Introduction
The automotive industry greatly contributes to the global economy, employing millions of people and transforming the transport industry forever. This report gives an insight into the automobile aspect of Tesla Inc., a company that focuses primarily on manufacturing electric cars and giving greener energy solutions.
The fact that Tesla Inc. invested solely in electric cars in its automobile production, therefore, leading the campaign against the use of fossil fuels, fascinated me and drew my interest to research more about the company. My admiration for the entrepreneurial skills and leadership style of the company’s CEO, Elon Musk, was also one of the main reasons I chose Tesla Inc.
The report uses findings from research about Tesla Inc. to gauge whether it fits in the Bartlett and Ghoshal model of international business. Tesla’s business strategy and organizational structure have favored the company as it successfully expands and cements its place among top automobile manufacturers and energy problem solvers.
A Brief History and Expansion Abroad
Tesla, Inc., earlier known as Tesla Motors, is an American producer of electric vehicles, solar energy systems, and battery packs for automobiles and residential energy storage founded in 2003. The firm was named after a prominent Serbian inventor, Nikola Tesla, and was formed by American entrepreneurs Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning. Tesla swiftly became one of the world’s most popular automotive brands after successfully introducing its first electric car, the Roadster, in 2008. (Schreiber and Gregersen, 2023).
The majority of its success may be imparted to its efficient organizational makeup, which aids in the implementation of effective processes for decision-making and completing undertakings (Chen & Perez, 2018). Tesla’s aspiration towards an economy free of carbon and a transition away from fossil fuels, as noted on About | Tesla (no date), is one of the driving forces for Tesla’s global expansion.
Bartlett & Ghoshal Framework
The Bartlett and Ghoshal Matrix (1989) is a commonly used structure for distinguishing several types of globally running enterprises. Bartlett and Ghoshal grouped these firms based on two criteria: worldwide integration and local reaction. These two aspects yield four types of international corporate strategies: multi-domestic, global, transnational, and international (De Bruin, 2020).
Multinational
Companies with a multi-domestic approach attempt to suit the demands and expectations of local markets worldwide by substantially customizing and modifying their products and services. Multinational corporations frequently have a decentralized structure in which divisions abroad operate somewhat freely and independently of their main office (De Bruin, 2020).
Global corporations
Unlike multinational corporations, they provide a standardized product globally and strive to maximize efficiency to reduce expenses as much as possible. Global corporations are extremely centralized, and branches are frequently too reliant on headquarters. Their primary function is to carry out the parent company’s moves and implement them abroad (De Bruin, 2020).
Transnational companies
The transnational corporation combines elements of both global and multi-domestic firms. Transnational corporations frequently attempt to establish economies of scale at the top of the value chain while being more flexible and regionally adaptive in later stages, such as marketing and sales. Firms are defined as interconnected and reliant networks of branches worldwide (De Bruin, 2020).
International Corporation
Products are manufactured in the firm’s native country and sent to clients worldwide. Subsidiaries, if any, serve as the local routes via which the items are marketed to the end consumer. It is more like exporting (De Bruin, 2020).
Organizational Structure
Tesla uses functional centers to handle all operations, including financing, engineering, technology, advertising and promotion, architecture, hiring, and communications. Except for the software department, which the artificial intelligence director leads, every other department is led by a vice president. (CrowJack, no date)
According to Uygun and Sudhakaran (2021), the leaders of the various functional teams formed the heart of Tesla’s centralized control at its headquarters, which sets the company’s strategic direction, with the overseas divisions given limited independence.
An article by CrowJack (no date) highlights the functional organizational structure of Tesla Inc.
