Introduction
The desire to transition from conventional energy fuels to sustainable energy systems is urgent and evident in the research objectives. This thematic analysis evaluates complex factors influencing Gotland residents’ decisions to adopt alternative motor fuel. It explores the current and prospective motor vehicle fuel for the population surveyed and the primary factors influencing their transition. Moreover, the study explores alignment issues between actions and alignment intentions and the factors contributing to the inconsistencies. The study offers meaningful insights for scholars and administrators seeking to explore opportunities and address challenges in transitioning to sustainable energy options. It emphasizes the interplay of effective factors such as infrastructure education and awareness, convenience and social norms, which determine the migration of the population to greener fuel options. This analysis sheds light on multiple audiences, including industry stakeholders’ government agencies, researchers and policymakers, on implementing interventions that eradicate barriers and realize the region’s patience for a sustainable future.
Current fuel alternatives for passenger vehicles in Gotland and preferred alternatives for the next vehicle
This research question explores current fuel alternatives for Gotland residents utilized in their passenger vehicles. It provided insights into passengers’ preferred fuel alternatives and their next vehicle. A holistic exploration of the research question involved incorporating the theory of planned behaviour (TPB), offering criteria for understanding Gotland residents’ attitudes, perceived behaviour control and subjective norms inherent in the choices, intentions and actions regarding selecting fuel alternatives for their vehicles.
A thematic analysis of the findings shows that several residents in Gotland prefer convenience over environmental consciousness. Consequently, citizens rely on conventional fuel alternatives at the expense of environmentally friendly alternatives. According to the surveyed residents, these findings are evident in resident behaviour, where 42.10% rely on petrol vehicles as their alternative passenger vehicles. It shows the prevailing situation where traditional fossil fuel dominates residents’ attitudes and behaviour when selecting fuels for passenger vehicles. Moreover, diesel-powered vehicles account for 19.30% of the surveyed residents and their preferred vehicles. These statistical findings underline the substantial dependence on diesel fuel for Gotland residents. The findings underline subjective norms and attitudes towards traditional fuel alternatives of petrol and fuel for Gotland residents. The residents prefer conventional petrol and diesel fuel alternatives due to factors such as pre-existing infrastructure, perceived affordability and familiarity, which indicate an inclination towards convenience.
Table: Findings of Preferred Current and Next Cars with Alternative Fuels for Gotland Residents
| Type of private cars | Percentage | |
| Today | Next cars | |
| Diesel vehicle | 19.30% | 15.8% |
| Petrol vehicle | 42.10% | 26.3% |
| Electric vehicle | 17.50% | 49.1% |
| Hybrid electric vehicle | 14.00% | 36.8% |
| Hydrogen vehicle | 0.00% | 12.3% |
| Compressed natural gas vehicle | 5.30% | 3.5% |
| Liquefied petroleum gas vehicle | 0% | 1.8% |
| Ammonia vehicle | 0% | 0% |
| Methanol vehicle | 0% | 1.8% |
| Others | 22.80% | 3.5% |
Despite Gotland residents preferring conventional fuel alternatives of petrol and diesel, notable indications for shifting to environmentally friendly alternatives is evident. Residents are likely to shift away from conventional fuel for their next vehicle. Preferences for the next vehicle dropped slightly for diesel and petrol vehicles at 15.8% and 26.3%, respectively. The decline in resident preference for the next vehicle indicates an intention to continue relying on petrol and diesel fuel but gradually shift to other alternatives. The theory of planned behaviour provides a perspective and the decline in intention to adopt environmental consciousness and sustainability options in vehicle fuel. Moreover, the theory shows that Gotland residents need more consciousness over environmental consequences such as carbon emissions arising from conventional fuel alternatives and underwhelming intention to adopt alternative fuel options.
Given 17.5% of residents in Gotland prefer electric vehicles (E.V.s), the electric fuel option emerges as an alternative promising to address environmental consequences. The 17.5% figure highlights a significant attitude and adoption rate, with residents showing the potential to shift to alternative fuels. It shows residents’ willingness to adopt environmental consciousness in their vehicle fuels and a growing motivation to adopt environmentally-friendly energy and fuel for the transport sector that guarantees sustainability. The TPB offers a framework to analyze the potential interest in electric vehicles for the residents. This theory highlights the positive attitudes among Gotland residents to embrace electric vehicles. Several factors contribute to this change in attitude, including government incentives, cost-effectiveness, increased accessibility to charging infrastructure and increased awareness of the environmental impact of fossil fuels (Golbabaei et al., 2020). These factors sway residents ‘ mindsets leading to increased adoption of electric vehicles. Statistical findings for residents’ preference for the next vehicle stood at 49.1%. This finding highlights increased awareness and the possibility of shifting from diesel and petrol fuel to electric vehicles. It suggests increasing awareness about environmental impact and a robust inclination towards a green economy. Gotland residents have adopted positive attitudes and subjective norms towards environmentally friendly fuels, particularly shifting to electric vehicles.
