Introduction
Hospital organizations ought to understand the role of learning at the workplace as the foundation for recognizing the complexities of dealing with medication administration errors. The generation of insight into the parameters of learning should be within the purview of decision-making and involvement of the stakeholders in translating theory into practice. Learning and workplace extension of knowledge should consider the context of operations and embark on necessary transformative initiatives for quality service delivery. Regarding the Harvard Report 2018, it is apparent that conceptualizing the workplace as a learning environment should comprise diversity in activities and interactions to translate positive change. The context and purpose of influencing learning are through the involvement of stakeholders in decision-making and improving immediate performance.
As a nurse in the County hospital, workplace learning is crucial, especially for the interns to deal with medication administration areas. Individuals and workplace learning parameters should center on a participative mechanism geared at improving skills and competence to handle possible errors. Consequently, the hospital’s focus is developing expertise to handle the medical administration process professionally. Learning theory novices are crucial within the county hospital and can play an integral role in expanding the dimension of healthcare practice. Through the assessment of the hospitals, it is apparent that the creation of the best approaches to learning can be developed.
Thus, the essay’s primary purpose will be on the Facilitating Workplace Learning (FWL) Module through a case study analysis. Therefore, in the module, I learned about the need for cultural integration, knowledge expansion, and theory translation into practice to improve personnel skills. Emphasis on a learning style that would enhance service delivery and harness a reflective framework to operations is integral for a positive outcome. Learning activities such active approach to impacting knowledge, teamwork, and discussions led to an enabling platform to recognize the need to facilitate learning. Therefore, this paper will be divided into two sections to examine ways to facilitate learning. Through a background in the first section, the use of Bloom’s taxonomy should present insight into the progress made in accessing necessary knowledge.
Progressive measures that center on expanding strategic adaptation to the workplace require the need to accept learning and reflection for positive change. In the second section, the hospital workplace will play an essential part in highlighting the role of the assimilation theory of learning as a tool to promote interns to acclimate to the code of practice. Central to the section is to highlight my role as a nurse and the part I can play in expanding knowledge and skills about medication error management. Discussion of the nursing role in medication management through the theoretical framework should be the foundation for positive change.
Section 1 Reflection on the Facilitated Learning Session
At the county hospital, it became apparent that the need for strategic integration of the interns into the organization should entail awareness of the code of practice. Central to the review and preparation was the focus on introducing the interns to the organizational, operational mandate (Jiang et al., 2022). A descriptive assessment of the structures and systems that shape medication use management was crucial to establishing the goals and objectives (Di Simone et al., 2018). At the county hospital, it was evident that the need for inclusivity in accepting medication errors impacted business conduct.
Hence, the targeted learners were the interns who would be inculcated into the organizational operations. Throughout the reflection, the focus would be the need to acknowledge professionalism in the medication process as fundamental to positive-centric outcomes. While they were students, lessons about good medication management practices were within the performance mandate (Marquez Hernandez et al., 2019). Upholding the ethical codes while focusing on expertise in service delivery is within the mandate of conduct. Therefore, harnessing safety and dignity as dilemmas in medication error management would be the starting point in the reflective process (Di Simone et al., 2018). The involvement of the interns in decision-making and recognition of their place in medication error management entails the broad context of evaluation of immediate challenges that the county hospital places (Carreiraa & Jang, 2021). Arguably, the information relay on the part that the patients and healthcare colleagues play within the broad context of workplace learning culture is in line with the transformation of operations.
Therefore, in preparation for the facilitation learning session, the aim is to promote strategic adaptation to the workplace codes of practice on medication error management. Teaching and feedback management of the interns are within the goals and objectives to ensure they are aware of the workplace expectations. Most importantly, Bloom’s taxonomy should generate insight into the cognitive competence and determination of the appropriate response to medication error management (Di Simone et al., 2018). Bloom’s theory centers on the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor avenues of skill growth and knowledge acquisition. The cognitive approach denotes the knowledge-centric avenue that recognizes the input of the multiple stakeholders and service delivery parameters. The affective domain entails the improvement of the attitude of the interns through inclusivity in the learning paradigms (Hazen et al., 2018). Psychomotor areas denote skills-centric initiatives that can lead to education as a tool for education and empowerment. Leveraging the levels of the Taxonomy can lead to strategic development and implementation in medication error management.
