Introduction
The increased unemployment rate in the United States has given rise to a discussion of the major causes of unemployment. With the rising unemployment rates in the U.S., there are several consequences that specifically influence the lives of young people (Diette et al., 2019). Thus, the proposed study will examine the reasons for the increased unemployment rates and the impacts of the rising unemployment rate in the United States. The unemployment rate is now a national concern in the U.S. However, prior studies carried out by different economists and scientists showed mixed results regarding the causes and impacts of youth unemployment. For instance, people who tend to stay longer without jobs live destructive lives. This may result in mental and physical inactiveness leading to disruption in social disharmony.
Rationale of the proposed study
There are various reports published that concern the causes of unemployment and its impact on the lives of U.S. citizens. Most of these reports show the trends of youth unemployment, the causes, and its consequences. One of the significant causes of youth unemployment is the financial crisis. Though the financial crisis is a major cause of youth unemployment, the recession has adversely affected labour markets and education systems (Broyaka & Khaietska, 2020).). Economic recession also influence the quality and security of jobs available to youths and young adults. Thus, this has forced many young people to undertake precarious job paths such as part-time work and zero-hour contracts. These are the only options young people optimize to earn money and gain experience.
According to Liu (2021), some major causes of unemployment include skills mismatch, lack of life-skills education, inadequate capital, and the digital divide. Each of these factors contributes significantly to the rise in youth unemployment rates. Addressing the aforementioned factors of unemployment would help a country achieve sustainable development goals and ensure that young people secure decent jobs (Kassem, Ali & Audi, 2019). This will help curb the youth unemployment crisis and reduce unemployment rates as well. Such a remedy gives young people the opportunity to maximize their potential and participate in economic growth.
Problem Statement
According to Açci & Çuhadar (2021), the number of U.S. graduates without jobs increases every year. This is due to limited opportunities in the labour market. Such trends have resulted in destructive lifestyles due to depression among the graduates. Increased rural-urban migration has also been reported following limited formal jobs in rural areas. The young educated people also find the available limited jobs poorly-paying than the informal sector jobs. This has adversely influenced the attitude of the learned young people from tertiary institutions. Thus, the broader issue of unemployment can be defined by the limited number of formal jobs that have resulted in high unemployment rates. Following the limited opportunities in the labour market, many graduates opt to engage in vices such as drug trafficking, drug abuse, theft with violence, and immorality.
Study’s Objective
The general objective of the proposed study will be to examine the causes of increased unemployment rates in the United States and the association between various factors of unemployment.
Hypothesis
The hypothesis of the proposed study was generated from the research’s general objective. The proposed study hypothesized a significant association between unemployment factors. The following hypotheses will be used for the proposed study;
- Hypothesis#1
H0: There is no association between level of education and easiness of getting a job in formal Sector
H1: There is a statistically significant association between level of education and easiness in getting a job in the formal sector
- Hypothesis #2
H0: Unemployment rates in the U.S. does not vary significantly across social class
H1: Unemployment rates in the U.S. vary significantly across social class
Literature Review
According to Diette et al. (2018), the rate of unemployment measures the proportion of the total workforce that is not involved in any formal work and is actively seeking employment in the formal sector. The mismatch between job requirements, available opportunities, and graduate aspirations is the primary cause of increased unemployment rates in the U.S. However, stiff competition in the labor market, irrelevant curricula in educational institutions, and high pressure from respective universities and colleges to pursue courses not relevant to the industry have made the unemployment rate even more acute (Broyaka & Khaietska,2020). Besides, students graduating from colleges and universities have portrayed poor interaction skills such as critical thinking, communication, management, leadership, problem-solving, creativity, and self-confidence. It becomes difficult for fresh graduates to look for jobs that match their aspirations and qualifications with poor interaction skills.
According to Kassem, Ali & Audi (2019), lack of relationship between the industry and educational institutions, inadequate training to undertake the work, rapid population growth, economic recession, and capital intensive economy significantly contribute to the unemployment problem of young people. Many graduates have failed to demonstrate their working efficiency and have remained unemployed for a prolonged time. More employers recommend candidates with substantial experience in specific fields. Thus, the number of young people with less or no experience continues to increase, boosting the level of unemployment rate in the country. Besides, some youths once employed develop a negative attitude towards the job after realizing that the formal work is below their skill level and aspirations. A negative attitude toward poorly paying jobs and low-quality jobs has rendered many youths jobless.
Prior studies have emphasized on formal unemployment that would occur due to mismatch between job returns and career aspirations. Job markets require competent workers to meet societal needs. With the rising unemployment rate, the competition in the market is very stiff and only graduates whose their skills match the job requirements secure decent jobs in the formal sector. Another factor that would contribute to unemployment in the country is the social class of some people. Some societies are divided based on economic and social status. For instance, there are people who even after failing to secure a job in the formal sector cannot engage themselves in the informal sector. This has increased the number of unemployed people in the country. It is also evident from previous researches that the social class or status of different people influence the unemployment rate. People with highest level of education tend not to work in the informal sector even after failing to secure a job in the formal sector. This is because they believe that their qualifications and skills are above what is being offered to them. With this type of scenario, the number of unemployed graduates has continued to increase significantly in the U.S.
