Case Synopsis
This case study explores Amazon’s deliberate investigation of autonomous vehicle delivery, which has the potential to completely transform the e-commerce industry. This project has the ability to significantly change the dynamics of how items are delivered and moved. The tale revolves around the complex issues and auspicious prospects associated with the implementation of autonomous vehicles (AVs). Given its recognition of the revolutionary potential of AVs in the context of contemporary commerce, Amazon’s entry into this market demonstrates its dedication to innovation and forward-thinking strategy. The study examines the opportunities and challenges that come with using AV technology to deliver packages while navigating the intricacies of autonomous vehicle delivery. The difficulties include safety concerns, technological complexities, and regulatory nuances. Each of these issues poses a significant obstacle that Amazon must overcome. In addition, the study highlights the potential benefits of adopting AV, including shortened delivery times, improved operational efficiency, and a reorganization of traditional supply chain models.
Obstacles to AV Adoption
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) confront numerous obstacles to their broad adoption, including complex regulations, safety issues, and technology constraints. It will be difficult to overcome these obstacles, which will put significant barriers in the way of AVs’ smooth adoption into mainstream business (Parekh et al., 2022). These barriers are not directly related to the particular causes of Michael Aldrich’s e-commerce platform’s failure. They do, however, highlight the difficulties that come with bringing cutting-edge technologies into mature industries. One major obstacle is the regulatory environment, which requires navigating a complex web of rules and norms. The complicated regulatory environment surrounding autonomous vehicles (AVs) necessitates a sophisticated approach to compliance, which further complicates the integration of AVs into regular transportation systems. Another strong obstacle is safety concerns, which necessitate extensive testing and assurance procedures. Because customers and regulatory agencies are wary of newcomers, a comprehensive display of the dependability and security of self-governing systems is required.
Technological restrictions exacerbate the problems even more and necessitate ongoing improvements to overcome them. Because technology is advancing so quickly, AV developers need to keep up with the latest developments to make sure their systems are efficient, safe, and competitive (Dakić et al., 2021). In this scenario, the complex dance between innovation and established frameworks becomes especially apparent, highlighting the necessity of striking a careful balance between pushing technological frontiers and abiding by established norms. The proper identification and resolution of these obstacles are essential to the widespread adoption of AVs. It emphasizes how innovation and pre-existing structures interact delicately in the dynamic world of contemporary technology and business. A comprehensive approach that takes into account safety, legal, and technological issues is necessary to overcome these obstacles and pave the way for a time when autonomous cars and conventional transportation systems coexist peacefully in the future.
Impact on Retail with AV Adoption
Autonomous Vehicles (AVs) have the ability to completely transform the retail industry by bringing in a new era of efficiency, quick deliveries, and maybe lower costs. Beyond simple convenience, the revolutionary effects on retail would radically alter established supply chain patterns and reset consumer expectations (Khayyam et al., 2020). The considerable improvement in efficiency is one of the main advantages of AV integration for delivery services. Retailers may maximize routes and reduce delays by streamlining their logistical procedures using autonomous vehicles. This increased productivity results in deliveries that are more dependable and timely, which is essential for satisfying the ever-increasing needs of contemporary customers who value prompt service. Shorter delivery times signify a revolution in the way consumers interact with shopping. With their sophisticated navigation systems and capacity to adjust to traffic situations in real time, autonomous vehicles (AVs) are able to navigate urban environments at a speed and precision never seen before. This meets customers’ need for instant gratification and encourages loyalty by going above and beyond in terms of promptness.
Costs associated with transportation could be greatly decreased by autonomous cars. Fuel and labor are two costs that are immediately impacted. The median yearly salary for a Walmart truck driver is $73,000, according to CNN Money. Since the company employs over 7,000 drivers, a full transition to autonomous vehicles may save $511 million in labor expenses annually (Thielen et al., 2019). Moreover, fully automated cruise control and eco-navigation technology enable autonomous cars to display intelligent driving behaviors. In contrast to vehicles driven by humans, they make less needless braking movements, which improves fuel economy and significantly lowers greenhouse gas emissions. This efficient driving style is in accordance with the retail industry’s sensitive financial environment, where even little transportation cost reductions can spur higher sales and higher profit margins. Adoption of AV has spillover effects outside of operations, leading to a reassessment of conventional supply chain models. To take full advantage of the benefits that autonomous delivery offers, retailers might need to make adjustments to their inventory management plans, warehouse operations, and infrastructure. Customers’ expectations are simultaneously adjusted, with a focus on a seamless, quick, and economical purchasing experience.