Brief details of the learner
As mentioned, the targeted learners are the nurse interns who are regularly integrated into the country hospitals. The interns emanate from the local university and have been exposed extensively to theoretical models to deal with medication administration errors. Central to targeting them is the low level of firsthand experience in the healthcare organization. The emphasis on an enabling platform where the interns can expand their skills and competence bout medication errors should be within the purview of decision-making (Carreiraa & Jang, 2021). The interns should comprehend that errors are an integral part of the organization. With most errors emanating from the natural process of cognitive and behavioral transition to the organization, selecting interns is based on the need to ensure that they adapt the correct behavioral skills. Emphasis on their low levels of firsthand experience will be the primary reason for their selection since they require the necessary codes of practice and instructional process. The administration and nurses playing a prominent role in promoting learning for the interns should meet their cognitive and behavioral needs (Di Simone et al., 2018). Acknowledgment of the changing operational framework of the hospital will be the basis for the involvement of the interns, who will play a crucial part in the transformation of the parameters of medication error management (Hazen et al., 2018). The participative techniques that center on developing a care team and a committee to review performance and control measures will align with the project to involve the interns in the learning dynamics. Situational awareness of the cognitive and behavioral needs of the interns should define the goals and objectives that will be geared toward improving the current hospital’s code of practice.
Teaching Plan
While preparing for the facilitation learning initiative, the objective is to promote an enabling platform whereby the interns can adapt to the set codes of practice in medication error management. From intravenous injection management to dosage review and dilution, it will be prudent to expand the skill and competence of the interns (Marquez Hernandez et al., 2019). Management of the errors requires a focus on awareness and determination of an effective route for administrative competence in regulating medication errors. Hence, using Bloom’s taxonomy of learning will assist the teaching plan. Harnessing the principles of creation, evaluation, analysis, application, comprehension, and remembrance will be vital to decision-making (Edmondson, 2018). The six approaches will be the foundation for determining the sequence of events that will shape decision-making. The medication error management skills will depend on the learners conforming to the six-step initiatives for successful outcomes.
Teaching plan through six-step initiatives
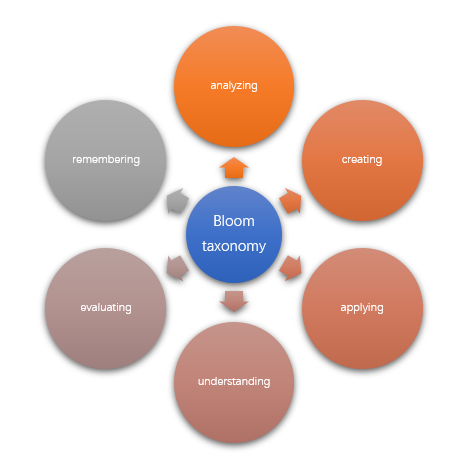
Figure 1: retrieved from Jiang et al. (2022)
The six significant activities are geared at implementing an enabling platform that the interns understand the hospital’s expectations in medication error management. Throughout the operational objective, minimizing confusion and expanding situational competence should translate into successful outcomes (Di Simone et al., 2018). Developing a comprehensive evaluation of the terminologies and action plan should ensure that the interns are empowered about the pathway to success.
Remembering the workplace operations entailed expanding competence in retrieving and recognizing the principles of medication error management (Carreiraa & Jang, 2021). The interns would recall the relevant knowledge and translate it from theory to practice. Developing skills and competence would be the appropriate measure for sustainable outcomes. Understanding the teaching process would denote the construction of meaning from the oral to the written platform. Interpretation and classification of the errors would be an appropriate approach to infer and explain the parameters of decision-making (Jiang et al., 2022).
On the other hand, applying denotes the execution of the diverse procedures and observation of the interns in meeting the performance expectations. Analysis and evaluation denote judgments about the set operational goals and objectives that would lead to positive implications (Carreiraa & Jang, 2021). Creating entails putting all the elements that constitute the organizational medication error management for functional outcomes. Reorganizing the goals and objectives and including the interns should translate into success.
Hence, as a teacher, it is apparent that the module was a memorable process that led to an appreciation of knowledge competence as the basis for learning. Throughout the module, it was central for the examination of the perceptions of the interns in the operational mandate (Di Simone et al., 2018). Upholding the tenets of teaching would be in line with functional competence in executing immediate services (Marquez Hernandez et al., 2019). Therefore, the teaching dynamics would comprise regular evaluation of the interns’ perspectives as the foundation for positive outcomes.
All in all, the learning parameter led to the recognition that it is a challenge to eliminate medication errors. The role of the staff should be within the purview of minimizing and preventing errors and conforming to the set expectations (Jiang et al., 2022). Hence, accepting the influence of supervision and planning were essential lessons that led to accepting the part that staff can play in maximizing patient care and safety (Carreiraa & Jang, 2021).
Section 2 Discussion of 2 topics from the module
Assimilation theory and learning at the workplace
As a teacher and nurse throughout the module, it was apparent that the assimilation theory is an essential framework throughout the learning process at work. The theory centers on accepting meaningful reception in teaching as dependent on a direct relationship with the stakeholders (Rahmat et al., 2019). Primary involvement in acquiring new meanings from the present learning material is within the purview of the assimilation theory (Hanfstingl et al., 2019). The interaction with multiple stakeholders in the module experience led to the acceptance of the learning set and the presentation of considerably meaningful material to the interns.
