Executive Summary
This report analyses Liberty Mutual (LBTY), a global insurance provider headquartered in Boston. As an insurance provider, the performance of LBTY is highly susceptible to macroeconomic trends in the US. Before venturing into the effects of the macroeconomic factors on the performance of the company, an evaluation of the company’s performance over the previous five years was provided. The insights indicated that the company had good financial health even though its equity declined in 2022. The exchange rate, interest rate, GDP growth rate and inflation rate. Based on the analysis, the US experienced GDP growth, and increasing inflation and interest rates presented potential negative consequences for the company.
The high rates of inflation and declining GDP growth prompted the proposition of the Federal Reserve to increase the rates. This was aimed at reducing the inflation rates in the long term. The implications of the increasing interest rates on LBTY are provided, besides the implications of climate-related risks. After the analysis, the issues and challenges identified were used to develop recommendations to provide direction for the company’s future operations.
1. Introduction
This report analyses Liberty Mutual (LBTY), a global insurance provider headquartered in Boston. This report provides a critical assessment of the performance of Liberty Mutual (LBTY) to identify some of the key issues in the current economic climate in the US that affect the operation of the company. The economic environment contains factors such as exchange rate, interest rate, GDP growth rate and inflation rate which significantly influence insurance companies’ performance. These macroeconomic trends are associated with either an opportunity or risk to the business based on how they affect its operations and consumer trends. The report also assesses the influence of climate-related risk on financial institutions’ outcomes while focusing on how the factor could affect the performance and operations of the exchange rate, interest rate, GDP growth rate and inflation rate. This report is therefore important in determining the performance of LBTY in line with the prevailing macro-environment factors in the US. These outcomes are therefore important in plotting the way forward for the company while enhancing its capacity to overcome the oncoming challenges and take the emergent opportunities. Based on the descriptions above, this report aims to meet the following objectives:
- To provide a summary of the current performance of LBTY
- To provide an assessment of the economic environment and its impacts on the performance of LBTY
- To assess the monetary and policy regulations in the US and their influence on LBTY operations
- To provide an analysis of climate-related risks and what they mean for the future of LBTY
- To provide recommendations to overcome the challenges and issues identified through the analysis.
2. Company Overview
Liberty Mutual (LBTY) was developed in 1912 and is headquartered in Boston. The company is the sixth-largest casualty and property insurance provider globally. In 2021, the company ranked among the Fortune 100 corporations. The company operates in 29 global economies employing more than 50,000 people with an annual consolidated revenue of $50.0 billion as of the 2022 financial year. The company offers a wide range of insurance services and products, including “personal automobile, homeowners, specialty lines, reinsurance, commercial multiple-peril, workers compensation, commercial automobile, general liability, surety, and commercial property” (LMG, 2023).
The consolidated financial statements of the company over the past five years indicate that revenues of the company experienced a sustained increase from 2018 to 2022, as indicated in the figure below. The revenues despite the sustained increase, the smallest increase in revenues was recorded between 2019 and 2020, which could be explained by the impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic in the US.
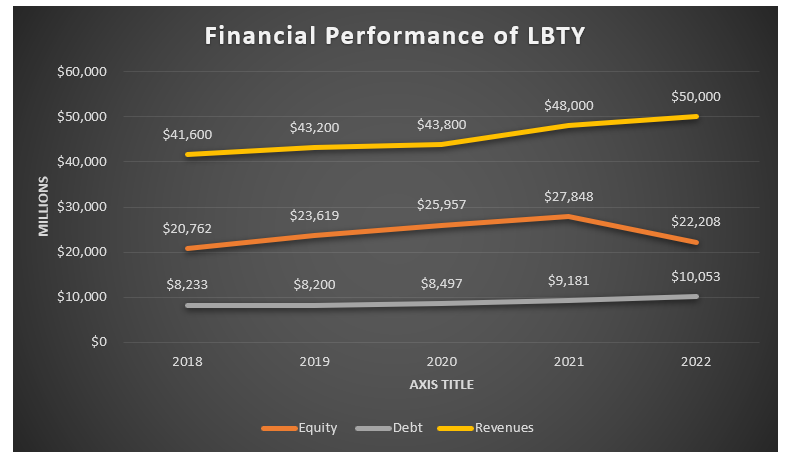
Figure 1 Financial performance of Liberty Mutual. Compiled by the author with data from (LMG, 2023)
Moving to the debt and equity balance, LBTY had higher equity across the five years. The company’s equity increased from 2018 to 2021 before experiencing a decline in 2022 at a time when the company’s debt increased to $10,053 million. The decline in equity and increase in debt in 2022 could be explained by higher reinvestment levels. Based on the data presented above, LBTY had adequate financial health over the five-year period.