Customer Readiness and Willingness to Pay
A thorough analysis of a number of crucial factors, such as technological trust, security apprehensions, and willingness to pay for the supplementary premium service, is required to determine the degree to which a client is prepared for the delivery of autonomous vehicles (AVs). The environment in which AV delivery services will function is shaped by these elements taken as a whole, and a thorough grasp of them is essential to the effective use of this novel strategy for retail logistics (Enoch et al., 2020). Building trust in autonomous technology is the foundation of being customer ready. Consumers want reassurance that AVs are safe, secure, and dependable technologically. Encouraging people to have faith in the technology means addressing concerns about self-driving cars, accidents, and malfunctioning systems. Creating open lines of communication about the strong safety features and fail-safes built into AV systems becomes essential to easing people’s fears and fostering confidence.
Customers’ readiness for AV delivery is greatly influenced by security concerns, both physical and data-related. Privacy concerns and the protection of sensitive data are brought up by the gathering and use of personal data during the delivery process (Miao et al., 2022). Retailers need to take the initiative to allay these worries by putting in place strong data security safeguards and open privacy guidelines. Furthermore, winning over customers’ trust and happiness during autonomous transit depends on guaranteeing the physical security of the items.
The clients’ willingness to pay more for AV delivery services is equally significant. Even if autonomous delivery offers substantial advantages in terms of speed and convenience, customers must believe that the value proposition justifies the extra expense. In order to defend the higher pricing, retailers must highlight the special advantages of AV delivery, such as increased speed, dependability, and efficiency. Adoption success depends on knowing the target market’s price sensitivity and matching it to the service’s perceived value. Understanding the complex relationships that exist between security concerns, perceived value of premium services, and technology trust is essential to determining and resolving client preparedness for AV delivery. Retailers pursuing this opportunity need to be skilled at navigating these factors in order to guarantee a smooth and prosperous integration of autonomous vehicles into the customer experience environment.
Risks of Amazon’s AV Investment
Although it is a calculated risk, Amazon’s investment in autonomous vehicles (AVs) is a smart move. The world of technical malfunctions presents one major concern. Accidents or disruptions in operations could result from failures in the complex network of sensors, algorithms, and hardware that drives autonomous vehicles. Amazon needs to balance the draw of autonomous vehicles (AVs) with the risks associated with developing cutting-edge technology. Another challenging issue is public opposition. When autonomous vehicles (AVs) grow more commonplace, public fear and skepticism may prevent them from being widely adopted. Even while the results of one survey may have been slightly biased, it nevertheless demonstrates that safety is a top issue with AVs, as just 12% of participants said they would feel comfortable buying one or driving one. The public has to be convinced that these cars are indeed safer than conventional driver-operated cars through additional testing and data collection, which will only address this worry. Making the public feel comfortable with autonomous vehicles (AVs) will only get harder if articles about their getting into or causing accidents continue to appear. In order to allay worries about safety, privacy, and the effects of autonomous mobility on society, and to overcome this barrier, communication skills as well as faultless technology are needed. If public concerns aren’t addressed, Amazon’s AV initiatives might meet with a lackluster reaction.
The regulatory environment pertaining to AVs is also always changing. Amazon’s investment viability and profitability may be greatly affected by unforeseen regulatory changes. It takes agility and adaptation to navigate this complex web of laws. The legislative landscape, which at first supports autonomous vehicles (AVs), may change as a result of unanticipated events or safety concerns. It is up to Amazon to predict and act quickly upon changes in regulations if it is to succeed in AVs.
A careful assessment of Amazon’s risk tolerance, technological readiness, and strategic direction is required before investing in AVs. Evaluating the company’s capacity for accepting uncertainty as well as its preparedness to deal with any disruptions is essential. Moreover, Amazon’s strategic strategy for maintaining its leadership position in innovation is applicable. AVs are a sign of technological leadership as well as a means of transportation. To guarantee that AVs are seamlessly integrated into its ecosystem, Amazon’s investment schedule must be in line with its larger innovation agenda.