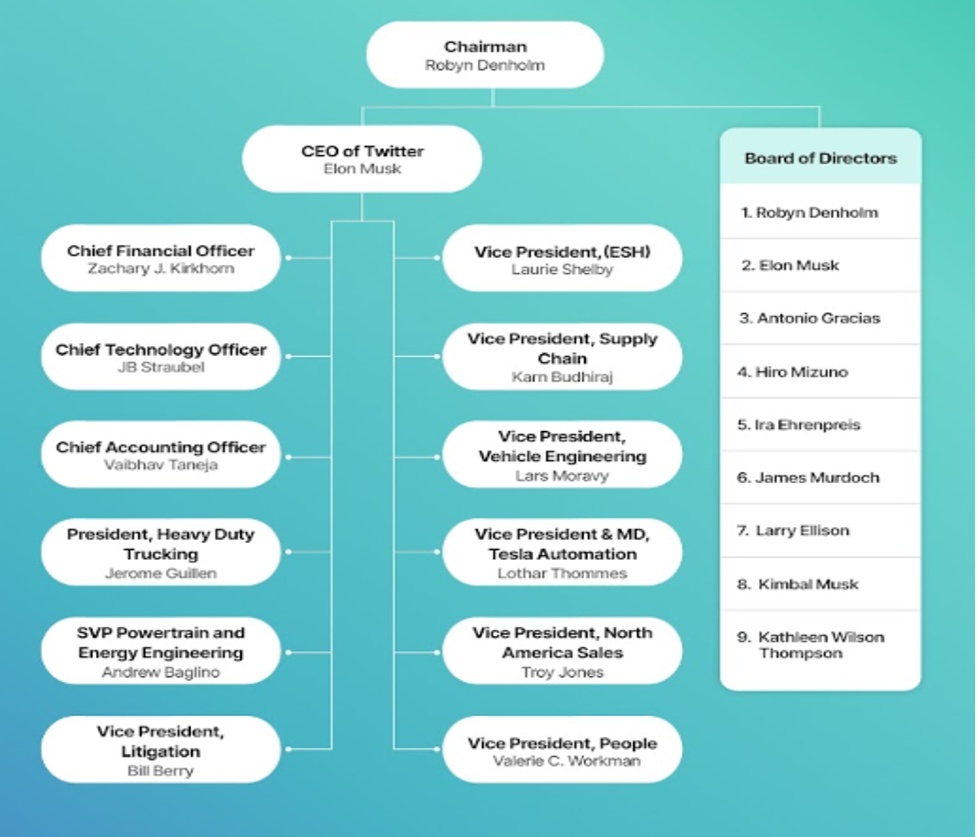
(CrowJack, no date)
An Insight into Tesla’s business operations strategies
Tesla’s corporate style has been heavily affected by CEO Elon Musk’s leadership style as it is intended to foster Innovation, active involvement, rapid managerial decisions, and department cooperation.
Product Design – Tesla’s product design is highly centralized, with the majority of work performed in the company’s previous headquarters in Palo Alto, California. Because of this centralized strategy, Tesla can keep a consistent design style and reputation across its line of goods.
Supply Chain – Tesla has a centralized vertical integration model in its supply chain, producing car engines, batteries, and other vehicle components. This approach allows the firm to acquire greater control over its manufacturing phases by eliminating several third parties in the form of suppliers. The technique smoothes the process since there is greater risk management, faster decision-making, and product delivery to clients, and product quality is not jeopardized.
Marketing – The marketing approach taken by Tesla is mostly centralized, with the company relying on online advertising and a direct-to-client sales approach. This offers Tesla total control over the look and messaging of its brand. The company also depends heavily on referral marketing since satisfied customers are typically enthusiastic brand advocates.
Manufacturing – Although Tesla’s highly robust product design, the manufacturing process is fairly dispersed. Tesla has multiple manufacturing facilities worldwide, including its headquarters in Fremont, California, and operations in Shanghai, China, and Berlin, Germany. Each of these manufacturing sites is in charge of producing a separate range of Tesla products. For instance, the Fremont facility produces the Model S, Model X, Model 3, and Model Y vehicles, while the Shanghai factory produces the Model 3 and Model Y vehicles for the Chinese market. The decentralized production strategy allows Tesla to better serve customers in various areas by minimizing the need for vehicles to be transported across long distances.
Product Development – While Tesla’s headquarters generate the primary concept and principal design of a product, the company also has teams of engineers and research centres in Germany and China. These groups collaborate to develop the multiple components of new goods, such as the engine, battery, and software. This Model also enables Tesla to draw into local expertise and resources in various nations, potentially accelerating development and lowering costs.
As seen from Tesla’s operational and decision-making strategies, it integrates the centralization of certain key decision-making activities. It decentralizes market-related services to suit the need and tastes of a particular market while at the same time controlling production at a central point to maintain quality and brand. This meets Bartlett & Ghoshal’s matrix, and the company can be categorized as transnational.
Creation and management of Worldwide Innovation
Global Innovation
It is critical for businesses to generate ideas in order to survive and develop. As markets and technology evolve at a rapid pace, entrepreneurs must constantly innovate in order to compete, expand, and remain in touch with their clients (BDC.Ca, 2023).
