Patient care quality involves providing adequate healthcare services or processes to people to achieve desirable or appropriate outcomes. For maximum benefit, quality care must feature timely delivery, equity, integration, and efficiency of health services to patients. However, diagnostic errors by physicians can affect the quality of care delivered to individuals in hospitals. Some critical diagnostic errors in healthcare facilities accounting for high risk to patients’ safety include misdiagnosis and delayed or missed diagnostic errors. These errors inhibit the chance to provide an appropriate and prompt diagnosis, affecting patients’ safety and care quality. The paper assesses diagnostic errors, solutions, implementation, timeline, and analysis and dissemination plans.
Problem or Issue
Physicians diagnose patients with different diseases, making them an integral part of quality care. They play a critical role in influencing the safety of patients and the quality of care provided in healthcare facilities. However, physicians could cause diagnostic errors resulting in adverse health outcomes among hospitalized and non-hospitalized patients. Some actions, such as missed diagnosis, misdiagnosis, or physicians delaying diagnosing patients, emanate from negligence, miscommunication, limited experience, and lack of appropriate time with individual patients. Diagnostic errors are among the critical medical or quality care issues affecting the well-being of patients seeking treatment from healthcare facilities. According to Baylor College of Medicine (2015), about twelve million individuals in the U.S. are victims of diagnostic errors in different hospitals but asserts that need to change this problem to avert a potential health crisis among Americans. Therefore, diagnostic errors are a risk to clinical practice towards achieving maximum patients’ benefits from treatment processes.
One of the prevalent diagnostic errors is misdiagnosis, which involves diagnosing individuals for health disorders they are not suffering from or patients testing positive for medical or ailment conditions which are not accurate. Another serious diagnostic error is delaying to diagnose patients as per the stipulated schedule. Finally, missed diagnosis is another severe quality care lapse that occurs when patients are not diagnosed at all by the physicians or responsible medical practitioner. These diagnostic errors affect the quality of care people get from hospitals by deterring quality treatment, impeding patients recovery, prolong hospitalization, or even cause mortality among the affected patients.
Proposed Solution
Diagnosis is the background of healthcare processes and quality care provision without which patients wellbeing is at risk. Therefore, it is critical for healthcare facilities to encourage a culture of quality diagnosis to guarantee appropriate treatment and medication for their patients. Comprehending diagnostic errors is challenging and evidence-based approaches should be used to detect and prevent such errors from regularly happening in a healthcare facility. Since the safety of patients is conventionally evaluated on the basis of successful healthcare service delivery other than failures, it sometimes becomes difficult to detect diagnostic errors in a complex work setting involving different team members in the diagnosis of patients. Experienced physicians, clinicians, or doctors will train their colleagues concerning diagnostic safety using different training techniques.
The training will enlighten physicians how to effectively communicate with their clients during diagnosis. Effective communication with patients being diagnosed will allow physicians or doctors to get in-depth information to understand patients’ medical history. Physicians and doctors will about allocating enough time per patient in order to robustly diagnose their condition without leaving important details. Olson et al. (2021) suggest that medical staff burnout affects quality time for delivering quality care causing diagnostic errors. Taking appropriate time with patients can allow a doctor to understand their physiological processes and determine the causes of body’s malfunction. The training will also focus on teaching physicians on building effective teamwork to ensure that diagnoses made by different physicians, doctors or clinicians give similar outcomes. If the diagnosis made by a team give varied results, then further diagnosis should be conducted until the source of the diagnostic error is determined and eliminated. Enhancing a culture of safety within health facility reduces risks against patients and enhances quality care impacts on patients’ recovery (Weaver et al., 2013). Teamwork will also help physicians or doctors to work closely with other health practitioners like radiologists or lab technicians to interpret sophisticated lab test results or diagnosis data. Physicians or doctors will also learn how to use technology in the diagnosis process to eliminate or minimize probable diagnostic errors.