Preference for hybrid electric vehicles in Gotland stands at 14.00% among the surveyed population and their current vehicles. Hybrid electric vehicles combine an electric motor and an internal combustion engine using petrol or diesel fuel. Incorporating electric motors in the internal combustion engine reduces carbon emission levels while improving vehicle efficiency. This improvement represents a positive step in environmental consciousness and a foundation for achieving full electrification (Golbabaei et al., 2020). Hybrid electric vehicles represent an attractive alternative to Gotland residents compared to fully electric vehicles or petrol or diesel fuels that are environmentally disastrous. The theory of planned behaviour highlights the possible increase in adopting hybrid electric vehicles owing to their substantial convenience and significant reduction of carbon emissions. Residents prefer the performance and familiarity of the vehicle, which indicate their preference for hybrid electric vehicles for fuel-saving and perceived environmental benefits. The attitude of hybrid electric vehicles as the next vehicle for Gotland presidents stands at 36.8%. This percentage increase in referring to hybrid electric vehicles highlights a change in behaviour and attitudes with increasing awareness of the environmental impact of fossil fuels and inclining towards cost-effectiveness in fuel consumption.
The absence of hydrogen vehicles in Gotland indicates underlying factors hindering residents’ adoption of hydrogen fuel. It shows the limited availability of hydrogen fuel and vehicles and the lack of infrastructure supporting hydrogen cell fuel technology. The lack of infrastructure and availability of hydrogen cell fuel technology is evident when statistical findings show it as the next vehicle preference at 12.3%. It indicates an emerging interest among Gotland residents in adopting hydrogen cell fuel technology and vehicles using hydrogen cell fuel. Residents are interested in its potential for longer driving ranges and zero-emission properties.
Moreover, residents are interested in hydrogen cell fuel due to its capacity to improve infrastructure. The theory of planned behaviour highlights the value of perceived environmental benefits, energy diversification and cost-effectiveness as significant in attitude and behaviour change among Gotland residents. It shows the subjective norms arising from an inclination towards technological advancements and exalting social factors pushing residents to adopt hydrogen cell fuel vehicles.
Statistical findings for compressed natural gas (CNG) in Gotland is 5.30%. This statistical finding is relatively insignificant compared to conventional diesel and petrol fuels among residents. Compressed natural gas is fuel for vehicles with lower carbon emissions than conventional fuels. The statistical findings show a decline in residents’ preference for compressed natural gas as fuel for their next vehicle. This alarming decline indicates waning interest in compressed natural gas as a vehicle fuel in Gotland. TPB offers perspective showing potential attitude and behaviour change in adopting compressed natural gas. The theory outlines accessibility to infrastructure, long-term sustainability and availability of compressed natural gas as factors hindering its adoption and causing negative resident attitudes and behaviour. It shows a preference for other alternative fuels, such as hybrid electric vehicles and electric vehicles, which have become popular and convenient for utilization to achieve significant environmental benefits.
Gotland residents shy away from methanol vehicles, with the statistics showing a 0% adoption among surveyed residents. Methanol is a renewable energy source emanating from captured carbon dioxide for biomass. The promising energy fuel shows significant environmental benefits of reducing carbon emissions and air pollutants. However, the absence of methanol fuel among Gotland residents is a concern and underlines factors hindering its adoption. The primary Factor hindering methanol fuel in the region is inadequate understanding and lack of awareness among residents on the availability and applicability of methanol fuel in vehicles (Swaroop et al., 2022). Methanol vehicles have substantial benefits to the users and environment owing to their cost-saving benefits, improving air quality and reducing carbon emissions. It offers opportunities for residents to utilize renewable sources. Technically methanol can serve as a blended fuel in an internal combustion engine or be utilized as a sole fuel. Gotland residents show interest in methanol vehicles, with a 1.8% indication of owning them as their next vehicle. This percentage represents emerging interest among residents in methanol vehicles, highlighting the necessity for increased awareness through campaigns and education programs. Policymakers and stakeholders should address underlying misconceptions and disseminate information on methanol fuel as a viable alternative.
