Introduction
An organization can become more productive by using strategic planning to help direct the distribution of resources to achieve goals. It is a tool for strategic management. Good strategic management requires strategic planning. Strategic management is the continuing process of creating, implementing, and evaluating choices that aid an organization in achieving its objectives. A corporation can exert more influence over its path of action and forge its destiny by simply starting and influencing actions rather than responding to them (George et al., 2019). The studies, decisions, and activities a firm takes to create and safeguard competitive advantages are referred to as strategic management. The strategic management process, which involves a variety of studies and decisions, can enhance the likelihood that a corporation will choose a “good strategy” or one that gives it a competitive edge. The vision, which comes first, describes the organization’s ideal future condition. The long-term goals and short-term errors that an organization intends to make are both outlined in its mission statement. The second phase is the strategic management process. Setting goals is the third step in the strategic management process. The specific objectives that an organization wants to achieve are its objectives.
The second step in the strategic management process is the SWOT analysis. A company can determine its competitive environment’s critical threats and opportunities through an external assessment. It also looks at how competition is anticipated to change the environment and how opportunities and dangers may evolve. While external analysis focuses on the environmental problems and possibilities to which a firm is exposed, internal analysis helps an organization learn about its strengths and limitations. Additionally, it assists in determining whether the internal assets and competencies of a company are more or less likely to serve as sources of competitive advantage. Businesses may make the best decision using the SWOT Analysis results. Implementing the strategy is the following step in the strategic management process. A plan is only effective if it is put into practice. Strategy implementation happens when a company creates organizational policies and processes that align with its strategy (Fernandez et al., 2019). The last stage of the procedure is establishing a competitive edge.
What Is Swot Analysis?
SWOT analysis is a method used by businesses for management and strategic planning. It assists in creating competitive and organizational strategies. The system approach contends that organizations are composed of numerous interrelated subsystems that communicate with one another and their surroundings. According to this notion, an organization has two habitats: the inside and the outside. Evaluating these ecosystems is crucial in order to develop strategic management methods. A SWOT analysis is a technique for evaluating the business and its environment.
The Components of Swot Analysis
The SWOT analysis process includes the division of four sections into two ways. Its four sections are strengths, constraints, opportunities, and threats. Opportunities and dangers are external features and characteristics of the environment, whereas strengths and weaknesses are internal elements and characteristics of the company. The following table is a SWOT Analysis, with its four elements in a 2×2 matrix
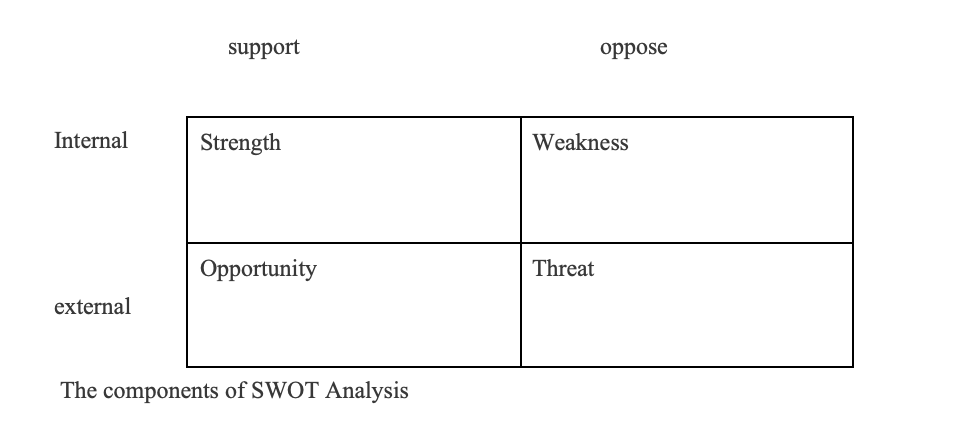
A SWOT analysis examines an organization’s environment to determine its strong and weak points. Environmental opportunities and dangers can be identified by examining the components that make up its external environment. A SWOT analysis is a method for strategic planning used to evaluate a company’s opportunities, threats, weaknesses, and strengths. It provides pertinent information that will help the company match its resources and capabilities to the fiercely competitive environment in which it works. Opportunities and strengths can help a company accomplish its goals. Threats and weaknesses hamper the achievement of business goals. Therefore, an analysis company’s inside strengths and weaknesses, as well as the opportunities and threats projected by its external environment, form the core of any effective strategy decision. The manager’s responsibility is to balance the firm’s strengths and weaknesses in light of the opportunities and risks presented by the environment and any externalities and internalities that need to be considered.
