1. Introduction
Coca-Cola is one of the world’s top manufacturers and providers of nonalcoholic beverages (Gomez, 2019). The business, which has its headquarters in Atlanta, Georgia, is best known for its flagship beverage, Coca-Cola. It is currently a well-known soft drink company aiming to broaden the brand’s appeal. The majority of soft drinks sold in vending machines and refrigerators in Western nations are owned by the company. The most significant soft drink manufacturer in the world is Coca-Cola. Products from Coca-Cola are available in more than 200 countries worldwide. The corporation sells soft drinks under an estimated 500 labels, ranging from sodas to energy and soy-based drinks. The top five soft drinks are Coca-Cola, Sprite, Fanta, and Diet Coke. Other well-known brands include Minute Maid, PowerAde, Dasani, and Vitamin Water. Additionally, the corporation manufactures products like Fruice, Deep River Rock, Avra, and Amita. The Coca-Cola Company also manufactures more than 3,500 different beverages. Because every product that Coca-Cola makes sets itself apart from comparable goods produced by its rivals, it has cultivated its reputation as the most dependable brand. Coca-Cola hopes to make a difference and renew the globe by offering its customers refreshing drinks. The paper aims to present a marketing strategy for the Coca-Cola Company.
2. Core Marketing Concepts
2.1 Markets and Target Market Segments
- Geographical segmentation Variables
The business has geographically broadened its operations. It prioritizes suburban and metropolitan locations and ensures its products are distributed across the country. This is because it is understood that demand from far-flung areas would rise as the firm expands.
- Demographic segmentation Variables
Sub-segments of the demographic are created based on social class, age, income level, and other variables. These criteria are the ones that are most often used to divide customer groups.
- Psychographic segmentation Variables
The consumer is segmented psychologically according to lifestyle, social position, and values, which impact consumer choices. The emphasis shifts from the salient characteristics to the consumer’s lifestyle and ways to improve it.
- Behavioral segmentation Variables
It focuses on how customers perceive, respond to, and comprehend how to utilize the company’s goods. Most marketers construct market groups using behavioral factors as the optimal starting point. (Liu, 2020).
2.2 Customer Profile
People between the ages of 10 and 25 make up most of Coca-Cola’s consumers, with people between the ages of 25 and 40 making up another market. In terms of flavor, the company caters to a client that desires a strong taste in their traditional beverages. The primary psychological and social factors that affect consumer behavior at Coca-Cola are these two. Customers may assert their goal in buying Coca-Cola beverages is to quench their thirst. However, since Coca-Cola gives people a sense of modernity and power, the true motivation is to demonstrate their economic and social status. Therefore, it is clear that drinking Coca-Cola is a conscious decision, and the company needs to have an impact on its promotional strategy if it wants to evoke emotion and engage consumers.
2.3 Needs, Wants, and Demands
Coca-clientele Cola’s is diverse and has various requirements, such as a preference for high-quality, freshly prepared foods (Ozretic-Dosen, Brlic, & Komarac2018). As the desires of Coca-Cola consumers are classified as healthy, this has a lot to do with food safety. It suggests that the company’s goods must be beneficial to satisfy its consumers’ desires. Consumers of the Coca-Cola firm finally expect the product they desire right now (Ashley, 2017). These clients are prepared to pay more for items supplied to suppliers for the Coca-Cola firm.
3. Marketing Environment
3.1 Demographic Forces
The study of the population’s size, density, location, age, gender, race, and profession is known as the demographic environment (Armstrong & Kotler, 2022). Regardless of the customer’s origin, religion, or color, the key demographic characteristics are age—Coca-Cola targets the age segments of young people and the elderly—gender (men and women), with minor variances in taste and preferences and other demographic aspects. By catering to customer wants and interests, this division hopes to reach all market groups in the more than 200 countries where the corporation works. Sub-segments of the demographic are created based on social class, age, income level, and other variables. These criteria are the ones that are most often used to divide customer groups.
