Introduction
In international infrastructure development, effective project management is the key to success, comprising complex processes set up within the scope of each project due to the unique nature of large-scale initiatives. Amidst the scope of such an environment, ABC Ltd., a leading construction company in Cyprus with a prudent yearly turnover, is recognised as the number one firm steering the wave of development on behalf of the authority. Given that it participates in a competitive international tender, ABC has to achieve a set of public investment projects that will successfully unfold over the next four years. This paper aims to divide and critically analyse the multifaceted management fields associated with ABC’s projects and the different challenges and opportunities those projects involve. More specifically, the examination will focus on exploring the project management processes and methodologies ABC uses in its ventures, considering the project’s variation in scope and scale. Besides, a comparative lens will unravel the differences between different types of project management, governance, and program management, as Lock’s typology specifies, thereby laying bare their implications for ABC’s strategic goals and operational process. ABC should adopt a strategic vision consistent with realistic operationalities throughout the project’s governance. This report aims to crystallise an approach to functional effectiveness through unifying corporate objectives with project management prerogatives.
Project Management Processes and Methodologies
Adequate project management systems and procedures are one of the most essential elements of achieving success in international infrastructure development. ABC Construction Firm operates in a diversified field. It has to effectively compete in the market by constructing airports, deploying telecommunication networks, and developing bridges. Consequently, it has to follow a structured strategy regarding the project’s scope, complexity, and scale. According to empirical studies by Takagi and Varajão (2021), this framework would serve as ABC’s baseline for building a system to manage large-scale projects, enable stakeholder involvement, mitigate risks, and allocate resources. Throughout the initiation and planning phases of the project, the apparent direction will be achieved through well-defined objectives, appropriate resource allocation, and strategic planning to meet the requirements. Effective communication strategies that will facilitate collaboration, monitoring, and control will, therefore, create the mechanisms that will enable ABC to track progress, identify risks, and implement corrective actions (Irfan et al., 2021). By integrating a plan that encompasses all the factors considered in terms of time, cost, quality, resources, and communication, ABC succinctly works through the complexities of infrastructure challenges and handles the utilities for the strategic objectives.
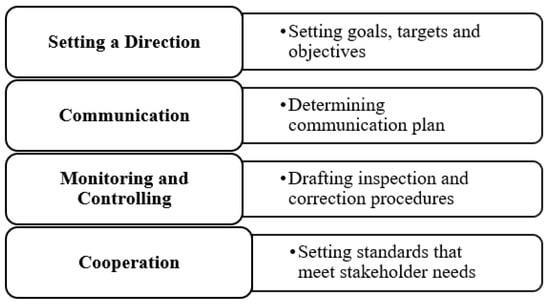
Figure 1: Traditional Planning
(Irfan et al., 2021).
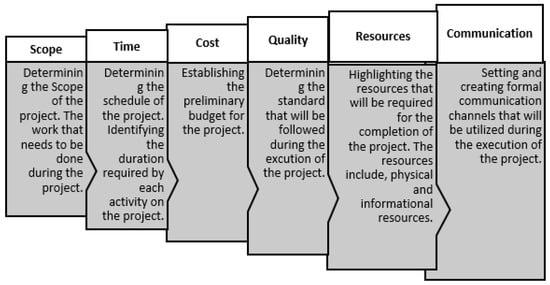
Figure 2: Project Management Planning
(Irfan et al., 2021)
Even with international infrastructure, projects can be characterised by their constantly changing nature; therefore, flexibility must be added because project management methodologies alone need to correspond to this fully. According to Alderman’s study (2021), agile principles should be applied in project management, mainly in unstable environments and fast change (Alderman, 2021). The emphasis on constantly changing development, collaboration, and adaptability of Agile methodologies can give ABC the agility to negotiate the unpredictability of project requirements and external factors (Alderman, 2021). By adopting a hybrid model that combines the planned approach of conventional methodologies with the adaptive features of agile techniques, ABC will efficiently deal with the multi-faceted proceedings that arise in its overseas infrastructure projects.
