by working closely with suppliers to ensure that they can meet the demands of the business (Fuchs, Aghajanzadeh, & Therkelsen, 2020). Additionally, the company can consider working with government bodies to relax the regulations and make it easier for the company to hire drivers from outside the EU.
Another change that can be made is to improve forecasting and inventory management to meet customer demands better. This can be done by using data analytics to track sales trends, identifying patterns in customer behavior, and using these insights to optimize inventory levels. Another change that can be made is to increase the flexibility of the supply chain. This can be done by implementing a just-in-time delivery system, which allows the company to respond quickly to changes in demand, and by establishing a strong relationship with suppliers to ensure that they can meet the company’s needs.
The benefits of these changes will be measurable. Addressing the lack of HGV drivers will reduce delays and shortages of products, which will lead to increased customer satisfaction and sales. Improving forecasting and inventory management will better meet customer demands, resulting in higher customer satisfaction and retention. Increasing the supply chain’s flexibility will reduce logistics and transportation costs, which will lead to cost savings for the company.
Using a quality tool such as the Pareto chart help the company to identify the root causes of the problem, prioritize the changes that need to be made, and track the progress of the implementation of the changes. This will enable the company to measure the impact of the changes and make any necessary adjustments to ensure that the supply chain is operating as efficiently as possible. The changes that can be made to improve the current business condition of the Coca-Cola Company’s supply chain include addressing the lack of HGV drivers, improving forecasting and inventory management, and increasing the flexibility of the supply chain. These changes will lead to measurable benefits such as increased customer satisfaction, increased sales, higher customer retention, cost savings, and improved supply chain efficiency.
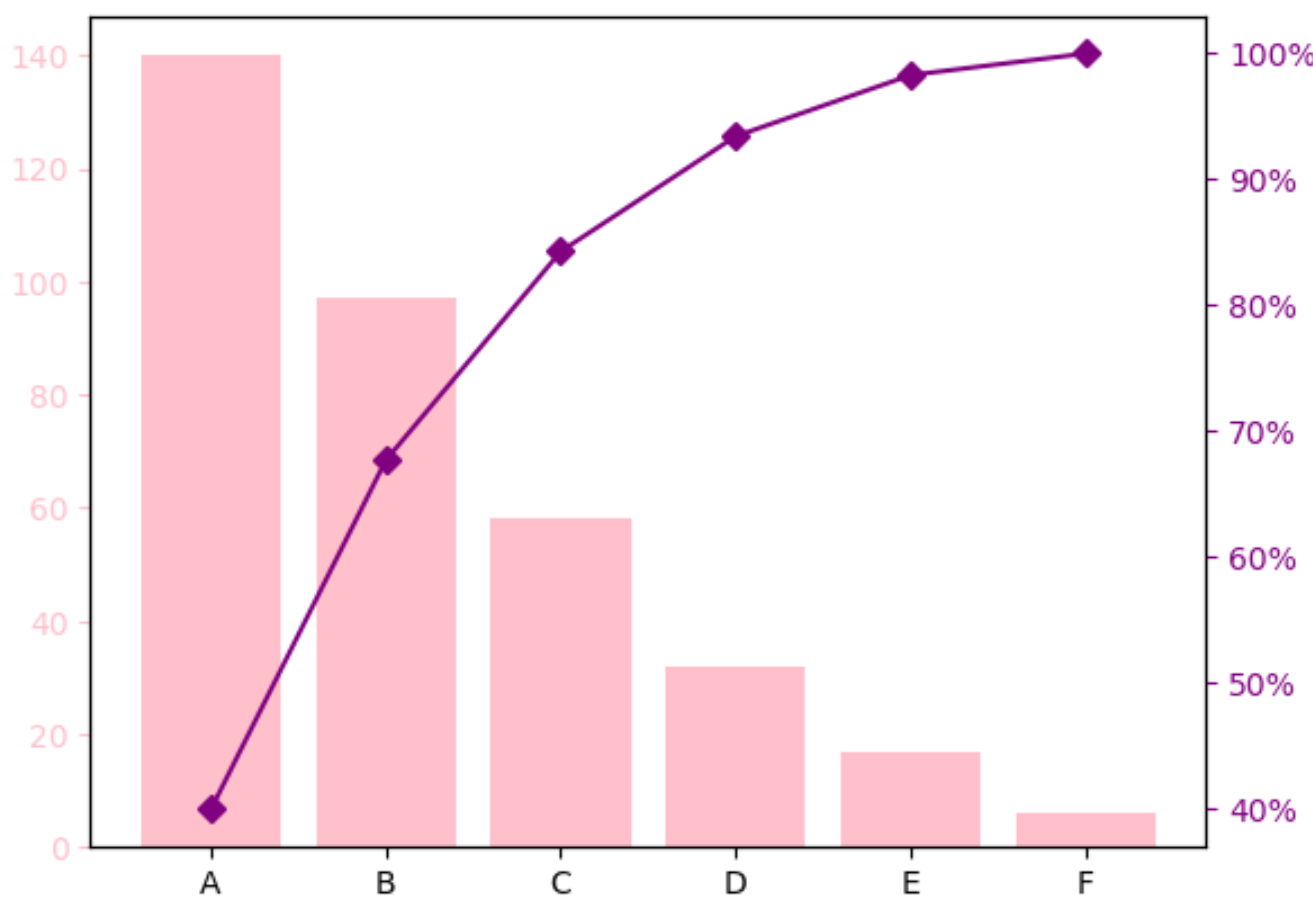
Pareto chart showing the order of priority of events in Coca-Cola’s supply chain
Conclusion
the current supply chain challenges faced by the Coca-Cola Company are impacting the company’s ability to provide fast and reliable service, maintain product availability, and keep costs low. The proposed changes to address the lack of HGV drivers, improve forecasting and inventory management, and increase the flexibility of the supply chain are viable solutions that can improve the performance of the problem statement.