3.2 Regulatory Forces
Regulatory forces are the impacts of rules and regulations on the marketing environment that are addressed in this marketing environment. Athletic brands are impacted by several rules and regulations, including international consumer laws and growing health and safety standards. As the government regulates and oversees the practices and processes of soft drinks, Coca-Cola complies with all applicable regulations. Law changes have a significant influence since they might modify taxes, which the business has to deal with properly. The agreement has become a big worry for most enterprises and people operating globally. For other marketplaces and different nations, different regulations apply. The U.S. regulations are so rigorous that non-compliance might cost the brand money and result in billions of dollars in penalties (Bonsu, 2019). There are several areas, from labor to product quality, where submission is essential. Coca-Cola has historically battled regulations in numerous places, from the organization of the products and quality to labor abuses inside the United States of America. Because of this, compliance, ethics, and corporate governance have taken center stage. To guarantee that all of its associates are obedient in the USA and wherever they are working around the globe, it has its agreement and ethical program. There are already sugar restrictions in place for drinks in several countries. Given that they provide a variety of services, the corporation needs to take this into account. If they do not follow this, they can face punishment. The company must also consider labor practices and labor ethics. If Coca-Cola pays its employees less or fails to provide a safe workplace, it may face legal problems.
3.3 Competitive Forces
Direct rivals of Coca-Cola include Tetra Pak, Red Bull, and PepsiCo, among others. These rivals influence the firm’s quality, advertising, and, most significantly, pricing, among other things. By launching new items, expanding regionally, and investing in its distribution network, the corporation battles for profitability. Using a single approach and product variety are two of Pepsi’s advantages. Its overreliance on food and drink is one of its main flaws. Additionally, the company’s unsuccessful goods have negatively influenced sales.
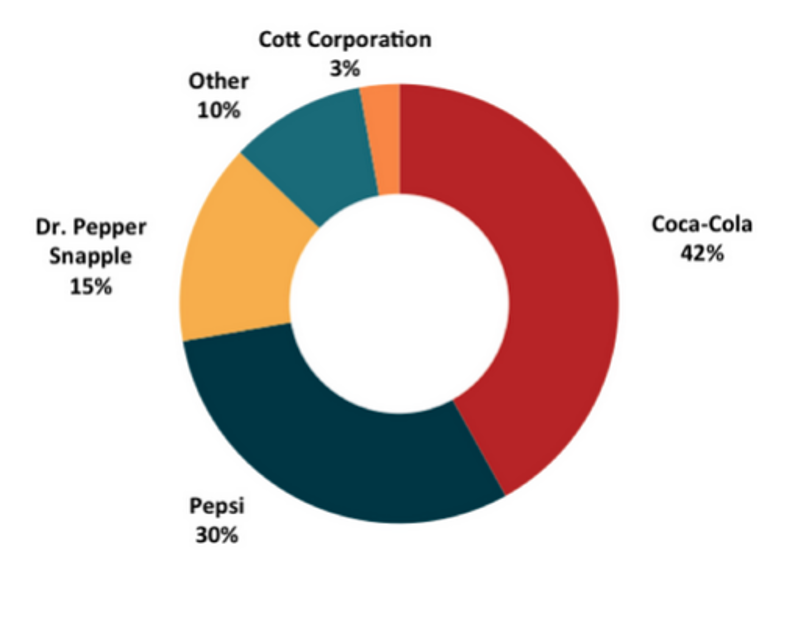
Coca-Cola has an advantage over PepsiCo in the marketplace because of its robust marketing strategy and wide range of products. Due to this, it enjoys a considerable market share compared to its competitors.