Besides that, the maturity of ABC’s project management processes should be at the top of the priority list for the company’s success. Hartono’s research (2019) highlighted that the best way to improve a project’s performance level is by emphasising project management maturity (Hartono, 2019). ABC should conduct an in-depth project management maturity assessment and target quick wins to drive the process improvement agenda (Hartono, 2019). Strengthening project management skills will enable ABC to realise global infrastructure success, thus optimising gains for all participants and consolidating its money to steer the whole construction business worldwide. This involves building a solid system, facilitating a creative environment, and applying best practices to meet changing project environments and industry standards (Locked, 2014). ABC will be able to remain a player in the game and survive in project managing complex infrastructure projects if it follows the path of maturing project management [Appendix 1].
Types of Projects Managed by ABC
Since ABC Construction Company is as diversified as it is, it can handle various projects for which different objectives and difficulties must be solved. Lock’s (2007) study estimates portfolio management, governance, and program management as the main types of projects based on their objectives, scale and organisational structures (Lock, 2007). As Shenhar et al. (2019) note, portfolio management is an executive decision-making process in which a selection of projects is made considering leadership goals and available resources (Shenhar et al., 2019, p. 700). Managing a portfolio for ABC Corporation will be crucial in allocating resources to infrastructure projects, from building airports to deploying telephone networks efficiently, while delivering the most significant value across them all, simultaneously making it the best value for money.
Amid the complexities of international infrastructure development, ABC is tasked with establishing robust governance mechanisms to ensure the success of projects and the satisfaction of beneficiaries. Jünge et al. (2019, p. 1120) state that governance is the overall framework jointly by policies, procedures, and decision mechanisms used to manage organisational projects (Jünge et al., 2019; p. 1120). ABC’s governance mechanism should be flexible to accommodate complex regulatory frameworks, stakeholder expectations, and contractual obligations within the presented environment. ABC needs to incorporate what it learns about governance structures and its governance framework to establish governance mechanisms that would create accountability, transparency, and compliance across all projects (Jünge et al., 2019; p1130). Through the adoption of the best practices of the industry, the company can minimise the risks associated with the project, optimise the decision-making process, and allocate the resources to stimulate project success.
Through programme management, ABC should develop a business strategy to meet the challenges of infrastructure projects in developing countries. As per Khan et al. (2019), program management is the critical element in bringing together different projects related to airport construction, telecommunication network deployment, and bridge construction projects that fall under the purview of the ABC portfolio (Khan et al., 2019). As put by Mortlock, Adam, and Reid (2022), the application of techniques similar to Program Management Professional (PgMP)® certification will help ABC achieve systematic management of project interdependencies, managing risks and maximising the use of resources to assist in the fulfilment of corporate strategic objectives (Mortlock et al., 2022). Such a proactive approach instead guarantees the compatibility of all projects, creating a flow that enhances effectiveness and efficiency in reaching ABC’s aims in the international construction landscape (Khan et al., 2019). Implementing program management principles will be a tool for ABC in solving the complexity of infrastructure development and delivering the project on schedule and per strategic vision and objectives.
It is imperative to ensure the optimal success rates of projects and organisational performance by aligning project types and managerial capabilities with strategic priorities. Lock (2014) emphasises principally that this alignment is necessary to improve the success of projects and organisational performance in general. Critical analysis of the project types in comparison with the managerial skills, market dynamics and stakeholder expectations may create the ground for information regarding the strategic making processes and resource division of the ABC Company (Lock, 2014). By considering project types, organisational competencies, and strategic goals, the enterprise can ensure the likelihood of desirable results and the organisation’s overall success. This strategic alignment ensures that the efforts of ABC projects are in sync with the company’s capabilities and strategic objectives, optimising value creation and stakeholders’ satisfaction (Takagi & Varajão, 2020). Through the indicators and alignment with a road map, ABC can choose the relevant projects and distribute the resources to reach maximum results in the competitive infrastructure development environment.
Achieving Operational Effectiveness
At ABC Construction Firm, the core nexus between the strategic, operational, and project levels is the critical determinant of success regarding project deliveries. Project strategy involves six elements: objective, product definition, market perspective, business perspective, project definition, and strategic focus (Poli, Shenhar 2003). For further details on this strategy, consult [Appendix 2]. The company’s ABC strategy stresses long-term visions, including exemplification of growth sustainability and expansion into new markets. The operational part of this strategic dimension is fulfilling these goals through practical assignments and activities throughout the whole organisation, from top to bottom (Musawir et al., 2017). Simultaneously, all tasks and deliverables are carefully set at the project level to meet each target milestone and objective (Hartono, 2019). The complex multilevelness guarantees the coherence of ABC’s operations with broader organisational goals.
