Introduction-Methodology
The retail industry is highly competitive and dynamic, distinguished by continuously changing customer tastes, technological improvements, and intense rivalry among market competitors. Companies must assess their strategic position, identify opportunities and risks, and design plans to establish a sustainable competitive edge in this ever-changing market. This report evaluates Dollar General’s strategic position as a significant American network of variety stores in the retail industry.
Dollar General, a popular U.S. discount retailer, sells groceries, seasonal goods, home goods, and clothes. It is a major US Retail – Big Box/Home Goods operator with over 17,000 shops in 46 states. Dollar General’s target market consists of price-conscious customers, and the firm generally operates in rural and suburban locations, where it can provide a handy alternative to bigger retail chains such as Walmart and Target. Dollar General has thrived in the retail industry despite the intense competition.
This report’s methodology section details the analytical framework and research methods used to assess Dollar General’s retail industry strategy. This report ensures that the analysis is well-structured, consistent, and correct. Strategic management frameworks, financial ratio analysis, and qualitative approaches are used in this report. This multidimensional method helps understand Dollar General’s performance, competitive environment, and strategic possibilities. First, the literature was evaluated to learn about the retail industry, its competitive dynamics, and the main factors affecting retail companies’ performance and success. This analysis incorporated news reports, industry reports, academic articles, and business filings.
The data gathered from these sources was a solid basis for the subsequent investigation. Dollar General’s external analysis focuses on both the macro and micro environments. The PESTEL framework is used in the macro analysis to study the political, economic, social, technical, environmental, and legal variables impacting the retail industry. This strategy thoroughly explains the numerous external dynamics driving the industry and their possible consequences for Dollar General. The micro-analysis employs Porter’s Five factors framework. This framework gives insights into the retail industry’s attractiveness and Dollar General’s competitive position.
An internal analysis of Dollar General is conducted using several strategic management tools and frameworks. The resource-based view (RBV) and VRIO framework assess the company’s resources and capabilities, revealing competitive advantages. A review of the company’s strategic activity systems, tangible and intangible effects, business model canvas, and financial performance utilizing different financial measures are also included in the report. A comparative study assesses Dollar General’s competitive advantage compared to its primary competitors, including Walmart, Amazon, TJX, and Target. This study includes a business model comparison, a SWOT analysis of Dollar General, and an assessment of the company’s performance in contrast to its competitors using several performance measures. Based on the external, internal, and comparative evaluations, suggestions will be made to assist Dollar General in achieving a long-term competitive advantage in the retail industry. These suggestions are based on best practices in strategic management, industry trends, and research findings.
Executive Summary (VMO)
Dollar General Stores is a publicly listed company governed and administered by a Board of Directors. Dollar General’s vision to become America’s favorite small-format value and convenience retailer reflects its commitment to providing its consumers with the best shopping experience possible. Dollar General stresses store accessibility to fulfill this vision, ensuring its sites are handy for clients and serve various communities. Furthermore, the company is constantly refining its product selection to meet its target audience’s specific needs and preferences, considering regional and demographic factors. This strategy enables Dollar General to provide a customized shopping experience that connects with its clients, cementing its position as a favored retail location.
Dollar General’s mission is to offer its consumers a pleasurable and easy shopping experience. The company can establish strong client loyalty and promote repeat business by concentrating on providing unrivaled value and ease. Dollar General’s dedication to operational excellence is a crucial component of its mission, which includes refining its supply chain, inventory management, and retail operations to guarantee that its stores are well-stocked, organized, and efficient. In addition, the company’s focus on constant development demonstrates its ambition to remain ahead of the competition and adapt to the ever-changing retail scene.
Dollar General’s core objective of achieving sustainable and profitable growth is backed by several strategic initiatives that use the company’s competitive advantages. The company, for example, is concentrating on extending its network of stores, especially in underdeveloped locations where it can create a significant presence and grab market share. Dollar General also adds new product categories, private label products, and seasonal goods to satisfy its consumers. The company is investing in mobile applications, e-commerce platforms, and data-driven marketing because it realizes the value of digital skills in the current retail environment.
The company wants to become the top dollar store in America and increase its consumer brands and items to the point where there are no reports of stockouts. It also aims to advance its workers’ careers by being the premier employer in the retail industry, delivering seamless services to its customers, and giving inexpensive items to everybody. Thus, the company’s objectives are to improve service quality and profitability.
Dollar General’s values serve as guiding concepts that create its company culture and impact decision-making (Dollar General, n.d.). These principles highlight the significance of helping others, keeping things simple, respecting individuals, striving for excellence, and encouraging collaboration. By following these principles, Dollar General can create a welcoming, inclusive workplace that inspires employees to work hard and achieve their personal and professional goals. These principles also help the company build strong customer and community connections, which boosts its reputation and long-term success.
