I. Introduction
Innovation management alludes to the most common way of overseeing and supporting innovation inside an association. It includes establishing a climate that empowers and supports imaginative reasoning and trial and error to foster new items, administrations, and business models. The significance of innovation management in business strategy and new business models couldn’t be more significant. Innovation is fundamental for organizations to stay serious, separate themselves from their rivals, and eventually make long-haul progress.
This exposition aims to look at how effective organizations structure an innovation strategy that is firmly associated with their business strategy and new business models. Like this, these organizations can use innovation to make a practical upper hand and make long-haul progress. The exposition will investigate different innovation management ideas, speculations, and procedures and how organizations have effectively adjusted their innovation strategy to their business strategy to make new items, administrations, and business models. The article will likewise examine the job of innovation management in making new business models and disrupting industries.
II. Innovation Management Concepts and Theories
Innovation management is a perplexing cycle that utilizes various ideas, hypotheses, and strategies to make new products, services, and business models. In this part, we will examine the most famous innovation management ideas and speculations and how they can drive innovation (Leonidou, Christofi, Vrontis, & Thrassou, 2018).
Disruptive Innovation
Disruptive innovation is a hypothesis created by Clayton Christensen that portrays how new products or services can disturb existing business sectors by giving a less expensive or more helpful other option. This hypothesis proposes that organizations should zero in on creating disruptive innovations instead of supporting innovations to make long-haul progress(Li, Porter, & Suominen, 2018). Disruptive innovations are regularly more straightforward, less expensive, and simpler to use than existing products, which can prompt the relocation of laid-out players on the lookout. Organizations can utilize disruptive innovation to enter new business sectors or to make new item classes (Christensen, McDonald, Altman, & Palmer, 2018). Figure 1 shows Disruptive Innovation
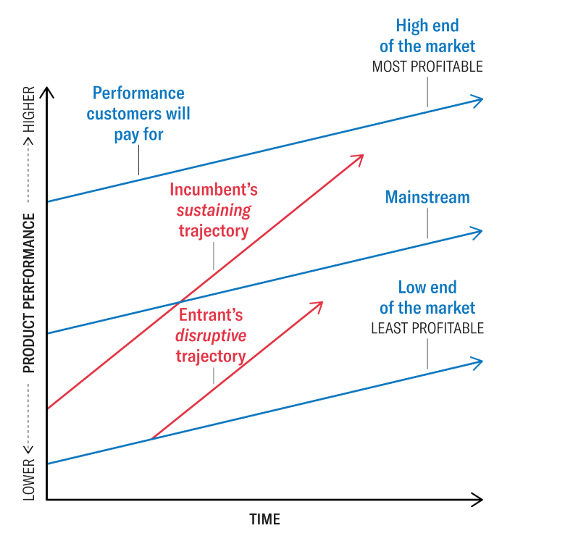
(Ecosystems, 2023)
Open Innovation
Open innovation is an idea created by Henry Chesbrough that depicts how organizations can use outside wellsprings of innovation to make new products, services, and business models. Open innovation includes teaming up with outer accomplices, like clients, providers, and organizations, to foster new thoughts and sell them to the public. This approach can assist organizations with getting to new business sectors, advances, and aptitude, which can prompt the formation of new products or services (Bogers et al., 2016). Figure 2 shows Open Innovation
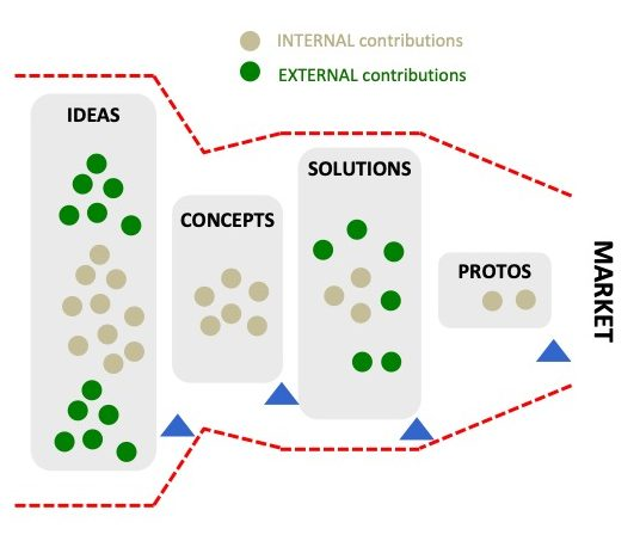
(Ennomotive, 2023)
Design Thinking
Design thinking is a human-focused way to deal with innovation that spotlights grasping the necessities of clients and designing products and services that address those issues. This approach includes a few phases, incorporating relating to clients, characterizing the issue, ideating arrangements, prototyping, and testing (Panke, 2019). Design thinking can assist organizations with developing products and services that are easier to understand, natural, and tastefully satisfying.