The best way for ABC Construction Firm to achieve this objective would be to customise the strategies according to the categories of projects’ breakdowns and possibilities. Evaluating these methods requires implementing flexible project management approaches, which may include the adaptive approach described in [Appendix 3], for rapid response to the project’s emerging requirements (Shenhar et al., 2001). Advanced risk management practices have become an effective investment in operational efficiency by minimising disruptions and ensuring smooth project execution (Lechler et al. l, 2017). Applying the existing knowledge base not only means capitalising on discovery and reducing the threats but also implies increasing the operational effectiveness of ABC through a wide array of projects. This preventative approach makes ABC adaptable and prompt to accommodate changes, which secures better project results and stakeholder happiness (Takagi & Varajão, 2020). Using these tactics, ABC Construction Company gains a competitive edge in the industry and establishes itself as a leader among contractors with successful projects.
The recommendations for the operational processes, strategy, objective and performance measurement include applying quantitative performance metrics like Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to measure and monitor progress responsibly [Appendix 4]. As stated by Hidalho (2019), operational activities, to a greater extent, support an organisation’s vision, favour better performance evaluation, and identify areas that need improvement (Hidalgo, 2019). In addition, promoting a culture of teamwork and knowledge sharing between project teams can bring about excellent efficiency within the operational processes (Lock, 2014). By fostering shared knowledge and exchanging ideas, ABC Construction Firm Inc. can recruit the intellect of everybody in the organisation to bring innovation, boost efficiency and help the organisation achieve its long-term goals. These recommendations highlight the need for strategic objectives to be in harmony with operational processes to maximise overall project performance and complete satisfaction of stakeholders (Lock, 2014; Hidalho, 2019). These strategies can make ABC’s operations more efficient, ensuring that projects are completed successfully and giving ABC a strong competitive surge in the industry.
Conclusion
The discussion emphasises the importance of successful project management in global infrastructure development, as shown by a field study of ABC Construction Company. Throughout the review, the paper looked into the comprehensive interaction between strategy, operations and projects, underlining the significance of alignment for successful project implementation. By translating strategic goals into working programs and initiatives, ABC will reach a high level of coherence and synergy across all levels of operations, which means that the project outputs will be maximised and there will be satisfaction among the stakeholders. Beyond that, self-evaluation of the necessity of comprehending the systems and approaches of management projects, methodologies and organisational dynamics will emerge as the fundamental success factor. Research results stress the importance of adaptive project management models and risk management standards and the creation of collaboration culture as the primary ways to overcome the complexities of international infrastructure projects. By incorporating these observations into its project management practices, ABC can reduce risks, seize opportunities, and affect project completion. Moving forward, critical activities for the future project include fostering operational excellence through project management practices and strategically aligning project objectives to achieve the highest value possible. A continuous learning and improvement culture is one of the critical pillars of ABC’s strategy for staying ahead of the curve, identifying new trends, and integrating the latest technologies and best practices, providing a substantial advantage and prospects for long-term growth. Besides, multiplying project management practices alignment with strategic goals guarantees that ABC always strives to deliver real value to the shareholders and stakeholders while maintaining operating efficiency and effectiveness. In a nutshell, competent project management is the foundation that enables international infrastructure projects to succeed. By adapting best practices, promoting collaboration and working out operational processes with strategic objectives, the ABC Construction firm has the tools to successfully concentrate on various projects without damaging productivity.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Alderman, N. (2021). The Paradoxical Profession: Project Management and the Contradictory Nature of Sustainable Project Objectives – Luca Sabini, Neil Alderman, 2021. [online] Project Management Journal. Available at: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/87569728211007660 [Accessed 18 Mar. 2024].
Hartono, B. (2019). The impact of project risk management maturity on performance: Complexity as a moderating variable – Budi Hartono, Deo F Wijaya, Hilya M Arini, 2019. [online] International Journal of Engineering Business Management. Available at: https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1847979019855504 [Accessed 18 Mar. 2024].
Hidalgo, E.S. (2019). Adapting the scrum framework for agile project management in science: a case study of a distributed research initiative. Heliyon, [online] 5(3), pp.e01447–e01447. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01447.
Irfan, M., Sanam Zaib Khan, Hassan, N., Hassan, M., Habib, M., Khan, S. and Hadi Hassan Khan (2021). Role of Project Planning and Project Manager Competencies on Public Sector Project Success. Sustainability, [online] 13(3), pp.1421–1421. doi:https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031421.
