Company T Sportswear Company Legal Structure
Company T Sportswear Company opted to incorporate after expanding to a sizable client base and significant market share. The company is now considered to exist independently of its founders. In the event of a business dispute, the proprietors’ assets are safeguarded as well.
Trademarking, Copyrights, and Patents
Company T Sportswear has registered its logo and several of its most recognizable designs to secure legal protection for its business. They have also sought patents for their one-of-a-kind textiles to protect their market share.
Licenses Required
Two permits are required before Company T Sportswear Company can open for operation. They must first obtain a business license from the appropriate government agency. In addition, they require a sales tax license to legally collect and remit sales tax to the appropriate state agency.
Insurance Required
Business T Sportswear has taken out numerous insurance policies to safeguard its operations. Accidents and injuries that may occur on their property or from using their products are covered by the general liability insurance they have sprung for (Bamford & Bruton, 2019). Property insurance has been obtained if the building or its contents are damaged by fire, flood, or theft. Last but not least, they have provided for their staff by purchasing workers’ compensation insurance in case they become ill or injured on the job.
Contracts and Lease
Business T Sportswear has signed several agreements, including a lease to help run its business. They have arranged for distributors in various areas to market their wares and have contracts with suppliers to obtain the necessary materials. They have a lease agreement with the store’s landlord that specifies the length of time they can operate out of the location and the rent they must pay.
Section 10: Human Resources Management & Operations
Business T, which specializes in sportswear, faces a number of challenges in human resource management and commercial operations. Here are just a few examples:
Organizational Chart
The employees of Company T need a detailed organizational chart outlining their specific responsibilities. Effective interaction, cooperation, and choice-making are all facilitated by this. Production, Sales, Marketing, and Finance are the company’s four divisions in a flat organizational structure at Company T Sportswear (Bamford & Bruton, 2019). Each employee answers to a department head, who answers to the owners.
Hiring Process
The organization must develop a systematic and open procedure for employing new staff. The process may include searching for candidates, interviewing them, and checking their references. The company’s proprietors want to promote from within when filling open positions whenever possible. If someone is qualified for the position, they will place an ad, narrow the pool of candidates, and hold interviews. Before hiring, they also verify the candidates’ identities and check their references.
Job Descriptions
The employees of Company T need accurate and detailed descriptions of their roles, complete with a list of mandatory skills and experience. Recruitment, induction, and performance assessment will all benefit from this.
Compensation
The organization must offer competitive pay, benefits, and perks to attract and retain talented employees. As a result, it will be easier to find and keep excellent staff members.
Foundational Company Policies
Business T must institute several ground rules to regulate employee conduct and foster a positive work environment. A few examples of such rules are a code of conduct, an anti-discrimination policy, a policy on how to communicate, and a policy on health and safety.
In order to fairly evaluate employees based on their productivity, quality of work, and other characteristics, the organization must establish clear performance evaluation standards and processes. In addition, the business must have a systematic and lawful procedure for firing workers who consistently fall short of expectations.
Company T must pay special attention to its human resources management and operations if it succeeds in the sportswear market.
Section 11: (Chapter 11)
The 4 Ps of Marketing:
- Product: Jerseys, shorts, trousers, and accessories are sportswear goods available at Company T Sportswear.
- Price: Company T Sportswear develops its prices by considering the market, manufacturing expenses, and competitive offerings. The company aims to provide affordable prices while still generating a profit.
- Promotion: Social media marketing, email blasts, and community sponsorships are part of Company T Sportswear’s grand promotional scheme. To bring in fresh business, the firm sometimes has sales and provides discounts.
- Place (Distribution Channels): T Sportswear sells its wares via several outlets, including a retail storefront, an e-commerce website, and wholesale channels. The organization has teamed up with distributors in various areas to expand further into the industry.
Marketing Strategy: The marketing strategy for Company T clothing is centered on reaching out to sports fans and professional athletes in the market for fashionable and functional clothing. The firm aims to establish itself as an industry leader in customer service, price, and innovation and to foster brand loyalty among its clientele.
Pricing Model: The final retail price at Company T Sportswear is calculated using the cost of manufacturing, the cost of overhead, and a markup %. In order to price its products competitively, the corporation considers both the pricing tactics of its rivals and the market’s needs.
