The paper examines the concept of inflation and explains why it is seen as a critical government goal. It employs relevant economic analysis to determine if monetary policy is the appropriate technique for the central bank to utilize to lower inflation. As a result, the paper attempts to defend the idea of inflation and why it is today seen as a vital government goal. Compared to alternative inflation-reduction approaches, the report contends that monetary policy is the most excellent choice for controlling inflation.
Inflation is an essential objective for the government.
Inflation is defined as a general increase in the pricing of goods and services over time. Costs of goods and services are tracked throughout time to determine inflation rates. Because of its effect on the economy, inflation is a primary policy goal for the government. There are a few different ways that inflation may manifest itself: demand-pull, cost-push, and built-in. When the public’s demand for goods and services rises faster than the economy’s ability to deliver them, a condition known as demand-pull inflation sets in (Bank rate increased to 2.25%, 2023). Rising input costs drive up overall production costs, a phenomenon known as cost-push inflation. Furthermore, adaptive prospects, or the idea that people believe present inflation rates will persist in the future, are linked to built-in inflation.
Cost-push
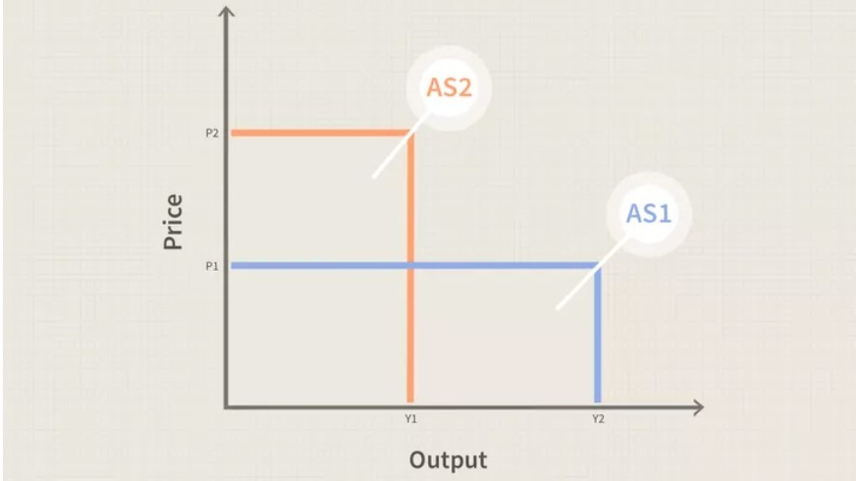
Source: https://www.investopedia.com/articles/05/012005.asp
The accompanying graph shows the maximum possible production at each pricing point. Since when it falls from AS1 to AS2, when production costs go up, the price goes up from P1 to P2. This is because corporations will have to raise the selling price reimbursed by consumers to maintain or grow profits, leading to inflation.
Demand-pull inflation
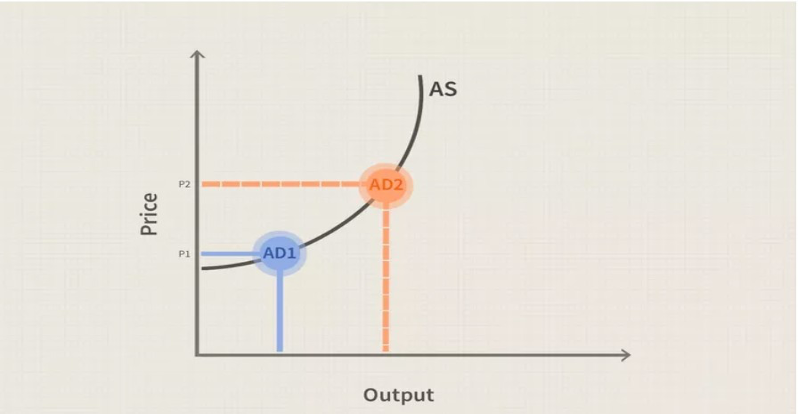
Source: https://www.investopedia.com/articles/05/012005.asp
The accompanying graph illustrates a connection between AD and available resources. When AD increases from AD1 to AD2, it will not immediately affect the AS. Consequently, there is a change in the AS curve’s undertaking, representing the quantity abundant (OECD Economic Outlook, interim report September 2022, no date). AS has evolved because AD has historically been more responsive to economic changes than AS (Bernanke, 2020, p.973). Companies cause inflation when they charge consumers more than they can afford to cover their increased manufacturing expenses.