External Analysis – Macro
PESTEL Analysis
The PESTEL framework evaluates the external macro-environmental factors that affect businesses in the retail industry, including Dollar General. This analysis covers Political, Economic, Sociocultural, Technological, Environmental, and Legal factors.
Political
Government regulations, trade policies, and political stability affect the retail industry. In the U.S., labor, taxes, and consumer protection regulations impact the operations of retail companies like Dollar General (U.S. Department of Labor, 2021). Trade rules may also influence import prices and availability, affecting the company’s supply chain and product pricing. The US-China trade war has raised tariffs and disrupted retail supply networks (Congressional Research Service, 2022).
Economic
Economic factors, such as GDP growth, inflation, and consumer spending, significantly impact the retail industry. Consumer spending and retail sales have improved as the U.S. economy recovers from the COVID-19 pandemic (Bureau of Economic Analysis, 2021). However, rising inflation and potential interest rate hikes may impact consumer purchasing power and spending habits (Egilsson, 2020). Dollar General must adapt its strategies to address these economic challenges and capitalize on opportunities presented by the recovering economy.
Sociocultural
Changing consumer preferences, demographics, and social trends shape the retail landscape. The growing choice for online shopping has accelerated due to the pandemic, leading to increased e-commerce sales and forcing traditional retailers like Dollar General to invest in digital channels (U.S. Census Bureau, 2021). The retail industry also demands eco-friendly goods and processes due to the increased emphasis on sustainability and corporate social responsibility (Nielsen, 2021). Dollar General must adapt to these changing consumer preferences and social trends to stay competitive.
Technological
Technology improves supply chain management, customer experience, and data-driven decision-making in the retail industry. Dollar General must use emerging technologies like A.I., AR, and IoT to be competitive and satisfy consumer expectations. A.I. can optimize inventory levels and save expenses, while augmented reality can improve in-store shopping.
Environmental
Climate change and resource shortages provide retail problems and possibilities. Retailers must comply with higher environmental standards, decrease their carbon footprint, and practice sustainability (Vadakkepatt et al., 2021). Moreover, incorporating eco-friendly initiatives can create a positive brand image and attract environmentally-conscious customers. Dollar General should consider these environmental factors when making strategic decisions and developing its sustainability initiatives.
Legal
Legal factors, such as labor laws, consumer protection regulations, and data privacy laws, affect the retail industry’s operations. Retailers like Dollar General must comply with various laws and regulations, which can impact their costs and operational strategies. These rules must be followed to avoid legal and reputational consequences (Retail Law Conference, 2021). For example, compliance with the GDPR is crucial for retailers operating in the European market, as it sets stringent data privacy and protection requirements (Hoofnagle et al., 2019).
Major Trends Affecting the Retail Industry
E-commerce’s explosive growth is one of the retail industry’s biggest trends. Traditional retailers like Dollar General must invest in their online presence and enhance their digital capabilities to remain competitive in the evolving retail landscape.
As consumer preferences and behaviors evolve, retailers must adapt their strategies to provide a seamless shopping experience across various online and offline channels. Omnichannel retail integrates physical storefronts, internet platforms, and mobile apps to provide a seamless purchasing experience (Deloitte, 2021). Omnichannel retailers can match consumer expectations, boost customer loyalty, and increase revenue.
Personalization and customer experience are two more significant trends impacting the retail business. Consumers now want customized experiences suited to their tastes, requirements, and values. Retailers increasingly rely on data analytics and artificial intelligence to better understand their consumers and provide targeted product suggestions, personalized promotions, and customized content. By implementing these technologies and methods, retailers may improve consumer engagement and promote long-term loyalty.
Sustainability has also become a major issue for both customers and merchants. Consumers increasingly seek environmentally friendly goods and activities, encouraging retailers to embrace more sustainable business strategies (Nielsen, 2021). From sourcing to waste management, retailers must evaluate the environmental effect of their operations and develop methods to decrease their carbon footprint and encourage sustainable consumption.
Geopolitics
Geopolitical considerations significantly affect the retail business because they affect global commerce, supply chain operations, and customer behavior. The US-China trade war has recently been one of the most urgent geopolitical worries, resulting in higher tariffs and disrupted supply chains for numerous merchants (Congressional Research Service, 2022). This disagreement has increased the cost of importing products from China, forcing firms to rethink their sourcing strategy and diversify their supply networks.
Regional conflicts and political instability can also impact the retail industry by disrupting global trade and creating uncertainty. For example, the ongoing conflict in Ukraine has led to economic sanctions and strained relations between Russia and Western countries, which can affect the operations of retailers with a presence in these regions. Retailers must closely monitor geopolitical developments, adjust their strategies to mitigate risks and maintain stable operations. In addition, global policies and regulations also impact the retail industry.
