Introduction
Since its conception in 1956 by Amar Bose, a teenage and electronics enthusiast, Bose has boasted a significant reputation in fulfilling its respective customers’ experiences (“The First 50 Years of Bose,” 2022). The website affirms that Bose is a product of an idea that became an obsession to a genius teenager who has proved to be a legitimate guru in his radio repair premise at his school, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). For more than half a century, Bose has followed its founder’s philosophy by showing determined efforts toward maximizing customer satisfaction through its effective deployment of innovations. The organization has enjoyed a significant share in the Australian lifestyle audio entertainment market, courtesy of its innovative products, programs, discounts, and adherence to values. However, Bose’s series of electronic products face stiff competition from HARMAN Internationals. Bose should gain by benchmarking the latter’s internationalization and portfolio management competencies. This report seeks to deploy the specific lenses of product, price, placement, promotion, and the overall marketing mix, thus providing a comprehensive analysis and insights into the Bose SoundLink micro-Bluetooth product in the Australian market.
Product 4/5
The company’s electronic products usually leverage the concept of psychoacoustics to maximize the quality of audio output from the customers’ perceptions (Schlieper et al., 2021). The concept argues that the specifics of modern music speakers are based on how the quality of music output is heard rather than how the output sounds. Therefore, the Bose SoundLink Micro Bluetooth speaker satisfies the core customer value product level, the actual product level, and the augmented product level. Buying the Bose SoundLink Micro-Bluetooth speaker guarantees customers core customer value. It seeks to sell reliable, portable, and high-quality Bluetooth devices that facilitate the cultivation of positive perceptions by prospective customers. The actual level of the micro-Bluetooth innovations is that the devices are chargeable through a USB cable. The waterproof and dustproof speaker is available in black, stone blue, and white smoke colours (“Bose SoundLink Micro Bluetooth speaker,” 2022). The micro-Bluetooth speaker’s battery can last up to 6 hours. The micro-speakers may be connected to other larger audio inputs to amplify the Bose micro-Bluetooth speakers. At the actual level, the Bose SoundLink micro-Bluetooth speakers produce audio output devices and sell them to prospective customers Lastly, the augmented level of the new product is manifested through the company’s 90 days risk-free trial and the free delivery and free return policies for orders that surpass $30.
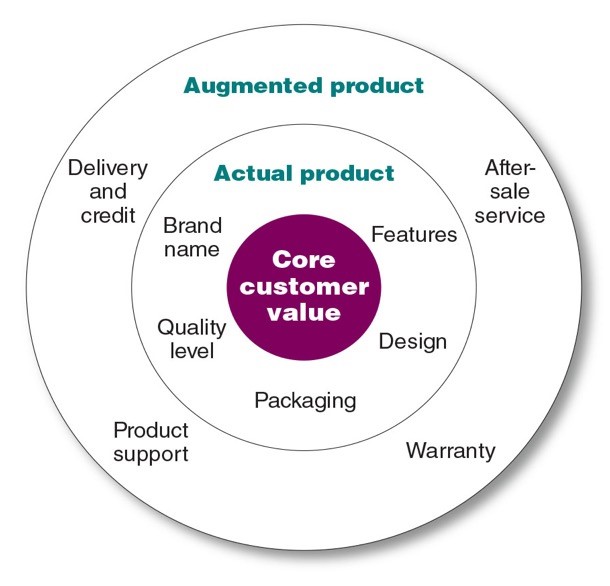
Figure 1: Levels of Products
Furthermore, the Bose SoundLink Micro Bluetooth speakers would be an in the shopping type of product. Although the Bluetooth speakers are bought less frequently, there is much planning and shopping effort, less comparison of brands and prices, quality and style. The product sells at relatively higher prices and in selective distribution centers around the country. According to Sagagi (2022), managers would use advertisements and personal selling strategies when promoting and marketing shopping products. The author adds that televisions, furniture, clothing, and technological appliances are some of the common products in the shopping consumer products’ category. Therefore, the Bose SoundLink Micro Bluetooth speakers are in the shopping consumer goods.
Bose utilizes a product-focused approach to reach prospective customers in the Australian market. The company integrates a premium brand reputation and lowkey advertising policy compared to competitors within the audio lifestyle market in the country. For instance, the organization advertises through e-commerce sites such as Amazon and social media influencers and celebrities such as Nicky Minaj, Lil Wayne, and P. Diddy to hold people’s attention about its innovative products. Furthermore, the organization uses the direct sales strategy where enthusiastic Bose salespeople go door-to-door, demonstrating the speaker to target customers (Purkayastha et al., 2021). The authors admit that the integration of advertisement and direct sales strategy has been registering success. Considering that the strategies target online and offline customers, Bose’s marketing strategy would be rated 4 out of 5. The online marketing strategy is bolstered by celebrity marketing, thus increasing its influence on the young population that mostly idolizes their celebrities. The company’s online presence also enables Bose to update its customers regularly about innovations and prices.