3. Economic Environment and Asset Allocation
- Economic Factors Influencing the Performance, Return and Risks of the Company
The performance of Liberty Mutual (LBTY) is affected by a variety of macroeconomic factors. It is therefore important to acknowledge the influence of exchange rate, interest rate, GDP growth rate and inflation rate on the performance, return and risks experienced by LBTY. Slow GDP growth negatively affects firms operating in the financial sector. The US GDP experienced a decline from 5.90% in 2021 to 2.10% in 2022 (United States GDP Annual Growth Rate, 2023). The slow economic growth indicates the low contribution to the insurance schemes with a low entrepreneurial attitude which negatively affects the returns of the insurance companies (Peleckienė et al., 2019). Besides GDP growth, inflation in the US experienced an increase in 2021, reaching a high of 9.06% before starting to decline in 2023 reaching 4.99% as of March 2023. The inflation rate in the US remains above the 2% targeted by the Federal reserves. The high inflation negatively affects investment which is a risk considering that the inflationary environment negatively affects insurance investment. Interest rate risk is a key determinant of the profitability of the insurance companies. The trends in the US interest rates indicate that it is projected that the interest rates will increase by 4.25 in 2024, indicating that the value of fixed-income investments will decrease hence reducing the insurer’s profitability (Maverick, 2022). LBTY also experiences foreign exchange risk in that the fluctuations in the dollar exchange rates increase the company’s potential to lose money on international trade (Avdjiev et al., 2019).
- Does the company have more rate-sensitive liabilities than rate-sensitive assets? What will happen to its net interest margin during rising interest rates?
Rate-sensitive liabilities rate to the interest-bearing liabilities in that their values depend on the interest rate trends (Möhlmann, 2020). The rate-sensitive liabilities are revalued or repriced with changes in interest rates. The rate-sensitive assets include the assets whose values are responsive to interest rate fluctuations in that they are revalued or repriced with changes in interest rates (Möhlmann, 2020). The case of LBTY indicates the possession of more rate-sensitive assets, which explains the higher exposure of the company to the changes in interest rates from the assets side. In the 2022 financial year, LBTY had $160.3B in consolidated assets compared to $138.108 billion in consolidated liabilities (mutual liberty group, 2023).
The rate-sensitive assets owned by LBTY include equity securities, mortgage loans, fixed maturities and deferred tax assets (mutual liberty group, 2023). In contrast, the rate-sensitive liabilities by LBTY include Short-term debt, Long-term debt, unearned premiums, deferred tax liability, future policy benefits and d claim adjustment expenses, among others.
4. Monetary Policy and Regulations
- Consider the current economic conditions, including inflation and economic growth. Do you think the Central Bank should increase, reduce, or leave interest rates at their present levels? Would the Central Bank be more concerned about increasing economic growth or reducing inflation?
The economic conditions in the US indicate a decline in GDP growth amidst growing inflation (Matheson & Starvev, 2014). The current trends indicate that the interest rates in the US are increasing while the inflation rate is declining. Based on the conventional economists’ view, an increase in interest rates translates to lower inflation (Peleckienė et al., 2019). The statement provided above is explained by the view that the cost of borrowing increases with an increase in the interest rates reducing demand within the economy which increases supply translating to lower inflation.
The high-interest rates affect inflation in various ways. The increasing interest rates on the inflation rates are through the bank-balance-sheet, credit and exchange rate mechanism. In this case, increasing the Federal funds rate would increase the cost of borrowing hence a decline in the aggregate demand in the economy, pulling back the inflation rates to the desired levels (Matheson & Starvev, 2014).
In this case, the Federal Reserve would be more concerned with lowering inflation. Inflation targeting is important to keep the prices within the economy stable, which will, in the long term, keep the economic growth of the US stable (Hellwig, 2014). Reducing the inflation rate back to the target of 2% to stimulate the economic output in the country, considering that the US has experienced a decline in economic growth between 2021 and 2022. Based on the discussion provided above, the interest rates should be increased.
- What is your forecast of how recent, existing or potential regulations will affect the company’s performance?
