As a progressive fast-food chain, we are starting significant operational improvements to improve productivity and customer satisfaction. Introducing self-service kiosks, which have revolutionized our ordering procedure, is key to this progression across all stores. With most things arriving pre-prepared for simple onsite finishing, there is a deliberate push towards simpler food preparation to accompany this technological advancement, greatly simplifying kitchen operations.
In keeping with these developments, we are optimizing our personnel by cutting the number of employees at each location to a quarter. However, we’re aggressively growing the number of our outlets and providing relocation possibilities for current employees over the coming year to counteract any job losses. To manage these modifications effectively, we’re utilizing the McKinsey 7S Model.
This thorough foundation, which includes Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared Values, Style, Staff, and Skills, is essential to managing organizational change. The 7S Model guides us in adjusting to and prospering in this new operating environment by lining up these seven components.
Analysis of Current Gaps in Each of the 7S Steps
Strategy. The present approach is centered on conventional fast-food operations, which include normal meal preparation and human ordering (Harrison et al., 2021). With a focus on kiosk-based arrangement and simplified pre-prepared food procedures, the new model shifts towards automation and efficiency to better accommodate changing customer preferences and operational cost-effectiveness.
Structure. The current system has to change, which calls for active management and a large degree of employee participation in food preparation and customer service. By supporting automated ordering and streamlined meal processing, the new structure will reduce staffing needs and promote an operating strategy focused on technology (Errida & Lotfi, 2021).
Systems. According to Teh et al. (2020), system upgrades are necessary to switch to a more efficient model. It entails installing new kitchen equipment designed to handle food that has already been prepared and using cutting-edge kiosk technology for client ordering. These improvements are essential for improving customer satisfaction, expediting processes, and guaranteeing uniformity throughout all locations.
Shared Values. Keeping with our new strategic direction, we are building a culture emphasizing efficiency and technology, which fosters an atmosphere that values efficiency and promotes creativity (Javied et al., 2019). By highlighting these common values, we can ensure that our team is motivated and cohesive when accepting these operational adjustments.
Style. We are promoting an adaptable and flexible leadership style in reaction to our operational revamp. It advises leaders to be versatile, encourage creativity, and cultivate an environment of lifelong learning (Suwanda & Nugroho, 2022). This strategy is essential for completing the transition smoothly and motivating employees to adopt new procedures and technology.
Staff. We are implementing workforce realignment initiatives in light of the operational changes that entail providing possibilities for movement to other locations and training for new positions, especially in technology management and customer support (Harrison et al., 2021). By keeping important workers on board, we can ensure a seamless transition and continuity within our team.
Skills. Our personnel prepare for the new operating paradigm by implementing extensive training programs. These concentrate on competencies for overseeing self-serve technologies, handling prepared food, and offering superior customer support (Masfi & Sukartini, 2022). By upskilling, we ensure our employees stay knowledgeable and self-assured in the ever-changing fast-food industry.
Steps for Alignment in Each of the 7S Categories
Strategy. We are working on a roadmap incorporating kiosk technology and pre-arranged food logistics to connect our approach with modern operational techniques better. This strategic realignment aims to maximize customer satisfaction and operational effectiveness while maintaining our business model’s competitiveness and adaptability to changing consumer demands and market conditions.
Structure. We are modifying our organizational structure to incorporate kiosk technology and make room for a smaller workforce. Our goal is to establish a flexible system that can quickly adapt to the changing demands of a tech-enhanced fast-food industry by promoting cross-functional teams and flattening hierarchies.
Systems. We’re modernizing our processes to guarantee efficiency and incorporate inventory management and kiosk ordering software designed specifically for prepared food items. By streamlining processes, cutting down on wait times, and offering real-time data analytics, these system improvements will improve decision-making and improve the customer service experience.
Shared Values. To encourage innovation and efficient operations, we are realigning our shared values and cultivating a culture that places a high priority on efficiency and technology. A cultural transformation is needed to fully embrace the changes and ensure that our team’s attitudes and actions align with our operational procedures and strategic objectives.
Style. Our approach to leadership is changing to encourage resilience and adaptation. We can ensure leaders effectively lead their teams through the transition by promoting flexibility and proactivity, advocating creativity, and creating an environment where change is anticipated and welcomed as a constant.
Staff. Staff restructuring and retention methods are being implemented to keep a skilled workforce in line with our new technology-driven service model. Ensuring that our personnel are respected and essential to our progress entails retraining, creating new jobs, and offering chances within the growing network of outlets.
Skills. Filling up the talent gaps is critical to our shift. Our main goal is to teach staff members how to use the new kiosks and efficiently handle prepared meals. Our workforce is upskilled by keeping up with the most recent technological advancements and culinary techniques and can consistently provide high-quality cuisine and customer service.
