Executive Summary
Who General Motors is
General Motors (GM) is an American universal automotive firm headquartered in Detroit, Michigan that manufactures and sells trucks, automobile parts, crossovers, and cars. William Durant established it in 1908. GM operates universally in Europe, America, the Middle East, and Africa. It operates under the following four segments:
- GM International (GMI)
- Cruise
- GM Financial
- GM North America
Company Vision
GM aims to create a future with no emissions, crashes, or congestion to promote a promising future for the society it is privileged to serve.
Company offerings
GM’s leading vehicle brands are Cadillac, Chevrolet, Buick and GMC. Besides manufacturing and selling automobiles, trucks, and automobile parts, GM offers its clients financial services under GM Financial. The firm provides its clients with about one hundred and twenty facilities, including Assembly, Die and Stamping, Battery, Engineering, and Office and sales services.
Company model and financial performance
GM’s business model focuses on vehicle electrification and increasing the firm’s service-linked recurring services, like the OnStar model, that enhance clients’ personal experiences and customer satisfaction. GM witnessed outstanding financial performance from 2019 to 2023, with 2023 seeing the most impeccable performance due to increased revenues and vehicle sales. It faces main competition from Ford, Paccar, and Toyota. It received an “overweight rating” as of 1 November 2023, making GM’s stock a good investment as it will perform greatly in the future.
Background
General Motors (GM) is among the universe’s biggest auto manufacturers. It manufactures and sells crossovers, trucks, automobile parts, and cars. It also offers “software-enabled services and subscriptions worldwide under well-known brands such as Buick, Cadillac, Chevrolet, and GMC” (D&B Hoovers, 2023). The firm’s GM International and GM North America sections deal with automotive operations. On the other hand, its section of General Motors Financial Co. offers funding services. The headquarters of GM are in Detroit, Michigan. GM has over ninety thousand and eight hundred workers in America and offers about one hundred and twenty facilities. The facilities include Battery, Engineering, Die and Stamping, Marketing, Assembly, GM Financial Cruise Offices, and Office and Sales services. GM’s vision entails working towards “ a future with zero crashes, zero emissions, and zero congestion” to develop the future of all societies it serves (2023). GM aspires to be the universe’s top inclusive firm and to act fairly and transparently towards every person it interacts with. It is an inclusive firm with an environment where every person’s voice is heard. Additionally, it puts customers at the centre of every decision-making process. Under GM’s executive leadership, the Chief Executive Officer, Mary Barra, is at the top (D&B Hoovers, 2023). The President, Mark Reuss, is next in line, followed by the Executive Vice President, Paul Jacobson. Jacobson is also the Chief Financial Officer. After that is the other Executive Vice President, Craig Glidden, also the General Counsel. The last person is the Vice President, Christopher Hatto.
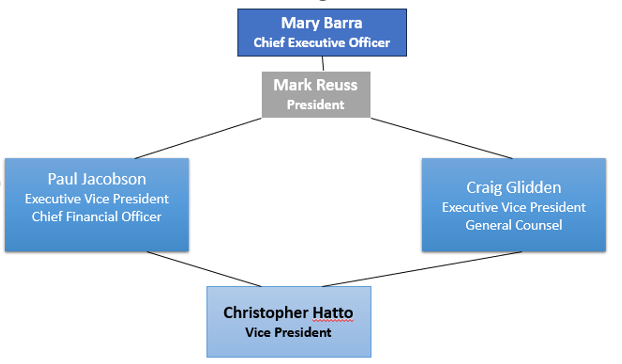
Figure 1.
Executive Leadership of General Motors.

Figure 2.