The growing cost of goods and services is an issue when dealing with inflation. When inflation occurs, prices increase everywhere and disrupt the economy. This issue hampers consumers’ ability to spend money, and actual income loss is inflation’s major drawback. Inflation also reduces savings and a decline in available goods and services. Therefore, actions are required to address the rising inflation affecting our global economy. The main difficulty now is picking the most effective strategy for the central bank to adopt in its fight against inflation. However, monetary policy may provide central banks with the most effective means of addressing the issue.
The use of Monetary Policy to reduce inflation
What “monetary policy” means is the central banks’ overarching approach to the economy. State governments use this demand-side economic approach to attain macroeconomic goals, including liquidity, inflation, development, and consumption. In the UK, for instance, the MPC determines monetary policy to achieve the 2% inflation target in a way that safeguards employment and growth. To accomplish its goal, the MPC uses interest rates. To determine whether the economy is overheating and whether or not inflation is imminent, the MPC first examines a variety of economic indicators. Inflation over the goal will likely cause MPC to increase interest rates.
Diagram displaying fall in Aggregate Demand (AD) to minimize inflation
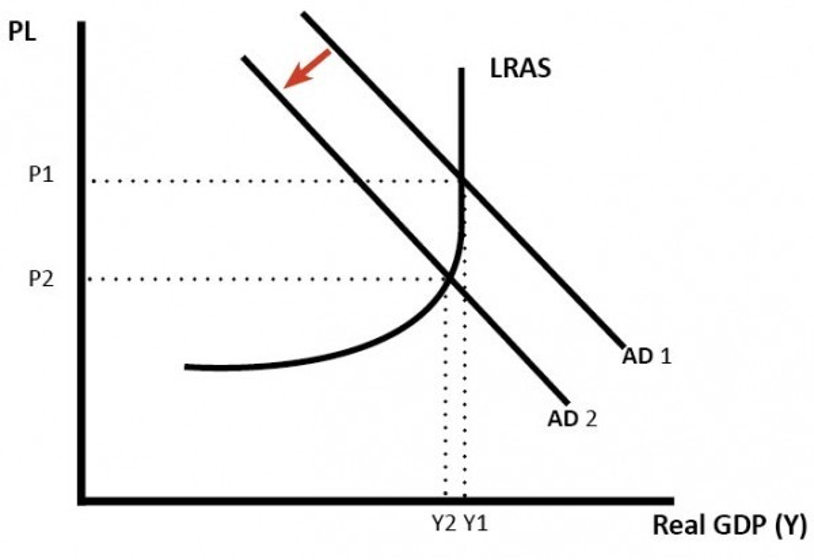
Source: https://www.economicshelp.org/macroeconomics/economic-growth/aggregate-demand/
Raising interest rates in monetary policy to reduce inflation, as indicated in the figure above, will help to limit the increase of aggregate demand (AD) in the economy. As the picture shows, a fall in AD leads to decreased inflation—lower inflation results from slower growth (Ridwan, 2022, p. 5). High-interest rates reduce consumer spending by boosting the exchange rate value, resulting in more imports and fewer exports. Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing, deterring consumers from spending and borrowing; higher interest rates reduce persons with mortgages’ disposable income; and raised interest rates to make it simpler to conserve money.For example, in the UK in 2022, interest rates rose somewhat in reaction to the fast growth in inflation (as illustrated in the graphic below). Raised interest rates limit aggregate demand, resulting in lower CPI inflation.
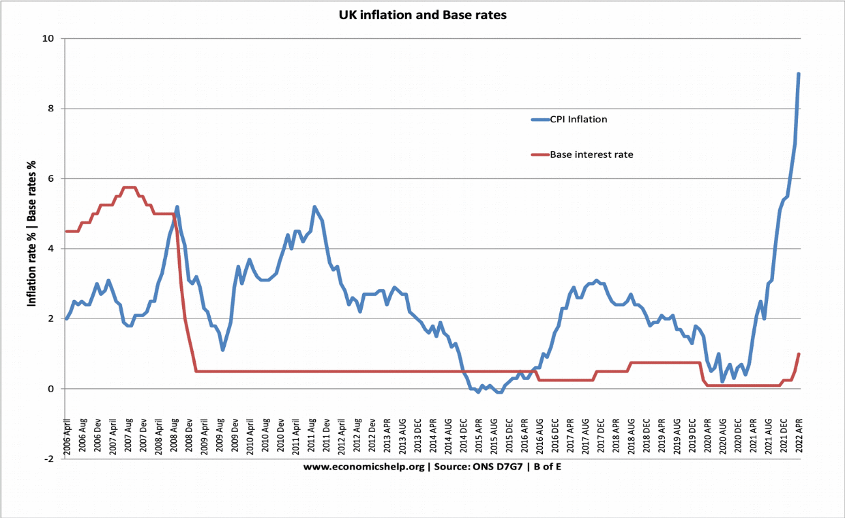
Source: https://www.economicshelp.org/blog/171249/economics/increasing-interest-rates-in-the-time-of-a-recession/
One area for improving the monetary policy strategy to lower inflation is how difficult it is to deal with cost-push inflation. In addition, faith is essential to the policy’s success. If confidence is strong, companies and individuals will keep spending despite high-interest rates. The benefits, conversely, include that central banks may put the policy into effect without prejudice since they are independent of politics (Bartsch et al., 2019, p. 14). It also implies that unpopular monetary policy may be enacted before or after elections without raising political hackles. Since monetary policies maintain economic stability, they are the most robust tool for reducing and halting rising inflation. The price and production levels are both stabilized by monetary policy. The policy controls the amount of money in the economy, and a drop in the money supply causes a decrease in demand for goods and services, lowering prices.