Global/National Inflation
Global and national inflation wield significant effects on the retail sector, as they impact consumer buying power, operational expenses, and pricing tactics. Inflation denotes how an economy’s overall price level for goods and services escalates over time, eroding money’s purchasing power and increasing costs for consumers and businesses (Federal Reserve, 2021).
The COVID-19 pandemic has profoundly affected global inflation, disrupting supply chains, generating labor shortages, and prompting extraordinary fiscal and monetary stimuli from governments and central banks globally. Consequently, international and U.S. inflation rates have increased. Recent U.S. Consumer Price Index (CPI) increases have reached decade-high levels (Bureau of Labor Statistics, 2021). Demand for goods and services has increased after the epidemic, causing supply chain disruptions, labor market imbalances, and inflation.
Elevated inflation may present several challenges to the retail sector. Firstly, surging raw materials, labor, and other input costs can result in higher operational expenses for retailers. These cost increases may force merchants to raise their prices, potentially harming consumer demand and sales significantly if customers’ disposable incomes do not grow at a rate commensurate with inflation (Barnes et al., 2021). Secondly, mounting inflation can make it difficult for businesses to predict price changes and adjust their pricing strategies. This uncertainty may lead to more variable profit margins and risk for retailers, especially those with low margins like Dollar General.
Retailers may counteract inflation in many ways. One strategy to minimize operating expenditures while maintaining profitability is investing in cost-cutting techniques like automation and supply chain optimization (Deloitte, 2021). Another method for retaining customers and driving sales in a high-inflation climate is to provide value to consumers via cheap pricing, promotions, and loyalty programs. Retailers should also diversify their supply networks and sourcing techniques to mitigate the risk of cost increases caused by interruptions in the supply chain or currency changes (Magableh, 2021). Finally, businesses may anticipate changes in demand by monitoring economic data and customer attitudes and adjusting their pricing tactics appropriately.
External Analysis – Micro
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Threat of New Entrants
Owing to considerable capital demands, well-known brand recognition, and economies of scale held by current players like Walmart, Amazon, TJX, and Target, the risk of newcomers in the retail sector, specifically in the large-scale and home goods segment, could be higher. Although e-commerce has diminished entry barriers for specific retailers, the prevalence of market leaders and the necessity for extensive logistics and distribution networks hinder new entrants from effectively competing.
Suppliers’ Bargaining Power
Supplier negotiating power in the retail industry is modest. Large shops with significant buying power, such as Dollar General, Walmart, and Target, may negotiate advantageous terms with suppliers. However, as retailers seek to maintain their reputations and meet consumer demands for responsible products, the growing emphasis on sustainable and ethical sourcing practices has given suppliers more bargaining power (Nielsen, 2021). In addition, supply chain interruptions induced by geopolitical tensions and the COVID-19 pandemic have raised the value of supplier relationships, possibly enhancing suppliers’ negotiating power.
Buyers’ Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of buyers in the retail industry is high. Consumers may compare prices and products at many online and offline retailers. The growth of e-commerce and the increasing popularity of price comparison websites and apps have intensified price competition among retailers, further empowering consumers (Statista, 2021). Retailers must offer competitive prices, superior customer service, and a seamless shopping experience across channels to retain customers and build loyalty.
Threat of Substitute Products
Retailers face moderate substitution threats. While consumers can choose from various product categories and retailers, there are few direct substitutes for the big-box and home goods retail experience provided by companies like Dollar General, Walmart, and Target. However, some consumers may opt for alternative retail formats, such as specialty stores or online marketplaces, to meet their shopping needs. Retailers must continuously innovate and adapt their product offerings to stay ahead of consumer preferences and emerging trends (Deloitte, 2021).
Competitive Rivalry within the Industry
Competitive rivalry within the retail industry, particularly among big-box and home goods retailers, is intense. Market leaders like Walmart, Amazon, TJX, and Target compete aggressively on price, product selection, and customer experience, forcing other retailers, including Dollar General, to continually improve their offerings to maintain market share (BenMark et al., 2017). The growth of e-commerce has further intensified competition as retailers expand their online presence and invest in digital capabilities to attract and retain customers.
Strategic Group Maps
Strategic Group Maps visually represent an industry’s competitive landscape, allowing businesses to identify their position relative to competitors. The group companies within an industry are based on vital strategic dimensions, such as market segment, geographic focus, or value proposition (Porter, 1980).