GM’s logo
(2023)
Body
Company history
The history of GM started in Flint, Michigan, with Josiah Dallas Dort and William Crapo “Billy” Durant in 1886. The two established the Flint Road Cart Company and started making horse-drawn carts to develop a carriage manufacturing firm. Durant then took over as the general manager of Buick Motor Co. in 1904, which had come to Flint in 1903 (2023). He advanced it to become the country’s greatest volume automobile maker in less than five years. His prosperity with Buick made him create GM on 16 September 1908. During the earlier years of the automotive industry, millions of car manufacturers each made few car models. In 1904, William Durant purchased a deteriorating Buick Motors firm. He later felt that car makers could get significant advantages and elevate the auto industry if they united, making him form the General Motors Company in Flint, Michigan, in 1908. GM bought AC Spark Plug, Rapid Motor Vehicle Company, and Cadillac in 1909 (D&B Hoovers, 2023). The firm then created and advanced the General Motors Export Company, Chevrolet Motor Company of Michigan, General Motors of Canada, and the General Motors Truck Company, which would then become GMC.
Firm products and services
The largest single market of GM is America, which accounts for approximately eighty percent of overall sales (D&B Hoovers, 2023). The firm works through four sectors, namely GM International (GMI), Cruise, GM North America (GMNA), and GM Financial. It operates globally throughout America, Europe, Africa, and the Middle East. Cruise ensures the advancement and trade of independent vehicle technology. GMNA gives approximately eighty percent of sales and makes vehicles that Cadillac, GMC, Buick, and Chevrolet brands market. GM Financial contributes roughly ten percent of the firm sales. It offers automotive funding, retail loans, and lease credit products and services. It also gives trading products to dealers like new and already-used funding. GMI also generates ten percent of the firm’s overall sales. It sells those similar brands to clients living out of North America. Besides, it sells the “Holden lineup of vehicles” (D&B Hoovers, 2023). Additionally, GM possesses ownership shares in firms in China where cars are manufactured and traded under the brands of Wuling, Cadillac, Buick, and Chevrolet.
GM has over one hundred locations in America doing assembly, distribution, manufacturing, testing, engineering, and warehousing (D&B Hoovers, 2023). It possesses locations with those same operations in approximately thirty other nations. GM’s main facilities outside the USA are in South Korea, Brazil, Mexico, China, Canada, and Colombia. GM Financial works at more than thirty-five locations worldwide. About twenty are in America. Its main facilities outside the USA are in Mexico, Brazil, Canada, and China. Its trucks and cars are marketed and traded via a system of twelve thousand autonomous distributors, permitted sales, dealers, and “part outlets” worldwide. “Vehicles are sold directly to fleet customers, including rental car companies, commercial fleet customers, leasing companies, and governments” (D&B Hoovers, 2023). Its advertising and promotion expenditures totaled four billion dollars in 2022, three billion in 2021, and two billion in 2020. The company’s growth-centered strategy is to ensure the investment in different things. These include autonomous vehicles (AVs), software-linked services and subscriptions, electric vehicles (EVs), and innovative enterprise prospects. The strategy also encompasses solidifying the firm’s market positioning within lucrative Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) cars like trucks.
Firm performance
GM’s revenue rose by twenty-nine billion dollars to one hundred and fifty-six billion dollars for 2022, in comparison to the revenue of one hundred and twenty-seven billion dollars for 2021 (D&B Hoovers, 2023). Nevertheless, its net income was reduced to nine billion dollars for the financial year end of 2022, in comparison to 2021’s net income of ten billion dollars. GM’s cash when 2022 was ending was twenty-one billion dollars. Its investing undertakings utilized seventeen billion dollars, and funding activities gave three hundred and eighty-three million dollars. Operating activities gave sixteen billion dollars. Primary cash utilization was for buying finance receivables and procuring “available-for-sale marketable securities” (D&B Hoovers, 2023). GM witnessed a “21% year-over-year” rise in American vehicle sales during the start of 2023 (New York Stock Exchange, 2023). The increase was promoted by solid client demand for the firm’s SUVs and trucks, encouraging sales for every brand. The overall sales of GM for 2023 are up by nineteen percent. The company now focuses on promoting an “all-electric future.” It aims to do that under its Ultium battery program, which aims to offer power to wide-ranging vehicles.