Jünge, G.H., Alfnes, E., Kjersem, K. and Andersen, B. (2019). Lean project planning and control: empirical investigation of ETO projects. International Journal of Managing Projects in Business, 12(4), pp.1120-1145.
Lock, D. (2014). The essentials of project management. Routledge.
Musawir, A. ul , Eduardo, C., Zwikael, O. and Ali, I. (2017). Project governance, benefit management, and project success: Towards a framework for supporting organisational strategy implementation. International Journal of Project Management, [online] 35(8), pp.1658–1672. doi https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijproman.2017.07.007.
Poli, M. & Shenhar, A. (2003). Project Strategy: The Key to Project Success. [online] ResearchGate. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/4029624_Project_Strategy_The_Key_to_Project_Success [Accessed 18 Mar. 2024].
Shenhar, A.J., Dvir, D., Levy, O. & Maltz, A.C. (2019). Project Success: A Multidimensional Strategic Concept. Long Range Planning, [online] 34(6), 699–725. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/s0024-6301(01)00097-8.
Steyn, H. (2002). Project management applications of the theory of constraints beyond critical chain scheduling. International Journal of Project Management, [online] 20(1), 75–80. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/s0263-7863(00)00054-5.
Takagi, N. and Varajão, J. (2020). Success Management and the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK): An Integrated Perspective. [online] AIS Electronic Library (AISeL). Available at: https://aisel.aisnet.org/irwitpm2020/6/ [Accessed 18 Mar. 2024].
APPENDICES
Appendix 1: The Portfolio, Program and Project Management Maturity Model (PM3M)
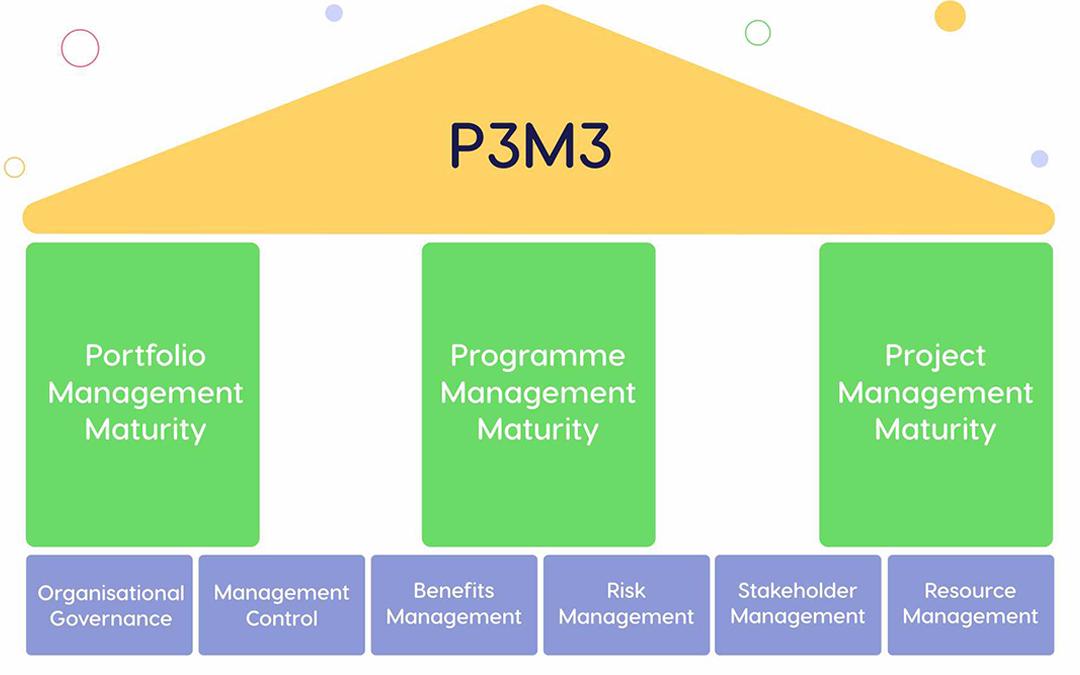
Source: Sokolova, V. (2022). An Overview of Project Management Maturity Models – EpicFlow. [online] Epicflow. Available at: https://www.epicflow.com/blog/project-management-maturity-models-a-basis-for-reaching-your-organizations-business-success/ [Accessed 18 Mar. 2024].