Promotional Plan: Advertising on social media sites like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter is part of company T Sportswear’s marketing strategy. In addition to sponsoring local sports teams and events and sending out email newsletters to subscribers, the corporation also participates in seasonal advertising activities.
Distribution Channels: Company T Sportswear utilizes many retail and wholesale channels, including a brick-and-mortar shop, an e-commerce website, and a network of independent distributors. The company’s retail outlet is conveniently situated in a busy shopping district. Those who would instead buy in the comfort of their own homes will appreciate the online shop’s availability. The firm has formed partnerships with wholesale distributors to further its global expansion.
Section 12. Operations (Chapter 11)
Critical Path Chart:
- Product Design – 2 weeks
- Material Procurement – 3 weeks
- Production – 4 weeks
- Quality Control – 1 week
- Packaging and Shipping – 2 weeks
| Task Name | Duration | Dependencies |
| Product Design | 2 | |
| Material Procurement | 3 | Product Design |
| Production | 4 | Material Procurement |
| Quality Control | 1 | Production |
| Packaging and Shipping | 2 | Quality Control |
The critical path, which represents the most extended sequence of tasks that must be completed in order to finish the project, is:
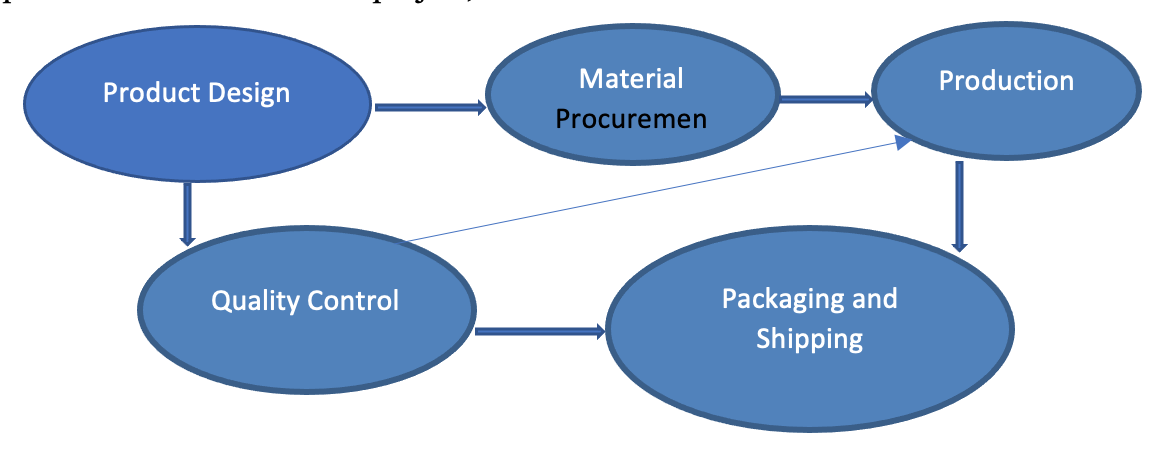
The project’s total duration, based on the critical path, is 12 weeks.
Facilities Required: Company T Sportswear needs a factory with sewing machines, cutting machines, and printing equipment. The firm also needs a place to keep its supplies and completed goods. A storefront and retail display fixtures are necessary for a brick-and-mortar establishment.
Inventory Needed: Products such as jerseys, shorts, and accessories are required in addition to raw materials, including textiles, threads, and printing materials for Company T Sportswear. The business has to have enough inventory to satisfy demand but not so much that it goes to waste.
Production Process: Company T Sportswear goes through a multi-stage manufacturing process. In the initial phase, the firm focuses on product design, developing original patterns for its sportswear. The following phase in the manufacturing process is material procurement, during which the firm acquires all of the high-quality components it will need. Products go through a series of stages in manufacturing, including cutting, sewing, printing, and finishing. The items undergo rigorous quality control inspections to guarantee they meet the firm’s expectations. When production is complete, the next phase is packaging and distribution to retailers and consumers. Although outsourcing manufacturing may save money, companies still need quality control to ensure their goods are up to pace.
References
Bamford, C. E., & Bruton, G. D. (2019). Entrepreneurship: The art, science, and process for success. McGraw-Hill Education.
 write
write