3.4 Technological Forces
Technology continues to be a crucial component of big businesses like Coca-Cola. Their production, packaging, and transportation all rely heavily on equipment. In larger companies like Coca-Cola, machinery is essential. The Coca-Cola company has made significant investments to stay profitable (Fragouli & Nikolaidou, 2019). The effectiveness of technology has allowed for timely manufacturing and a reliable supply chain. These elements are necessary for the business to generate income. The technology in this field only advances a few times a week. To prosper requires upkeep and investment. Processing the finished product and packaging it both need significant technological investments. Therefore, the technical features have a substantial and crucial impact on the Coca-Cola market.
3.5 Economic Forces
The economy impacts consumers’ spending and buying power (Armstrong & Kotler, 2022). There are numerous chances for sales and profits for Coca-Cola’s business due to the worldwide rise in athletic gear demand. The economy’s national income was so great, which increased demand for all Coca-goods. Cola’s commercial activities of multinational and giant firms are also directly and significantly impacted by the financial crises. The heated global catastrophe drastically reduced corporate revenues both in the United States of America and globally. Coca-Cola nonetheless managed to avoid any market impact since businesses involved in finance were the ones that felt this influence the most (Fragouli & Nikolaidou, 2019). However, the earnings it earned were somewhat impacted. Unexpectedly, Coca-Cola was able to recover the profits. An economic crisis of this magnitude affects customers. Under such extreme circumstances, people decide to purchase necessities. Like Coca-Cola, many businesses turned to other methods of dealing with the financial catastrophe, such as cost-cutting and downsizing. However, Coca-Cola surprised other companies by pulling through during such difficult times. Every multinational firm is significantly impacted by economic crises of this magnitude, like the one we are now experiencing. The most significant factor disturbing the Coca-Cola business is the rising price of unfinished goods. One such concern is water scarcity (Bertozzi, Ali, and Gul, 2016). Coca-Cola needs water to create its products. However, accessibility is often insufficient. The price of other raw materials and labor has increased; these factors have significantly impacted the business and global brands’ sales. The Coca-Cola company in the United States has been affected by all these causes, endangering its stability. The financial crisis is over, but Coca-Cola will still be affected by the strengthening of the dollar.
3.6 Socio-cultural Forces
A society’s fundamental beliefs, perceptions, and actions are influenced by institutions and other influences that make up the cultural environment (Armstrong & Kotler, 2022). Primary and supporting beliefs are involved (Armstrong & Kotler, 2022). Core values and beliefs are maintained with a high degree of consistency. In contrast, secondary variables are more change-resistant (Armstrong & Kotler, 2022). The frequent problems are essential to the industry. Most people have recently switched from flavorful beverages to healthier ones. The popularity of Coca-Cola products in the United States of America is declining due to this tendency (Rothaermel, 2016). The firm’s profitability was influenced by significant changes in customer taste and demographic choices. Coca-cola items are often preferred due to their emotions. However, more people are switching to healthier beverages due to the allegations that Coca-Cola utilizes several additives and chemicals in its products that affect customers’ health. Coca-Cola has focused its marketing efforts on domestic and international markets to address this difficulty (Bonsu, 2019). The mainstream media has also been crucial in transforming people’s perceptions about soda drinks, which are said to have more calories. The international campaign against obese individuals has influenced how people choose food products. Sales of carbonated beverages and junk food have recently declined globally. People have adopted a healthy lifestyle, and avoiding foods and drinks that may make them gain weight is no exception. Coca-Cola has launched several low-calorie beverages to keep up with the times. Societal trends, such as the shift in perception of American-made products or other related problems, also impact Coca-Cola. The American war against Iraq resulted in extreme economic concentration in several countries (Dimitriou, 2017). Studies have previously acknowledged the importance of culture as the driving force behind international commerce. Never undervalue the impact on the company. From the advertising perspective, it is possible to agree on the importance of ethos. Coca-Cola has never downplayed its significance, particularly in developing nations.