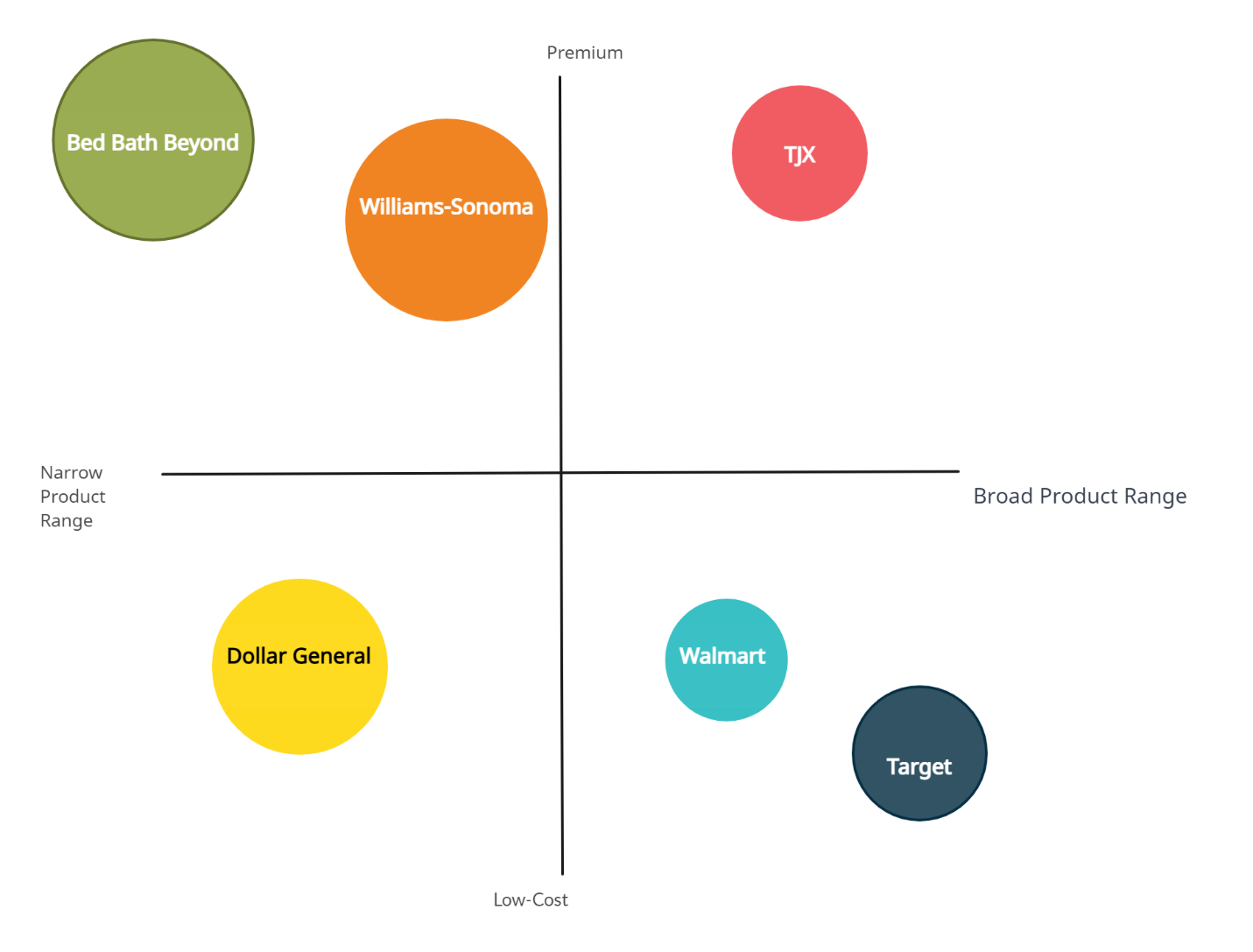
Price positioning (low-cost vs. premium) and product variety (narrow vs. broad) may create a strategic group map in the U.S. retail industry, notably big-box and home goods. The following is the Strategic group map of the sector that Dollar General competes:
Low-cost / Broad Product Range
Walmart and Target provide an extensive range of low-cost items. Their varied client base seeks to value and one-stop shopping.
Low-cost / Narrow Product Range
Dollar General offers a restricted product range at affordable pricing. They target price-sensitive consumers and are known for their small-format stores in rural and suburban areas.
Premium / Broad Product Range
TJX, which operates retail chains like T.J. Maxx, falls into this category. They offer various products, including apparel, home goods, and accessories, at discounted prices compared to department stores. Still, they provide higher quality and more premium brands than their low-cost competitors.
Premium / Narrow Product Range
Companies like Bed Bath & Beyond or Williams-Sonoma fit in this category, offering a more focused range of products at premium prices, such as home goods and kitchenware. They cater to consumers seeking higher-quality and specialized products.
The strategic group map for the big-box and home goods retail industry highlights the competitive dynamics and varying value propositions the leading players offer. Dollar General’s position in the low-cost/narrow product range quadrant indicates that its main competitive advantage lies in providing affordable products in a more focused assortment, catering to price-sensitive consumers. To maintain or improve its competitive position, Dollar General should consider strategies that enhance its value proposition, such as expanding its product range, optimizing store locations, or investing in digital capabilities to improve the customer experience.
