Abstract
This report will thoroughly evaluate Mulberry, the brand acclaimed worldwide for its perfection in craftsmanship and eminent recognition. By touching not only on the external and the internal environments, but also on the main obstacles and the decision-making directions, this investigation uses the SWOT, PESTLE, and Porter’s Five Forces frameworks to a great extent. A comprehensive idea of the targeted market is formed through exploiting these grounds. Also, the report incorporates a detailed evaluation of Mulberry’s financial performance, its unique brand personality, and the road ahead for its progress. Through an elaborate analysis of the macroeconomic trends in conjunction with the micro-level factors, we aim to provide indispensable guidelines to Mulberry in completion with market research of the luxury goods sector on its present condition and future roadmap. As part of a marketplace, your main task is examining market trends and noting changes in consumer behavior and industry dynamics. A thorough PESTLE analysis shows Mulberry’s business environment’s political, economic, social, technical, legal, and ecological factors—otherwise, a brand positioning map positions Mulberry as the embodiment of refined sustenance. Mulberry explores the critical actions that might be done differently in the business model canvas’s inside. Partner and value proposition definitions continue. A resource-based view canvas highlights the company’s strengths, while a VRIO framework evaluates strategic resources. Porter’s Value Chain Analysis identifies Mulberry’s operational efficiency issues. Therefore, The BCG Matrix examines its product lines. The paper summarizes the analysis’s primary findings and offers practical suggestions to boost Mulberry’s competitiveness and luxury goods market share. This study uses purposeful research and critical thinking to equip decision-makers with the tools and navigational methods to handle qualitative and quantitative luxury fashion industry data.
Introduction
Mulberry is a symbol of respect as the peak of luxury brands, and it is well known for its branding capabilities and the high quality of handicrafts guaranteed to customers. This part of the profile aims to give you a holistic understanding of Mulberry’s premium brand while exploring its long legacy and uniqueness. In addition to the stage analysis of Mulberry’s financial performance during the previous two years, the underlying reason that caused its stock movements, by carefully analyzing it, will be disclosed. At the very heart of Mulberry’s appeal, there is a never-ending dedication to creating the perfect products of outstanding quality and absolute elegance staying forever. Located amid luxury brands, Mulberry has gained a reputation as a priceless item with a mix of tradition, appeal, and fashion that can never go out of fashion, appealing to customers who appreciate the best things. The brand is defined by its attention to detail and dedication to craft, a management philosophy that endures in a changing market.
Along with its high-quality products, Mulberry’s brand image is crucial to its commercial success, a significant indicator of its market position and competitiveness. The study analyzes significant financial counts and stock performance from the past two years to demonstrate Mulberry’s luxury goods industry trends and drivers. Macroeconomic trends, industry dynamics, and strategic goals will be examined to understand Mulberry Financial’s growth.
External Audit
Market Analysis and Trends:
In the fast-changing environment of the luxurious goods market, only brands like Mulberry can survive and find the balance between their creative tendencies and consumer demand. The market for luxury goods behaved uniquely, as the factors that changed consumer preference, economic fluctuations, or emerging trends had an impact on it (Runfola et al., 2022, p. 51). Indeed, consumers’ tastes have transformed in such a way that there is an increasing demand for ethically sourced and environmentally friendly items due to the falling standard of ordinary luxury and the growing importance of sustainability consciousness. Mulberry needs to ensure that it is constantly updated on current fashion trends to align with the dynamic consumer tastes and to ensure that it remains the most competitive option for the market.
PESTLE Analysis (Johnson & Scholes, 1993):
A comprehensive PESTLE analysis enables Mulberry to assess the external factors impacting its operations across six key dimensions: power, market, society, technology, law, and environment. Political factors play their part in the form of trade policies and regulations on practices of the manufacturing industry, which affect Mulberry’s supply chain and international expansion. Economic factors like exchange rates and consumer purchasing trends determine currency power and market demand. Besides social factors that make people change their fashion tastes, sustainability consideration also shapes consumer choices and brand perception (Ozkavruk Adanir et al., 2022, p. 6). Mulberry faces both opportunities and challenges in reaching and engaging its target audience as e-commerce and digital marketing evolve. Intellectual property and consumer protection laws affect Mulberry’s operations and compliance. Environmental factors like sustainability and carbon footprint reduction are becoming essential to the brand image and company operations.