GM faced major market competition from Ford Motor Company, Paccar Inc. and Toyota Motor Corporation whose overall yearly sales as of 2022 totalled about one hundred and fifty-eight million dollars, twenty-eight million dollars and thirty-one billion dollars respectively. GM’s yearly sales were around one hundred and fifty six million dollars . Also, the gross profit margin of Ford, Paccar and Toyota was fourteen percent, eighteen percent and nineteen percent respectively. That was for the year ending 2022 (D&B Hoovers, 2023). GM’s profit margin was thirteen percent. Besides, the twelve-month revenues of GM, Ford, Paccar and Toyota amounted to twenty-three percent, fifteen percent, twenty-two percent and fifteen percent respectively.
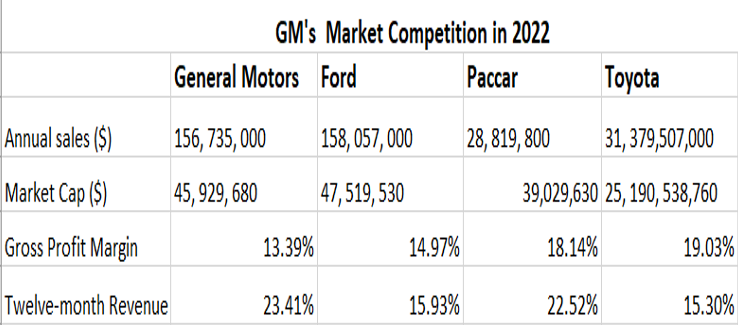
Figure 3
GM’s market competition
GM prides itself on being a universal firm that focuses on developing an all-inclusive, all-electric future that offers accessibility to everyone. The Ultium battery program will provide power to high-performing, medium- and low-performing, and mass-market vehicles. Financial analysts from Barclays PLC announced that GM possesses an “overweight rating” (Zolmax, 2023) on 1 November 2023. That means they acknowledge the firm will perform impressively in the coming twelve months and outperform other automotive stocks within its market. They assert that it has a thirty-seven dollar price mark on its stock. GM’s performance has incredibly increased throughout the last five years. It reduced within the first half of the time frame and increased year after year, with 2022 being the greatest-performing year (D&B Hoovers, 2023). Thus, its good record earnings and overweight rating as of 2023 make its stock a good investment. Investors should buy GM’s stock and add it to their portfolios. That will increasingly promote that overweight stock’s weight within their portfolios to gain excessive financial returns when GM finally outperforms other market stocks.
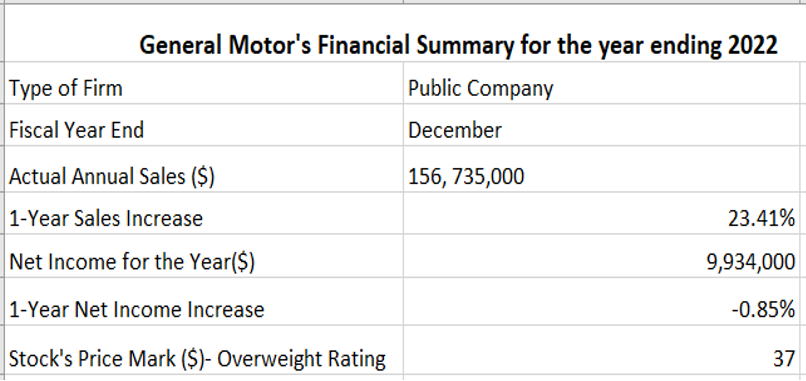
Figure 4.