The findings indicate other females attract 28.80% of interest among Gotland residents, according to surveyed vehicles. It encompasses diverse alternative fuels, including minor alternatives such as bioethanol and biodiesel. Besides biofuels, this category covers other alternative fuels under experimentation, including synthetic fuels and fuel technologies. This category highlights existing alternative fuels beyond conventional fuels among region residents. Despite residents showing interest in using other alternative fuels, they demonstrate an underwhelming likelihood of adopting other females for their next vehicles. The 3.5% interest for other females for the next vehicle indicates limited knowledge and underwhelming appeal of other options among the surveyed respondents. Policymakers and stakeholders must invest in subsequent research programs to explore alternative fuels and develop infrastructure for implementation. Moreover, policymakers must address underlying barriers to adopting innovative fuel in transportation while educating the public on the benefits and shortcomings of various fuel alternatives.
The research findings offer valuable insights into the current fuel options Gotland residents adapt. Additional findings outline preferences for the next vehicle for the residents. It shows how residents in the region prefer convenience over environmental consciousness, as indicated by significant reliance on diesel and petrol passenger vehicles. Nevertheless, the findings highlight a potential shift among residents indicated by the adoption of electric vehicles and hybrid electric vehicles. The theory of planned behaviour provides a framework that visualises factors promoting and hindering the adoption of alternative fuel options. Moreover, the TPB indicates the perceived behavioural control and subjective norms influencing residents in the region to adopt alternative females. Overall the findings underline the increasing interest in electric vehicles and an emerging motivation among residents to adopt hydrogen cell fuel (Swaroop et al., 2022). The theory informs policymakers to adopt measures that promote alternative fuels that are environmentally friendly such as increasing awareness through campaigns and education programs, offering government incentives and improving infrastructure for sustainable fuel options.
Cost environmental impact and convenience factors in deciding motor fuel alternative in Gotland
Cost environmental impact at convenience is primary factor influencing the choice of residence in Gotland to various fuel alternatives. For instance, fuel cost is a crucial factor for residents to decide on vehicles using a particular fuel. Residents prefer cost-saving vehicles and affordable fuel alternatives. High fuel prices for conventional fuel alternatives such as petrol and diesel compel residents to explore cost-effective options such as biofuels and hydrogen cell fuel (Swaroop et al., 2022). Moreover, presidents explore natural gas and electricity over conventional fuels when reducing costs over long distances and sustaining transport services. According to the theory of planned behaviour, policymakers must target fuel costs for changing attitudes and behaviour. It involves providing government subsidies, improving infrastructure, tax incentives and making alternative fuel options readily available to influence their cost. The study findings show the president’s willingness to adopt New Energy fuels by considering the financial subsidy the car (70.2%), reduction in vehicle tax (54.4%), free parking at 38.6% and reduction in road tax at 31.6%.
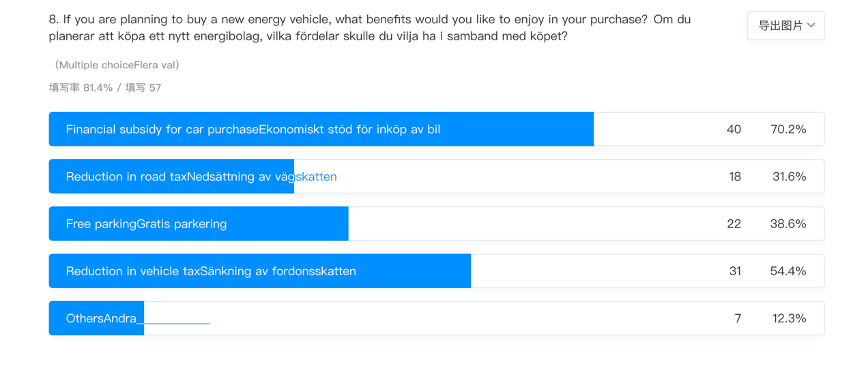
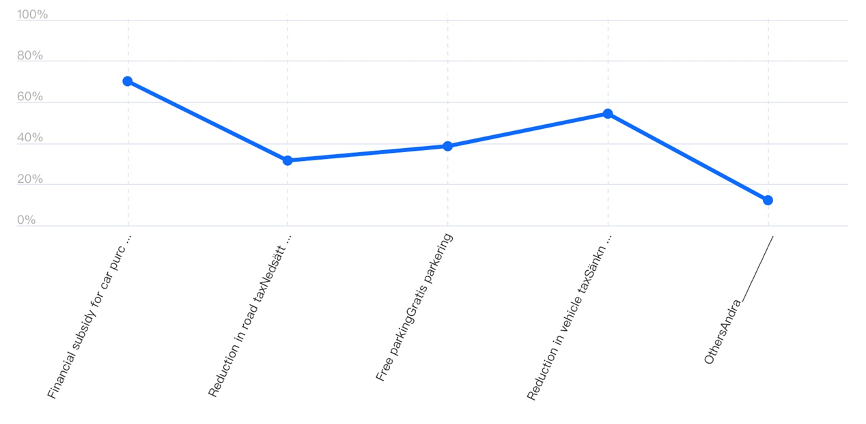
People’s decisions in motor fuel alternatives considering their sustainability intentions and factors encouraging alignment and inconsistency of people’s decisions
Gotland residents consider the cost of refuelling vehicles in selecting vehicles with a particular fuel alternative. For instance, the study questioning an individual’s perception of the availability of refuelling facilities for renewable energy sources showed a 77.2% objection and 22.8% agreement. This finding indicates residence preference for readily available refuelling infrastructure on selecting vehicles with alternative fuels. It compels policymakers to reduce the cost of refuelling for renewable energy sources such as electric vehicles and natural gas to lower refuelling costs.