4. The Marketing Mix
4.1 Product
As a business, Coca-Cola offers a variety of goods under its brand. For instance, 500 Coca-Cola products have been produced over time. Customers may choose from more than 3000 options in the beverage sector. One of the most well-known and reputable brands in the world is Coca-Cola. Its brand alone is worth $21 billion. 19 of its numerous items offered to customers are low in calories. The sizes of Coca-Cola products range from 300ml to 2-liter bottles. Thanks to the range, customers still have a wide selection of items to pick from (Alhawsawi, 2016). The Coca-Cola products are all distinctive since they are prominently marked with the company’s insignia. The Coca-Cola, Sprite, and Fanta brands have the most significant market shares. As mentioned earlier, the growth rates of the items are essentially flat. Minute Maid is another product inside the Coca-Cola Company with a more robust growth rate and larger market share.
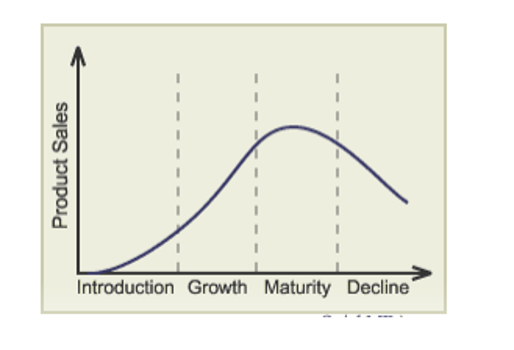
Coca-Cola is now at the maturity stage in Western nations. Contrary to the other locations, this one of adulthood is usually the longest. Management must concentrate on the products during maturity because these products frequently experience a slowdown in sales growth.
4.2 Price
Price has a significant impact on marketing strategy. Coca-Cola has a distinct pricing discrimination tactic in its marketing mix. Coca-Cola products in various markets are priced differently. The beverage products’ target market is an oligopoly. In other words, there are fewer vendors than buyers or vice versa. Coca-Cola has a pricing strategy that puts the prices of its goods in the same ballpark as those of its rivals (Sheth & Koschmann, 2018). As a result, they continue to have clients, particularly in emerging nations where consumers are more price-conscious. However, the business provides clients discounts if they purchase large quantities.
4.3 Place
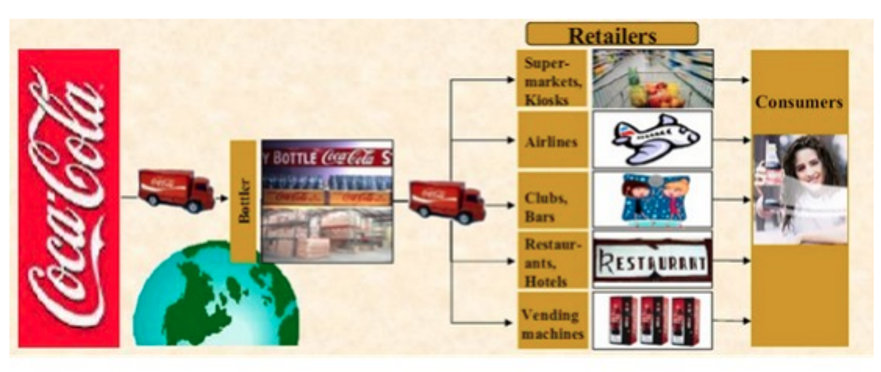
The Coca-Cola Company has a long history in the beverage industry. The Coca-Cola Company has access to a broad range of distribution channels thanks to its global agents. The bulk of their distribution agents are located in different nations worldwide, and they create their drinks using a secret recipe. Coca-Cola decides the sizes and forms of the bottles as a corporation. The bottlers send the various items in bottles and deliver them to customers in multiple nations. Products are provided by road from the agency to the consumer store (Kotler, 2017). Most often, wholesalers receive goods from the distributor and subsequently distribute them to retailers. Because of its extensive distribution network, the Coca-Cola Company’s interests are simple to locate practically anywhere.
Due to extensive distribution, Coca-goods Cola’s are widely accessible. With the aid of this technique, the business has increased customer involvement and increased profitability. It is typically linked to aggressive marketing, low costs, and a large target audience. The dual distribution approach can increase both market share and sales volume.