An organization’s ability to outperform competitors and other organizations are called organizational strength. These traits and skills can be discovered by investigating the organization’s internal environment. In other words, organizational strength is the combination of characteristics and conditions that enable a company to outperform its competitors in terms of productivity and effectiveness. The five aspects that need to be considered are the relative market environment, financial structure, production and technological competence, the relative potential for R&D, relative human capacity, and managerial effectiveness. This might reveal if a company is firm, equal to, or poor compared to its competitors (Teoli et al., 2019).
Organizational strengths are those organizational competencies that actively aid in achieving organizational goals. Before responding to a challenge or opportunity, a company must know its potential and the characteristics that make it stand out from its competitors. Being decisive and robust is crucial for an organization. There is no other way to take advantage of the opportunities the outside world provides. The company must employ its resources to handle the issues brought on by the external environment. These issues highlight the importance of organizational strengths (Teoli et al., 2019).
An organization is said to have a weakness when its existing existence and competency capacities are weaker than those of similar and rival organizations. The areas or tasks where a corporation executes less expertly and effectively than its competitors are considered to be its vulnerabilities. These elements weaken the competitiveness of the company and organizational effectiveness. As a result, the business cannot respond to changing circumstances or seize opportunities. Equally crucial to understanding the organization’s strengths are its flaws. The argument makes the idea that the only way to improve a strategy is to exploit its flaws. It is vital to identify and strengthen any company’s shortcomings that could result in inefficiency and ineffectiveness. Plans and initiatives for the extended future must consider current conditions that present challenges and constraints.
In organizational management, an opportunity is a suitable situation that the environment presents the company with in order to achieve its objectives. Examining the company’s surroundings revealed opportunities that might be advantageous to the business. Businesses have a variety of chances because of competitiveness and the severe workload. Opportunities are external environmental factors that give a company a chance to strengthen its areas of strength, address its shortcomings, or reduce environmental concerns (Lamb et al., 2021).
A threat makes it more difficult or impossible for an organization’s management to accomplish its goals. Threats develop due to adverse changes to the organization’s immediate or long-term environment. These occurrences can make the organization unable to survive or cause it to lose its competitive advantage (Shet et al., 2019). Both they and the organization could be negatively impacted, which can be irreparable. Any environmental factors that could reduce an organization’s performance and efficiency are considered threats.
Future economic, social, cultural, demographic, environmental, political, legal, governmental, technological, and competitive trends and events that could materially help or hurt a firm are referred to as “external opportunities and threats.” Forces that are mainly outside the control of one specific organization are referred to as “external” elements. Internal organizational actions can be handled and done incredibly well or represent organizational strengths and weaknesses. They are present in every aspect of an institution’s management, marketing, finances, accounting, operations, production, research, and development functions. When utilizing the management information system, they can also be observed. Strategic management is crucial to finding and evaluating organizational strengths and weaknesses in a company’s functional areas. Businesses aim to use strategies that leverage their resources.
Making a list of the four components in a SWOT analysis is not the only step. The two most valuable aspects of a SWOT analysis are finding out what the four lists reveal about the firm’s position and considering the best course of action. In summary, the critical element of a SWOT Analysis is that for the firm to succeed, internal actions must be in line with external reality. The SWOT analysis offers a framework for analyzing internal strengths and weaknesses and potential external threats. It could be beneficial to focus on minimizing defects and maximizing available chances. In order to better comprehend the environment in which the business or unit operates, it is essential to consider both internal and external elements.
Advantages of Swot Analysis
Managers and employees of any company must be able to create plans or make decisions. Businesses often use SWOT analysis as a marketing and strategic management tool. This approach of strategic analysis has proven to be effective. Various characteristics influence the acceptance and utility of SWOT Analysis. These characteristics, which are also seen favorably, comprise the following: SWOT analysis is a method of analysis that provides broad perspectives and general solutions. Following the SWOT Analysis, the ensuing assessments would focus more on specifics and challenges. A SWOT analysis is a framework that guides you from the general to the specific in this way. Macro studies are possible with the interactional analysis technique known as SWOT analysis. Using a single, integrated perspective, the SWOT analysis method enables you to focus on the good and negative aspects of the firm’s internal and external environment or the factors in this environment that bring value in both directions.
Utilizing SWOT analysis, organizational management can identify profit opportunities. Through an understanding of weaknesses, threats can be managed and eliminated. A SWOT analysis of a business can help develop strategies that set it apart from its competitors. SWOT analysis develops a conceptual framework for organizational management as a method and analysis tool. A SWOT analysis of a company can assist in the creation of strategies that differentiate it from its rivals. As a method and analysis tool, SWOT analysis creates a conceptual framework for organizational management. SWOT analysis, then, lays the foundation for making strategic decisions.
SWOT analysis promotes conversations about strategic issues and the creation of strategies. Through the use of creative participatory techniques like group discussions and brainstorming, it encourages the sharing of information. A SWOT analysis makes it feasible to start a discussion about the organization’s goals and aspirations by looking beyond current problems and conditions.