The increasing interest rates are in response to the inflationary pressure in the US at a period where high-interest rates exist in tandem with high inflation. The announcement of the quarterly rate by up to 25 basis points in March 2023 concerning the economic conditions could immensely affect the operations of LBTY (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2023). The higher interest reduces the cost of rate guarantees just as it affects the reinvestment risk. A sharp rise may manifest into disintermediation risk with a negative influence on the company’s balance sheet. Additionally, the rising rates will increase the capitalization ratios, where the insurer provides long-dated interest guarantees. The insurer will therefore be expected to divest some of the interest sensitive-assets to avert the consequences of the rising interest rates (Seltzer, 2022). Finally, the increasing interest rates in the US amidst the fluctuation in the equity markets will reduce the attractiveness of equity-indexed annuities and life insurance, where the insurer will be expected to provide a “substantive interest rate guarantee” (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2023).
5. Sustainability Prospects
- Discuss how climate-related financial risks are impacting the financial sector. How might your chosen company be negatively affected by climate change?
Climate-related risks are becoming a reality for companies operating in the financial sector, even though measuring climate change economic costs is still an issue (GRAPPA et al., 2019). The costs of changing weather patterns affect the financial sector in two key ways: physical and transition risks. Physical risk arises from damage to property, land, and other infrastructure. Financial risks often materialize directly for financial institutions based on how they affect countries, households and corporations affected by climate shocks. The financial institutions also experience the impacts of these physical environmental risks indirectly based on how they affect the wider economy and their shocks on the financial system. The heightened exposure to the climate is related to a lower value of assets besides an increased likelihood of loan defaulting, which will negatively affect the performance of LBTY (Feridun & Güngör, 2020). Climate change also increases the risk of some accidents, such as fires which could affect multiple institutions simultaneously. The physical risks manifest in both the liability and asset sides of the financial sector institutions where the insurance policies may draw severe and higher claims than initially anticipated.
Transition risk from the climate manifest from changes in environmental and climate policy within a region or a country, the market sentiment, consumer adjustment and adjustment to carbon regulations. Transition risks affect LBTY’s asset side, where losses are mostly incurred where the model of the firms does not follow environmental policy directives. The firms which have not adhered to the climate policies could experience a decline in their income amidst an increase in funding costs.
- What might be the company’s opportunities and challenges for green and sustainable finance?
For the case of LBTY, the climate-related financial risks can potentially increase the insurance claims due to environmental policy change to severe levels at a higher frequency than expected. Additionally, the growing incidences of natural disasters pose the challenge of increasing the insurance cost or even resulting in unavailability for areas considered highly prone to these natural disasters (GRAPPA et al., 2019). Therefore, the increased cost of insurance may make LBTY less diversified, as diversification could increase the likelihood of experiencing insurance claims that were initially perceived as uncorrelated due to the effects of floods and droughts.
The climate-related financial risks provide avenues for LBTY as an insurer to acknowledge the potential impacts of climate change on their financial stability (Feridun & Güngör, 2020). The knowledge generated from such cases is important in developing greener financial systems with adequate supervision and monitoring new policies. The large impacts of weather-related issues on asset prices also pave the way for LBTY to champion improved policies that recognize and adapt the systemic climate risk.
6. Conclusion
This report provides an assessment of the performance of LBTY, factoring in the current economic climate in the US. The economic environment factors with the strongest influence on the performance of LBTY included factors such as exchange rate, interest rate, GDP growth rate and inflation rate. Based on the analysis, the US experienced GDP growth and increasing inflation and interest rates, which negatively present potential negative consequences to the company’s operation. The exchange rate risk is also high with the fluctuations in dollar value. The analysis also indicated that it had more rate sensitive-assets than its rate-sensitive liabilities. The monetary policy and regulations evaluations indicated the need for the government to increase the interest rates to reduce consumption in the domestic economy to drive down the inflation rates. These trends are in line with the growing interest rates in the US, which present diverse implications for LBTY. The analysis indicated that the growing interest rates would increase the potential for disintermediation risk besides increasing the capitalization ratios of the company for the long-dated guarantees. The pressures mentioned above indicate the need for LBTY to divest some interest-sensitive-assets. The high rates will also affect the attractiveness of equity-indexed annuities for the company. In relation to the sustainability prospects, the report acknowledged the potential impacts of climate-related risks on firms within the financial sector. The climate-related risks that influence LBTY were explained based on the physical and the translation risks, which can increase the insurance claims more than anticipated. In response to the issues highlighted above, various recommendations are provided to respond to the diverse risks that could affect the operations of LBTY in the short, medium and long term.
7. Recommendations
The recommendations above are based on the analysis of LBTY and its environment. The recommendations are aimed at providing the way forward for the company based on the outcomes of the analysis.