Internal Analysis
RBV_VRIO Analysis
The Resource-Based View (RBV) and VRIO frameworks aid in analyzing a company’s internal resources and skills to identify its potential for building sustainable competitive advantage. Essential resources and competencies for Dollar General include its retail network, efficient supply chain, and private-label products (Euromonitor International, 2021). Their excellent supply chain management lets them keep operating expenses down and give clients competitive pricing. Dollar General has also created private-label solid brands like Clover Valley that increase profit margins and generate consumer loyalty (Rueter, 2020).
We may evaluate these resources using the VRIO framework as follows: Dollar General’s store network, efficient supply chain, and private-label brands are vital assets that allow the company to compete successfully in the retail business. These resources are limited since only some rivals match Dollar General’s size and efficiency. The company’s resources are also challenging to replicate, owing to the time and money required to establish a comparably broad shop network and supply chain. Dollar General’s organization is built to capitalize on these resources, as indicated by continued store growth, supply chain enhancements, and private-label development (Forbes, 2021).
Tangible vs. Intangible Impact Analysis
Tangible assets are tangible resources that can be measured and contribute directly to a company’s financial success. The physical assets of Dollar General include its vast retail network, inventory, and distribution hubs. These assets help the organization access an enormous client base, deliver consistent products, and manage its supply chain effectively.
Intangible assets are non-physical resources that boost a business’s competitive edge and long-term success. Intangible assets of Dollar General include its brand reputation, private-label brands, and organizational culture. Customer loyalty and repeat business are driven by the company’s excellent brand image, predicated on its dedication to affordability and convenience (Euromonitor International, 2021). Furthermore, the organizational culture of Dollar General emphasizes teamwork, innovation, and customer-centricity, fostering a positive work environment and driving continuous improvement.
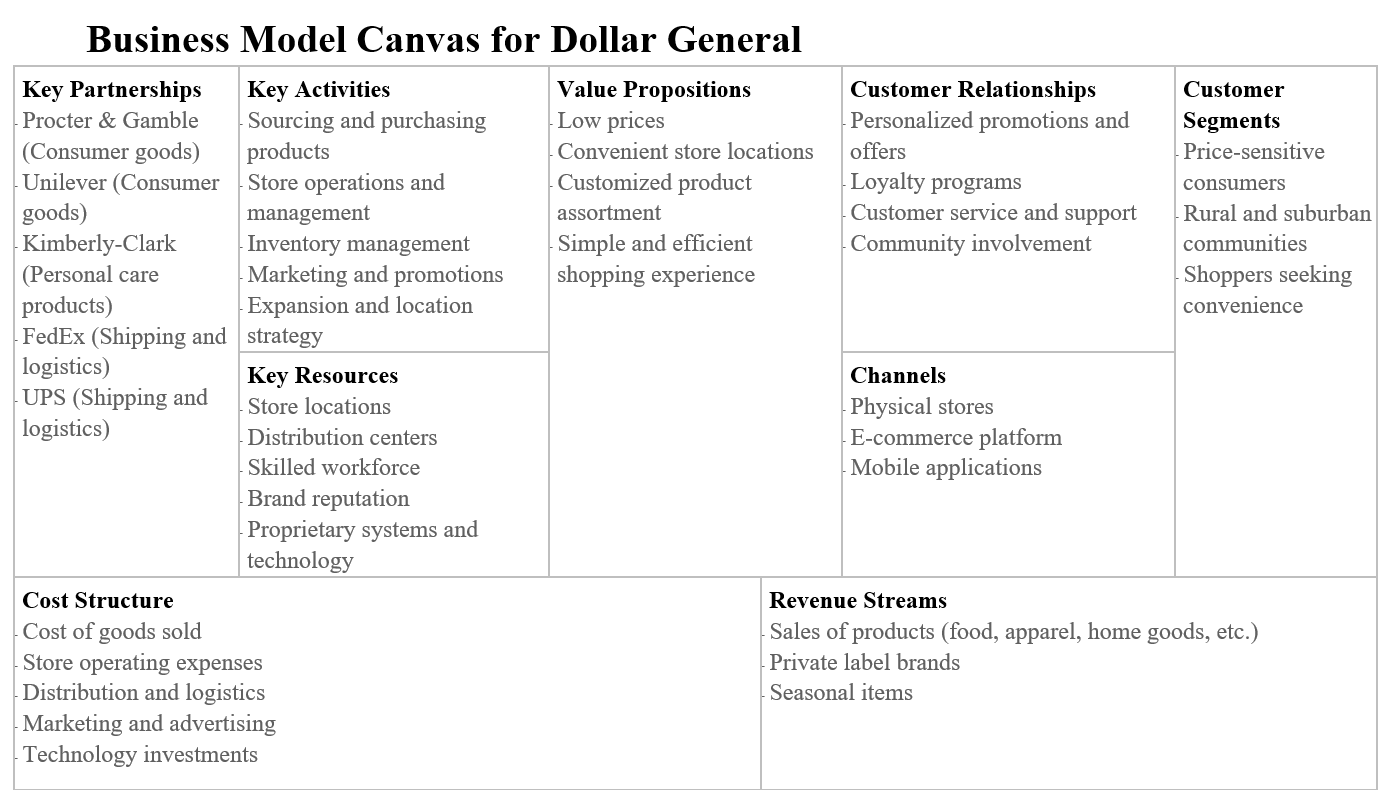
Business Model Canvas
Dollar General’s Business Model Canvas may be summarized as follows:
Financial Ratio Evaluation
Financial ratio analysis gives valuable insights into a company’s financial performance and position, allowing for competitor comparisons. Dollar General’s retail industry position may be understood by examining its financial ratios.