Thus, reflecting on the module, it is clear that the promotion of learning at the workplace requires situational awareness of the diverse models that can enhance and meet the set goals and objectives. The assimilation theory of learning proposes that anchoring ideas whereby new material can be related entail comprehending the cognitive structure and role in decision-making (Clark, 2018). The evaluation of the actual and practical meanings of the goal and objective development can lead to unique approaches to the empowerment of the stakeholders (Murtazin et al., 2022). Navigating the need to deploy the assimilation approach is based on the role of inclusivity and instructional competence in the learning paradigm. The theory is experimental and requires regular improvement to conform to the immediate requirements for the empowerment of the personnel.
Throughout the module, it became clear that the concept of assimilation emerged as a vital tool to promote positive change. The generalized assessment of the business situations can be the blueprint for instigating disruptive mechanisms for organizational improvement (Hanfstingl et al., 2019). Despite the critics of promoting an enabling platform for educating and empowering people on medication error management, it is crucial to assess faults and define factors in decision-making (Rahmat et al., 2019). Considering the assimilation theory from experience would be the basis for assessing the interplay of integration and participative process in decision-making. Navigating the social boundary would be the basis for the assimilation theory that would play a pivotal part in improving decision-making (Murtazin et al., 2022). The general assessment of the underlying situations would translate into strategic measures for enhancing operations (Clark, 2018). Current theory shows that the dynamism of embracing change entails openness and regular inclusivity as the objective for success.
Assimilation theory should be the standard for harnessing positive change in the institutional setting. The framework depends on the appreciation of the process of acculturation as the strategic initiative to ensure adaptation to the set expectations (Hanfstingl et al., 2019). Hence, the process in the module was recognized as comprising of the negotiation of identities, determination of developmental needs, and focus on the social or economic transition to the new environment. Therefore, Clark (2018) emphasizes that the classical assimilation theory portrays adaptation to the environment as an integral component of dealing with immediate challenges. A review of the essential factors that may enhance or dissuade strategy implementation should be the way forward.
Assimilation theory is vital for recognizing the sociological and economical dimensions that influence decision-making. Acknowledgment of the unique paradigm that shapes decision-making can lead to establishing the principles of operations (Hanfstingl et al., 2019). A primary approach of the assimilation model is conformity to a holistic initiative that emphasizes situational benefits in the improvement of the well-being of the individual.
Thus, the module on diverse theories that can reshape the learning process led to recognition of the assimilation framework as the basis for transforming the organizational environment. Focus on a holistic-centric approach to the transformation of learning experiences denotes the assessment of the goals and objectives to define the pathway to success (Rahmat et al., 2019). Learning outcomes geared toward improving well-being can be influential in the progress of the individual and can lead to positive implications in the service execution (Hanfstingl et al., 2019). Assimilation theory is a vital lesson that presents insight into the change paradigms that ought to be deployed in the learning dynamics.
Bloom’s taxonomy and workplace learning framework
The module was an empowering session that recognized Bloom’s taxonomy as a blueprint for transforming operations. Accordingly, the theoretical model involves facilitating change in the individual’s position through detachment from overreliance on supervision (Hewett et al., 2018). Hence, as a facilitator in the learning outcomes, the focus on the active engagement of the participants was based on the taxonomy that set the standard for translating theory into practice (Di Simone et al., 2018). Evaluation of the workplace components throughout the course was apparent as the basis to reflect the transition into a knowledge-centric environment.
Through the module, the learning activities in the organizational setting are based on observation, application, and extensive reflection (Murtazin et al., 2022). For example, the module’s specific case was based on medication error management at the local hospitals that required the best learning strategy (Himmler et al., 2022). Arguably, the emphasis on reflection and demonstration of knowledge construction would be the transformative pathway in the learning process (Di Simone et al., 2018).
Most importantly, adopting Bloom’s taxonomy was a learning platform to comprehend the work-integrated objectives and demonstrate efficiency in conduct (Marquez Hernandez et al., 2019). Constructing one’s learning outcomes entails the taxonomy that emphasizes evaluating cognitive and behavioral expectations. Examined six levels highlight the need for a guide that defines the pathway to success (Himmler et al., 2022). Execution and reporting of the tenets of operation entail an all-inclusive learning platform.