These ideas and hypotheses can be utilized in various ways to make new products, services, and business models (Micheli, Wilner, Bhatti, Mura, & Beverland, 2018).
- Creating new products
Organizations can use these ideas and speculations to foster new products addressing client issues. For instance, design thinking can make products easier to understand, while disruptive innovation can be utilized to make new products that upset existing business sectors. Open innovation can be utilized to get new advances and aptitude that can be utilized to foster new products.
- Developing new services
Organizations can use these ideas and hypotheses to foster new services addressing clients’ issues. For instance, design thinking can be utilized to make services easier, while disruptive innovation can be utilized to make new services that upset existing business sectors. Open innovation can be utilized to get new advancements and abilities that can be utilized to foster new services (Henriksen, Richardson, & Mehta, 2017).
- Creating new business models
Organizations can utilize these ideas and speculations to foster new business models that can assist them with making long-haul progress. For instance, disruptive innovation can be utilized to make new business models that disturb existing business sectors. Open innovation can be utilized to get new advances and skills that can be utilized to foster new business models.
III. Innovation Management Techniques
Innovation management techniques are a fundamental piece of the innovation process. These techniques empower associations to create, create, and execute novel thoughts, items, administrations, and action plans. In this part, we will look at changed innovation management techniques, their applications, and how they can be combined to make a comprehensive innovation management process (Watson, Wilson, Smart, & Macdonald, 2017).
Ideation Sessions
Ideation sessions are collaborative meetings to generate new ideas where people from various divisions and levels of an association come together to produce groundbreaking thoughts. These sessions are usually worked with by a mediator and can be organized or unstructured. The reason for ideation sessions is to produce enormous thoughts, which can be assessed and refined later. Ideation sessions encourage innovation inside an association by making a culture of thought, age, and investigation (Hatcher et al., 2018).
Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping is a strategy to rapidly foster a utilitarian model of another item, administration, or action plan. This method includes making a model utilizing materials that are promptly accessible and can be handily changed or disposed of. Rapid prototyping permits associations to test and approve novel thoughts rapidly without the requirement for broad examination or improvement. This method cultivates innovation inside an association by encouraging trial and error and hazard-taking (Robinson, Lagnau, & Boon, 2019).
Customer Co-Creation
Customer co-creation is a strategy that includes collaborating with customers to foster new items, administrations, or action plans. This method includes connecting with customers in the innovation process, requesting their thoughts, and incorporating their criticism into the improvement process. Customer co-creation is utilized to cultivate innovation inside an association by utilizing the innovativeness and ability of customers (Hidalgo & Herrera, 2020).
Combining Techniques
Innovation management techniques are not fundamentally unrelated and can be combined to make a comprehensive innovation management process. For instance, ideation sessions can be utilized to create groundbreaking thoughts, which can then be rapidly prototyped to test and approve their practicality. Customer co-creation can be utilized to draw in customers in the improvement process, guaranteeing that new items, administrations, or plans of action address their issues and assumptions. By combining various techniques, associations can make an innovation management process that is proficient, compelling, and comprehensive (Kianto, Sáenz, & Aramburu, 2017).
IV. Innovation Strategy and Business Strategy
Innovation strategy and business strategy are firmly related and ought to be adjusted to guarantee that an association can make long-haul progress. In this segment, we will examine the significance of aligning innovation strategy with business strategy, look at influential companies that have framed a tight connection between innovation and business strategy, and talk about how they have utilized innovation to make long-haul progress (Amit & Zott, 2020).
Significance of Aligning Innovation Strategy with Business Strategy
Aligning innovation strategy with business strategy is essential to the progress of an association. By aligning these techniques, an association can guarantee that its innovation endeavors are centered around making items, administrations, or plans of action lined up with its general business targets. This arrangement likewise guarantees that innovation endeavors are not sought after in seclusion but are coordinated with the association’s general strategy, guaranteeing that they are successfully carried out and have a more prominent effect (Sjödin, Parida, Jovanovic, & Visnjic, 2020).
Successful Companies that have Framed a Tight Connection between Innovation and Business Strategy
Apple and Google are two companies that have framed a tight connection between innovation and business strategy, empowering them to make long-haul progress. Apple has fabricated its business strategy around creating inventive and exceptionally beneficial items intended to address its customers’ issues and inclinations. This strategy has been empowered by a culture of innovation, where representatives are encouraged to think innovatively and face challenges (Kohtamäki, Rabetino, Parida, Sjödin, & Henneberg, 2022).
Google, then again, has assembled its business strategy around innovation through its open innovation model. Google uses its tremendous organization of workers, accomplices, and customers to create groundbreaking thoughts and foster imaginative items, administrations, and action plans. This strategy has empowered Google to stay at the very front of innovation and disturb businesses like promoting, searching, and portable (Lee, Suh, Roy, & Baucus, 2019).