Brand Positioning Map:
Luxury positioning will be the brand’s leverage to conquer the market and attract its desired customers who are fond of the timeless and elegant. As it puts itself in the highest position in the luxury brand category, it becomes very differentiable from the competitors and naturally creates a sense of uniqueness and exclusivity in the customers’ minds (Vijayalaxmi & Kalluraya, 2023, p. 49). Contrasting with attributes such as handmade made, trad, tuition, and refinement, Mulberry fills a particular segment in the high-end products market and serves connoisseurs looking for the best quality, long-lasting sting, and elegance.
Competitor Analysis and Blue Ocean Canvas:
In order to outgrow competitors and establish effective market differentiation, Mulberry should be benchmarked against its industry leaders and its performance. Market analysis, including competitor analysis, can help Mulberry determine the gaps in the market and identify innovation opportunities. It lets the company build a unique competitive value proposition. Blue Ocean Canvas allows Mulberry to explore new market sectors and products, allowing the company to occupy a market space unoccupied by competitors and stand out (Boardman., 2020, p. 505). Mulberry, a luxury goods leader, can uncover new development avenues by detecting underutilized resources and being receptive to new technologies.
Internal Audit
Business Model Canvas:
Mulberry’s business model gives us a deeper understanding of its main activities, partners, market (customer segments), value proposition, sources of income, and the resources it uses. The primary operations carried out by Mulberry are designing, producing, and selling top-quality leather goods. Its close working on the terms of cooperation with the suppliers, distributors, and retailers leads to its operational effectiveness and market intensity (Dey et al., 2023, p. 1232). The markets of Mulberry customers include elite consumers of luxurious yet elegant clothing and aficionados of beautiful and unique leather goods that it provides. Revenue channels, including product sales, accessories, and collaborations, are diversified and used where steady revenue can be guaranteed. Essential resources of the firm, like skilled designers, artisans, and its brand name, will be crucial for surviving the cut-throat competitive environment.
Resource-Based View (RBV) Canvas:
Through the RBV framework, this analysis reveals Mulberry’s resources, giving it a competitive edge. Mulberry owes much of its sales to its diverse attributes, such as its excellent brand reputation, skilled workforce, design capabilities, and well-developed retail network in the luxury goods market. These resources are irreplaceable, unique, and difficult to imitate, giving Mulberry an enduring and sustainable edge. Effective allocation of such resources to the stated goals and objectives through the strategy’s organization component ensures that the strategy is aligned with Mulberry’s overall performance and market positioning.
VRIO Framework (Barney, 1991):
The VRIO model strengthens the resource audit by focusing on the value, uniqueness, imitatability, and organization of the opportunities portrayed by Mulberry. Mulberry’s brand image and design capabilities are an inalienable part of its products’ values, which is why they are worth paying more when compared to competitors’ offers. Only Mulberry can offer artisanal craftsmanship and unique designs, and limited resources bring this brand a level of exclusiveness and desirability. On the other hand, these inimitable resources also make it difficult for rivals to imitate them, thus ensuring a very high competitive advantage. Efficient organization and a specific alignment of resources bring about the best of what every luxury goods market can offer. Through such means, long-lasting competitiveness is achieved.
Porter’s Value Chain Analysis:
Porter’s Value Chain Analysis serves to delineate the main and auxiliary activities to provide a detailed report of what value-added processes take place in the operations of Mulberry. Direct activities of inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing, and sales stand between the end customer and the product value, resulting from all these processes (Tonti, 2022, p. 33). Business processes such as procurement, human resource management, technology development, and the firm infrastructure function as a support system for primary activities and help advance them towards a coherent end.
BCG Matrix:
Through the BCG Matrix, it is possible to analyze which products are vital to the company and which should be reduced by resource allocation and product development. Product groups are parked into stars, cash cows, question marks, or dogs by accounting for their market growth rate and share (Blasi et al., 2020, p. 118). The selection of products with high growth performance and market-leading position will determine the strategic allocation of resources to achieve maximum profit and dominance. At the same time, the challenges associated with underperforming segments will be addressed.