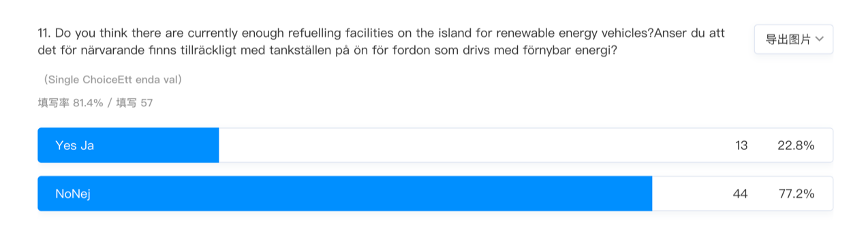
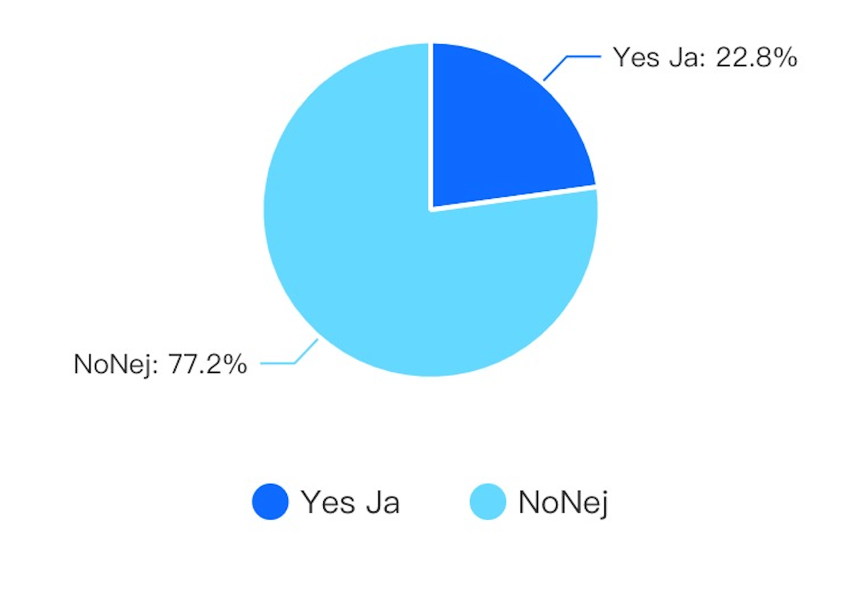
The findings show a significant impact attributed to environmental consciousness when selecting vehicles of a specific fuel. Environmental awareness has increased globally owing to increased information flow. Consequently, residents recognize the adverse consequences associated with the excessive combustion of fossil fuels. This situation highlights increased attitudes and behaviour towards renewable sources that reduce carbon emissions and lower air pollutants in the atmosphere. It explains the increasing attitude towards greener alternatives, including hydrogen cell fuel, natural gas biofuels and electricity and ditching petrol and diesel fuels that have high carbon emissions. Individuals have become aware of their environment as evidenced by changes in climatic conditions hence preferring attractive options that have zero or low carbon emissions. Environmental consciousness among Gotland residents is evident in their fuel decision-making and preference for their next vehicle fuel.