Graphical Representation of the 7S Model
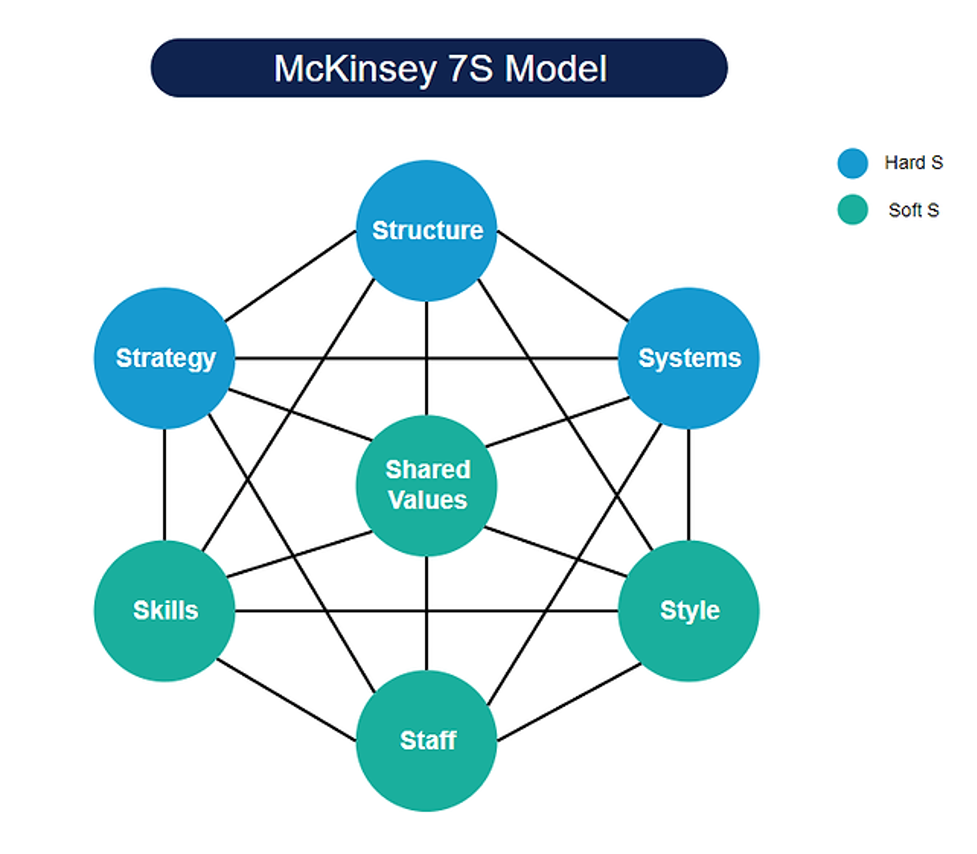
The McKinsey 7S Model is seen visually in the uploaded hexagon. It is composed of a core hexagon with an extra node in the middle, where each point stands for one of the model’s seven elements: Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared Values, Style, Staff, and Skills. The ‘Hard S’ elements (Strategy, Structure, Systems) are highlighted with a deeper hue, signifying their greater tangibleness. In contrast, the ‘Soft S’ components (Shared Values, Style, Staff, Skills) are generally paler, indicating their more individualized and culturally focused characteristics.
For change management to be effective, it is essential to visualize these elements’ intended and actual aspects. It makes it possible to compare the organization’s current state to its desired state with clarity, enabling focused adjustments. This diagram serves as a roadmap, outlining the components that must align for the change to guide the change process effectively. It ensures that everyone agrees with the goals of the change and the actions required to attain them by giving a concise overview that stakeholders throughout the organization can readily comprehend.
Implementation Plan
Our implementation strategy is designed to emerge in successive phases for the following two years. To upskill our employees on new kiosk technology and food preparation techniques, we will initially concentrate on an extensive training program that we want to finish within the first three months. At the same time, we will start putting up kiosks in a few high-traffic places to complete the deployment in these test sites. The next three months will revamp kitchen operations to integrate pre-prepared meal products smoothly.
We will be realigning our personnel over the next six months as we move into the medium term, including position transfers and relocations essential to our growth. We plan to implement a feedback mechanism to enhance the effectiveness of our recently developed operational model. Long-term goals for the upcoming year include completing the installation of kiosks at every location, promoting an efficient and technologically-driven corporate culture, and increasing the number of outlets. This systematic, phased approach guarantees a seamless transition by capitalizing on our workforce’s capabilities and harmonizing with our strategic goals.
In summary, aligning the seven S’s: Strategy, Structure, Systems, Shared Values, Style, Staff, and Skills is essential to our company’s shift to a more technologically advanced, efficient business model. The crucial phases include strategic integration of kiosks, personnel training and realignment, system improvements, and cultural adaptation. These adjustments should lead to improved customer happiness and efficiency as well as future development and sustainability for the business. We are assuring a comprehensive and harmonic transition using the 7S model as our guide, resulting in a coherent, forward-thinking company well-positioned for future success, with each area of our organization complementing the others.
References
Errida, A., & Lotfi, B. (2021). The determinants of organizational change management success: Literature review and case study. International Journal of Engineering Business Management, 13(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1177/18479790211016273
Harrison, R., Fischer, S., Walpola, R. L., Chauhan, A., Babalola, T., Mears, S., & Le-Dao, H. (2021). Where Do Models for Change Management, Improvement, and Implementation Meet? A Systematic Review of the Applications of Change Management Models in Healthcare. Journal of Healthcare Leadership, Volume 13(13), 85–108. NCBI. https://doi.org/10.2147/JHL.S289176
Javied, T., Deutsch, M., & Franke, J. (2019). A model for integrating energy management in lean production. Procedia CIRP, 84, 357–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2019.04.252
Masfi, A., & Sukartini, T. (2022). Effectiveness Of Using The Mc Kinsey 7s Framework Model In Assessing Organizational Performance: A Systematics Review. Journal of Positive School Psychology, 6(8), 9136–9148. https://mail.journalppw.com/index.php/jpsp/article/view/11416
Suwanda, & Nugroho, B. Y. (2022). Literature Reviews: McKinsey 7S Model to Support Organizational Performance. Technium Social Sciences Journal, 38, 1. https://heinonline.org/HOL/LandingPage?handle=hein.journals/techssj38&div=2&id=&page=
Teh, D., Khan, T., Corbitt, B., & Ong, C. E. (2020). Sustainability strategy and blockchain-enabled life cycle assessment: a focus on materials industry. Environment Systems and Decisions. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10669-020-09761-4
 write
write