According to BDC.Ca (2023), the following five steps can be used to improve how new ideas are generated;
- Building an innovative culture among personnel in an organization.
- Identifying problems and gathering suggestions.
- Investigate and investigate the thoughts that arose further.
- The idea’s implementation and assessment.
- Analyze the performance of the implemented ideas.
Technological Innovation, organizational Innovation, market innovation, and business model innovation are all examples of global Innovation. Global innovation management is an organized method that creates, captures, discusses, and improves task and activity coordination in a company (Global Innovation Management: Definition, Strategy, Examples, 2022).
Global innovation management strategies
According to an article titled Global Innovation Management: Definition, Strategy, and Examples (2022), several strategies can contribute to effective global innovation management. They are as follows:
Starting discussions – Innovation is seldom effective when done alone. For the culture of Innovation to be effective, every employee must be involved. Bringing individuals together increases the likelihood of organizational success. Sharing ideas is one of the most effective methods for doing so.
Drawing staff – To increase involvement, organizations must cultivate the inner side of Open Innovation. Companies may include people in creativity and explain how this might lead to success.
Conduct public awareness campaigns – Developing fresh ideas necessitates a strategic mindset. This aids in the generation of new ideas and the adoption of the culture.
Creating an open setup – Employees rarely have time or space to share ideas. Creating a shared space allows them to collaborate better and debate various ideas and methods to ensure the organization’s success.
Transparency – Transparency helps to foster an innovative culture. Employees must be informed of the organization’s ideas, difficulties, and future strategies. This will assist them in prioritizing the necessary duties and recommending ideas for similar tasks.
Importance of Global Innovation
We have a higher chance of responding to changes and uncovering new opportunities through Innovation. It may also provide businesses with a competitive edge by producing better goods and services for the market. The optimal approach depends on the type of firm and the market structure of the country. Having highly skilled personnel in faraway locations who can fully engage in cutting-edge research and development initiatives enables round-the-clock discovery activity at a speed and scale previously unthinkable (What is Global Innovation? 2021).
Global Innovation is critical in tackling global issues such as climate change, food security, and healthcare. Innovation is also a crucial engine of economic progress, raising living standards and helping businesses access new markets and ideas that would offer them a competitive edge.
Collaboration with local companies
Tesla has its presence in many countries, with notable stores in the United States, United Kingdom, Germany, China, Canada, France, Switzerland, and Norway. Given its wide market base, it has partnered with several local companies worldwide to ensure effective service delivery for customer satisfaction.
Companies with close partnerships with Tesla Inc.
In the United States, Target Corporation has installed Tesla superchargers at some of its locations to boost the automaker’s charging infrastructure. Tesla partners with PPG Industries, which makes its car paints and coatings.
In Germany, where Tesla has a production plant, it has a partnership with Globus, which has installed superchargers to power the Tesla automobiles at its 51 stores.
Contemporary Amperex Technology (CATL) is a major supplier of batteries to Tesla Inc. in China. According to Klender (2022), CATL said in June 2021 that it intended to develop a new electric vehicle battery production plant close to Giga Shanghai, Tesla’s electric vehicle production site in China.
New Management Capabilities
According to Team (2021), the project management process consists of the following stages: preparation, initiation, operation, tracking, and closure. Every project must have a plan detailing how things will get started, how they will be created, and their completion.
Project management frameworks
There are different approaches in which specific projects can be managed depending on the nature of the project and the specific needs of the ones handling the project. Team (2021) suggests the following as major methods of project management;
- Waterfall project management
This is comparable to standard project management but with the added constraint that each job must be completed before moving on to the next. As a result, paying close attention to work sequences and schedules is critical in this sort of management of projects (Team, 2021).
- Agile project management
Agile project management continuously focuses on persistent result monitoring and enhancement. It does not use an orderly approach, but portions of the project are done simultaneously by multiple team members inside a corporation. This method can detect and correct mistakes without rerunning the entire operation (Team, 2021).
- Lean project management
This methodology’s concepts were derived from Japanese industrial practices. The fundamental concept behind them is to provide greater value to consumers while using fewer resources and reducing wasteful use of time and resources.
Ethical Considerations and Contributions of Tesla Inc.