Research findings showed reluctance among Gotland residents to adopt environmental-friendly fuel alternatives and retain petrol and diesel as their primary fuel alternatives. This situation was evident in their findings showing several residents’ disagreement with using new energy vehicles as a remedy to environmental problems. Several residents appear to have limited knowledge of the impact of adopting sustainable energy sources in reducing environmental degradation. In the statistical graphs below, 40.4% of surveyed residents neither agree nor disagree on whether new energy sources address environmental degradation. In the findings, 7% and 10.5% strongly disagree and agree on adopting sustainable fuel sources to address environmental challenges bedevilling humanity.
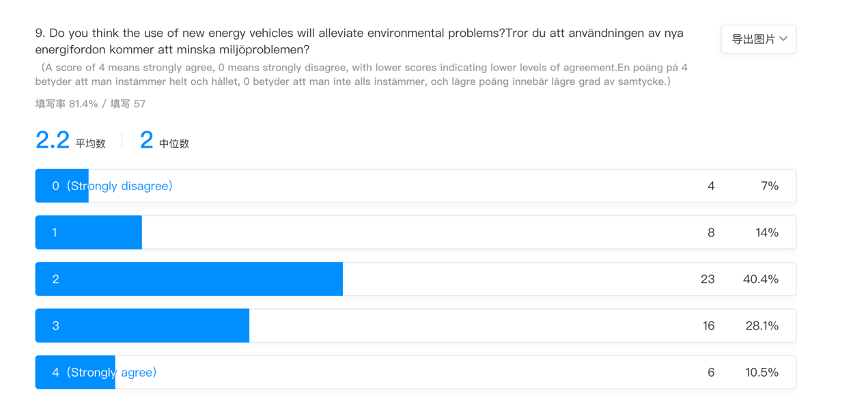
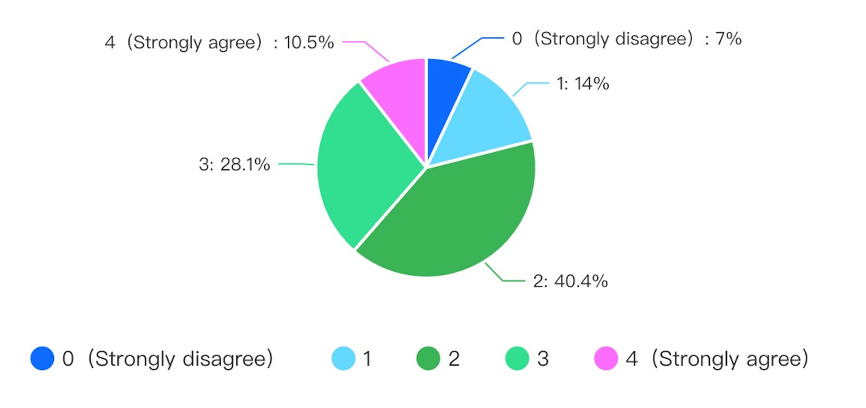
The surveyed individuals indicated concern over environmental consequences when receiving information through a relevant press or online media. It shows 57.9% of residents in Gotland demonstrate environmental consciousness when receiving information from online media or relevant press such as print and broadcasting media. This concern pushes individuals to adopt sustainable fuel choices depending on their relationship with other factors, such as convenience and cost (Yan and Mohamed, 2022). It shows a positive correlation between individuals receiving information from relevant sources and adopting sustainable vehicle fluids such as electric vehicles, hybrid electric vehicles and natural gas. It highlights information penetration for residents’ awareness and education using primary sources of information in changing their attitudes and behaviour toward sustainable vehicle fuel. Nevertheless, this finding shows that cost saving remains a primary motivator in adopting alternative fuels in transportation.

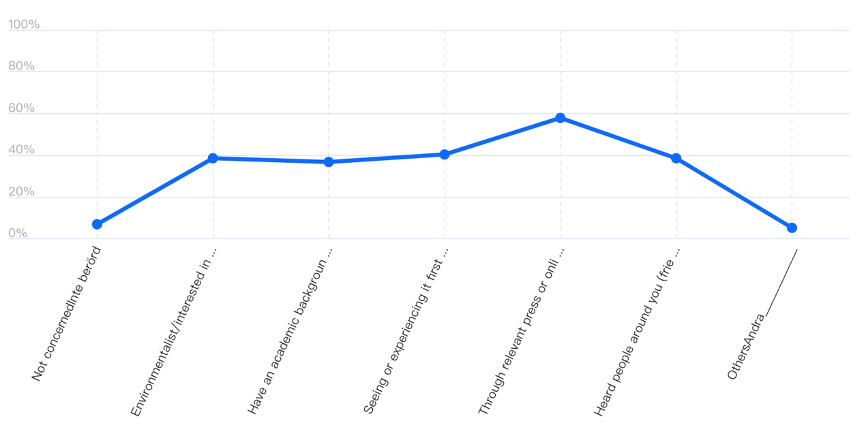
The strength and direction of the relationship between information flow and awareness of adopting sustainable fuels are evident in other sources of information. Experiencing or seeing environmental consequences first-hand, environmentalists’ warnings and word-of-mouth, our information sources come second to relevant press information. The three sources influence people’s environmental consciousness by 40.4%, 38.6% and 38.6%, respectively. It shows the strength and direction of information flow and reaches as significant determinants of people’s decision in selecting vehicle fuels. However, 38.8% of the surveyed residents demonstrated concern over environmental issues owing to their academic background or working in a related field. Gotland residents expressing a lack of concern at 7% and other factors drawing their concern at 5.3% shows the impact of information in increasing awareness and adopting sustainable practices that reduce environmental degradation. These findings show the value of information sources in swearing the public towards a specific fuel source for their vehicle.