Profitability Ratios
Gross, operating, and net profit margins indicate a company’s profitability. Dollar General has consistently high profitability ratios. The firm recorded a gross profit margin of 31.2% in Q3 2021 (Macrotrends, 2023). Dollar General’s operating profit margin was 9.1%, and its net profit was 6.5% (Macrotrends, 2023). These margins imply that the firm has managed its expenses and generated profits, providing a competitive advantage in the retail industry.
Liquidity Ratios
As of Q3 2021, Dollar General’s current balance was 1.59, meaning its current assets exceed its current liabilities (Macrotrends, 2023). The company’s 0.21 quick ratio raised concerns about its capacity to satisfy short-term obligations without inventories. This is common for a retailer with a significant inventory, and Dollar General’s overall liquidity situation remains solid.
Solvency Ratios
Dollar General’s debt-to-equity ratio was 1.48 in Q3 2021, indicating a modest financial risk (Macrotrends, 2023). The company’s interest coverage ratio was 8.9, suggesting that it earns enough to pay its interest expenditures, bolstering its financial stability.
Efficiency Ratios
Efficiency ratios like inventory and asset turnover measure how successfully a company utilizes its assets. These ratios reveal a company’s operational performance. Dollar General reported an inventory turnover ratio of 5.1 in Q3 2021, indicating that it can sell and replace inventory 5.1 times yearly. This demonstrates that the corporation has managed its inventories well (Macrotrends, 2023). Furthermore, the company’s asset turnover ratio was 2.0, indicating that its assets were successfully used to create revenue. A high asset turnover ratio is desired since it demonstrates effective asset management.
Comparative Analysis and Competitive Advantage
Business Model Identification
Dollar General’s business model centers on providing customers with a convenient and affordable shopping experience. The company primarily operates small-box store formats in rural and suburban areas, offering a carefully curated assortment of everyday items at low prices. This strategy allows Dollar General to cater to underserved communities, often being the only retail option available. The company’s business model is built on several key elements:
The first element is store location. Dollar General strategically locating stores in underserved rural and suburban areas provides customers convenient access to essential products. This approach sets the company apart from larger competitors focusing on urban and suburban markets with larger store formats.
The second element is the limited assortment of products. Dollar General focuses on offering a select range of the most popular and essential items, which allows the company to maintain low inventory costs and pass on savings to its customers through competitive pricing.
The third element is a balance between private label and national brand products. Dollar General’s merchandise mix includes private-label offerings and products from well-known national brands, allowing the company to cater to varying customer preferences while maintaining attractive price points.
The fourth element is low operating costs. Dollar General’s small store formats, efficient supply chain management, and focus on cost control enable it to maintain low operating costs, further contributing to its competitive pricing strategy. This cost-efficient approach allows the company to compete with larger retailers while maintaining its unique value proposition for customers in rural and suburban markets.
SWOT Analysis
Dollar General, a top discount retailer in the U.S., possesses strengths contributing to its success and weaknesses, opportunities, and threats that influence its strategic outlook.
Strengths
Dollar General’s solid brand recognition distinguishes it as a trusted retailer with quality products at competitive prices. Its extensive store network allows the company to serve a broad range of customers in various areas. Efficient supply chain and inventory management practices help maintain low costs and offer competitive prices, attracting price-conscious customers. Consistent financial performance, marked by steady revenue growth and robust profitability margins, showcases its resilience and adaptability in a competitive market.
Weaknesses
A limitation of Dollar General is its restricted product assortment, which might deter customers from seeking a more comprehensive shopping experience. Relying on rural and suburban markets exposes the company to demographic and economic shifts in those areas. Dollar General’s relatively small e-commerce presence compared to Amazon and Walmart may limit development in the growing online retail sector.
Opportunities
Dollar General may develop by expanding into urban areas, improving its e-commerce platform to compete with online retailers, and expanding its private-label product assortment. This provides customers with low-cost, high-quality options and enhances its competitive edge.