GM’s financial summary
Progression of business model
GM’s business model has progressed impressively throughout the past few years (Barabba, 2019). The firm suffered a great sales decrease and degradation in its market share due to a growth in the number of rivals in 1992. That promoted the firm’s survival in the market to a great extent. That made it need strategic, operational changes like reducing warranty costs to promote the firm’s competitive edge, decreasing material costs, and increasing “product quality standards” (Barabba, 2019). For instance, GM implemented the MS2000 car advancement scheme to focus on the real needs of consumers desiring middle-sized vehicles in 1998. Thus, GM realized that a minor array of greatly designed models at affordable prices would be the optimal method of making many clients buy their vehicles. The MS2000 scheme focused on making “ seven cars more cost efficiently within just four well-defined categories” (Barabba, 2019). The classifications included family leisure, household affordability, chic sports, and basic transport. That development for the firm greatly boosted its sales and profits. That happened since GM sold vehicle models more preferred by consumers than the extra-generalized ones sold by market rivals.
Furthermore, its CEO organized a market study to determine a business model to encourage impressive innovations. To effectively sate clients’ desires for “personal experiences,” they created the “OnStar” model in 1996 (Barabba, 2019). It was an automatic gadget connected to dealerships, enabling it to call emergency facilities when airbags get triggered. Also, under it, a customer possessed a live interaction point with a counselor by telephone via the OnStar service. The firm’s senior managers implemented another thought process by availing the service and extra extended services to promote GM’s return on capital utilized in manufacturing every car. Additionally, GM decided to redesign its truck under an investment of one billion dollars into that remodeling program in 2002 (Barabba, 2019). The firm wanted to preserve its great power over fifty percent of its market. In the span of eleven years, the firm changed its losses to become profits of three billion dollars in 2003, thanks to the mentioned 2002 and 1992 programs.
Furthermore, the firm’s CEO led the firm in making and implementing self-driving vehicles, joint mobility services, linked services, and electric vehicles. Thus, GM established the “driverless car project site in San Francisco and the car-sharing service ‘Maven’ in 2013 (Barabba, 2019). The company introduced Maven in 2013. It operated in fifteen cities and supplied cars to Lyft and Uber drivers under weekly rental agreements by 2019. Thus, GM reduced the number of its manufactured models and introduced service-linked recurrent revenue sources like the OnStar within in-car communication services from 1992 to the twenty-first century. That enabled it to survive against intense and ever-rising rivalry in its market.
Conclusion
In conclusion, General Motors (GM) is a global American automotive manufacturing firm headquartered in Detroit, Michigan. Its main products include trucks, cars, crossovers, and automobile parts. GM also offers automotive funding services under General Motors Financial Company. The firm majorly sells its vehicles under the Buick, GMC, Chevrolet, and Cadillac brands. It sells its vehicles through an extensive system of independent distributors, permitted sales, part outlets, and dealers universally. GM is a customer-centric firm and aspires to create a future of no emissions, congestion, or crashes to enhance the welfare of the society it serves. The firm’s business model has developed over the years from increasing models of vehicles manufactured to increasing service-based recurring services and vehicle electrification. That has promoted its competitive advantages against rivals in the market. Such service-based services include the OnStar model that promotes clients’ personal experiences and effectively satisfies their needs. The major market rivals of GM are Toyota Motor Corporation, Paccar Inc. and Ford Motor Company. The financial performance of GM has been impressive over recent years, with 2022 seeing the most impressive performance, with increasing revenues and vehicle sales. Thus, investing in GM’s stock is a good investment as the firm has an overweight rating, enabling investors who buy it to gain excessive earnings in the coming year.
References
Barabba, V. (2019). Assessing General Motors’ innovation strategy over three decades using the “Three Box Solution.” Strategy & leadership, 47(2), 34-42.
D&B Hoovers. (2023, 2 June). General Motors Company Profile. Proquest.com. https://www.dnb.com/business-directory/company-
(2023). General Motors: Pushing the Limits of Transportation & Technology. https://www.gm.com/
New York Stock Exchange. (2023). Contify Automotive News; New Delhi. https://caldwell.idm.oclc.org/login?url=https://www.proquest.com/magazines/general-motors-u-s-q3-sales-trucks-new-suvs-drive/docview/2872170343/se-2?accountid=26523
Zolmax. (2023). American Consumer News: General Motors (GM) Investment Rating. Newstex Global Business Blogs.
 write
write