Convenience was a predominant Factor among Gotland residents’ decision to select petrol and diesel fuels for their current vehicles. This reason highlights the inconvenience associated with adopting alternative and sustainable fuels such as electric vehicles and hybrid electric vehicles. This inconvenience extends to other sustainable fuels, including hydrogen cells and natural gas, whose availability and infrastructure is a barrier to their adoption. Besides refuelling infrastructure, other factors hindering the adoption of sustainable fuels include charging time and upfront costs in acquiring vehicles. Hydrogen cell vehicles require advanced infrastructure for dedicated refuelling, while electric vehicles require specialized refuelling points as their charging stations. Convenience in retaining conventional fuel success is evident in the findings of residents’ perception of the severity of environmental impact (Yan & Mohamed, 2022). Several respondents indicated their perception of the severity of environmental impact, with the majority agreeing with the seriousness of global warming. 56.1% of respondents agreed with the global warming issue against 0%. Additionally, between 26% and 29% of surveyed residents outlined the extreme concern about the severity of environmental impact supporting anthropogenic toxicity, acidification potential, eutrophication abiotic resource depletion, depletion of ozone stratosphere and terrestrial eco-toxicity as factors for the severe impact.
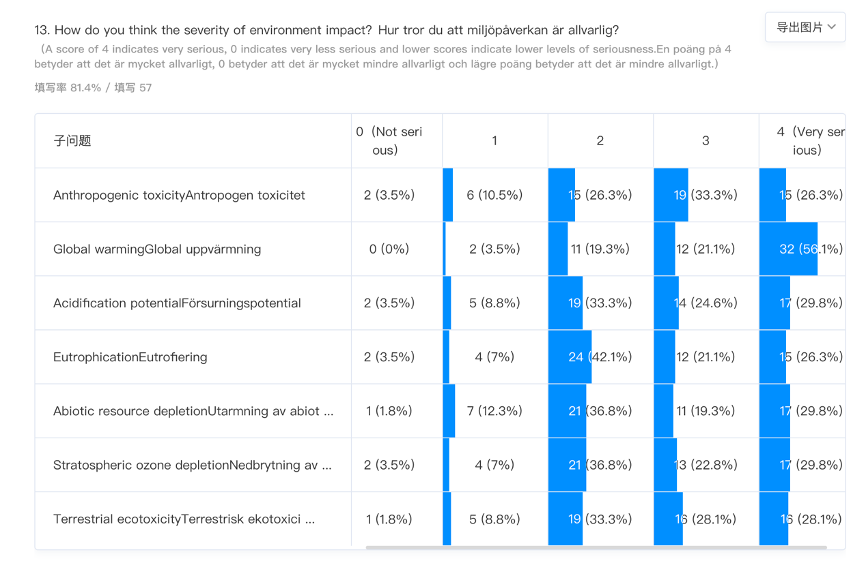
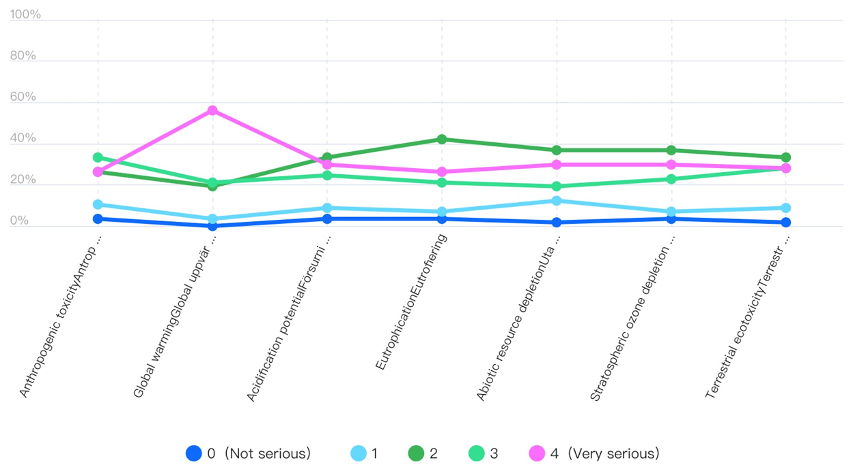
Despite the surveyed population indicating their perception of environmental impact severity, they remained with petrol and diesel Fuels for convenience.