Threats
Dollar General faces intense competition in the retail industry from other big players like Walmart, Amazon, TJX, and Target. Moreover, consumer spending might drop during economic downturns, affecting sales and profitability. Global supply chain disruptions like the COVID-19 pandemic may increase expenses and inventory shortages, affecting Dollar General’s operations and finances.
The following diagram shows the summary of the SWOT analysis for Dollar General:
| Strengths | Weaknesses | Opportunities | Threats |
| · Strong brand recognition
· Expansive store network · Efficient supply chain · Strong financial performance |
· Limited product assortment
· Reliance on rural and suburban markets · Limited e-commerce presence |
· Expansion into urban markets
· Strengthening e-commerce capabilities · Expanding private-label offerings |
· Intense competition
· Economic downturns · Supply chain disruptions |
Comparison with Competitors
Dollar General competes with Walmart, Amazon, Target, and TJX in various ways. These companies primarily compete on price, product variety, customer experience, and geographic reach. Customers often want the most value for their money in the retail industry; thus, price is an important consideration. Dollar General is noted for its low-cost stance, selling necessities cheaply. Walmart and Target provide competitive pricing on various items, while Amazon competes by delivering low prices online.
In comparison to its low-cost competitors, TJX provides lower pricing on more premium and higher-quality products. Another element of competitiveness is product range. Walmart, Target, and Amazon have diversified product offerings that cater to various client demands and offer a one-stop shopping experience. TJX sells a variety of goods but prioritizes luxury brands. Dollar General offers a limited variety of essential things at low prices. In the retail industry, customer experience is critical. Companies compete to provide a unified shopping experience in-store and online. Walmart, Target, and Amazon have significantly invested in their online platforms and delivery systems to assure client happiness. TJX seeks to provide a treasure-hunt shopping experience, while Dollar General aims to serve clients via conveniently situated small-format shops. Geographic reach is also essential for competitiveness. Walmart, Amazon, Target, and TJX all have a strong presence in cities, suburbs, and rural regions. On the other hand, Dollar General serves rural and suburban communities, often filling gaps left by bigger shops.
Dollar General, a prominent discount retailer in the U.S., competes with Walmart, Amazon, TJX, and Target within the retail sector. Assessing Dollar General’s business approach and strategy against competitors reveals its competitive strengths and hurdles. The world’s largest retailer, Walmart, possesses thousands of stores and a considerable online footprint. Its competitive advantage lies in economies of scale, vast product offerings, and robust online presence, enabling it to attract a diverse customer base. On the other hand, Walmart’s huge store formats and concentration on urban and suburban regions distinguish it from Dollar General’s small-box store strategy and rural market focus (Euromonitor, 2021).
Amazon is a worldwide e-commerce behemoth with a diverse product assortment, competitive prices, and quick delivery. Its primary features include superior technological infrastructure, a large client base, and innovative offerings such as Amazon Prime. Dollar General confronts the issue of competing with Amazon’s internet reach and convenience as a predominantly brick-and-mortar business. On the other hand, Dollar General’s concentration on underdeveloped rural and suburban communities presents a distinct value proposition differentiating it from Amazon’s mainly urban and suburban client base.
TJX is a major off-price retailer that owns T.J. Maxx, Marshalls, and HomeGoods. TJX’s leading competitive edge is its ability to acquire low-cost branded items, attracting value-conscious buyers. Dollar General’s limited product selection and concentration on daily necessities distinguish it from TJX’s emphasis on branded and stylish products. Target, another important competitor, provides a mix of daily basics and exclusive, trend-driven items in its large-format stores. Target separates itself from Dollar General’s small-box, value-focused approach by creating a distinct shopping experience via partnerships with designers and emphasizing customer service. The following is a table showing how Dollar General competes with Walmart, Amazon, TJX, and Target:
| Dollar General | Walmart | Amazon | TJX | Target |
| Small-box store format | Large store format | E-commerce giant | Off-price retailer | Large-format stores |
| Rural and suburban focus | Urban and suburban focus | Urban and suburban focus | Urban and suburban focus | Urban and suburban focus |
| Value-oriented product offerings | Extensive product assortment | Vast product offering | Discounted branded merchandise | Exclusive, trend-driven products |
Recommendations for Strategic Comparative Advantage
Dollar General can keep its competitive edge by strengthening its digital skills. Dollar General should invest in upgrading its digital capabilities, such as updating its website and mobile app, allowing online ordering with in-store pickup, and extending its delivery choices, as e-commerce continues to rise and customer buying patterns alter. This approach will allow Dollar General to compete with e-commerce behemoths like Amazon while better serving its consumers’ changing demands (Davey & Sanders, 2012). Another suggestion is for Dollar General to continue developing and marketing its private label products, which give better profit margins and help the firm distinguish itself from competitors. Dollar General can attract more value-conscious consumers and establish customer loyalty by delivering unique, high-quality items at competitive costs.