Implementation Plan
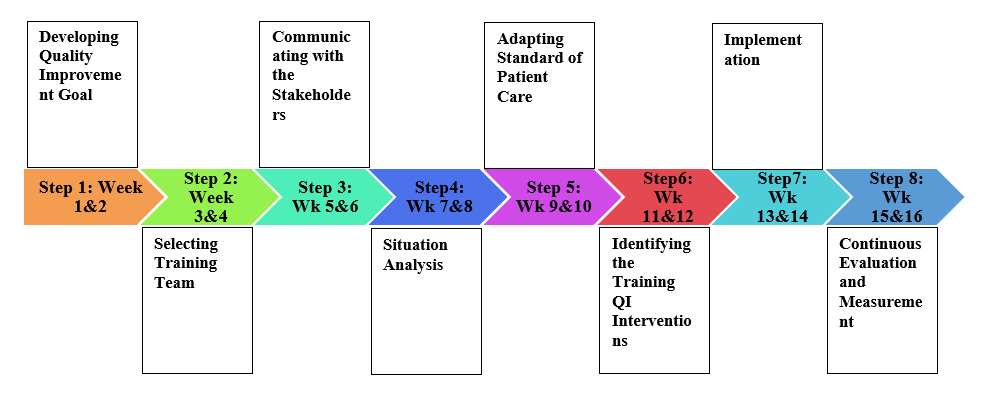
Step 1: Develop Quality Improvement Goal
The first step will involve identifying and defining vision or goal of improving quality of care for patients concerning diagnosis safety. The goal involves enhancing healthcare workers understanding of standards and processes for achieving diagnosis safety.
Step 2: Selecting Training Team
The step will include a selection of qualified and skilled trainers to conduct the training sessions with the selected physicians, clinicians and doctors to participate in the diagnostic safety training program.
Step 3: Communicating with the Stakeholders
The stage will help in communicating with relevant stakeholders, such as physicians, clinicians, and doctors about the goal of the training program.
Step 4: Situation Analysis
Situation analysis will involve determining the level of diagnostic errors prevalence in the healthcare facility over the past six months. It will include evaluating data on reported misdiagnosis, delayed and missed patients’ diagnosis. There will also be an examination of near miss diagnostic error incidences.
Step 5: Adapting Standard of Patient Care
This step will include defining standards associated with the quality of care improvement. Therefore, the leadership team will adopt standards of training the healthcare workers involved in diagnosis processes.
Step 6: Identifying the Training Quality Improvement Interventions
This step will involve brainstorming the most effective and appropriate diagnostic safety training techniques to teach those involved in the exercise. Some of the interventions to be used in this process include in-class presentation, group sessions, and in-service training.
Step 7: Implementation
The step involves implementing the diagnostic safety training for physicians, clinicians and doctors, among other practitioners. This step will include implementation of the training through daily sessions lasting no more than two hours.
Step 8: Continuous Evaluation and Measurement of the Quality Improvement
This step will involve on-site evaluation of the success of the training accorded to the physicians, doctors, and clinicians, among others. It will involve measurement of the quality improvement outcomes associated with reduction in near-miss cases and diagnostic errors in the healthcare facility.
Timeline
The training period or schedule is four months and will involve daily sessions using different training approaches or techniques. Each activity as stipulated in the implementation plan will run for two weeks, with each activity not going for more than two hours every day with the exception of weekends. The training will be implemented in eight phases totaling to sixteen weeks with each activity being undertaken in two weeks. Some of the training techniques will include presentations, group-focused activities, and workplace simulation exercises to assess the healthcare practitioners understanding of diagnostic safety concepts taught in the sessions. Please refer to Appendix A for more information on the figure highlighting activities and their timeline.
Evaluation Plan
Step 1: Engage the Stakeholders
This step will involve designing a conceptual framework and determination of essential evaluation terms, which will be shared with the participants of the training program. It will help comprehend the expected evaluation outcomes.
Step 2: Explain the Evaluation Process
The step includes describing the evaluation process by defining its realistic measurable output. The process involves designing evaluation questions to determine the short and long-term results of the diagnostic safety training.
Step 3: Developing Evaluation Design
This step will involve aligning the diagnostic safety training goals and visions while addressing the limitations of the training. In this process, the subject of evaluation is assessing physicians, doctors and clinicians’ adherence to diagnostic safety procedures as taught during the training. Evaluation techniques include assessing a number of safe diagnostic procedures and that of failure to adhere with diagnostic procedures during work.
Step 4: Collecting Reliable Data
Collection of data is a critical step in the evaluation process of quality care improvement program. The phase will involve deciding on which methodological design to use and the tools to use for the data collection procedure. The training program’s data collection techniques will include observation, surveys, and retrieval of diagnostic data from files recording diagnostic errors and near-miss incidences.
Step 5: Analyzing Data and Justifying Findings
Data analysis on the success of diagnostic safety training program will help to determine the rate of adherence to diagnostic safety by the physicians and clinicians involved in the training sessions or program. It involves grouping data into themes that will make it easy to justify the findings of evaluation as shown in the data gathered.