Throughout the module, it became evident that the integrated learning experience would depend on using strategic measures that recognize the input of diverse stakeholders. Taking a central stage is harnessing the productive and distributive competence of knowledge in the review of the performance mandate of stakeholders (Murtazin et al., 2022). In theory, the focal point of the learning platform is harnessing an integrated approach to generate learning that reflects immediate needs. Assessment of the taxonomy highlights the practice-centric approach to education that broadly aims at moving from theory to practice (Murtazin et al., 2022). Effectiveness and efficiency in deploying necessary models of operations are through a welfare-centric learning platform (Himmler et al., 2022). Timely assessment of the learning dynamics is apparent as the strategic initiative in the taxonomy’s mandate.
It is crucial to firmly endorse the taxonomy within the workplace since it provides step-by-step measures to enhance learning. The practice-centric initiatives promote workplace learning and conceptualize the systematic features that shape decision-making (Jiang et al., 2022). Assessment of the skills implied through the framework can have a transformative implication in analyzing the part played in workplace teaching (Di Simone et al., 2018). The relationship of the multiple stakeholders with the professional expectations is integral to the theoretical expectations.
Accordingly, the theory demonstrates the professional transition of the taxonomy throughout the workplace. Harnessing the operational competence characteristic of the theory entails the six stages of learning and improvement of the personnel’s wellbeing. The level of knowledge ought to be improved by leveraging knowledge and skills for successful outcomes (Carreiraa & Jang, 2021). Hence, the paradigm shift in the deployment of the theory can lead to the definition of the practical measures of change that can be implemented.
Conclusion
Addressing workplace learning is an integrated aspect that entails harmonizing theory and practice. The module played a significant part in recognizing the adoption of Bloom’s taxonomy and assimilation theories as crucial in improving staff welfare. Focus on empowerment and education was within the purview of the reflective initiatives and expansion of knowledge. In the quest to strategically integrate the interns into medication error management, it is vital to leverage the Taxonomy and assimilation theories as the basis for positive change. Recognition of their input in improving operations should be the foundation for progressive initiatives. Through the assessment of the learning paradigm, it is apparent that the module was an enabling platform to recognize the workplace factors that shape empowerment and knowledge expansion.
References
Carreiraa, P., & Jang, H. (2021). The benefit of implementing Bloom’s Taxonomy to improve job-based Learning Quality: A study of junior programmer internship. The Journal of Worker Competence and Performance (JWCP), 1(01), 18-26.
Clark, K. R. (2018). Learning theories: cognitivism. Radiologic Technology, 90(2), 176-179.
Di Simone, E., Giannetta, N., Auddino, F., Cicotto, A., Grilli, D., & Di Muzio, M. (2018). Medication errors in the emergency department: knowledge, attitude, behavior, and training needs of nurses. Indian journal of critical care medicine: peer-reviewed, official publication of Indian Society of Critical Care Medicine, 22(5), 346.
Edmondson, A. C. (2018). The fearless organization: Creating psychological safety in the workplace for learning, innovation, and growth. John Wiley & Sons.
Hanfstingl, B., Benke, G., & Zhang, Y. (2019). Comparing variation theory with Piaget’s theory of cognitive development: more similarities than differences? Educational Action Research, 27(4), 511-526.
Hazen, A., de Groot, E., de Gier, H., Damoiseaux, R., Zwart, D., & Leendertse, A. (2018). Design a 15-month interprofessional workplace learning program to expand the added value of clinical pharmacists in primary care. Currents in Pharmacy Teaching and Learning, 10(5), 618-626.
Hemmler, Y. M., Rasch, J., & Ifenthaler, D. (2022). A categorization of workplace learning goals for multi-stakeholder recommender systems: A systematic review. TechTrends, 1-14.
Hewett, S., Becker, K., & Bish, A. (2018). Blended workplace learning: The value of human interaction. Education+ Training.
Jiang, Y., Lin, W., Huang, X., Duan, L., Wu, Y., Jiang, P., & Wang, X. (2022). How to prompt training effectiveness? An investigation on achievement goal setting intervention in workplace learning. Journal of Workplace Learning, (ahead-of-print).
Marquez Hernandez, V. V., Fuentes-Colmenero, A. L., Cañadas-Núñez, F., Di Muzio, M., Giannetta, N., & Gutiérrez-Puertas, L. (2019). Factors related to medication errors in the preparation and administration of intravenous medication in the hospital environment. PloS one, 14(7), e0220001.
Murtazin, K., Shvets, O., Meeter, M., & Piho, G. (2022, May). Characteristics of Learning Outcomes for Integrating Work-Based Learning into the Business Information Technology Study Program. In 2022 45th Jubilee International Convention on Information, Communication and Electronic Technology (MIPRO) (pp. 1307-1312). IEEE.
Rahmat, N. H., Othman, N. A., Muhammad, A. M., Anuarudin, A. A. S., & Arpin, M. (2019). Assimilation and accommodation: exploring the dynamics of class discussions. European Journal of Education Studies.
 write
write