Impact on the Labor Market
Delivery industry labor markets could change significantly with the arrival of autonomous vehicle (AV) delivery systems. Still, there are important consequences to this change, especially with regard to manual labor. The introduction of autonomous vehicles (AVs) that can manage deliveries has sparked worries about the potential decline in demand for several jobs that were previously performed by humans (Leonard et al., 2020). One potential consequence of technology taking over the role of goods transportation is the potential loss of jobs in the delivery sector. This change in the dynamics of the job market calls for a critical analysis of the moral implications of AV integration. This raises a basic question: What obligations do businesses have to employees whose jobs could be automated out of necessity? The possibility of employment displacement adds a moral component since it calls into question the moral foundation of technological advancement. In order to address these issues, a thoughtful strategy that recognizes the effects of automation on people is needed.
Proactive steps are essential to traverse this changing terrain. It is imperative that strategic planning and forethought be prioritized above responding hastily to possible labor market repercussions. Programs like reskilling and upskilling can give workers the tools they need to move into professions that enhance the capabilities of autonomous vehicles. Businesses can actively reduce the negative effects of automation on employment by making investments in education and training. Furthermore, in order to create moral standards and regulations that guarantee a just and equitable transition, a more extensive social dialogue is necessary. In order to create laws that safeguard workers’ interests in the face of automation, companies, labor unions, and government agencies must work together. In the delivery sector, striking a balance between social responsibility and technological growth becomes critical throughout this revolutionary time. To put it simply, even while AV delivery systems have the potential to be efficient and convenient, their possible effects on the labor market call for a careful and moral approach (Golbabaei et al., 2021). Ensuring a healthy cohabitation between technology and the workforce and addressing the obstacles provided by automation requires proactive steps, ethical considerations, and collaborative initiatives.
Amazon’s Winning Strategy
Amazon’s success in the field of autonomous vehicle (AV) delivery depends on a complex plan that includes skillfully navigating legal and regulatory environments, building public confidence, and never stopping innovating. The intricate network of laws pertaining to autonomous vehicles necessitates a calculated strategy. Amazon may influence regulations to support its goals and create an atmosphere that facilitates the smooth integration of autonomous vehicles (AVs) into the supply chain by actively interacting with legislators.
A key factor in the success of Amazon’s AV initiatives is establishing and preserving public trust. Resolving concerns about safety, privacy, and the overall impact of autonomous delivery on society is essential as these cars become more and more visible on the road. Instilling trust among communities and consumers requires open communication, strong safety protocols, and a dedication to moral AI behavior (Sadaf et al., 2023). When it comes to becoming recognized as a reliable leader in AV delivery, Amazon’s capacity to handle these complexities will be crucial. A fundamental component of Amazon’s successful strategy is ongoing innovation. By using data analytics, one can optimize delivery routes, gain insightful knowledge about consumer behavior, and improve overall operational effectiveness. It’s also critical to improve artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms so that autonomous vehicles (AVs) can function with high reliability and adjust to changing real-world conditions. Working together with stakeholders such as local communities, technological partners, and regulatory agencies creates a knowledge and resource sharing ecosystem that leads to Amazon becoming a leader in AV innovation. Amazon can establish itself as not just an adopter but also a leader in AV delivery by utilizing data strategically, enhancing AI capabilities, and encouraging cooperation. In addition to improving operational effectiveness, this approach tackles societal issues related to self-driving technologies. AV delivery leadership at Amazon is based on a comprehensive approach that combines technology expertise, regulatory knowledge, and public perception—all of which are necessary for success in the current market.