Price 3/5
One unit of the Bose SoundLink Micro Bluetooth speaker sells at $179.95. Bose’s price is lower than the Harman Kardon Onyx Studio 7 Portable Stereo Bluetooth speaker, which sells at $429.00 (“Bluetooth Speakers | Harvey Norman,” 2022). The product’s lower market price allows Bose to gain a larger market due to the many Australians who may afford to part away with $179.95 rather than $429.00 for Bluetooth speakers. The low prices would enable the company to gain from a wider pool of customers than its competitor, HARMAN International. Therefore, Bose would reach more customers and sell more units than its competitor.
Although Bose’s price is relatively lower than that of HARMAN Internationals’ product, the components of the micro-Bluetooth speaker come in a high price range. Therefore, Bose follows the premium pricing strategy in its marketing mix, targeting to gain from willing and able customers in the target market. The primary influence in Bose’s pricing strategy would be its customers, whose tastes and preferences significantly impact the product sales and penetration in the Australian market. Based on effectiveness, the customer-focused pricing strategy would be ranked 3 out of 5. The pricing strategy enables the company to leverage the large number of customers that prioritize price when making purchase decisions. Furthermore, the customer-focused approach allows the company to identify the underlying and ensuing customer tastes and fashions, thus designing its products to maximize their value and experiences. However, the marketing approach may be insensitive to the rising costs of input electronic materials and competition from incoming companies in the industry.
Placement 3/5
Bose headquarters are based in the USA. However, the company has already extended its base, covering technologically advanced countries such as Japan, Korea, and Australia. The organization stores and sells its products through various stores, ranging from Bose stores, Bose factory outlets, Bose showcase stores, Bose airport kiosks, and Bose personal audio stores. The company uses direct distribution channels to cut down on intermediaries by using directly employed territory managers. The managers work closely with existing dealers, integrators, and new partners to ascertain premium services to the end customers. The reduction of intermediaries functions to streamline Bose’s distribution channels and reduce the time the products would reach prospective customers. The emphasis on reduced intermediaries also ascertains quality products reach the final customer, thus protecting Bose’s brand image and perception. The organization’s indirect distribution channels include online e-commerce portals such as BestBuy, Walmart, Target, and Amazon.
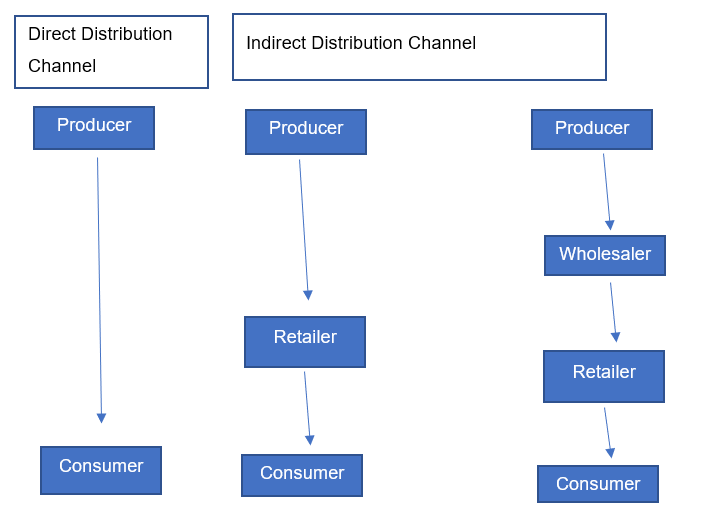
Fig 2: Bose’s Direct and Indirect Distribution Channels
Bose utilizes selective distribution channels to market and distributes its products to its end customers. The selective distribution channels enable companies to distribute their products through specific networks of retailers, resellers, or wholesalers, thus integrating and combining intensive and extensive forms of distribution channels (Materljan & Materljan, 2019). The scholars affirm that although the selective form of distribution channel may involve more than one intermediary, the selective distribution channel involves lesser intermediaries than the intensive and extensive forms of distribution channels (Hosseinpour, 2018). At Bose, the company seeks to reduce the number of intermediaries through direct selling and using reputable stores such as BestBuy, Walmart, Target, and Amazon as its intermediaries. Bose’s placement strategy could be ranked 4 out of 5 because it effectively integrates direct and indirect distribution channels to maximize sales to prospective customers. The organization is in a position to utilize reputable retail and wholesale stores to distribute products to customers in their respective regions. Furthermore, the organization leverages online platforms to extend its distribution channels and cover customers from different parts of the world. However, Bose has not yet consolidated its channels into a single and robust channel. Furthermore, the company’s reverse logistics channel has not been adequately integrated into the distribution channels.