Step 6: Use of Findings and Sharing Lessons Learned for Quality Improvements
The findings of the evaluation processes must help in further improving quality care plan by refining the diagnostic safety adherence in the health facility or among the healthcare practitioners like physicians or clinicians. The lessons learned will help in bridging the gaps identified during the evaluation process to promote a culture of diagnostic safety among physicians or clinicians and other relevant healthcare practitioners.
Dissemination Plan
The dissemination is the process of sharing or spreading information concerning a given project or product to its target users. Therefore, a dissemination plan is the plan stipulating how an organization or program will share vital information about specific details of its outcome with its users. Organization of roundtable meetings will help communicate different issues and share perspectives. The hospital administration and the contacted trainers will conduct the roundtable meetings, which will target physicians, doctors, and clinicians. Interim and final conferences will also help communicate with the relevant stakeholders and will be organized by the healthcare facility’s administration.
The training team and the healthcare facility leadership will organize the feedback surveys with the relevant healthcare workers to get their feedback concerning compliance and progress of training and diagnostic safety adherence. Seminars and workshops run by the trainers will help disseminate relevant information to the healthcare practitioners on effective diagnostic safety approaches. Email communications will help to communicate with the relevant participants of the training about training session activities and expected outcomes. Finally, the training team and the leadership of the facility will undertake participation in giving regular opinion with the participants to share their insights about the progress and satisfaction rates of the training program. Kindly see the detailed dissemination plan attached in Appendix B.
Conclusion
Diagnostic errors issue is emerging as one of the serious threats against patients’ safety and quality care provision in healthcare facilities. At least every person once in their lifetime have been subjected to a diagnostic error while seeking medical treatment in a healthcare facility or from a healthcare worker. Therefore, it should be countered using evidenced-based measures to inhibit its adverse impacts on patients seeking treatment or medication in hospitals. Diagnostic errors can result in adverse health outcomes if not monitored and inhibited, such as wrong treatment, prolonged hospitalization, increased morbidity, injury, and mortality among patients. Therefore, the diagnostic safety training program is essential in building the capacity of healthcare staff intrinsically involved in diagnosis of patients to improve diagnosis safety in hospitals.
References
Baylor College of Medicine. (2015). Reducing misdiagnosis: time for the next chapter in improving patient safety. https://www.bcm.edu/news/reducing-misdiagnosis-patient-safety.
Olson, A., Linzer, M., & Schiff, G. D. (2021). Measuring and Improving Diagnostic Safety in Primary Care: Addressing the “Twin” Pandemics of Diagnostic Error and Clinician Burnout. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 36(5), 1404–1406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-021-06611-0.
Singh, H., Graber, M. L., & Hofer, T. P. (2019). Measures to Improve Diagnostic Safety in Clinical Practice. Journal of Patient Safety, 15(4), 311-316. https://doi.org/10.1097/PTS.0000000000000338.
Weaver, S. J., Lubomksi, L. H., Wilson, R. F., Pfoh, E. R., Martinez, K. A., & Dy, S. M. (2013). Promoting a culture of safety as a patient safety strategy: a systematic review. Annals of Internal Medicine, 158(5 Pt 2), 369–374. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-158-5-201303051-00002.
Appendices
Appendix A: Timeline of the Training Program
Appendix B: Dissemination Plan
| Activity | Done by Whom | Target Audience | Purpose of the Activity | Deadline |
| Roundtable Meetings | Trainers with support of hospital leadership | Physicians, Clinicians, and Doctors. | Sharing information about planned sessions and needed preparations. | Every Week |
| Interim Conferences | Trainers with support of hospital leadership | Physicians, Clinicians, and Doctors. | Communicating vital issues about the training and offering clarity on the training program. | Every Week |
| Feedback Surveys | Trainers with support of hospital leadership | Physicians, Clinicians, and Doctors. | Requesting feedback concerning insights of the training sessions. | Every Two Weeks |
| Seminars and workshops | Trainers with support of hospital leadership | Physicians, Clinicians, and Doctors. | Getting perspectives of participants and brainstorming on the training success and lapses. | Every Two Weeks |
| Email Communications | Trainers with support of hospital leadership | Physicians, Clinicians, and Doctors. | Sharing vital information every day concerning training issues. | Everyday |
| Regular Opinion Sessions | Trainers with support of hospital leadership | Physicians, Clinicians, and Doctors. | Getting participants opinions concerning the training and how it can be personalized. | Every Week |
| Final Conference | Trainers with support of hospital leadership | Physicians, Clinicians, and Doctors. | Sharing information about the progress and success of the training sessions held with the participants. | The Last Week |
 write
write