Methods
Research Design
The proposed study will utilize a survey design to answer the research questions. The survey method consisting of 100 questionnaires will gather information from the research respondents. The questionnaire will collect data on demographic characteristics and perceptions of youth unemployment. The questionnaires will be closed-ended and open-ended to help the researcher collect quantitative and qualitative data. In-depth interviews will also be contacted to collect relevant information from the research respondents. The proposed study will target fresh graduates from respective universities and colleges.
According to Nardi (2018), Survey design is used by researchers to understand and analyze new trends, opinions, and market demands. For example, the survey results of the proposed study will be used to identify patterns in participants’ responses that will offer clear insights into the phenomenon under investigation. The proposed research will explore factors that describe graduate unemployment and the causes of the increased unemployment among the youths. Thus, survey methods adopted for the proposed will be used to identify the patterns in the unemployment rate in the United States. The major advantage of survey methods is that they are cost-effective and relatively easy to administer (Nardi, 2018). These methods also consume less time in collecting data. On the contrary, the reliability of survey data depends on closed-ended questions that may have a lower validity rate than other types of questions.
Theoretical and Operational definition of concepts
The operational definition will be designed to model or represent theoretical or concept definitions in the proposed study. The operations, including procedures and processes of the proposed research, will be described to help the audience understand the overall objective of the proposed study. The key constructs for the proposed study will include;
- Labor force: This refers to the number of people who are employed and who are actively looking for work but currently are unemployed
- Unemployment rate: This is the percentage of the people who are working (i.e., employed) in relation to the comparable total population
- Social class: This refers to a division of society based on the economic and social status of the people.
The proposed conceptual framework of the study will be used to show the relationship between the key study variables. The proposed study’s conceptual framework will be developed based on existing literature and theories about the phenomenon under investigation. Figure 1 below shows the proposed conceptual framework of the study.
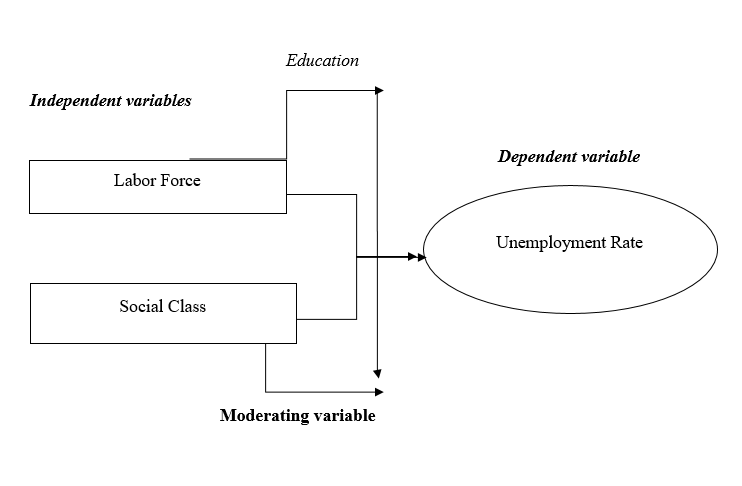
Unit of analysis and sampling design
The proposed study will target graduates from U.S. universities and colleges. Thus, the unit of analysis in the proposed study will be young people who have graduated from universities and colleges. Using the survey to collect data, the respondents will be interrogated to answer given questions regarding the unemployment rate in the U.S. A simple random sampling procedure will be adopted to select subjects from the study population. Simple random sampling uses probability sampling, in which the researcher is allowed to randomly choose participants from the study population. In this sampling technique, every subject from the study population has an equal chance of being included in the sample size. This minimizes the level of bias in subjects’ selection. However, the researcher has to ensure the sample size is large enough to represent the target population.
Conclusion
There are many factors that contribute to youth unemployment in the United States. These factors can be classified as social or economic. For instance, the labor force is one of the economic factors that would influence the unemployment rate in the country. Some people who are not actively looking for work may also land good jobs unexpectedly. This causes a significant increase in the labor force without affecting the unemployment rate. Social factors such as level of education may also influence the unemployment rate. For example, educated people are more privileged to get jobs than uneducated people. However, a higher level of education does not translate to securing decent jobs in a formal sector. Therefore, the proposed study hypothesized that social class and labor force significantly influence the unemployment rate in the U.S. However, other factors mediate the relationship between labor force, social class, and unemployment rate. Therefore, there is a need for further research to examine other factors that contribute significantly to the unemployment rate other than the ones incorporated in this study. Further research will also help address other existing research gaps in this study area.
References
Liu, Y. (2021). The high unemployment rate in Britain during the interwar period. In SHS Web of Conferences (Vol. 123, p. 01027). EDP Sciences.
Diette, T. M., Goldsmith, A. H., Hamilton, D., & Darity, W. (2018). Race, unemployment, and mental health in the USA: what can we infer about the psychological cost of the great recession across racial groups?. Journal of Economics, Race, and Policy, 1(2), 75-91.
Broyaka, A., & Khaietska, O. (2020). Unemployment as a major socio-economic problem of society development. Polish Journal of science.-2020.-№ 27, Vol. 2.-P. 57-67.
Açci, R. C., & Çuhadar, P. (2021). Unemployment or Inflation? What Does the Misery Index Say about the Causes of Crime?. METU Studies in Development, 48(2), 185-200.
Kassem, M., Ali, A., & Audi, M. (2019). Unemployment rate, population density and crime rate in Punjab (Pakistan): an empirical analysis. Bulletin of Business and Economics (BBE), 8(2), 92-104.
Nardi, P. M. (2018). Doing survey research: A guide to quantitative methods. Routledge.
 write
write