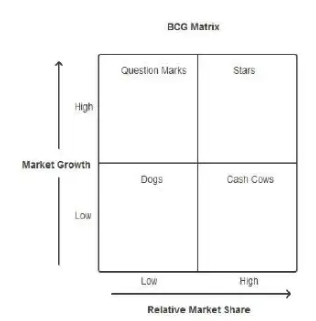
Figure: BCG Matrix
Major Issues Facing the Brand
Porter’s Five Forces:
A Porter 5 forces analysis explains the competitive landscape that influences the environment where the brand Mulberry operates. The five forces relevant here are the threat of entering the market by new competitors, the power of customers’ bargaining, the power of suppliers’ bargaining, the threat of new substitute products, and the competition between firms. These criteria help us assess industry competition and market attractiveness. Mulberry has two significant risks to its growth: fierce rivalry from existing premium brands and rising companies and replacement materials (Xie & Youn, 2020, p. 55). In addition, suppliers’ bargaining strength, especially for high-quality materials, can affect production costs and Mulberry’s profitability. By identifying these fluctuations, Mulberry can decide how to respond to threats and market events or profit from them.
TOWS Analysis:
TOWS analysis helps Mulberry Tufts work out strategic options by assessing the company’s internal strengths and weaknesses against the external environment characterized by opportunities and threats. Leveraging its capabilities, comprising of a solid brand image and a distinctive design talent, the company is poised to take advantage of the opportunities present in those markets that are in ascension and those consumer groups that are growing (Casadei & Iammarino, 2023, p. 2151). Another side of the coin is that dealing with disadvantages like narrow product assortment and substantial exposure to economic imbalances could be pivotal to counteracting threats and gaining an edge in a competitive environment. With the step-by-step analysis of internal and external determinants, Mulberry can formulate strategic initiatives that fit its overall objectives, thus promoting sustainable growth and competitiveness.
Ansoff Matrix:
The Ansoff Matrix offers a framework for recommending growth strategies for Mulberry based on four strategic options: the penetration of markets, product development, market development, and diversification. Market penetration strategies are opportunities for market development in which a company aims to grow its market share through product promotion campaigns and better distribution channels. Product development strategies include launching new products or modifying existing ones to meet evolving consumer preferences, increasing product diversity, and generally maintaining consistent growth (Ventura, 2021, p. 96). Market development strategies often involve expanding into new markets or segments to give the organization untapped growth potential. Mulberry’s strategy includes targeting new markets and creating products or services to diversify income and lessen risks. Mulberry can choose a path for sustainable growth and market expansion while avoiding competing forces and volatile markets by analyzing the feasibility and consequences of the strategic options.
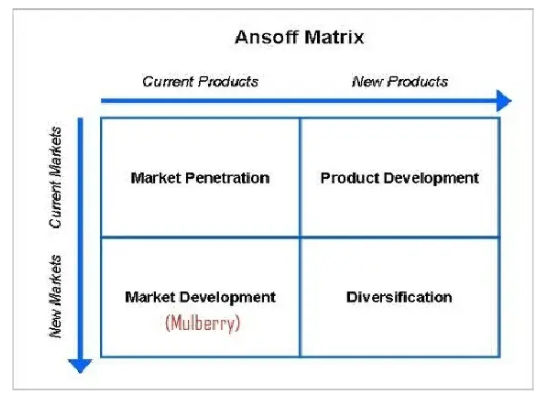
Figure: Ansoff matrix of Mulberry
Selecting Strategies
The strategic recommendations become the basis of how the company plans to grow in the market and the direction it shall take to achieve this growth through in-depth competitor analysis and growth opportunities analyzing information obtained from the analyses conducted, a particular strategy is identified to enhance the companies eliminate weaknesses and take advantage of the opportunities presented by the luxury market. The proposed strategy will be accompanied by a specific timeline, where the critical steps for implementation are outlined, and the expected milestones further indicated. Through the development of straightforward and implementable directional steps, Mulberry can implement its strategic initiatives and cope with the complexity of its competitive arena. Through such a strategy, the company will adhere to the general objectives of Mulberry, which promote sustainable expansion, ensure competitive advantage, and achieve success in the luxury goods market.
Conclusion
In a conclusive overview, this report captures the main conclusions and proposes strategic directions for Mulberry to implement to achieve success amid the fast-changing luxury goods market. Multi-pronged strategies, including brand equity, artisans’ skills, and innovative design, can help seize new opportunities for the brand while avoiding the industry’s challenges. The impact of proactive steps toward marketing pressure and consumer trend change must be Mulberry’s core of strategic thought, which must adapt and be innovative. Presumably, through a main focus on customers, sustainability, and further market expansion, Mulberry will become the leading luxury brand as it is with permanent popularity. Such recommendations only emphasize the need for the business to keep a farsighted creative style, continually adapting to the dynamic market and catching growth opportunities. Mulberry can maintain its luxury goods industry leadership by carefully aligning the brand with its strategic objectives and executing flawlessness; Mulberry’s success comes from its flexibility and consumers in a fast-changing, competitive business focus. By considering the report’s suggestions and advice, Mulberry will be better able to face the luxury goods market’s problems fearlessly and steadily, ensuring a bright future for the brand and its owners.