Promotion 3/5
In its promotional strategies, Bose primarily uses product-focused approaches to persuade and convince its target audiences about its products’ effectiveness, efficiency, and convenience. The company mainly advertises its products in mainstream media and social media platforms. Through these advertisements, the organization is in a position to integrate marketing communication (IMC), which seeks to build relationships and synergy with prospective customers. Building relationships and synergies objectives enable Bose to view customers as partners rather than targets. Building customer relationships and synergies functions to streamline communication issues in the promotional mix due to increased possess, clarity, consistency, and marketing impact.
Although the advertisement strategy was previously relied upon for effective delivery of promotional messages, the strategies are slowly losing some of their lusters as stakeholders are growing concerns over the ability of the strategies to reach more people (Blut et al., 2018). Furthermore, many people in the century have lost interest in mainstream media sources and thus would not watch most of the advertisements in mainstream media. Contemporary audiences’ shift to digital platforms necessitates Bose’s marketing teams to integrate direct selling and e-commerce strategies. The organization also leverages social media marketing strategies through celebrity promotion and advocacy. Considering that the organization does not use innovative promotional strategies, brand repositioning, and word of mouth marketing, the organization ranks 3 out of 5. The organization should consider utilizing innovative promotional tools to explore new geographies and reposition its brand. Although the current strategies may allow Bose to retain its esteemed customers, the promotional strategies are not adequate to attract many new customers.
Marketing mix evaluation 3/5
Bose’s product, pricing, placement, and promotion strategies interact cohesively to facilitate the adequate sale of the Bose SoundLink micro-Bluetooth speakers. In essence, the organization offers its high-quality and convenient shopping consumer products at a high price. Shopping for consumer products are characterized by high prices (Sandy, 2019). The pricing of the product fits its high-end customers and thus, aligns with a promotional strategy that uses reputable retail stores such as Walmart and Target as distribution channels. Lastly, advertisements as a critical promotional strategy enable the organization to reach prospective audiences that would afford its products.
Bose’s marketing mix aligns with the positioning statement that sought to render comprehensive analysis and provide insights for the Bose SoundLink micro-Bluetooth product in the Australian market. The product, pricing, placement, and promotion strategy supports the perception that the company produces high-quality products intended to maximize the positive experiences for high-end customers. Overall, the market mix strategy and implementation would rank 4 out of 5 because all the four Ps in the marketing mix strategy align towards brand positioning.
Conclusion
Bose’s marketing team has effectively created favorable brand positioning for its SoundLink micro-Bluetooth speaker. The organization essentially sells its high-quality products at a relatively low price than its main competitor. Furthermore, the organization has employed distribution channels that strategically fit its target audiences. Lastly, the integration of advertisements, direct selling, and digital marketing would be attributed to the company’s growth in the lifestyle audio market. The alignment of the marketing mix and the positioning statement implies that the company has excellently deployed the tools to translate into increased sales, revenues, and profits from the Bose SoundLink micro-Bluetooth speakers.
References
Blut, M., Teller, C., & Floh, A. (2018). Testing retail marketing-mix effects on patronage: A meta-analysis. Journal of retailing, 94(2), 113-135.
Bose SoundLink Micro Bluetooth speaker. (2022, February 7). Retrieved from https://www.bose.com.au/en_au/products/speakers/portable_speakers/soundlink-micro.html?mc=20_PS_SO_BO_00_GO_&gclid=Cj0KCQiAuP-OBhDqARIsAD4XHpf4NYBFg6NrDY_S-1RIQNop1FwMiYXyDEKHQPonDuhk6VRcTAfprwkaArJeEALw_wcB&gclsrc=aw.ds#v=soundlink_micro_black
Harvey Norman. (2022). Bluetooth speakers. Retrieved from https://www.harveynorman.com.au/headphones-audio-music/sound-systems/bluetooth-speakers/harman+kardon/993
Hosseinpour, A. (2018). The Analysis of Intensive Distribution Approach. Journal of System Management, 4(2), 67-78.
Materljan, I., & Materljan, G. (2019). Selective Distribution of Trademarked Products and Restrictions of Online Sales. EU and comparative law issues and challenges series (ECLIC), 3, 830-865.
Purkayastha, D., Anirudhan, A., & Dutta, S. (2021). Bose Corporation’s Competitive Advantages and Its Shift to an Online-Only Model. IUP Journal of Business Strategy, 18(1), 41-57.
Sandy, M. L. (2019). Methods in NPD for startups: evaluating stage gate, design thinking & lean startup key concepts with students. In DS 95: Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Engineering and Product Design Education (E&PDE 2019), University of Strathclyde, Glasgow. 12th-13th September 2019.
Sagagi, S. S. (2022). Virtual Market: How Online Products Offering Affects Consumers Shopping Behavior in Northern Nigeria. Global Journal of Research in Business Management, 2(02).
Schlieper, R., Li, S., Preihs, S., & Peissig, J. (2021). Psychoacoustic optimization of a robust feedback active noise controller for headphones. JASA Express Letters, 1(12), 124801.
The First 50 Years of Bose. (2022). Retrieved from https://www.bose.com.au/en_au/better_with_bose/dream_and_reach.html
 write
write