The use of Tight Fiscal Policy to reduce inflation
The state may influence the AD rate by adjusting its tax and expenditure policies. The government may increase taxes and reduce expenditures to reduce inflationary pressures. That will happen when AD cases drop (Sriyana, 2022, p. 85). Though politically costly due to widespread distaste for high taxes and reduction in state expenditure, fiscal policy may help keep government indebtedness to a minimum.
Diagram displaying the impact of expansionary policy
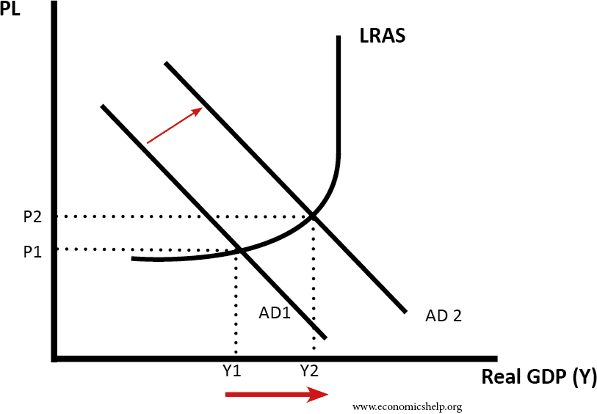
Source: https://www.economicshelp.org/macroeconomics/fiscal-policy/fiscal_policy/
Specifically, it entails elevating AD, as seen above. As a result, the government plans to reduce expenditure and increase revenue. Customers have a lot of discretionary income (C); thus, lowering taxes on them will increase their spending. It generally worsens the state’s budget gap, necessitating a higher level of borrowing (Yakubova & Raimova, p. 659). For instance: In 2009, the government in the UK lagged in its use of expansionary fiscal policy. The state reduced VAT in response to a severe decrease (GDP fell 6%) to encourage more consumer expenditure. As a consequence, government borrowing skyrocketed in the years following. When the new coalition government took office in May of 2010, they argued about how large the gap was before announcing their intention to reduce public borrowing as much as possible. Budget constraints were involved (What is the UK inflation rate, and why is the cost of living rising? 2023). Less economic growth occurred in 2011 and 2012 due to these strenuous efforts.
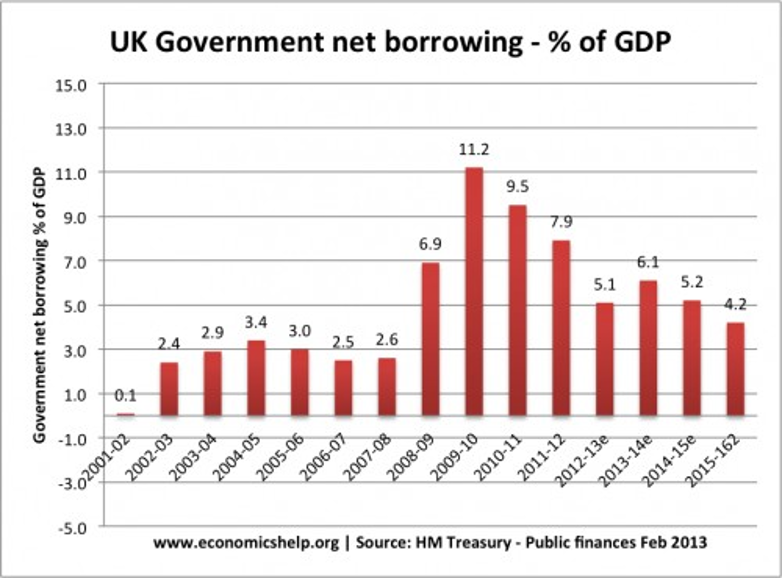
Source: https://www.economicshelp.org/blog/7072/economics/how-important-is-the-budget-deficit/
One of the benefits of using fiscal policy is that it can be used to allocate funds toward particular objectives, whether they are projects, regions, or sectors. By placing a monetary cost on those who cause pollution, the fiscal policy seeks to discourage the practice. Among the drawbacks of budgetary policy are Government-mandated tax breaks for purchasing imported goods. It also results in fiscal deficits when government spending exceeds annual revenue (Stupak, 2019, p. 6). Fiscal policy is preferable to interest rate rises in the battle against inflation because it reduces government financing costs.