Reference List
Blasi, S., Brigato, L. and Sedita, S.R., 2020. Eco-friendliness and fashion perceptual attributes of fashion brands: An analysis of consumers’ perceptions based on Twitter data mining. Journal of Cleaner Production, 244, p.118701.
Boardman, R., Haschka, Y., Chrimes, C. and Alexander, B., 2020. Fashion “see-now-buy-now”: implications and process adaptations. Journal of Fashion Marketing and Management: An International Journal, 24(3), pp.495-515.
Casadei, P. and Iammarino, S., 2023. Backshoring, offshoring and staying at home: evidence from the UK textile and apparel industry. Operations Management Research, 16(4), pp.2148-2173.
Dey, B., Alwi, S.F.S., Babu, M.M., Roy, S.K. and Muhammad, S.S., 2023. Brexit or brand it? The effects of attitude towards Brexit and reshored brands on consumer purchase intention. British Journal of Management, 34(3), pp.1215-1237.
Ozkavruk Adanir, E., İleri, B., Can, F. and Ulasli, B., 2022. An Ethical Approach to Sericulture: Production of Peace Silk in Hatay/Turkey. TEXTILE, pp.1-11.
Runfola, A., Milanesi, M., Guercini, S., Runfola, A., Milanesi, M. and Guercini, S., 2022. The Internationalization of Luxury Fashion. Internationalization of Luxury Fashion Firms: Examining the Business Models of SMEs, pp.39-70.
Tonti, L., 2022. Sundressed: Natural Fibres and the Future of Fashion. Black Inc..
Ventura, D.B., 2021. Exploring the Convergence of Eco-Friendliness and Fashion: A social-media Perceptual Analysis. Journal of Empirical Social Science Studies, 5(1), pp.90-107.
Vijayalaxmi, K. and Kalluraya, S., 2023. ANALYZE THE PRESENT STATUS OF COTTAGE INDUSTRY, ANALYZING THEIR CONTRIBUTION TO GDP, EMPLOYMENT POTENTIAL AND THEIR ROLE IN ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT. EPRA International Journal of Economic and Business Review (JEBR), 11(12), pp.46-53.
Xie, J. and Youn, C., 2020. How the luxury fashion brand adjust to deal with the COVID-19. International Journal of Costume and Fashion, 20(2), pp.50-60.
Appendix
Figure: Market positioning of Mulberry
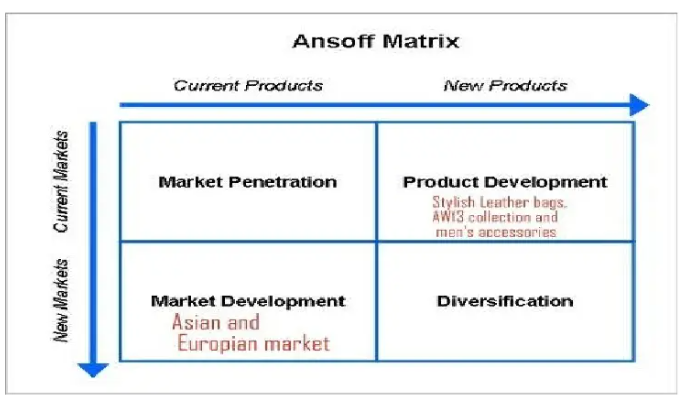
Table 1: Market Analysis Trends
| Market Trends | Consumer Behavior |
|---|---|
| – Shift towards sustainability-conscious products | – Increasing preference for ethically sourced materials |
| – Growing demand for experiential luxury | – Desire for unique, personalized luxury experiences |
| – Rise of online luxury retail |
Table 2: PESTLE Analysis Results
| Factor | Impact on Mulberry |
|---|---|
| Political | Trade policies can affect international operations |
| Economic | Exchange rates influence pricing and profit margins |
| Social | Changing fashion trends impact consumer preferences |
| Technological | E-commerce trends require adaptation of sales channels |
| Legal | Intellectual property laws protect Mulberry’s designs |
| Environmental | Sustainability initiatives enhance brand reputation |
 write
write