People’s decisions in motor fuel alternatives considering their sustainability intentions and factors encouraging alignment and inconsistency of people’s decisions
The choice of motor fuel alternatives for Gotland residents did not align with their sustainability intentions owing to an increased preference for convenience. Despite sustainability being a critical concern among residents, the factors determine their toys of motor fuel alternatives. These factors trigger inconsistencies between intentions for sustainability and actual action in purchasing a motor vehicle. Gotland ambition to embrace sustainable vehicle fuel positive attitude from stakeholders to encourage alignment through policy measures and identifying and understanding contributing factors and levels of misalignment. Statistical findings show several residents of Gotland express consciousness of the severity of an environmental impact at 56.1%. Conversely, several residents in the region prefer petrol vehicles at 42.10% and diesel vehicles at 19.30% regardless of their environmental degradation potentials. Residents show a high potential in adopting environmentally friendly options, with 49.1% indicating interest in adopting electric vehicles and 36.8% in adopting hybrid electric vehicles as their next vehicles. These findings show the willingness of positive attitudes, values, and beliefs in sustainability but experiencing barriers to adopting sustainable fuel options.
Multifaceted factors undermine the adoption of sustainable fuel options among the residents despite their awareness of environmental degradation. Knowledge gaps and inadequate information is the first-factor hindering the adoption of sustainable fuel options in Gotland. These factors hinder the understanding of benefits such as cost-saving and environmental conservation when adopting fuel options such as compressed gas and hydrogen cell fuel (Kumar et al., 2017). Consequently, residents make choices to purchase petrol and diesel vehicles without aligning with their sustainability intentions. It requires policymakers, government agencies and other stakeholders to increase public campaigns and education forums to disseminate information on environmental benefits associated with sustainable energy fuels in the transport sector.
Technical and practical constraints represent the second Factor hindering the adoption of sustainable fuels in Gotland. For instance, the insufficient refuelling infrastructure and inadequate availability of fuel options such as compressed gas and hydrogen cell undermine people’s attitudes towards sustainable alternatives. The region has a scarcity of electric vehicle charging stations and specialized facilities for hydrogen cells leading to residents’ intention to retain fossil fuel vehicles. Policymakers and government agencies address infrastructural issues when investing in advanced infrastructure and having adequate charging stations and facilities. Moreover, policy directions that support the implementation of projects aligning with new fuel options are necessary to increase the alignment of residents’ decisions with their sustainability intentions and motor fuel choices.