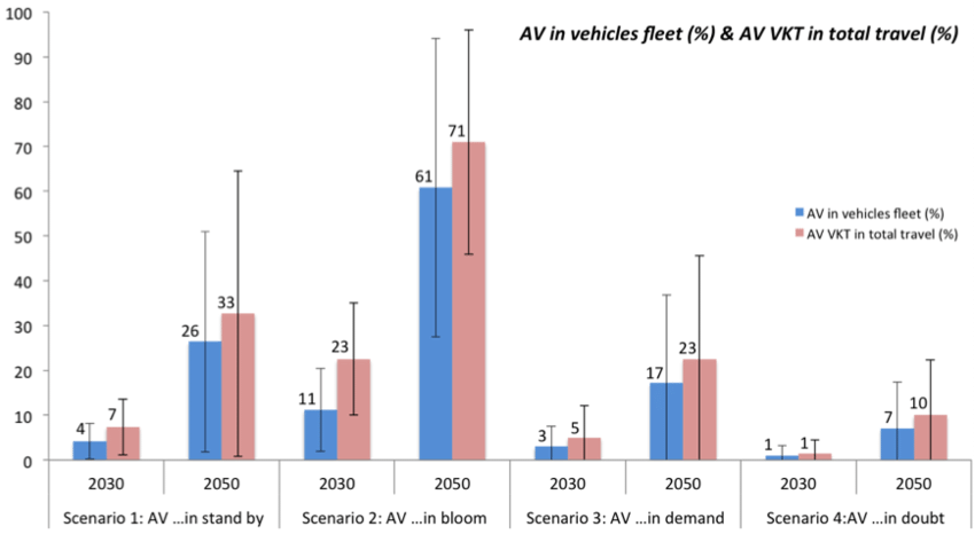
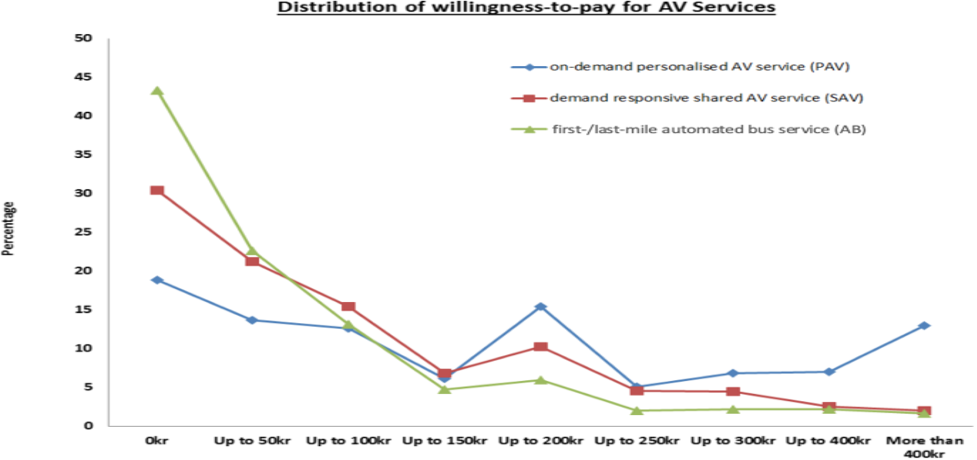
References
Parekh, D., Poddar, N., Rajpurkar, A., Chahal, M., Kumar, N., Joshi, G. P., & Cho, W. (2022). A review on autonomous vehicles: Progress, methods and challenges. Electronics, 11(14), 2162.
Khayyam, H., Javadi, B., Jalili, M., & Jazar, R. N. (2020). Artificial intelligence and internet of things for autonomous vehicles. Nonlinear Approaches in Engineering Applications: Automotive Applications of Engineering Problems, 39-68.
Thielen, C., & Weinschenk, P. (2019). Analyzing the Effects of Minimum Wages: A Microeconomic Approach. Available at SSRN 3074494.
Enoch, M. P., Cross, R., Potter, N., Davidson, C., Taylor, S., Brown, R., … & Potter, S. (2020). Future local passenger transport system scenarios and implications for policy and practice. Transport policy, 90, 52-67.
Miao, M., Jalees, T., Zaman, S. I., Khan, S., Hanif, N. U. A., & Javed, M. K. (2022). The influence of e-customer satisfaction, e-trust and perceived value on consumer’s repurchase intention in B2C e-commerce segment. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 34(10), 2184-2206.
Leonard, J. J., Mindell, D. A., & Stayton, E. L. (2020). Autonomous vehicles, mobility, and employment policy: the roads ahead. Massachusetts Inst. Technol., Cambridge, MA, Rep. RB02-2020.
Dakić, P., & Źivković, M. (2021, May). An overview of the challenges for developing software within the field of autonomous vehicles. In 7th Conference on the Engineering of Computer Based Systems (pp. 1-10).
Sadaf, M., Iqbal, Z., Javed, A. R., Saba, I., Krichen, M., Majeed, S., & Raza, A. (2023). Connected and Automated Vehicles: Infrastructure, Applications, Security, Critical Challenges, and Future Aspects. Technologies, 11(5), 117.
Golbabaei, F., Yigitcanlar, T., & Bunker, J. (2021). The role of shared autonomous vehicle systems in delivering smart urban mobility: A systematic review of the literature. International Journal of Sustainable Transportation, 15(10), 731-748.
 write
write