- Tesla Inc. has grown significantly since its inception in 2003 and the subsequent takeover of Elon Musk as the CEO in 2008.
- The ability to produce and deliver electric cars and products on time and enough installation of superchargers across various stations where the company has its market has been contributed by Tesla’s control of its supply chain and partnership with local companies worldwide.
- Tesla’s autopilot system, which employs cameras, sensors, and machine learning in its semi-auto vehicles, represented a significant advancement in the company’s technological capabilities.
- Tesla is also developing energy storage systems. Tesla’s battery technology is used in the company’s power wall and powerpack systems to store energy from renewable sources such as solar and wind power. This enables more efficient and long-term energy consumption in households and enterprises.
- The leadership style of Tesla Inc. is a great contributor to its success as it accommodates the market’s needs and tastes as well as organizational ambitions and the need to maintain its brand reputation.
- Tesla’s marketing strategies are customized from location to location, and decisions concerning sales are decentralized to better suit the consumer’s needs.
- In light of the global warming challenge, Tesla has contributed to reducing carbon emissions by moving to green energy in electricity and solar power.
Challenges encountered by Tesla
- Working in new markets often means navigating through different regulatory environments.
- Low gas price brings competition to Tesla automobile since people tend to go for cheaper gasoline cars instead of electric ones.
- Increased electric vehicle competition as other automobile companies is closing in by producing electric cars as an alternative to their gasoline ones.
- Tesla cars are expensive. As Ross (2022) highlights that as of November 2021, the Model S costs $94,990 before any incentives or rebates.
Conclusion
The assessment of Tesla Inc.’s organizational and operational process shows the importance and advantages of implementing different frameworks that suits both the company’s ambitions as well as the needs and taste of consumers. Tesla Inc. does well because of its complex organizational structure and the influence of its ambitious CEO Elon Musk. Transnational organizations from Bartlett and Ghoshal model have been seen as the best Model of international business since there is minimal pressure from the organization and the market because of its approach.
References
Schreiber, B.A. and Gregersen, E. (2023) Tesla, Inc. | History, Cars, Elon Musk, & Facts. Available at: https://www.britannica.com/topic/Tesla-Motors.
Klender, J. (2022) Tesla-CATL partnership strengthens as new facility sends cells to Giga Shanghai. Available at: https://www.teslarati.com/tesla-catl-new-facility-sends-cells-gigafactory-shanghai/.
Chen, Y. and Perez, Y. (2018) “Business model design: Lessons learned from Tesla Motors,” Towards a Sustainable Economy, pp. 53-69. Available at:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-79060-2_4.
Uygun, H. and Sudhakaran, P. (2021) (PDF) Tesla Inc management report – researchgate, www.researchgate.net. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/353104682_Tesla_Inc_Managment_Report (Accessed: December 30, 2022).
BDC.Ca (2023) “How to generate new ideas: 5 steps that lead to innovation,” 6 February. Available at: https://www.bdc.ca/en/articles-tools/business-strategy-planning/innovate/how-generate-new-ideas-steps-lead-innovation.
About | Tesla (no date). Available at: https://www.tesla.com/about.
De Bruin, L. (2020) “International Business Strategy,” B2U – Business-to-you.com [Preprint]. Available at: https://www.business-to-you.com/international-business-strategy/.
Global Innovation Management: Definition, Strategy, Examples (2022). Available at: https://mitidinnovation.com/recreation/global-innovation-management-definition-strategy-examples/#:~:text=The%20term%20global%20innovation%20combines,%2C%20business%20model%20innovation%2C%20etc.
What is Global Innovation? (2021). Available at: https://mitidinnovation.com/recreation/what-is-global-innovation/#:~:text=Importance%20of%20Global%20Innovation,and%20services%20for%20the%20market.
Team, I. (2021) “Project Management: What It Is, 3 Types, and Examples,” Investopedia [Preprint]. Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/p/project-management.asp#:~:text=Generally%20speaking%2C%20the%20project%20management,and%20how%20they%20will%20finish.
TESLA Forecasting Solutions (2022) Strategic Partners | TESLA Forecasting Solutions. Available at: https://www.teslaforecast.com/about-tesla/strategic-partners/.
Ross, S. (2022) “6 Big Risks of Investing in Tesla Stock,” Investopedia [Preprint]. Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/articles/markets/102815/biggest-risks-investing-tesla-stock.asp.
 write
write