The first recommendation is based on the impacts of the monetary policy and regulations. Despite an increase in the interest rates in the US, the inflation rates are expected to remain high in the foreseeable future, an issue which concerns the performance of LBTY. The claim costs have increased in the short term and are expected to continue in the long term, provided the inflation rates remain high. The inflation rates also lead the premiums, increasing the potential of asset-liability mismatch within the company. Although the changes in the interest rates are expected to be gradual, for LBTY to mitigate the disintermediation risk, it recommended that the company should price more frequently and resent the guarantee rates as a response to the changes in the book value guarantees compared to how it behaved previously (GRAPPA et al., 2019).
The fluctuating equity markets and increasing interest rates are expected to reduce the attractiveness of equity-indexed annuities and life insurance in the short and medium term (GRAPPA et al., 2019). In line with the increasing rates, it is recommended that LBTY provide substantive interest rate guarantees when issuing insured products to boost its position in the market.
The second set of recommendations comes from sustainability prospects analysis of LBTY in relation to climate-related financial risks. The analysis indicated the likelihood of risks from climate-related events, which could make insurance claims severe and at a higher frequency. To mitigate this risk, it was recommended that LBTY mobilize resources to adapt itself to respond to the price signals by ensuring the company has an improved capacity to respond to changes in externalities (PricewaterhouseCoopers, 2023).
References
Alhassan, A.L., Addisson, G.K. and Asamoah, ME (2015) “Market structure, efficiency and profitability of insurance companies in Ghana,” International Journal of Emerging Markets, 10(4), pp. 648–669. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1108/ijoem-06-2014-0173.
Avdjiev, S. et al. (2019) “The dollar exchange rate as a global risk factor: Evidence from investment,” IMF Economic Review, 67(1), pp. 151–173. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1057/s41308-019-00074-4.
Feridun, M. and Güngör, H. (2020) “Climate-related prudential risks in the Banking Sector: A review of the emerging regulatory and supervisory practices,” Sustainability, 12(13), p. 5325. Available at: https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135325.
GRIPPA, P.I.E.R.P.A.O.L.O., SCHMITTMANN , JOCHEN and SUNTHEIM , FELIX (2019) Climate change, central banks and financial risk – IMF F&D: December 2019, IMF. Available at: https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/fandd/issues/2019/12/climate-change-central-banks-and-financial-risk-grippa#:~:text=As%20a%20result%2C%20insurance%20is,such%20as%20droughts%20and%20floods. (Accessed: May 3, 2023).
Hellwig, M.F. (2014) “Financial Stability, monetary policy, banking supervision, and Central Banking,” SSRN Electronic Journal [Preprint]. Available at: https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2475780.
libertymutualgroup (2023) Fourth Quarter and full year 2022 results – libertymutualgroup.com. Fourth Quarter and full year 2022 results – libertymutualgroup.com. Available at: https://www.libertymutualgroup.com/about-lm/investor-relations/documents/q4-2022-earnings-presentation.pdf (Accessed: May 3, 2023).
LMG (2023) Company profile, Company Profile. LMG. Available at: https://www.libertymutualgroup.com/about-lm/investor-relations/our-company/company-profile (Accessed: May 3, 2023).
Matheson, T. and Stavrev, E. (2014) “News and monetary shocks at a high frequency: A simple approach,” Economics Letters, 125(2), pp. 282–286. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econlet.2014.09.021.
Maverick, JB (2022) Do changes in interest rates affect the profitability of the insurance sector?Investopedia. Investopedia. Available at: https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/061515/how-much-do-changes-interest-rates-affect-profitability-insurance-sector.asp (Accessed: May 3, 2023).
Möhlmann, A. (2020) “Interest rate risk of life insurers: Evidence from Accounting Data,” Financial Management, 50(2), pp. 587–612. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1111/fima.12305.
Peleckienė, V. et al. (2019) “The relationship between insurance and economic growth: Evidence from the European Union countries,” Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja, 32(1), pp. 1138–1151. Available at: https://doi.org/10.1080/1331677x.2019.1588765.
PricewaterhouseCoopers (2023) How insurers can respond to higher interest rates, PwC. Available at: https://www.pwc.com/us/en/industries/financial-services/library/higher-interest-rates.html (Accessed: May 3, 2023).
Seltzer, M. (2022) Council post: How life insurance is affected by rising interest rates, Forbes. Forbes Magazine. Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbesfinancecouncil/2022/07/19/how-life-insurance-is-affected-by-rising-interest-rates/ (Accessed: May 3, 2023).
United States GDP Annual Growth Rate (2023) United States GDP annual growth RATE2023 data – 2024 forecast, United States GDP Annual Growth Rate – 2023 Data – 2024 Forecast. United States GDP Annual Growth Rate. Available at: https://tradingeconomics.com/united-states/gdp-growth-annual (Accessed: May 3, 2023).
 write
write