I recommend that the Coca-Cola Company proceeds with these changes. By addressing the lack of HGV drivers, the company will be able to reduce delays and shortages of products, which will lead to increased customer satisfaction and increased sales. Improving forecasting and inventory management will allow the company to meet better customer demands, leading to higher customer satisfaction and retention. Increasing the flexibility of the supply chain will lead to cost savings and improved efficiency in the supply chain.
It is important to note that implementing these changes will require a significant investment of time, resources, and money. However, the benefits of these changes will outweigh the costs in the long run. The company should use a quality tool such as the Pareto chart, Ishikawa diagram, or a cause-and-effect diagram to identify the root causes of the problem, prioritize the changes that need to be made, and track the progress of the implementation of the changes.
In conclusion, the Coca-Cola Company should proceed with the proposed changes to address the lack of HGV drivers, improve forecasting and inventory management, and increase the flexibility of the supply chain. These changes will lead to measurable benefits such as increased customer satisfaction, increased sales, higher customer retention, cost savings, and improved supply chain efficiency. The company must take a comprehensive approach, examining all aspects of the supply chain and identifying areas for improvement to ensure the success of the changes.
References
Bos, D. (2022). Financial Visibility in Supply Chain Losses.
Brondoni, S. M. (2019). Shareowners, stakeholders & the oversize global economy. The coca-cola company case. Symphony. Emerging Issues in Management, (1), 16-27.
Bwakea, E. (2020). Ethical Practices in Procurement towards Customers Satisfaction: A case of Coca Cola Kwanza Ltd Dar es Salaam (Doctoral dissertation, Mzumbe University).
Feleke, H. (2022). The Effect of Supply Chain Integration on Operational Performance: An Empirical Evidence from Coca Cola Company, Bahirdar Plant (Doctoral dissertation).
Fuchs, H., Aghajanzadeh, A., & Therkelsen, P. (2020). Identification of drivers, benefits, and challenges of I Fuchs, H., Aghajanzadeh, A., & Therkelsen, P. (2020). Identification of drivers, benefits, and challenges of ISO 50001 through case study content analysis. Energy policy, 142, 111443. SO 50001 through case study content analysis. Energy policy, 142, 111443.
Murtaza, M. B., Gupta, V., & Carroll, R. C. (2004). E‐marketplaces and the future of supply chain management: opportunities and challenges. Business Process Management Journal.
Rajeev, A., Pati, R. K., & Padhi, S. S. (2019). Sustainable supply chain management in the chemical industry: Evolution, opportunities, and challenges. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, pp. 149, 275–291.
Sangode, P. B., & Metre, S. G. (2019). Green supply chain practices for environmental sustainability: a proposed framework for manufacturing firms. International Journal of Mechanical and Production Engineering Research and Development (IJMPERD), 9(2), 287–298.
Smith, B., Xiang, J., & Medlin, D. (2021). Case Study of Blockchain Applications in Supply Chain Management Opportunities and Challenges. J. Inf. Syst. Appl. Res, pp. 14, 22–50.
Sodhi, M. S., & Tang, C. S. (2021). Supply chain management for extreme conditions: research opportunities. Journal of Supply Chain Management, 57(1), 7-16.
 write
write