Merits and demerits of swot analysis
Although SWOT analysis is a standard analytical tool, it is criticized. There have been comments that it needs to be more effective as a part of organizational strategy, that it is just helpful in defining the existing condition, and that it should be considered something other than an analysis approach. A SWOT analysis gives wide-ranging solutions and a broad perspective. A SWOT analysis was performed once the environmental circumstances were steady. It must be developed and used methodically, which requires knowledge and training. Shvardak claims that in 2021, executives debating an organization’s advantages, disadvantages, and distinctive competencies while seated at a table will resemble students in a case study class. Both quality and quantity are problems with the analysis technique known as SWOT analysis. SWOT analysis can be used to find many elements. . However, the quantity may only occasionally be a good indicator of quality. It is impossible to determine the importance of the SWOT Analysis components, concentrate on them intensely, resolve developments and conflicts in different dimensions, and include thoughts and ideas based on numerous facts and research.
Critiques of swot analysis
Putting factors into one of the four SWOT quadrants can take time, as two categories may fit the same data. A factor could simultaneously have its advantages and disadvantages. It is also possible for maintainable strengths to turn into weaknesses. Missed chances that rivals take advantage of could develop into dangers. The practice’s objective also influences the classification of a variable. It might be more difficult to specify the requirements for placing a variable in one of the four quadrants. The SWOT analysis is based on the current strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. However, SWOT must alter its inventory to create one that accurately reflects the If not, producing plans will be grounded in the present or the past rather than the future.
Competitive comparisons are excluded from the SWOT analysis. A quantitative index to provide an operational criterion for benchmarking is particularly necessary for competitive analysis in a highly interdependent environment where an organization needs to know the appropriate performance levels of all its close competitors to assess the size of competitive gaps. The data in a SWOT Analysis may need to be more precise under the influence of corporate culture as it is linked to the expectations, prejudices, and goals of those in charge of leading the firm.
Conclusion
SWOT analysis is a valuable technique for strategic management planning and decision-making. Using a variety of analytical approaches, the strategic management process helps a business achieve its long-term objectives. SWOT analysis has been widely utilized to enhance strategic decision-making in internal and external environment investigations. This method has been used in various situations where it is essential to do a strategic analysis of a field, organization, person, project, or city. It comprises selecting a goal and identifying the internal and external factors that are beneficial and detrimental to reaching it.
Reviewing the internal analysis of the organization serves as the first step in the strategic management process. Internal analysis is used to identify internal resources and abilities for competitive advantage. The external analysis aids in the identification of market possibilities and threats by looking at the overall environment, the competitive industry environment, and rivals. The external analysis enables an organization to align its strategies with the business environment, while the internal analysis identifies resources that need to be protected and improved. They consider present and future opportunities and dangers when evaluating strengths and weaknesses. Fewer implausible options will be sought out the more one can identify one’s strengths and weaknesses. Additionally, vulnerabilities can be rectified, and hazards can be eliminated using actual chances.
SWOT analysis shows how a company is currently doing and makes it possible to develop long-term action plans. When applied correctly, the methodology can provide a solid basis for formulating strategies. There are drawbacks and restrictions, even if it is a straightforward administrative tool with numerous planning benefits. SWOT analysis illustrates the challenge of employing qualitatively articulated aspects in decision-making and presenting a list of variables that affect the micro and macro contexts in which an organization operates. Only the first step toward a more thorough examination may be made by qualitatively examining the planning process’ internal and external components. The SWOT method is insufficient for strategic planning, as evidenced by the growing corpus of research.
References
Fernandez, M. E., Ten Hoor, G. A., Van Lieshout, S., Rodriguez, S. A., Beidas, R. S., Parcel, G., … & Kok, G. (2019). Implementation mapping: using intervention mapping to develop implementation strategies. Frontiers in public health, 7, 158.
George, B., Walker, R. M., & Monster, J. (2019). Does strategic planning improve organizational performance? A meta‐analysis. Public Administration Review, 79(6), 810-819.
Junça Silva, A., & Coelho, N. (2022). The moderating role of organizational culture on the relationship between workers’ attitudes towards telework and happiness. Kybernetes.
Lamb, K., Farrow, M., Olymbios, C., Launder, D., & Greatbatch, I. (2021). Systematic incident command training and organizational competence. International Journal of Emergency Services, 10(2), 222-234.
Shet, S. V., Patil, S. V., & Chandawarkar, M. R. (2019). Competency-based superior performance and organizational effectiveness. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, 68(4), 753-773.
Shvardak, M. (2021). SWOT analysis as a strategic management tool for the quality training of the future educational institution head.
Teoli, D., Sanvictores, T., & An, J. (2019). SWOT analysis.
 write
write