Leveraging Innovation to Achieve Long-Term Success
Both Apple and Google have utilized innovation to make long-haul progress. Apple’s emphasis on plan and customer experience has empowered it to make profoundly helpful items that command premium costs and produce critical income. Apple’s innovation endeavors have empowered it to make new business sectors and upset existing ones, like cell phone and music ventures (Provasnek, Sentic, & Schmid, 2017). Google’s innovation endeavors have empowered it to make new items and administrations that have become fundamental apparatuses for people and organizations all over the planet. Google’s web search tool, promoting stage, and portable working framework have become omnipresent, producing critical income and solidifying its situation as the most imaginative company on the planet.
V. New Business Models and Innovation
Innovation management is essential in making new plans of action that empower associations to disturb businesses and gain a competitive benefit. In this segment, we will examine how innovation management can be utilized to make new plans of action, dissect fruitful companies that have disturbed ventures with new plans of action, and clarify how these companies involved innovation in making a competitive benefit(Ulvenblad, Ulvenblad, & Tell, 2018).
Making New Plans of action through Innovation Management
Innovation management can be utilized to make new action plans by recognizing and utilizing arising advancements and changing customer needs and inclinations. This process includes recognizing valuable open doors for innovation, creating groundbreaking thoughts, creating models, and testing and approving new action plans.
One way to deal with making new plans of action is to utilize configuration thinking, which is a client-focused way to deal with innovation that includes figuring out the requirements and inclinations of customers, producing thoughts, prototyping, and testing. Another methodology is to utilize open innovation, which includes collaborating with outer accomplices, like customers, providers, and colleges, to create groundbreaking thoughts and foster new action plans (Sjödin, Parida, Jovanovic, & Visnjic, 2020).
Successful Companies That Have Upset Enterprises with New Plans of Action
Uber and Airbnb are two companies that have upset ventures with new plans of action, making a competitive benefit through innovation (Sjödin, Parida, Jovanovic, & Visnjic, 2020).
Uber upset the taxi business by utilizing another plan of action that empowered customers to effectively, immediately find and book rides through a portable application. Uber’s action plan depended on connecting drivers with travelers, utilizing continuous information to enhance courses and costs, and giving a consistent installment experience. By utilizing innovation and changing customer needs and inclinations, Uber could make a more convenient and cost-powerful option in contrast to customary taxi administrations.
Airbnb disturbed the inn business by utilizing another plan of action that empowered people to lease their homes or condos to explorers. Airbnb’s plan of action depended on making a stage that connected hosts with visitors, giving a scope of choices and costs to suit various requirements and inclinations. By utilizing the sharing economy and changing customer needs and inclinations, Airbnb could make a more customized and reasonable option in contrast to conventional lodgings(Ulvenblad, Ulvenblad, & Tell, 2018).
Utilizing Innovation to Make a Competitive Benefit
Both Uber and Airbnb utilized innovation to make a competitive benefit, empowering them to disturb customary enterprises and gain a portion of the overall industry. Uber utilized innovation and information to make a more convenient and cost-successful option than customary taxi administrations(Micheli, Wilner, Bhatti, Mura, & Beverland, 2018). Using constant information to upgrade courses and costs, Uber could give a superior customer experience and gain a competitive advantage over customary taxi administrations. Airbnb utilized the sharing economy and changing customer needs and inclinations to make a more customized and reasonable option in contrast to conventional lodgings. By giving a scope of choices and costs to suit various requirements and inclinations, Airbnb had the option to make a superior customer experience and gain a competitive benefit over conventional lodgings(Ulvenblad, Ulvenblad, & Tell, 2018).
VI. Conclusion
Innovation management is essential for associations looking to make long-haul progress and gain a competitive benefit in the commercial center. This exposition has discussed the significance of aligning innovation strategy with business strategy and utilizing innovation management techniques to encourage innovation inside an association. It has also investigated fruitful companies like Apple, Google, Uber, and Airbnb that have utilized innovation to make new items, administrations, and action plans. This essay has featured the significance of making new action plans through innovation management by recognizing and utilizing arising advances and changing customer needs and inclinations. The utilization of innovation management techniques like ideation sessions, rapid prototyping, and customer co-creation has been examined as a method for encouraging innovation inside an association. To further develop their innovation management process, associations ought to adjust their innovation strategy to their business strategy, develop a culture of innovation, and influence outside accomplices to create novel thoughts and foster new action plans. They ought to likewise put resources into innovation management techniques, for example, plan thinking, open innovation, and rapid prototyping to encourage innovation inside the association.