4.4 Promotion
The Coca-Cola Company provides a lot regarding marketing, making them the undeniable masters of promotion. Their marketing approach is more aggressive and original. Coca-Cola advertises on television, the internet, and in print media. Additionally, they use their brand reputation to collaborate with large event organizers to purchase and sponsor the event. Their tactics include releasing promotional songs that may be repeated in several languages (Gillespie & Riddle, 2015). Coca-Cola can contact everyone in that manner, regardless of their ethnic origin.
5. Conclusion
Coca-Cola Company should evaluate its market strategy yearly to assess how it is doing relative to its competitors. If the firm keeps introducing fresh, cutting-edge items like “Bubble Buzz,” it will maintain its position as the industry leader in creating nonalcoholic beverage brands. However, to guarantee that customers continue to purchase their goods, the new product has to stand out from identical offerings from other companies (LOPEZ, 2013). The research demonstrates that certain economic, administrative, financial, and technological factors mainly affect the world beverage market. Technology-related goods may fall within its jurisdiction, but political, social, and economic factors require that its advertising approach be modified to account for changing circumstances. The Coca-Cola Company is experiencing enormous problems due to the water shortage. Long-term problems with the water deficit in the U.S. would persist. It will turn out to be the company’s most fortified region. Increasing the availability of low-calorie drinks encourages consumers to purchase healthier goods, and the U.S. economy will inevitably expand.
References
Alhawsawi, R. (2016). Marketing Mix in FMCG’s leading Companies: Four Ps Analysis. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, 7(2), 734-737.
Armstrong, G., Kotler, P., & Opresnik, M. O. (2022). Marketing: An introduction. Pearson.
Ashley, R. (2017). Coca-Cola Amatil: Insights from the company monitor. Equity, 31(6), 16–17.
Bertozzi, F., Ali, C. M., & Gul, F. A. (2016). Resource-Based View of an Organization and PESTEL Analytical Tool; An Analysis of Hotel Corallo, Rimini. EPH-International Journal of Science and Engineering (ISSN: 2454-2016), 2(11), 57-71.
Bonsu, S. (2019). Strategic Management: The Concept of Competing with Self. Journal of Marketing and Management, 10(2), 20–44.
Dimitriou, M. (2017). Example of Analysts’ Valuation Process: Information Context, Research Findings, and Future Priorities. In Multinational Finance Conference Booklet (Vol. 24, p. 87).
Fragouli, E., & Nikolaidou, Z. (2019). A Case Study Approach for Managing Risks & Challenges When Expanding to Emerging Markets. Risk and Financial Management (ISSN 2690-9790 e-ISSN 2690-9804), 1(1), p44-p44.
Gillespie, K., & Riddle, L. (2015). Global marketing. Routledge.
Gómez, E. J. (2019). Coca-Cola’s political and policy influence in Mexico: understanding the role of institutions, interests and divided society. Health policy and planning, 34(7), 520–528.
Kotler, P. (2017). From sales obsession to marketing effectiveness. Graduate School of Business Administration, Harvard University.
Liu, L. (2020). Coca-Cola: A Study on the Marketing Strategies for Millenniums Focusing on India. Scientific Journal of Intelligent Systems Research Volume, 2(01)
Ozretic-Dosen, D., Brlic, M., & Komarac, T. (2018). Strategic brand management in emerging markets: consumer perceptions of brand extensions. Organizations and markets in emerging economies, 9(1), 135-153.
Sheth, J., & Koschmann, A. (2018). Do brands compete or coexist? How persistence of brand loyalty segments the market. European Journal of Marketing
Singaram, R., Ramasubramani, A., MEHTA, A., & Arora, P. (2019). Coca-Cola: A study on the marketing strategies for millenniums focusing on India. International Journal of Advanced Research and Development, 4(1), 62-68.
 write
write