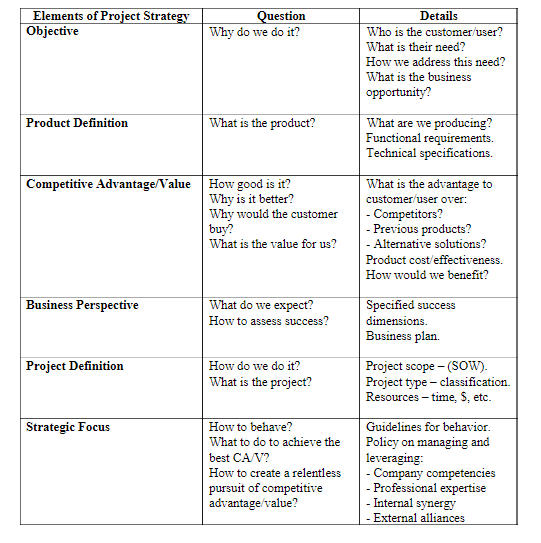
Appendix 2: Six Steps for Effective Project Strategy
Source:(Poli & Shenhar, 2003)
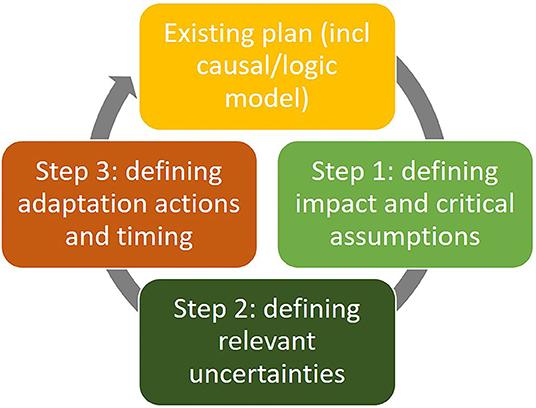
Appendix 3: Three Adaptive Planning Steps
Source:Versteeg, N., Hermans, L.M., Ahrari, S. and De, V. (2021). Adaptive Planning, Monitoring, and Evaluation for Long-Term Impact: Insights From a Water Supply Case in Bangladesh. Frontiers in water, [online] 2. doi:https://doi.org/10.3389/frwa.2020.621971.
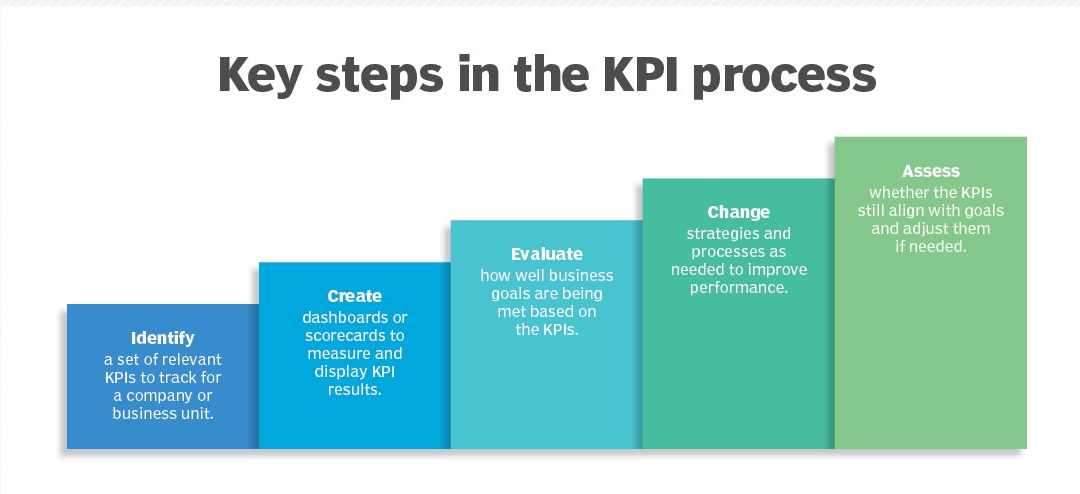
Appendix 4: Key Steps in the KPI Process
Source: Kinza Yasar and Stedman, C. (2023). key performance indicators (KPIs). [online] Business Analytics. Available at: https://www.techtarget.com/searchbusinessanalytics/definition/key-performance-indicators-KPIs [Accessed 18 Mar. 2024].
 write
write