References
Amit, R., & Zott, C. (2020). Business Model Innovation Strategy: Transformational Concepts and Tools for Entrepreneurial Leaders. In Google Books. John Wiley & Sons. Retrieved from https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=utP5DwAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR15&dq=Innovation+Strategy+and+Business+Strategy+&ots=p72OEUDdWf&sig=F1tXsDB2dF1Y8gtis8rb5nfC448&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=Innovation%20Strategy%20and%20Business%20Strategy&f=false
Bogers, M., Zobel, A.-K., Afuah, A., Almirall, E., Brunswicker, S., Dahlander, L., … Radziwon, A. (2016). The open innovation research landscape: established perspectives and emerging themes across different levels of analysis. Industry and Innovation, 24(1), 8–40. https://doi.org/10.1080/13662716.2016.1240068
Christensen, C. M., McDonald, R., Altman, E. J., & Palmer, J. E. (2018). Disruptive Innovation: An Intellectual History and Directions for Future Research. Journal of Management Studies, 55(7), 1043–1078. https://doi.org/10.1111/joms.12349
De Massis, A., Audretsch, D., Uhlaner, L., & Kammerlander, N. (2017). Innovation with Limited Resources: Management Lessons from the German Mittelstand. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 35(1), 125–146. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12373
Ecosystems. (2023). What Is the Theory of Disruptive Innovation? | ccecosystems.news. Retrieved November 14, 2022, from https://ccecosystems.news/en/what-is-the-theory-of-disruptive-innovation/
Ennomotive. (2023). 💡 Open Innovation: Definition and Types of Innovation. Retrieved April 24, 2023, from Ennomotive website: https://www.ennomotive.com/open-innovation/
Hatcher, G., Ion, W., Maclachlan, R., Marlow, M., Simpson, B., & Wodehouse, A. (2018). Evolving improvised ideation from humour constructs: A new method for collaborative divergence. Creativity and Innovation Management, 27(1), 91–101. https://doi.org/10.1111/caim.12256
Henriksen, D., Richardson, C., & Mehta, R. (2017). Design thinking: A creative approach to educational problems of practice. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 26, 140–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2017.10.001
Hidalgo, A., & Herrera, R. (2020). Innovation management and co-creation in KIBs: An approach to the ICT services sector. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 161, 120278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120278
Kianto, A., Sáenz, J., & Aramburu, N. (2017). Knowledge-based human resource management practices, intellectual capital and innovation. Journal of Business Research, 81, 11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2017.07.018
Kohtamäki, M., Rabetino, R., Parida, V., Sjödin, D., & Henneberg, S. (2022). Managing digital servitization toward smart solutions: Framing the connections between technologies, business models, and ecosystems. Industrial Marketing Management, 105, 253–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indmarman.2022.06.010
Lee, J., Suh, T., Roy, D., & Baucus, M. (2019). Emerging Technology and Business Model Innovation: The Case of Artificial Intelligence. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 5(3), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc5030044
Leonidou, E., Christofi, M., Vrontis, D., & Thrassou, A. (2018). An integrative framework of stakeholder engagement for innovation management and entrepreneurship development. Journal of Business Research, 119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2018.11.054
Li, M., Porter, A. L., & Suominen, A. (2018). Insights into relationships between disruptive technology/innovation and emerging technology: A bibliometric perspective. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 129, 285–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2017.09.032
Micheli, P., Wilner, S. J. S., Bhatti, S. H., Mura, M., & Beverland, M. B. (2018). Doing Design Thinking: Conceptual Review, Synthesis, and Research Agenda. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 36(2), 124–148. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12466
Panke, S. (2019). Design Thinking in Education: Perspectives, Opportunities and Challenges. Open Education Studies, 1(1), 281–306. https://doi.org/10.1515/edu-2019-0022
Provasnek, A. K., Sentic, A., & Schmid, E. (2017). Integrating Eco-Innovations and Stakeholder Engagement for Sustainable Development and a Social License to Operate. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 24(3), 173–185. https://doi.org/10.1002/csr.1406
Robinson, D. K. R., Lagnau, A., & Boon, W. P. C. (2019). Innovation pathways in additive manufacturing: Methods for tracing emerging and branching paths from rapid prototyping to alternative applications. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 146, 733–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2018.07.012
Sjödin, D., Parida, V., Jovanovic, M., & Visnjic, I. (2020). Value Creation and Value Capture Alignment in Business Model Innovation: A Process View on Outcome‐Based Business Models. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 37(2), 158–183. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12516
Ulvenblad, P., Ulvenblad, P., & Tell, J. (2018). An overview of sustainable business models for innovation in Swedish agri-food production. Journal of Integrative Environmental Sciences, 16(1), 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1080/1943815x.2018.1554590
Watson, R., Wilson, H. N., Smart, P., & Macdonald, E. K. (2017). Harnessing Difference: A Capability-Based Framework for Stakeholder Engagement in Environmental Innovation. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 35(2), 254–279. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12394
 write
write