Dollar General should explore increasing their product variety to include more sustainable and eco-friendly items to distinguish itself from competitors and meet evolving customer preferences. This strategy aligns with the rising consumer trend toward environmentally conscious purchase choices and can boost the company’s business image (Mukonza & Swarts, 2020). Maintaining a competitive edge in physical retail may also improve the in-store experience. Dollar General should prioritize store layout, customer service, and a more pleasant shopping experience. A better in-store experience may assist the company in attracting and keeping consumers who appreciate the physical shopping experience.
Dollar General may also sustain its competitive edge by forming strategic alliances. The firm should pursue strategic alliances with other companies or brands to increase its product lines, strengthen its supply chain, or boost its online capabilities. These collaborations might assist Dollar General in diversifying its income sources and improving its overall competitiveness. Finally, Dollar General should implement more sustainable business practices in response to growing consumer interest in corporate social responsibility. The firm may distinguish itself from competitors and appeal to environmentally sensitive customers by concentrating on sustainability and adopting eco-friendly activities into its operations.
Bibliography
Barnes, M., Bauer, L., & Edelberg, W. (2021). 11 Facts on the Economic Recovery from the COVID-19 Pandemic. Hamilton Project Economic Facts.
Bea.gov. “Gross Domestic Product, Fourth Quarter and Year 2021 (Advance Estimate).” https://www.bea.gov/news/2022/gross-domestic-product-fourth-quarter-and-year-2021-advance-estimate.
BenMark, G., Klapdor, S., Kullmann, M., & Sundararajan, R. (2017, March 27). How retailers can drive profitable growth through dynamic pricing. Mckinsey.com; McKinsey & Company. https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/retail/our-insights/how-retailers-can-drive-profitable-growth-through-dynamic-pricing
Congressional Research Service (2022). Retrieved April 30, 2023, from https://crsreports.congress.gov/product/pdf/IF/IF11284
Davey, K. S., & Sanders, T. J. (2012). Serial strategic innovation and sustainable competitive advantage: A longitudinal case study. Journal of Case Research in Business and Economics, pp. 4, 1.
Deloitte (2021). Retrieved April 28, 2023, from https://www2.deloitte.com/content/dam/Deloitte/xe/Documents/consumer-business/me_the-retail-future.pdf
Egilsson, J. H. (2020). How raising interest rates can cause inflation and currency depreciation. Journal of Applied Economics, 23(1), 450-468.
Euromonitor (2021). “World Market for Retailing in 2021.” Retrieved April 28, 2023. https://www.euromonitor.com/world-market-for-retailing-in-2021/report.
Federal Reserve (2021). Retrieved April 28, 2023. https://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/20210709_mprfullreport.pdf.
Forbes. “Dollar General.” Retrieved April 28, 2023. https://www.forbes.com/companies/dollar-general/?sh=7af76697470e.
Hoofnagle, C. J., Van Der Sloot, B., & Borgesius, F. Z. (2019). The European Union general data protection regulation: what it is and what it means. Information & Communications Technology Law, 28(1), 65-98.
Macrotrends (2023). “Dollar General Financial Statements 2009-2023.” Retrieved April 28, 2023. https://www.macrotrends.net/stocks/charts/DG/dollar-general/financial-statements.
Magableh, G. M. (2021). Supply chains and the COVID‐19 pandemic: A comprehensive framework. European Management Review, 18(3), 363-382.
Mukonza, C., & Swarts, I. (2020). The influence of green marketing strategies on business performance and corporate image in the retail sector. Business Strategy and the Environment, 29(3), 838-845.
Sustainability connects retailers & brands with conscientious consumers. (2021, November 18). NIQ; NielsenIQ. https://nielseniq.com/global/en/insights/report/2021/sustainability-connects-retailers-brands-with-conscientious-consumers/.
Porter, M. E. (1980). Competitive strategy: Techniques for analyzing industries and competitors.
Retail Law Conference. (2021). Rila.org. Retrieved April 28, 2023, from https://www.rila.org/conferences/retail-law-conference
Rueter, T. (2020, December 2). Private label remains a priority at Dollar General. Store Brands. https://storebrands.com/private-label-remains-priority-dollar-general
Statista (2021). “Global Retail E-Commerce Sales 2026.” Retrieved April 28, 2023. https://www.statista.com/statistics/379046/worldwide-retail-e-commerce-sales/.
Vadakkepatt, G. G., Winterich, K. P., Mittal, V., Zinn, W., Beitelspacher, L., Aloysius, J., … & Reilman, J. (2021). Sustainable retailing. Journal of Retailing, 97(1), 62-80.
Van Loo, R. (2015). Helping buyers beware: The need for supervision of big retail. University of Pennsylvania Law Review, 1311–1392.
 write
write