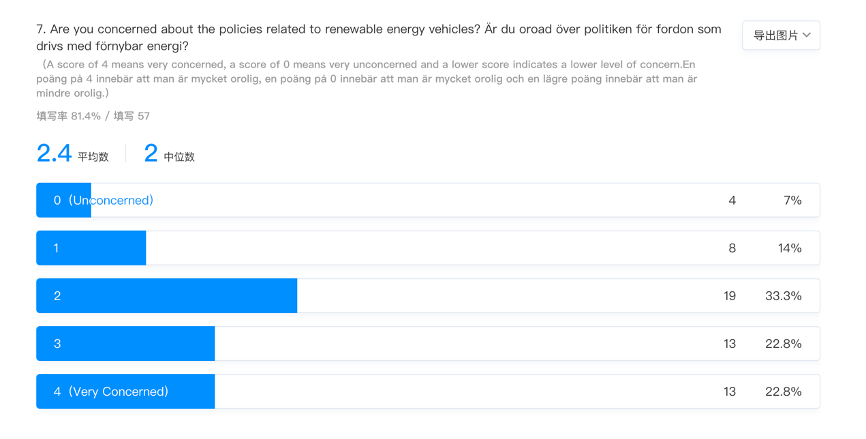
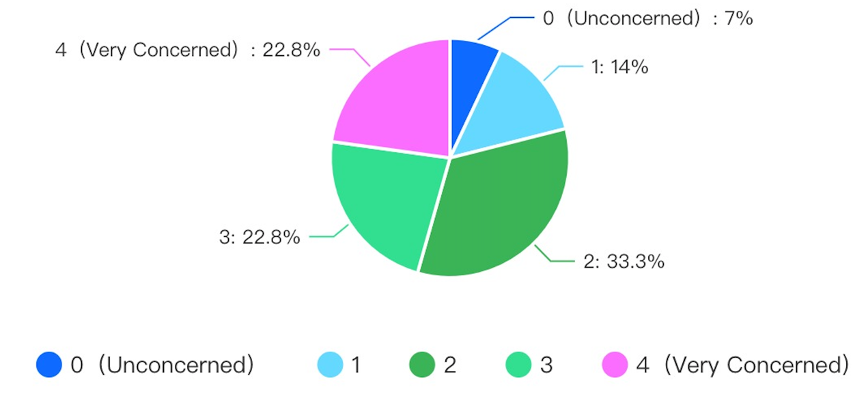
Economic considerations are the third Factor determining the adoption of sustainable fuel options that align with residents’ intentions. The higher upfront costs associated with acquiring vehicles and fuel and sustainable options are barriers. For instance, residents prefer petrol or diesel vehicles with lower upfront costs compared to hydrogen and electric vehicles, as upfront costs are higher. This Factor determines the choice of sustainable vehicle fuel, undermining sustainability in tensions among residents, particularly regarding long-term financial benefits (Yan and Mohamed, 2022). Consequently, policymakers and governments in the region must encourage alignment of fuel choices and sustainability intentions by offering tax incentives and extending subsidies to potential buyers of sustainable options and other financial incentives.
The fourth Factor is the peer influence and social norms that influence choices for motor vehicle fuel. The lack of social value and widespread adoption of sustainable options undermine interest and alignment intentions among residents. Individuals develop negative attitudes towards sustainable fuel options if they have limited penetration within the public (Yan and Mohamed, 2022). Consequently, stakeholders must promote a sustainability Culture by using success stories of individuals using sustainable motor fuel options. Additionally, achieving a culture of sustainability requires regular and extensive community engagement and public awareness campaigns. These strategies promote a shift of social norms among individuals, increasing the alignment of actions with their sustainability intentions.
Conclusion
Ultimately, the research offers insights and individual decision-making regarding motor fuel options. It outlines how individuals align their purchasing actions of motor vehicles with sustainability intentions regarding motor vehicle fuel. The findings show individuals’ positive intention towards sustainability as evidenced by their perception of environmental impact severity. However, individuals prefer petrol and diesel fuel options for convenience. This situation underlines existing barriers such as technical and practical constraints, economic considerations, awareness and social norms that hinder aligning actions and sustainability intentions when selecting motor vehicle fuel. Additionally, this research highlights cost, environmental impact and convenience as primary factors determining people’s attitudes towards particular motor fuel options. In Gotland’s case, individuals rely heavily on conventional fossil fuels despite having an interest in sustainable options. Results indicated their interest in adopting electric vehicles and hybrid-electric vehicles in their subsequent purchase of motor vehicles. This situation highlights the role of stakeholders in addressing barriers to adopting sustainable intentions among the residents.
Reference List
Golbabaei, F., Yigitcanlar, T., Paz, A. and Bunker, J., 2020. Individual predictors of autonomous vehicle public acceptance and intention to use: A systematic review of the literature. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 6(4), p.106. retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2199853122010812
Kumar, A., Sah, B., Singh, A.R., Deng, Y., He, X., Kumar, P. and Bansal, R.C., 2017. A review of multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) towards sustainable renewable energy development. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 69, pp.596-609. Retrieved from https://tarjomefa.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/8289-English-TarjomeFa.pdf
Swaroop, K.R., Someswararao, K.M., Naidu, N.G. and Nagaraj, K.V., 2022. A Study On Factors Influencing On Purchase Of E-Vehicles With Reference To South India. Journal of Positive School Psychology, 6(11), pp.200-208. Retrieved from https://ijcrt.org/papers/IJCRT2304681.pdf
Yan, C.W. and Mohamed, M.I.P., 2022. The Factor That Influences Consumers’ Buying Intention of Electric Vehicle (E.V.) In Malaysia. Research in Management of Technology and Business, 3(2), pp.312-327. Retrieved from https://publisher.uthm.edu.my/periodicals/index.php/rmtb/article/view/9637
 write
write