The use of Supply-side policies to reduce inflation
When the government works to increase economic production and efficiency, it pursues a “supply-side” policy. They would shift AS to the right, promoting sustained, robust economic growth if viable. Supply-side policies may be classified into two broad categories: interventionist and free-market. Interventionist procedures include governmental involvement to overcome market failure, whereas free-market policies aim to increase market competence and competitiveness.
Profit of supply-side policies
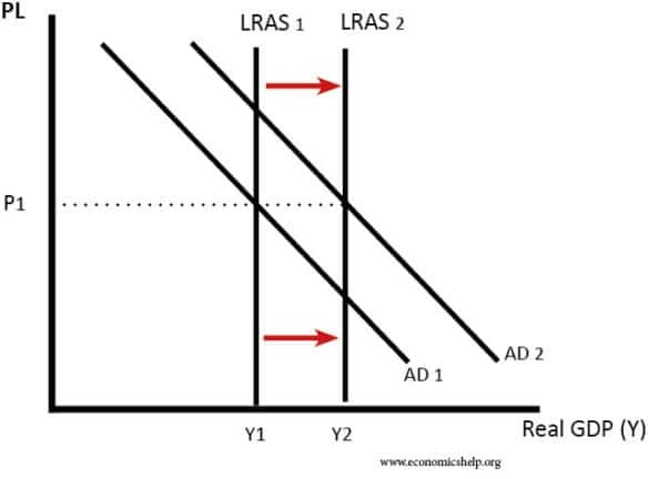
Source: https://www.economicshelp.org/macroeconomics/economic-growth/supply-side-policies/
According to the theory of demand and supply, supply-side measures should increase productivity and shift LRAS (long-term aggregate supply) to the right. Lower inflation via rightward AS fluctuation will result in a lower price level, lower unemployment, increased economic growth through an increase in LRAS, and improved trade and balance payments are all advantages of the supply side.
One of the supply side’s many benefits is that it helps reduce inflationary pressure over the long term by encouraging more excellent skill and productivity in the marketplace. The increased efficiency and productivity that results in helpful in fostering economic growth and sustainable development. Supply-side policies have several drawbacks, including high implementation costs, slow economic effects, and opposition from special-interest organizations since they weaken their influence. Since Supply-side measures are costly, there are better choices for reducing inflation.
In conclusion, inflation is a major policy priority for the government due to its effect on the economy. Inflation affects almost every part of the economy, from consumers’ purchasing power to the cost of borrowing money. Monetary policy is the most effective in lowering inflation compared to fiscal and supply-side policies.
References
OECD Economic Outlook, interim report September 2022 (no date) OECD iLibrary. Available at: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/economics/oecd-economic-outlook/volume-2022/issue-1_ae8c39ec-en (Accessed: 18 June 2023).
Bank rate increased to 2.25% – September 2022 (2023) Bank of England. Available at: https://www.bankofengland.co.uk/monetary-policy-summary-and-minutes/2022/september-2022 (Accessed: 18 June 2023).
What is the UK inflation rate, and why is the cost of living rising? (2023) BBC News. Available at: https://www.bbc.co.uk/news/business-12196322 (Accessed: 18 June 2023).
Bernanke, B.S., 2020. The new tools of monetary policy. American Economic Review, 110(4), pp.943-83.
Ridwan, M., 2022. DETERMINANTS OF INFLATION: Monetary and Macroeconomic Perspectives. KINERJA: Jurnal Manajemen Organisasi dan Industri, 1(1), pp.1-10.
Bartsch, E., Boivin, J., Fischer, S., Hildebrand, P. and Wang, S., 2019. Dealing with the next downturn: From unconventional monetary policy to unprecedented policy coordination. Macro and Market Perspectives, 105, pp.1-16.
Stupak, J.M., 2019. Fiscal policy: economic effects. Congressional Research Service, pp.1-8.
Yakubova, S.S. and Raimova, M.D., 2022. Peculiarities of inflation targeting in our country. ISJ Theoretical & Applied Science, 3(107), pp.655-661.
Sriyana, J., 2022. Fiscal and monetary policies to reduce the inflation rate in Indonesia. Jurnal Kebijakan Ekonomi dan Keuangan, pp.82-91.
 write
write